Molluscum contagiosum is a fairly common viral skin disease that occurs primarily in childhood (usually preschool age). The causative agent of molluscum contagiosum is the molluscum contagiosum virus, which is pathogenic exclusively for the human body and has a certain similarity to the smallpox virus.
Quite often, patients with this dermatological disease do not consult a doctor due to weariness or complete absence of symptoms, as a result of which molluscum contagiosum becomes chronic.
What it is?
Molluscum contagiosum is an infectious disease caused by the smallpox virus that affects the skin and sometimes mucous membranes. Typical manifestations of the rash are erythematous, dense, shiny nodules. Treatment of the disease is mandatory, provided that the disease does not pose a threat to human life and health.
How can you get infected?
Molluscum contagiosum is most often transmitted through contact and household contact; it can lead to outbreaks in children's groups and damage to family members. The virus is transmitted through direct contact with a sick person, as well as through contaminated household items, clothing, water in a pool or natural reservoirs, and toys.
In the environment, the virus is quite stable and can persist in the dust of residential premises and gyms, infecting more and more people. In adults, the disease can occur after tattooing if the pathogen remains on the instruments used by the artist.
Penetration of the pathogen occurs through microdamages of the skin. Therefore, the risk of infection increases in the presence of dermatological diseases with itching, dryness or weeping of the skin, and disruption of the integrity of the epidermis. In women, the molluscum contagiosum virus often penetrates through the mucous membrane of the genital organs and the skin of the perineum. Moreover, to transmit the infection from a partner, sexual intercourse itself is not required; only contact with the affected skin areas is necessary. Therefore, although infection with molluscum contagiosum in adults is often associated with sexual contact, it is incorrect to classify it as a true STD.
Pathogen
The virus affects only humans, is not transmitted by animals and is close to smallpox viruses. There are 4 types of molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV-1, MCV-2, MCV-3, MCV-4). Of these, MCV-1 is the most common, while MCV-2 usually appears in adults and is often sexually transmitted. Can also be transmitted through water (eg swimming pool). Inside the formation there is a liquid through which it is transported and multiplies.
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a virus (molluscum contagiosum virus), which is part of the poxvirus group. This virus spreads from person to person through direct contact and is most common in children. In addition, it can be infected through sexual intercourse; people with impaired immune system functioning are most susceptible to the virus. Molluscum contagiosum can spread by scratching or rubbing the affected skin.
Skin lesions of molluscum contagiosum are sometimes confused with lesions caused by the acrochordona virus.
Molluscum contagiosum during pregnancy
During pregnancy, against the background of a natural decrease in immunity, activation of an existing infection or a fresh infection with molluscum contagiosum may occur. The clinical picture has no peculiarities. The molluscum contagiosum virus does not pose a danger to the fetus, but during childbirth and subsequent contact with the mother's skin, the child can become infected.
Treatment must be carried out immediately after detection of the disease, taking into account contraindications for some procedures. Shortly before birth, a repeat examination is carried out even in the absence of complaints. This is necessary to identify possible recurrent rashes on the genitals and areas of the skin that are inaccessible for self-examination.
Symptoms and photos
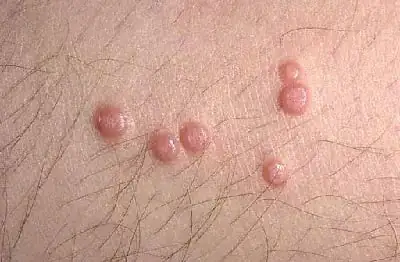
Most often, papules, which are direct signs of molluscum contagiosum (see photo), are localized in children on the face, torso and limbs, in adults - in the genital area, on the stomach and inner thighs.
Most often papules:
- small size (from 2 to 5 mm in diameter);
- do not cause pain, but are sometimes accompanied by itching;
- have a dimple in the center;
- have a core of white, waxy material;
- At first they are dense, dome-shaped, flesh-colored, and become softer over time.
Molluscum contagiosum usually goes away spontaneously in people with normal immune systems after several months or years. In people with AIDS or other diseases that affect the immune system, damage associated with exposure to molluscum contagiosum may be more extensive.
Diagnostics
In the classic form, the diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum is easy to make. The following factors are taken into account: childhood age, the presence of children with molluscum in the team, multiple spherical formations on the skin with an umbilical depression.
