Description and causes of myositis, symptoms of musculoskeletal disease. Methods of treatment: traditional and folk medicine.
The content of the article:- Reasons for development
- Symptoms of myositis
- Treatment options
- Medicines
- Physiotherapeutic procedures
- Folk remedies
Myositis is a disease of the musculoskeletal system that affects skeletal muscles, causing inflammation and pain in them. It can occur once in the acute phase, but often becomes chronic. The appearance of the disease is associated with various factors, thus myositis can be infectious, traumatic, autoimmune and other in nature. The pathological process may affect one or more muscles, as well as the skin. It has an unfavorable outcome in the absence of competent and timely treatment. Possible consequences: significant limitation of range of motion, progressive increase in muscle weakness, complete atrophy of the affected skeletal muscles, suppuration in the tissues.
Reasons for the development of myositis
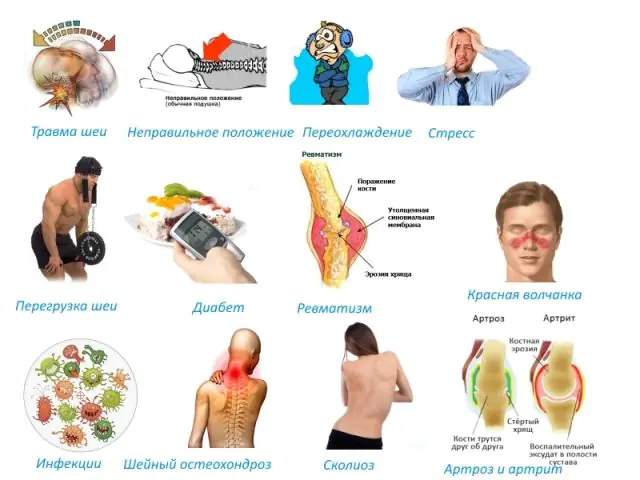
Inflammation of skeletal muscle tissue with pain syndrome is a fairly common pathology of the musculoskeletal system and can develop in both adults and children, both men and women. Muscle myositis, like any other inflammatory disease, can be caused by a number of negative factors - internal and external.
Reasons for the development of myositis:
- Infectious diseases. After infection and aggravation of influenza or other respiratory diseases of a viral nature, the microorganism spreads through the bloodstream throughout the body, which leads to aches in muscle tissue and pain. And during diseases caused by bacteria, muscle pain can be caused both by the pathogens themselves and by the toxic substances they secrete.
- Parasites. Problems with skeletal muscles can occur due to infection with echinococcus or trichinella, toxoplasmosis or cystericosis. Parasites penetrate muscle fibers and partially destroy them or form cysts in them.
- Autoimmune diseases. In some cases, the precursor to myositis is autoimmune disorders, when the immune system begins to attack the cells of its own body. So, the cause of myositis can be rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma.
- Toxic effects. As a result of intoxication of the body after consuming alcohol, drugs or certain chemicals, taking certain medications, for example, colchicine, hydroxychloroquine, alpha-interferon, statins, vincristine, etc., as well as after an insect or animal bite, moderate myositis is formed.
- Hypothermia. When the tissue is exposed to cold temperatures or drafts, excessive muscle tension occurs with the further development of inflammation. Both adults and children can be exposed to it.
- Excessive physical activity. Most often, as a result of playing sports or doing hard work, myositis occurs in people with weak physical shape. However, muscle inflammation can also develop in experienced athletes if the load is too strong.
In addition, various injuries, as well as uncomfortable body position that causes severe tension, can be a precursor to inflammation of the skeletal muscles. In this case, myositis can be considered an occupational disease of some professions, for example, pianists, violinists, drivers, and PC operators.
Therapy in each case includes both general therapeutic measures related to the fight against the inflammatory process and the elimination of pain, as well as individual ones aimed at eliminating the underlying cause, without which the risk of relapse remains quite high. Therefore, before treating myositis, it is necessary to correctly determine which factor caused the inflammation of the skeletal muscles.
