The only effective method to get rid of a mole is to remove it. This is done for aesthetic reasons and medical reasons. Surgery is required if the growth is constantly traumatized, if its size, contours or color change. What happens after a mole is removed and how to care for it to avoid complications?
Popular methods and care
Currently, there are several methods for eliminating moles; the choice is usually made by a specialist. The doctor takes into account many factors - localization, likelihood of malignancy, area of skin damage.
Laser
The most precise impact is achieved when using a laser. This method is currently the most optimal. Experts highlight a number of positive aspects of this manipulation:
- local anesthesia makes the procedure virtually painless, even a child can easily endure it;
- duration is only 5-10 minutes;
- narrowly targeted beam exposure and the ability to control the depth of action prevent damage to surrounding tissues;
- soft and layer-by-layer removal of the nevus occurs;
- no bleeding;
- There are almost never any traces left after manipulation;
- minimum rehabilitation period (no more than 1-2 weeks).
Despite the positive aspects of laser destruction, it also has some disadvantages:
- inability to conduct histology of a mole after removal;
- not all hospitals have the most modern equipment;
- For normal healing, it is necessary to exclude ultraviolet irradiation and thermal procedures for some time.
The application area is treated with any antiseptics that do not contain alcohol, otherwise a burn to the young skin may occur, after which a scar will form.
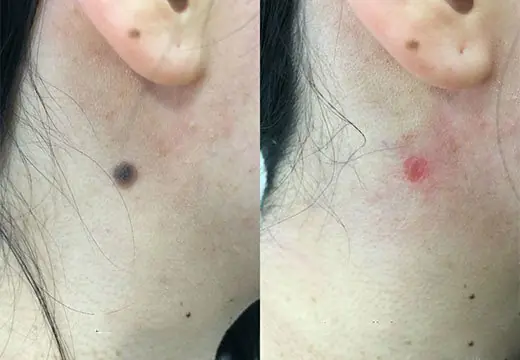
If everything is done correctly, the resulting crust falls off, and a red spot may remain in its place for some time. But then it disappears. Therefore, laser removal is used mainly to eliminate formations on open parts of the body.
If a scar forms at the site of removal, you can get rid of it by using a special patch with a silicone base. Contractubex or Dermatix ointment is also suitable. You can apply Panthenol or similar products to speed up regeneration.
Cryodestruction
This method uses liquid nitrogen, the temperature of which is minus 180 degrees Celsius. In this case, the tissue completely dies, a crust forms on top, under which the dermis is gradually restored. The procedure is not practiced in the facial area. Complete healing may take about a month.
Cryodestruction allows you to remove even a fairly large formation. During the session, the application site is completely disinfected due to the low temperature. The removal process itself proceeds quickly, leaving no traces in the form of a scar or scar. In addition, the patient does not experience pain.
The negative aspects of this method include:
- inability to conduct histological examination;
- getting burned;
- the need for a repeat procedure.
The doctor's lack of experience in such manipulations often leads to damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
On the first day, it is recommended to use hydrogen peroxide or a solution of potassium permanganate to treat a cold burn. For sensitive skin, antihistamine or antipruritic ointment (Fenistil, Nezulin) will help relieve itching. You should not scratch, as this easily damages the crust and the unformed tissue underneath it. For some time after the manipulation, a red spot may persist, gradually acquiring the color of normal skin.
Radio wave therapy
The radio wave method allows you to treat any problem area and at the same time preserve the tissue for research. The healthy part of the dermis is not disturbed, and no scars are left.
The method is especially suitable for cutting out tubercles that protrude greatly above the surface. The disadvantage of this technique is the impossibility of removing large formations. The risk of repeating the process, when the mole may appear again, is practically eliminated.
After radio wave removal, you should not wet the resulting crust and expose your body to the sun’s rays.. Only disinfection should be carried out: rinse with antiseptics in the first hours, lubricate with antibacterial ointments. The doctor may prescribe Chlorhexidine, potassium permanganate, Levomycetin, Pantoderm. You cannot use cosmetics.
Electrocoagulation
This procedure eliminates various formations using high current. In this case, tissue coagulation occurs, a crust appears, which then falls off. Manipulation is performed on any area of the skin. One session is enough. After this, no wound surface is formed, no bleeding is observed, since the vessels coagulate along with the mole.
After the crust is separated, a scar in this place can remain only in exceptional cases. Most often, a small spot appears, slightly lighter than normal skin, which will go away over time. If electrocoagulation or radioknife is used, the removed tissue is preserved. It can be examined for the presence of atypical cells.