Difficulties in diagnosis rarely arise with atypical forms. But even with atypical appearances, dermatoscopy clearly shows umbilical depressions in the center of the molluscan papules.
Differential diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum is carried out with the following diseases:
- pyoderma (ulcers on the skin),
- chickenpox (chickenpox),
- filamentous papillomas (read a detailed article about filamentous papillomas),
- vulgar warts (read about vulgar warts),
- genital warts on the genitals (read about genital warts),
- milia.
In difficult cases, the doctor resorts to squeezing the papule with tweezers. If crumbly masses are squeezed out of the papule, with a 99% probability it is molluscum contagiosum.
In even rarer cases, they resort to diagnosis under a microscope. To do this, the crumb-like masses are sent to the laboratory, where a picture corresponding to the given disease is determined under a microscope. In this case, eosinophilic inclusions are found in the cytoplasm of the cells.
Could there be complications?
The development of molluscum contagiosum in the normal course does not lead to the formation of any problems over time, and often the elements can gradually disappear from the skin without leaving any traces on it. This can happen even without treatment for about three to four years.
- Some treatments may cause scarring on the skin.
- Sometimes the infection can reactivate, in which case a larger area of skin is affected.
- In the presence of severely weakened immunity, the development of molluscum contagiosum can take a generalized and pronounced form.
When the elements appear abundantly on the face and body, or become large in size and can change in appearance, treatment becomes difficult. In such cases, active therapy with drugs, both local and to stimulate systemic immunity, is indicated.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum
Currently, molluscum contagiosum in women, unless the nodules are localized on the eyelids or in the genital area, is recommended not to be treated at all, since after 3 to 18 months the immune system will be able to suppress the activity of the orthopoxvirus, and all formations will disappear on their own, leaving no traces on the skin any traces (scars, scars, etc.).
The fact is that immunity to the molluscum contagiosum virus is developed, but this happens slowly, so the body needs not a week to heal itself from the infection, as in the case of ARVI, but several months or even up to 2 - 5 years. And if you remove the nodules of molluscum contagiosum before they disappear on their own, then, firstly, you can leave scars on the skin, and secondly, this increases the risk of their reappearance, and in even larger quantities, since the virus is still active. Therefore, given that self-healing always occurs, and it is only a matter of time, doctors recommend not treating molluscum contagiosum by removing the nodules, but simply waiting a little until they disappear on their own.
The only situations when it is still recommended to remove nodules of molluscum contagiosum are their localization on the genitals or eyelids, as well as severe discomfort caused by the formation to a person. In other cases, it is better to leave the nodules and wait for them to disappear on their own after the activity of the virus is suppressed by the immune system.
Removal of molluscum contagiosum
If a person wants to remove the nodules, then this is done. Moreover, the reason for such a desire, as a rule, is aesthetic considerations. For the removal of molluscum contagiosum nodules, the following surgical methods have been officially approved by the Ministries of Health of the CIS countries:
- Cryodestruction (destruction of nodules with liquid nitrogen);
- Curettage (scraping out nodules with a curette or Volkmann spoon);
- Laser destruction (destruction of nodules with CO2 laser);
- Electrocoagulation (destruction of nodules by electric current - “cauterization”);
- Husking (removing the core of nodules with thin tweezers).
In practice, in addition to these officially approved methods for removing molluscum contagiosum nodules, other methods are used. These methods involve exposing the nodules of molluscum contagiosum to various chemicals in ointments and solutions that can destroy the structure of the formations. Thus, currently, ointments and solutions containing tretinoin, cantharidin, trichloroacetic acid, salicylic acid, imiquimod, podophyllotoxin, chlorophyllipt, fluorouracil, oxolin, benzoyl peroxide, as well as interferons alpha-2a and alpha 2b are used to remove nodules.
Such chemical methods for removing shellfish cannot be called traditional methods, since they involve the use of medications, as a result of which they are considered to be unofficial, practice-tested methods, but not approved by the Ministries of Health. Since these methods, according to reviews from doctors and patients, are quite effective and less traumatic compared to surgical methods for removing molluscum contagiosum nodules, we will also consider them in the subsection below.
Folk remedies
The most effective means for treating the disease in question from the category of “traditional medicine”:
- Prepare a concentrated solution of potassium permanganate - it should be dark purple. A cotton swab is moistened in it and applied (cauterized) to the papule. Please note that after using potassium permanganate, burns may form on the skin - be extremely careful, treat the papule specifically, acting on it point by point.
