- What are papillomas
- What do nevi look like?
- What is the difference
- What is the danger
Papilloma and nevus are types of benign formations on the human body that appear for various reasons. Papillomas are viral growths; nevi, as a rule, are congenital. New growths can be visually very similar, and therefore it is not always possible to distinguish them on your own.
What are papillomas?
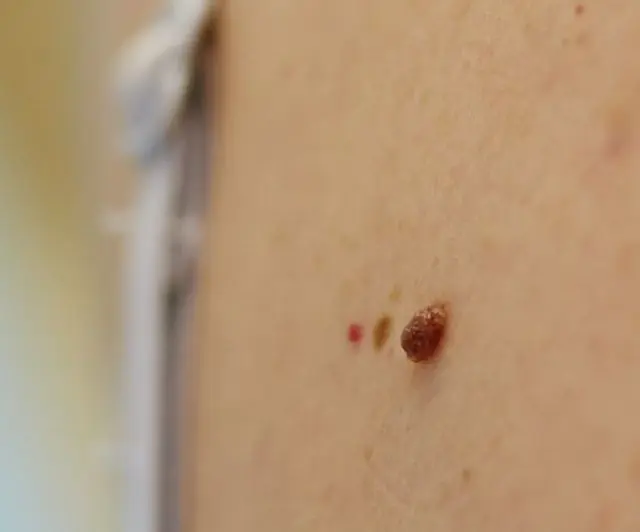
The photo shows what papilloma looks like
Papillomas are the result of the activity of a special virus in the human body - HPV. They do not appear immediately after infection. For some time the pathogen remains in the body in a passive state. If a person’s immunity is strong, then HPV may not manifest itself for years. Under favorable conditions, it is activated, and the accelerated formation of skin tumors begins.
HPV invades the epithelial structure in the upper layers of the skin and affects the DNA of healthy cells. Under such influence they begin to grow and divide intensively. This is how papillomas form on the body.
Growths can appear on the epidermis, mucous membrane, and less often on internal organs. Papillomas can be single or form groups. Depending on the strain of the virus, these neoplasms can have different shapes - filamentous, spherical, flat, or in the form of a rooster's comb. In most cases, these growths are soft and loose to the touch, painless and do not cause any discomfort other than aesthetic ones. Most often they form in the groin area, armpits, neck, face, and limbs.
The color of these growths is often the same as the skin, which is how papillomas differ from nevi. Sometimes they may take on a pinkish or light brown tint.
- Read also: what is a wart and how to treat it correctly
What do nevi look like?
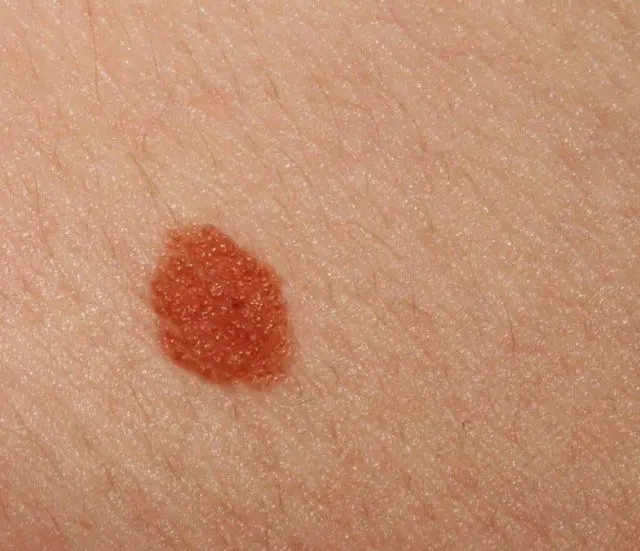
Photo of nevus
Nevi are otherwise called moles. These are congenital or acquired pigmented neoplasms on the skin. They can be genetically determined or appear under the influence of various factors during life. Nevi are formed as a result of the production of melanin by skin cells. It accumulates in the upper layers of the epidermis and forms melanocytes - a coloring pigment.
In most cases, children are born with clear skin, without nevi. It is quite rare for babies to appear with congenital birthmarks on their bodies. As a rule, the first pigmented neoplasms form at 1-2 years of age. With age, the number of nevi on the body increases.The number of nevi, their natural shade and size depend on genetic characteristics. This is the difference between nevi and papillomas. Typically, children inherit a general tendency to develop age spots from their parents. Identical nevi may also appear on the body of children, like one of the relatives.
In addition, prolonged and regular exposure to the sun can cause increased pigmentation. Also, nevi present on the skin can darken under the influence of ultraviolet radiation.
The nevus is dense and smooth to the touch. Its shape is quite symmetrical, and the edges are normally clear. The shade can vary from light brown to almost black.
What is the difference between nevi and papillomas?
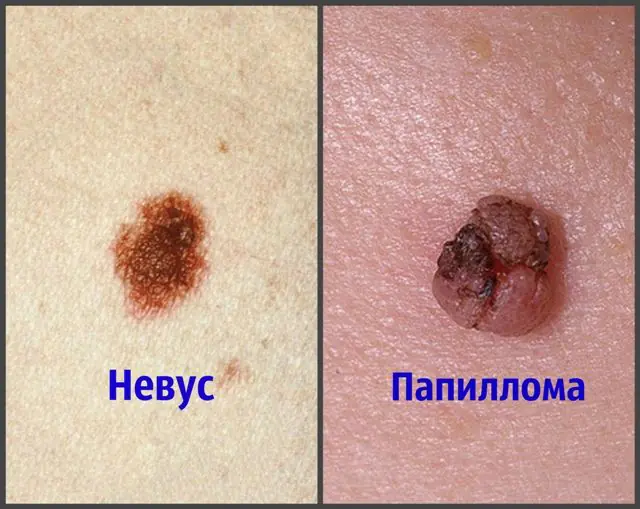
To determine for sure what kind of tumor you are dealing with, it is recommended to consult a specialist. However, the difference between nevi and papillomas is quite significant. There are a number of distinctive features by which these formations can be identified:
- Structure. Papillomas are loose, soft, mobile growths. Nevi are denser and harder growths. In addition, they rarely protrude above the surface of the skin. This is a significant difference between papillomas and nevi.