The procedure is prescribed if it is necessary to eliminate warts, papillomas, hemangiomas, keratomas (in old age), and complicated acne. It is successfully used in the treatment of atheroma, spider veins, and formations after the introduction of molluscum contagiosum. Electrocoagulation is effective for removing a mixed type of nevus when cancerous degeneration is suspected. A positive aspect of the method is the ability to control the depth of exposure.
Do not wet the crust at the surgical site or expose it to insolation.. Then she needs to be protected from traumatization. Additional care in the form of applying local antibiotics and antiseptics is required only in case of infection.
Using a scalpel
The oldest method is to cut out the spot or nevus using conventional surgery. It is time-tested, its price is affordable for everyone. The intervention is carried out under local anesthesia and lasts approximately an hour. After excision, a wound is formed that requires treatment. When a wart or mole is located deeply, a hole is formed. If a large nevus is removed, then for normal healing the doctor applies a suture, which is removed after a week.
- high probability of scarring;
- bleeding during and after surgery;
- the patient needs rehabilitation.
- no need to look for a clinic with expensive equipment;
- the operation can be performed by a surgeon without additional skills and long-term experience;
- It is possible to excise formations of any depth and area of the lesion.
It is also important that the operation allows you to preserve the tissue intact in order to ensure the absence of oncological pathology based on the results of histological examination. It is very important to properly care for the excision site after this.
Healing takes a long time - from 2 to 4 weeks. At this time, you should treat the surface in the same way as a regular wound:
- rinse with an antiseptic;
- carry out hygiene of the skin around the wound;
- apply a bandage for the first few days to prevent infection;
- if the wound is subject to frequent friction, you will need to wear a bandage for a long time.
It is also important to avoid injury and exposure to sunlight during the entire healing period.
Possible consequences
Most often, nevus removal proceeds safely, but in some cases negative consequences of manipulation may occur:
- the appearance of inflammation and infection;
- swelling or new formation (high probability of developing a tumor);
- swelling and hyperemia;
- bleeding;
- soreness and discomfort;
- keloid scar;
- compaction;
- area of hypo- or hyperpigmentation;
- increase in local or general temperature.
In some cases, a new one may appear at the site of the removed spot. This phenomenon occurs when the manipulation is carried out incorrectly, when some of the mutated cells remain in the tissue.
Relapse requires an even more thorough examination and is eliminated exclusively by repeated removal with mandatory histological examination. This is especially important if there is a sore that itches or bleeds.
Normal recovery after surgery
If the intervention is performed by an experienced specialist, then the wound healing process proceeds normally. All you need is time and proper care.
- In the first week, a crust forms. The most important thing is not to touch her. In the first few hours, the wound may bleed a little, especially if it was removed using a scalpel. Avoid getting it wet or accidentally damaging it. In some cases, it is recommended to rinse with a light solution of potassium permanganate and apply an antibacterial ointment prescribed by a doctor.
- Second week - the crust on a small growth often falls off. In larger formations, it may still persist, and the skin underneath may itch. The exposed layer of thin epidermis requires protection from sunlight, and visiting a solarium is prohibited at this time.
- By the third week, the operation site should no longer hurt or bleed, even when affecting a large area. The redness goes away. If the laser method was used, then everything should be fine by this time. The application site is no different from normal skin.
- The fourth week is considered the last. At this moment, the patient forgets that he was once bothered by a nevus or birthmark. And the wound heals completely.
Violations after removal
If the damaged area in the area of the removed lesion becomes inflamed and pus begins to ooze, the associated infection is treated with antibiotics. Sometimes Tetracycline ointment is combined with oral broad-spectrum agents. If the wound begins to spontaneously become wet and a light liquid is released, then the area can be smeared with Zinc ointment, which dries and destroys pathogenic microflora. You should use any product only after consulting a doctor.
A hypertrophic scar may remain if the patient independently tears off the crust or exposes the removal site to constant friction or pressure. In this case, the wound will take quite a long time to heal and may turn into a scar. To eliminate a keloid scar after mole removal, a laser is often used.
A hypertrophic scar may appear as a depression in the skin with crater-like edges. This pathology can be eliminated with the help of physiotherapy or cosmetic surgery.
The hypopigmented area after nevus removal may resolve over time and is not usually a cause for concern. In this case, it is recommended to avoid sunlight.
Hyperpigmentation, or recurrent nevus, can occur after any method of removing a mole or spot. It resembles melanoma, has ragged, uneven outlines, and is dark in color. Differential diagnosis is carried out on the basis of histological data. To eliminate this phenomenon, repeated removal is carried out.
A mole is a congenital pigmented formation on the skin that has a different color range - brown, black, red, purple, etc. People often resort to excision. If the wound does not heal after removing the mole, you should consult a doctor.