- The string grass is crushed and a decoction is made - 300 ml of water per 100 grams of raw material, cook for 3 minutes. Then the broth should brew for 60-90 minutes. Only after this can you strain it through a strainer or several layers of gauze. A decoction of the string is used as a lotion and for wiping off papules. There are no restrictions on the number of procedures per day.
- Grind a few cloves of garlic (in a blender or on a fine grater), add 30-50 grams of butter (soft) to them and mix everything thoroughly until a paste-like mixture is obtained. The product must be applied to the affected areas of the skin 2 times a day. Please note that garlic can cause burning and even irritation on healthy areas of the skin, so try to use this product with extreme caution.
You can also use some plants that will help get rid of papules in a short time. For example, juice from bird cherry leaves copes well with this task (it is squeezed out and stored in a cool, dark place) - a cotton pad is moistened in it and the skin is treated after removing the nodules. Moreover, this remedy can be used for a long period, until all wounds are completely healed.
Prevention
- examination of children in schools and kindergartens in order to prevent the spread of molluscum contagiosum;
- early detection of the disease;
- isolation of the patient from the team during treatment;
- regular wet cleaning of premises to eliminate dust containing viral particles;
- examination of co-residents and team members for the presence of papules;
- daily change of underwear;
- strictly personal use of personal hygiene items;
- selectivity when choosing sexual partners;
- mandatory shower after visiting the bathhouse, sauna, swimming in the pool and after sexual intercourse;
- patients are contraindicated from visiting massage rooms, swimming pools, saunas for the period of treatment;
- It is forbidden to comb papules; after accidental injury, treat the damage with an antiseptic;
- if papules are localized on the face, do not use harsh scrubs; men should be careful when shaving;
- isolation of the patient and the objects he uses within the family;
- strengthening the immune system (hardening, moderate physical activity, walking in the fresh air, swimming).
In the vast majority of cases, with molluscum contagiosum, the prognosis is favorable. The disease has virtually no complications and is easy to treat. The prognosis is significantly aggravated by the state of immunodeficiency, against which generalized forms of the disease develop with large formations that cannot be treated.
Molluscum contagiosum on the skin of a child is an infectious disease caused by a virus from the smallpox family. The disease manifests itself as neoplasms on the skin in the form of dense small nodules (papules) with a depression in the center. As a rule, infection occurs in preschool age; this is due to the immaturity of the child’s immune system. Adults and adolescents who are promiscuous are also susceptible to this disease.
What are shellfish on the skin?
Viral infectious contagious or contagious molluscum (molluscum epitheliale) is considered a benign disease, but it does not apply to tumor formations, because the growth and formation of nodules with fluid is caused by the impact of the virus on a small specific area of the skin. There is no inflammatory process in the epidermis of the nodules. Molluscum contagiosum is a common disease, and people of any age can get it. The infection occurs most often in children under 6 years of age, adolescents and pensioners.
As a rule, babies under one year of age almost never become infected with this disease, which is due to the presence of maternal antibodies, which are transmitted to the child through the placenta during intrauterine development. Molluscs on the skin of children is a parasitic disease that is characterized by local and general rashes on the mucous membranes and surface of the skin.
Causes
Molluscum contagiosum in children is a viral infection that affects the skin. The main cause of this disease is considered to be orthopoxvirus from the Poxviridae family. This pathogenic microorganism is widespread and can affect people of any age. Today there are 4 known varieties of the virus, which are designated by Latin letters and numbers: MCV-1, MCV-2, MCV-3, MCV-4.
This is a contagious disease that is usually caused by the orthopoxvirus MCV-1, and in adults - MCV-2. This happens due to the fact that the first type of virus is transmitted indirectly and through contact through household objects, and the type 2 virus is transmitted through sexual contact. As a rule, people who are more susceptible to infection with molluscum contagiosum are:
- those suffering from rheumatoid arthritis;
- with weak immunity (allergy sufferers, cancer patients, HIV-infected);
- taking glucocorticoid hormones and cytostatics;
- constantly in contact with the skin (doctors, massage therapists, pool trainers).