- Presence of vessels. Papillomas have a branched vascular network. Blood supplies the nutrients necessary for papillomas to grow and develop. Nevi do not have blood vessels in their structure.
- Form. Papillomas and nevi can have different shapes, but usually the viral growths are not symmetrical. Nevi, as a rule, have a more or less regular shape and are symmetrical.
- Location. Benign neoplasms can affect any part of the body. But papillomas have “favorite places”. These are the armpits, neck, chest, genitals, hands. Nevi most often concentrate on the arms and legs, back, and abdomen. In addition, papillomas can affect internal organs. Nevi never appear on the mucous membrane or lining surface of organs. This is how a nevus differs from a papilloma.
- Surface of neoplasms. Papillomas have an uneven, sometimes rough surface; they always protrude slightly above the epidermis. If we are talking about genital viral growths, they may resemble a cauliflower inflorescence. Nevi are smooth, do not have a skin pattern on the surface, and may protrude slightly, but not significantly.
- Color. Papillomas normally blend in with the skin tone. Over time, they may change color and become darker. Nevi always differ from the main skin. They can range from light brown to black. As a rule, healthy nevi do not change color over time.
- Genetic predisposition. Papillomas are viral tumors that are not inherited. Although a baby can become infected with HPV during childbirth from the mother. Nevi can be passed from parents to children genetically.
- Physical sensations. Papillomas and nevi normally do not cause any discomfort. However, with active growth, papillomas can itch, itch, or cause a slight burning or tingling sensation. Nevi cause discomfort in case of injury or malignant degeneration.
- Growth over time. Papillomas often increase in size and number with active HPV activity and weakened immunity. Sometimes these growths merge into large groups. Nevi can grow very slowly, and if they are grouped, then there are no more than 3 neoplasms together.
- Size. Papillomas are usually small in size - up to 15 mm. However, their groups can be quite large. Nevi can be either inconspicuous spots on the body or large formations, up to several centimeters in diameter.
- Read also: how to distinguish melanoma from papilloma
What is the danger of papillomas and nevi?
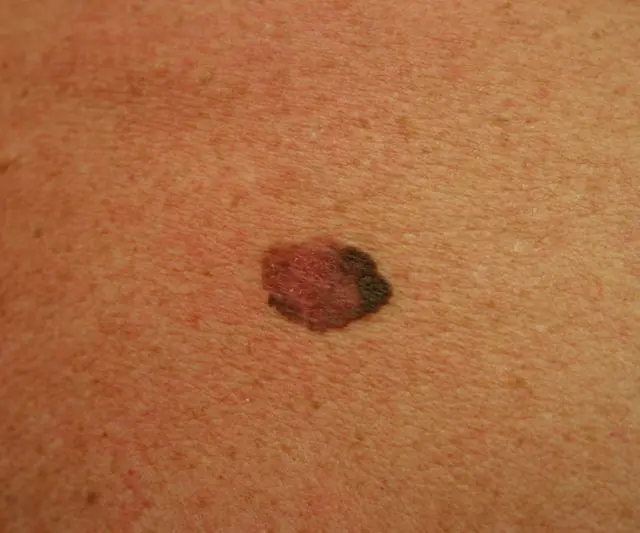
Photo of melanoma
In addition to their differences, these neoplasms also have certain similarities. In particular, papillomas and nevi can degenerate into malignant tumors. This malignant process is called malignancy.
It is worth noting that papillomas that were caused by an oncogenic strain of HPV become malignant more often. Non-oncogenic types of the pathogen rarely provoke the appearance of growths that become malignant in the future.
Signs of degeneration of neoplasms are:
- Fast growth. This is especially noticeable in relation to nevi, which normally can increase by no more than 2 mm per year.
- The appearance of new growths around existing ones. This applies to both nevi and papillomas.
- Discomfort in the area of the tumor. This may be soreness, swelling, redness, itching, burning, inflammation.
- Changing the appearance of the growth. It may crack, become dry and flaky. Also, nevus and papilloma can change color and become sharply darker.
- Other signs. The release of fluid or pus from the tumor, the formation of a light border around the growth.
All these symptoms should alert you and be a reason to visit a doctor.
Besides, papillomas and nevi can often be injured, especially if they protrude above the surface of the skin. Trauma is a pathway for pathogenic bacteria, which can cause inflammation, suppuration and even provoke an oncological process.
- See also the stages of degeneration of papilloma into a malignant formation
Watch a video about the types of nevi:
If you want to know how a nevus differs from a papilloma, then the best option is to visit a doctor who, after a visual examination and additional research, will be able to determine exactly the type of neoplasm. At first glance, these growths may be very similar, but their nature is completely different. In addition, nevi do not require treatment if they are healthy. It is recommended to remove papillomas.
- Related article: Difference between papilloma and condyloma