The need and features of mole removal
| Removal Features |
| A nevus is a collection of cells that produce the melanos pigment. A mole is a benign formation that has a risk of transforming into cancer. |
Laser removal is considered a popular and widespread procedure, but other methods and techniques for eliminating nevi also have the right to life.
- Laser (layer-by-layer removal of moles).
- Cryodestruction (liquid nitrogen at -180°C).
- Electrocoagulation (burning with electric current using an electric knife).
- Surgical method (excision of brown formation in a hospital setting).
- Surgitron (based on the action of radio waves and created to remove various skin formations).
It is necessary to seek advice from a doctor who is competent to determine the possible presence of affected areas of the dermis. After the necessary medical examination, it is possible to choose the most rational method for removing the nevus. In some cases, doctors do not advise eliminating a benign tumor; the results may lead to complications.
Typically, wound healing after any mole removal takes a period of two to four weeks.
Melanin is a special pigment produced by special skin cells called melanocytes. It is a natural dye in the body that is responsible for the color of hair, eyes and skin.
Necessity of removal Benign tumors must be removed in the following cases:- When a mole is located in a vulnerable place, is subject to constant friction against clothing, hurts, is injured (at the time of a haircut, shaving on the head, under the armpit) - it is necessary to get rid of them; due to constant damage, the nevus acquires a tendency to malignant degeneration.
- When there is a real threat of transformation of a benign tumor into a malignant one. The growths must be removed immediately.
Rules for caring for a wound after removal
For quick healing of wounds after eliminating the formation, it is important to follow simple rules. After the nevus is eliminated, the attending physician will leave special care instructions. The course of rehabilitation depends on the method of eliminating the formation.
| What measures to take on the first day after surgery. | Treat the wound with a weak manganese solution, which reduces the risk of infection and dries out the resulting crust. |
| How to care for a removed nevus after surgery | Use of antiseptics and antibiotics. Special creams and ointments to avoid complications that arise after treatment. |
| What else do you need to know | In summer, it is important to protect the wound from sunlight. |
When removing a mole from the face, the doctor prescribes a treatment method individually.
What time of year is it better to postpone surgery? The recommended period for removing a nevus is autumn, winter.Stages of mole healing
Subject to strict adherence to the rules of care in the area of nevus removal, the dermis is completely tightened and heals after three to four weeks, the color of the skin becomes uniform. You can forget about scars if you follow all the rules for caring for the wound area. You can speed up the healing process if you properly treat wounds after mole removal.
| Stage I |
(First 7 days)
Formation of a crust, which is strictly prohibited from being removed. Its function is protective, protecting the wound from infection. Under the cover, the epithelial tissue grows more actively and tightens. Important! In the first seven days, protect yourself from injuries and damage - do not scratch, avoid contact with cream or other cosmetics. Stage II(7-14 days)
At the second stage, the crust dries out, peels off from the dermis, and a new skin with a light pinkish tint remains in its area. Important! Do not expose the affected area to ultraviolet rays. To this end, use sunscreen with a high SPF level and avoid direct contact with the sun's rays, and postpone going to the solarium. Stage III(day 20+)
The hole is smoothed out, and the skin does not require further special care.
How long will it take to heal?
When a mole is removed using the laser method, in addition to a scar, a small burn remains on the skin. The healing process will take longer.
In other options, the nevus heals faster. After a few days, a dry crust forms, which performs a protective function and cannot be injured or torn off. When the crust itself comes away from the skin, a light spot will remain.
The most problematic areas for healing are the armpits, folds of the skin, and parts of the body covered with hair (including the groin). It is necessary to handle with greater frequency and, if possible, leave it open to avoid damage.
The duration of healing depends on the size and depth of the nevus legs. The maximum healing period is from 7 to 20 days. A small pigment spot may disappear within 3 days.
What to do if the wound does not heal
If the wound bothers you in the first days after mole removal, the redness scares you, or suppuration has begun, there may be two root causes:
- Penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the wound during surgery or when a chronic inflammatory process within an individual’s body worsens.
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules.
If the scar does not heal at all and has an unpleasant appearance, you can think about special silicone patches and preparations that help smooth the skin.
When to see a doctor and possible complications
You should seek help from a doctor in the following cases:
When a nevus seems suspicious:
- color changes;
- dimensions over 1 cm.
Dangerous transformation of a mole for human life:
- huge size;
- blood or ichor oozes from the nevus.
| Complications after mole removal using different methods | |
| Methods | Complications |
| Laser |
|
| Cryodestruction (removal using liquid nitrogen) |
|
| Application of a radio knife (radio wave surgery) |
|
| Surgical |
|
The presence of nevi and birthmarks on the body is a reason to regularly consult a dermatologist. Melanoma is increasingly becoming the cause of death in people of all genders, ages and conditions. Any change in education should be alarming.