Routes of infection
The causative agent of the disease affects only the skin, so when all papules are cured, the virus is completely removed from the body. The source of shellfish infection can only be a sick person. Transmission of infection occurs through the use of shared toys and bath accessories. Infection often occurs in country camps, swimming pools, schools, and kindergartens. The incubation period of the disease is long, often the first rashes appear only four to eight weeks after infection. The risk of developing the disease increases in the presence of the following factors:
- polluted environment;
- weak immune system;
- stress, nervous breakdowns, disorders.
Molluscs on a child’s body are transmitted indirectly, through household contact and through water. As a rule, infection often occurs through touching the skin of a person suffering from the disease. Any tactile contact (handshakes, hugs, massages, close contact on public transport) with a sick person can lead to infection. The indirect route of transmission is considered the most common; it involves infecting people through touching dishes, linen and other household items on which virus particles remain.
Symptoms
The main signs of the presence of the disease are skin neoplasms in the form of small flesh-colored or white nodules. As a rule, in children they can appear on any part of the body, often on the face and chest, almost never on the feet and hands. When you press on the papules, a white mass is released, similar in consistency to boiled cereal. Occasionally, the nodules merge to form a giant molluscum contagiosum - a large skin formation with a depression in the center.
Although molluscum contagiosum is an infectious disease, it has no symptoms other than a skin rash and small pimples with fluid. Fever, runny nose and sore throat often do not even appear in the baby. Rarely, mild itching occurs at the site of large papules. When scratching or traumatizing acne, the disease can be complicated by other skin ailments. In this case, the symptoms of contagious infection are:
- the appearance of pus;
- swelling and redness of the skin around the rash;
- temperature increase;
- the appearance of severe pain in the area of the rash.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum in children
Some experts believe that uncomplicated molluscum contagiosum does not require special treatment. Papules will go away on their own if you follow the rules of personal hygiene. Rarely do light areas remain at the site of the rash that are not subject to tanning. Other experts, on the contrary, insist on mandatory treatment to avoid complications. The doctor may prescribe vitamins, immunomodulators, restorative and antiviral drugs.
As a rule, removal of nodules is recommended for adult patients so that they do not serve as a source of infection for other people. When children become ill, dermatologists often advise not to treat the disease, but to wait a little (4-6 months) until the papules go away on their own, because any procedure can cause stress in the baby. If the disease lasts a long time, the doctor may prescribe the following methods for removing nodules in children:
- mechanical curettage using a Volkmann spoon;
- cryotherapy – removal using liquid nitrogen;
- the use of folk recipes using herbs;
- removal with tweezers;
- use of special compounds;
- removal by laser or electric current.
External treatment
Mollusca on a child’s face is a viral disease that can cause a lot of inconvenience for children. If the papules do not disappear on their own, a specialist may prescribe the use of special gentle and at the same time effective means. The most common drugs are:
- Infagel ointment and Viferon cream. These medications are based on interferon, which strengthens the immune system. These agents prevent the mollusk from penetrating healthy cells and disrupt the presence of the virus in the blood. To treat the disease, drugs must be applied in a thin layer to the nodules up to 5 times a day. The course of therapy is 7 days. Contraindications: under one year of age.
- Oxolinic antiviral ointment. Used externally. The drug prevents the proliferation and penetration of viruses into cells. A 3% ointment is used to cleanse the skin. Nodes and rashes must be carefully lubricated with the product 4 times a day, the treatment period is 2 weeks. The only contraindication is special sensitivity to oxolin.
Drug treatment
Parents often burn nodules on the skin of children with iodine, hydrogen peroxide, and celandine. This is allowed, but only under the supervision of a doctor. Although it is better to treat molluscs on a child’s skin with antiviral agents, also in consultation with the doctor. The most effective drugs are:
- Candles Viferon 500000 IU2. Antiviral and immunomodulatory agent. When using the drug, the level of immunoglobulins increases and the functioning of interferon is restored. Children over 7 years old are prescribed one suppository 3 times a day for two weeks. Children under 7 years old - one suppository 2 times a day.
- Isoprinosine tablets. Immunomodulator, complex synthetic antiviral drug. Blocks the reproduction of viruses and reduces the clinical manifestations of the disease. Strengthens the effect of interferon. Children over 3 years of age are prescribed 50 mg of the drug per 1 kg of weight. The dose is divided into 3 doses per day. The course of therapy is from 5 days until the nodules completely disappear. Contraindications: children under 3 years of age.
Folk remedies
Many parents try to cure cutaneous molluscum with traditional medicine: garlic, celandine, calendula. Often such methods are not always safe, especially without the supervision of a specialist. Although some of them, used together with medications, help to quickly get rid of an unpleasant illness. The most popular traditional medicine recipes are:
- Bird cherry juice. Fresh tree leaves should be washed with water and passed through a meat grinder. The resulting porridge should be placed on cheesecloth and the juice should be squeezed out. This mixture must be mixed with butter in a 1:1 ratio. The ointment should be applied to the nodules at night. The course of treatment is 2 weeks.
- Garlic lotions. For this recipe, you need to take several fresh cloves of the plant and grind them to a paste. Next, add butter in a 1:1 ratio and mix well. The prepared composition must be applied pointwise to the nodules and secured with a band-aid. The lotions should be changed to fresh ones 3 times a day. Such applications should be applied to papules until they completely disappear.
Removing shellfish from children
Dermatologists do not recommend removing molluscum contagiosum nodules in children on their own to avoid complications on the skin in the future. Only an experienced doctor can prescribe a treatment method. When a disease occurs, the child cannot attend school, kindergarten, or swimming pool. An infected baby should undergo a full course of therapy from a dermatologist. As a rule, removal of molluscum in children is rarely resorted to, because The rash may disappear from the skin on its own over time. Although in rare cases, mechanical removal of papules is simply necessary. Removal is indicated in the following situations:
- if there is a high risk of spreading the infection;
- in the presence of concomitant skin diseases (atopic dermatitis);
- if the rash is localized on the neck or face.
Mechanical removal
The doctor can remove the papules using tweezers and an alcohol solution of iodine. During this procedure, young children are often anesthetized with Emla cream or another surface anesthetic. To remove the nodules, the doctor squeezes the jaws of the tweezers and squeezes out the contents of the papules, after which he carefully removes the curdled mass and cauterizes the wound with iodine or hydrogen peroxide.
To remove molluscs from the skin, a specialist may use curettage or husking. This method involves mechanically scraping out the papules with a sharp Volkmann spoon. The procedure is unpleasant, and removal is often accompanied by bleeding, so the specialist uses local anesthesia with lidocaine. After removing all nodules, the wounds should be treated with a 5% iodine solution. This method of removal may leave scars on the body.
Surgical removal
As the infection progresses, the specialist may prescribe one of the following surgical treatment methods:
- Diathermocoagulation. You can remove a child's rash by cauterizing the papules with an electric current. This procedure is practically painless, but can sometimes be accompanied by burning, discomfort, and tingling.
- Laser therapy. Modern medical equipment makes it possible to quickly remove the mollusk with a laser using local anesthesia. This removal helps to achieve the destruction of 90% of papules after the first session. In this case, each nodule is irradiated with a laser during the procedure, after which the skin is treated with iodine (5% solution). If after a week the papules have not crusted over, then another irradiation session is performed.
- Cryodestruction (cryotherapy). Removing nodules with liquid nitrogen. Cells with the virus are frozen and killed during the procedure. When cryotherapy is carried out correctly, there are no scars on the skin.
Cutaneous dermatosis is a common disease that appears on the skin in different forms. Skin clams are one such form. It refers to viral diseases.
Molluscum are blistering rashes that can appear on literally any part of the body. Cases are often recorded when blisters appear on the mucous membranes. Due to their optimal size, the rashes themselves do not pose a huge threat to health, but still cause discomfort during development.
It is worth noting that the pathology belongs to the class of chronic. Having penetrated the human body, the infection lingers in it for an average of six to nine months. There are cases when the disease develops for several years if treatment is not started on time.
This type of skin dermatosis refers to smallpox diseases, so the blisters have a specific focus of development. Like other types of dermatosis, molluscs develop only in the human body. Accordingly, you can only become infected from a person. No animals are carriers of such an infection.
The shape of the rash is oval or round. The size of the bubbles, as a rule, does not exceed five millimeters, since the inflammations do not unite with each other in the first stages. Only if the disease is neglected can the rashes grow together and turn into large papules. These inflammations should not be confused with papillomas, which you can learn more about here.
How is molluscum contagiosum transmitted?
- Close physical contact with large crowds of people.
This pathology often affects children. The reason is that childcare centers often have crowds of people. Constant physical contact with carriers of the disease practically guarantees infection.