Moles do not always decorate the appearance; they often need to be removed. For this, the most proven method is often used - surgery. It will also help in cases where other methods are contraindicated.
Read in this article
Indications for surgical removal of moles
It is necessary to get rid of a nevus surgically under the following circumstances:
- it grows or has reached a size of more than 5 mm;
- the formation is deeply rooted in the skin;
- it consists of several parts;
- is located on an area of the body that is in close contact with clothing or shoes, and is therefore often injured;
- the mole bleeds, itches, changes color, its edges become uneven;
- she spoils the appearance.
Advantages of the method
The traditional method of excision of nevi with a scalpel has advantages that more modern methods do not have:
- safety, since the manipulation is performed by a surgeon and not in a beauty salon;
- painlessness, because the mole is removed under local anesthesia;
- the ability to examine the material using the histological method;
- a chance to get rid of a mole in a single operation;
- complete removal of formations that cryodestruction or laser cannot handle;
- affordable price;
- no absolute contraindications;
- almost zero risk of relapse.
Contraindications to surgical removal of a mole
There are no absolute prohibitions on intervention to get rid of a nevus with a scalpel. But there are relative contraindications:
- infection;
- inflammatory process in the body;
- acute period of chronic disease;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- herpetic rashes on the skin or mucous membranes.
Before removing a mole, you need to get rid of these problems.
Preparing for removal surgery
No special measures are required to prepare for surgical manipulation. A preliminary examination by a surgeon is necessary, who will explain the essence of the operation and give recommendations on how to behave before it.
The patient should not take blood thinning medications for several days, drink alcohol, and it is better to quit smoking. If a mole is being removed from the face, there should be no makeup on it.
How is surgical removal performed and how long does the operation last?
The intervention is carried out using one of two possible methods:
- Seamless. After disinfecting the surgical space and injecting the anesthetic, the formation is cut off with a scalpel just below the surface of the skin.
The wound is treated using special equipment to stop bleeding, and an antibiotic is applied to it. A sterile bandage is applied on top. This method is suitable for small, shallow moles.
- With sutures. The nevus and the skin around it are treated with an antiseptic and an anesthetic injection is given. Then the mole and adjacent tissues are excised. The wound turns out to be quite extensive and deep, which dictates the need for sutures. They are, as a rule, biodegradable, but for large moles they can also use non-absorbable ones.
After suturing the deep and outer layers of tissue, the surface is treated with an antiseptic and a bandage is applied.
The operation, regardless of the method, will not take more than 30 - 60 minutes.
To learn how micro-operation to remove a mole takes place, watch this video:
Recovery after surgery and suture care
The end of the intervention begins the rehabilitation period. A wound or suture remains at the site of the excised formation, which should be taken care of:
- do not allow water to enter this area;
- treat it with antiseptics 2 times a day;
- do not tear off the formed crust, avoid contact of hands and clothing with it;
- after 7 - 10 days, go to the doctor to remove the stitches if they are non-absorbable;
- protect the area from the sun.
The latter is especially important when the crust falls off and the young skin is exposed. This will happen in about 2 weeks. But ultraviolet radiation is contraindicated for at least another 2-3 months. The area of the healed wound should be hidden under clothing or a protective cream should be applied.
During the rehabilitation period, it is worth giving up alcohol and smoking so that healing is not disturbed and proceeds faster.
Will there be a scar after?
Even an operation with suturing does not necessarily require the presence of pronounced marks in this place. With proper care, the scar after the intervention remains almost invisible. If adjacent tissues were removed, the mole “sat” deep, it is more likely that the mark from the operation will be pronounced. To smooth out the scar, absorbable creams are applied to it or a special patch is used. And if their effect is not enough, the scar can be removed surgically.
Other possible complications after surgery
Excision of a mole can lead to new problems:
- Wound infection. Possibly during surgery, but more often it happens due to poor care of the wound and suture.
- Keloid scars. The complication occurs when healing is slow or due to a predisposition to its occurrence.
- The appearance of education in the same place. This is possible if the mole was not completely removed, or it was melanoma.
Cost of surgical removal of moles
The price for the operation depends on the size of the nevus. If it is less than 5 mm, it will be 1500 - 3000 rubles. For larger moles you will have to pay more. Preliminary examination and consultation are indicated separately in the price lists of clinics.
Alternative options to surgical removal of a mole
If the formation is small, you can get rid of it using:
- Radio wave method of mole removal
laser;
cryodestruction (low-temperature nitrogen); electrocoagulation; radio wave method.These methods are not always allowed to be used, unlike traditional surgery.
Don't be afraid to remove a mole with a scalpel. If the doctor insists on this method, it means that in a particular case it is optimal. And recovery after surgery is no more difficult than after using more modern methods.