- Household and airborne routes.
As is the case with many other skin diseases, you can become infected with molluscum simply by regularly using the carrier's things. So, if you live in the same room with a sick person, try to distance yourself from him as much as possible during the period of illness.
- Physical contact during sexual intercourse.
The virus spreads widely in the groin and thigh areas. Therefore, with constant friction of the skin of two sexual partners, the carrier transmits the virus to a healthy person. To avoid unexpected illness, protect yourself from promiscuity.
How is molluscum virus diagnosed?
To determine the presence of a virus in the human body, general tests are first taken and appropriate laboratory tests are carried out. If this method does not produce results, research begins on the contents of the mollusk itself. During such a diagnosis, the virus is necessarily compared with the parasite of chickenpox, basal cell carcinoma, syringoma and other diseases that have similar symptoms.
By the way, in terms of external signs in the first stages of development, the mollusk strongly resembles an ordinary wart. That is why it is recommended to immediately go to the hospital for an accurate diagnosis if you notice new formations on the body. The mollusk itself takes quite a long time to develop. Over the course of several months, it usually increases in diameter by only a few millimeters.
It is also worth noting that rashes are not always located in one area of the body. Molluscs often appear throughout the body in single inflammations. Moreover, the spread of time can be very large. For example, the next mollusk appears only 2-3 weeks after the previous one.
Main symptoms of molluscum contagiosum
The rash consists of small spherical blisters that do not cause thickening of the skin and are not particularly noticeable in the early stages of development. The location of inflammation varies depending on the age of the patient. Thus, in children, molluscs can actively appear throughout the body, including the limbs, neck and abdomen. In adults, the disease develops more actively in the groin and inner thighs.
Molluscum contagiosum can be identified due to the following symptoms:
- In the first stages of development, acne has a characteristic hard structure. But the longer they stay on the skin, the softer they become. So, after a few weeks, the papule feels like a regular callus.
- In terms of external characteristics, inflammation is very different from a regular pimple. A white rod is clearly visible inside it.
- The mollusk causes noticeable itching already during the incubation period. During the first week after the virus enters the body, the infected area begins to itch.
- Papules have a clear round shape. Over time, they greatly increase in size and rapidly spread over the infected area of the skin.
The subcutaneous mollusk begins to actively spread throughout the body in the later stages of development. If you do not start treatment on time, a period of self-infection may begin within a month. You independently spread the virus to all areas of the skin with your hands. Therefore, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor at the first suspicion of the disease.
A rare form of molluscum contagiosum
There are cases when papules characteristic of pathology have completely different external indicators. In this case, the nodules have a concave shape and grow literally up to two to three millimeters in diameter. This indicates a special form of molluscum contagiosum, which is most often a complication of other diseases.
This form is mainly observed in children suffering from leukemia, streptoderma and other skin diseases. In adults, this type of mollusk may indicate the development of HIV in the body. The pathology itself is closely related to AIDS. Therefore, it is recommended to immediately undergo all necessary tests after diagnosing molluscum in the body.
The listed symptoms will help you draw your own conclusions before seeing a doctor.
How to protect yourself from molluscum contagiosum. Basic methods of prevention
The pathology is quite serious and can lead to disastrous consequences. Therefore, it is necessary to take prevention seriously. In particular:
- Avoid promiscuous sexual intercourse. The virus can be transmitted from person to person even during the incubation period. Therefore, sudden sex with a stranger can lead you to serious problems. At the same time, any methods of protection will not help, because the virus is transmitted not through sexual contact, but through physical contact, in the groin and thighs.
It is also recommended to change sexual partners as rarely as possible.
- Special skin care at a resort by the sea and when visiting swimming pools and water parks. After visiting such places, you should carefully monitor your body and immediately contact a specialist when the first symptoms of molluscum appear. In public places, be sure to use only your own towels, robes and other personal items.
- Pay attention to personal hygiene. We are talking not only about hygiene of the body, but also of personal belongings. Change bedding and underwear daily. Be sure to wash your hands when you come home. By the way, hands should be washed not only after visiting the toilet, but also before the procedure.
- Regular examination of the child by the pediatrician.As practice shows, mollusks appear more often in children than in adults. This is due to the fact that the virus spreads very actively in children's institutions. In addition, a child’s immunity is much weaker than that of an adult. Make it a rule to take your child to see a doctor at least once a month. This will allow you to start treatment in time if the virus enters the body.
Any skin disease greatly affects the immune system and weakens it. Thus, even complete removal of molluscs from the skin does not guarantee your recovery. Relapse is quite possible if you do not strengthen your immune system.
Therefore, during the period of treatment and after it, the doctor prescribes you special medications that help strengthen the body and completely get rid of the pathology. At this time, your body is very vulnerable, so it is recommended to follow a special diet.
How to eat during treatment for subcutaneous molluscum
- Avoid alcohol and nicotine completely.
You need to avoid bad habits at least for the period of treatment. The fact is that such substances strongly “hit” the immune system and weaken the body. If you've heard that a glass of wine in the evening can be beneficial for the body, temporarily discard this thought. During illness, alcohol cannot be beneficial in any quantity.
- More fresh vegetables and fruits.
Now you urgently need vitamins and other biologically active substances. It is in fruits and vegetables that they contain the greatest amount. Make it a habit to eat fresh apples, bananas, oranges, cucumbers, tomatoes and so on every day. All this has a positive effect on your immunity.
- Consume fermented milk products.
Skin molluscs and similar types of diseases develop more actively due to problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Any type of fermented milk products helps your body get rid of waste and toxins. As a result, the digestive system works much better, and nutrients are absorbed by the body much faster.
- No sweets!
Sugar interferes with the absorption of vitamins. Replace your favorite cakes and chocolates with fresh fruits, and sweet tea or coffee with freshly squeezed juices. To somehow diversify your diet, you can experiment with such products. For example, a good fruit salad is in no way inferior in taste to cakes or pies.
Many nutritionists advise giving up meat if you have skin diseases. But such recommendations, in fact, do not make sense, since meat and fish contain large amounts of protein, which you need during this period. You should, perhaps, avoid heavy fried foods. This really slows down the gastrointestinal tract and interferes with digestion.
But there are a huge number of alternative cooking methods. For example, boiled, baked or steamed meat is in no way inferior in taste to fried meat. And at the same time, it has a much more beneficial effect on the entire body. Eat these dishes at least three times a week. Protein will also help you restore your immune system faster.
- More regular clean water.
Few people know, but the simplest water brings much more benefits to the body than the same juice. Try to increase the amount of water you drink during illness. Like fermented milk products, plain water will help you remove toxins and cleanse your stomach. The digestive system comes into order, which also affects your general condition.
Practice shows that people who drink at least two liters of water during the day feel much better. They have much more energy, which affects both productivity and performance, as well as their general mood. Experts recommend starting every day with a glass of clean drinking water without any additives.
How to cure molluscum contagiosum
Today there are a huge number of medications that accelerate the removal of infection from the body. But given the influence of such drugs on a person’s general condition, modern doctors are of the opinion that it is better to wait until the body overcomes the pathology on its own.
In most cases, this takes no more than six months. You just need to take proper care of yourself during the period of illness and strictly adhere to all the doctor’s advice.
But mollusks cause serious aesthetic problems for an adult, depending on where exactly they appear. Therefore, during the treatment period, papules can be removed using different methods.
Among the popular modern methods it is worth noting:
- Special antiviral ointments. They actively act on inflamed skin, soothe irritants (which helps relieve itching) and have a drying effect. As a result, the mollusks pass much faster and do not leave any marks on the body.
- If you need to get rid of inflammation very quickly, you can use cauterization. There are no universal recommendations here, since each case is individual. Some experts advise using celandine, but it is not a fact that this particular product will help you. To get accurate recommendations, be sure to consult your doctor.
- Laser removal allows you to get rid of mollusks without a trace literally within a few hours. To do this, you just need to go to a good clinic and first consult with a specialist. Lasers are usually used to remove shellfish from areas where other means would be dangerous. For example, if papules appear on the eyelids, it is not recommended to use both ointments and celandine. Such substances can be harmful to health if they come into contact with the eyes.
- Mollusk is the type of rash that can be squeezed out. But this must be done under appropriate conditions and using the right means. The hospital can help you squeeze out and scrape out the nodules from the right places.
In this case, the inflammation must be additionally treated before and after the process. You should also cauterize the wound after removal. You can use regular iodine for this.
But, again, it is better to entrust the process to specialists. By squeezing out the papules yourself, you are likely to introduce an infection into the body, since the immune system at this time is greatly weakened.
Removing molluscum contagiosum is a fairly simple process. But in order to avoid pathological complications, you should trust the procedure exclusively to professionals. The removal process is as follows:
Is it possible to cure molluscs on the skin at home?
Doctors categorically prohibit treating pathology on their own. There are several good reasons for this:
- Improper removal methods at home contribute to the development of new tumors on the body. An infection that enters the body can cause the development of lipomas or milia. But this is not the worst outcome. Cases are often recorded when self-removal of inflammation ends in the development of an oncological tumor. Moreover, this outcome occurs quite often.
- Some special forms of molluscum contagiosum are one of the complications of the AIDS virus developing in the body. By using the wrong treatment methods, you can provoke the accelerated development of pathology. In addition, it is necessary to take care of such inflammations with a special approach. Only a qualified doctor will prescribe a specific course of treatment for you.
- Self-treatment can provoke a rapid relapse of the disease. You can get rid of a few molluscs that appear on your body, but soon the rash will appear again and in larger numbers. And in this case, curing the disease is much more difficult. It is strictly forbidden to squeeze shellfish yourself. You definitely won’t be able to remove the root of the disease without practical skills and experience.
Cutaneous molluscum in children
In childhood, the human body is highly susceptible to this virus. The reason is the child’s weakened immunity and constant contact with a large number of peers, many of whom may be carriers of the virus in a latent state. As in adults, the incubation period for mollusk in children is 14-60 days. But when the pathology becomes active, it manifests itself much more slowly.
It all starts with one small inflammation that can appear in any part of the body.
One papule gradually increases in size. A full-blown rash appears approximately three weeks after the first papule. The molluscum causes itching that the child cannot control, so the rash will most likely appear in the place where the first inflammation was discovered.
The child's hands often come into contact with the face, neck and head during the day, so there is a chance that the rash will begin to actively develop in this area. This outcome can be avoided. First, you need to carefully follow your doctor’s recommendations for caring for papules. Secondly, modern medicine makes it possible to safely remove mollusks from a child’s body. The same methods are used for this. However, the treatment in such cases has some differences.
Treatment of molluscum in children
If inflammation appears in safe areas, it is recommended to use the squeezing method in a clinical setting for removal. The dermatologist has a special spoon in his arsenal, with which the mollusk is pressed and opened. Then all that remains is to extract the secret and the root from the inflammation.
Therefore, in most cases, painkillers are used. If the rash is widespread throughout the body, several appointments may be required. Wounds must be treated with iodine. Some specialists use additional products for post-treatment of inflammation, for example, zinc ointment. The specific selection of drugs is individual for each patient. Especially when it comes to a child’s body.
Many standard shellfish removal methods are also suitable for children of all ages. The exception is infants under one year of age. In this case, it is not recommended to use any procedures at all.
You can see a complete list of standard removal methods in this video:
Оставлять детский организм бороться с болезнью самостоятельно не рекомендуется. Дело в том, что иммунная система в этом возрасте еще недостаточно сильна, и правильное питания для ее усиления здесь не поможет. Как правило, болезнь затягивается на 18-25 неделю от появления первого моллюска на теле.
But there are cases when a child has to struggle with pathology for 2-5 years. Of course, special medications help the body get rid of the virus. But they don’t have any special effect. As a rule, these are ordinary antibiotics.
In modern medicine there are many ways to cope with the disease much faster, but this requires the direct intervention of a doctor in the development of the disease. Therefore, you need to be as careful as possible when choosing a hospital and a specialist.
Recommendations for the treatment of cutaneous molluscum in children
The pathology is very common among children under 10 years of age. Therefore, the best specialists of the CIS cannot ignore it. New speeches by the best doctors of Russian-speaking countries on this topic regularly appear on the Internet and television. Here, for example, is the opinion of one of the best children's doctors:
Сегодня существует много методов лечения моллюска у детей, но учтите, что многие из них очень болезненны. Поэтому постарайтесь на полную использовать все рекомендации по профилактике и уберечь ребенка от такой патологии.
Subcutaneous molluscum, like the human papillomavirus, is relatively safe for the human body. But it brings severe discomfort, if only for aesthetic reasons. Considering that the disease is very easily transmitted to other people around you, it is better to protect yourself from its occurrence in advance. Using the tips given correctly, it will not be difficult for you to avoid pathology.