Main symptoms of myositis
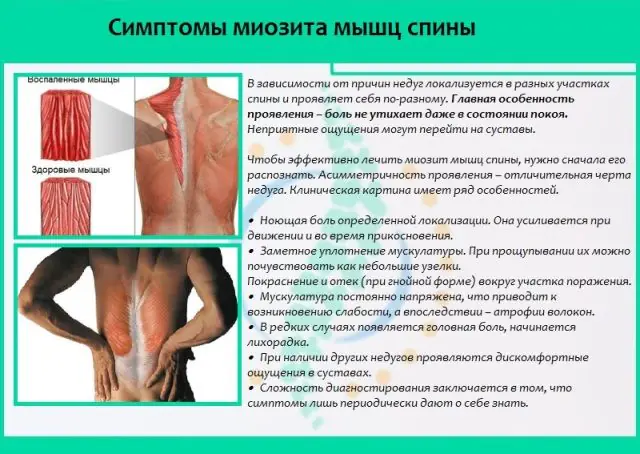
Inflammation of skeletal muscles is usually divided into types based on the causes of occurrence, forms of progression and localization of the inflammatory process. In each case, the clinical picture has some differences that help the doctor prescribe the correct diagnostic procedures and adequate therapy.
Types of inflammation of skeletal muscles by origin with their inherent general and individual signs of myositis:
- Non-purulent infectious. The reason is various infections. Manifestation: severe weakness in the body, muscle pain.
- Acute purulent. The main cause is osteomyelitis or other purulent-necrotic processes occurring in a chronic form. Sometimes purulent inflammation occurs after unsuccessful intramuscular injections, resulting in infection in the tissue. Symptoms: severe local pain, swelling in the affected areas, leukocytosis is detected in the blood, general body temperature often rises with chills.
- Traumatic ossificator. As the name suggests, this myositis develops after injury. As a result of damage to the musculoskeletal system, an inflammatory process begins, which mainly affects the articular ligaments. Muscle weakness and mild pain appear. Over time, atrophy forms. As a result, gradual pathological ossification of the injured areas occurs. In this case, surgical treatment is indicated.
- Congenital ossificans. A very rare species. Its cause is the genetic characteristics of a person, against the background of which ossification also occurs in muscle tissue. Moreover, it is impossible to predict at what point the pathological process will begin. Over time, the disease affects not only the skeletal muscles, but also the rest, which leads to death.
- Parasitic. It is a special response of the body to infection by parasites, as well as to those toxic substances that are the product of their vital activity. With the onset of the disease, when parasites settle in a certain part of the muscle tissue, local pain and severe muscle tension appear. Common symptoms include weakness and fever. In this case, the intensity of the symptoms depends on the vital activity of the foreign parasitic organism and has a wave-like character.
- Toxic. Intoxication with hazardous substances causes local swelling and severe soreness in muscle tissue. Against this background, myoglobinuria, renal failure, polyneuritis often develop, and subsequently atrophy appears.
- Polymyositis. This is the name of a condition when a large number of different muscles are affected by the disease, and it usually occurs against the background of autoimmune diseases characterized by systemicity. Polymyositis is considered the most severe type of the disease. Muscle weakness increases quite rapidly and can cause atrophy and disappearance of reflexes in the tendons. In childhood, the skin, lungs, heart, and blood vessels are often subject to inflammation. And in a large number of males over the age of 40, the formation of tumor neoplasms was recorded against the background of polymyositis.
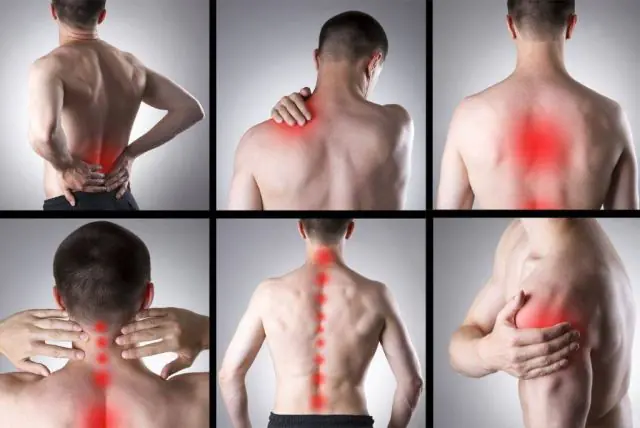
Types of myositis
The exact diagnosis and type of pathology is made based on the results of tests performed for myositis.
According to prevalence, myositis is divided into the following types:
- Dermatomyositis. It is a systemic disease, because the inflammatory process occurs not only in skeletal muscles, but also in smooth muscles, and also affects internal organs and the epidermis. It occurs more often in females in middle age. Sometimes there is the appearance of red or purple rashes on the skin, a slight increase in temperature, exhaustion of the body with further weight loss, and weakness. As it progresses, muscle flabbiness develops followed by shortening. Metabolic disorders with excessive accumulation of calcium salts are also observed.
- Cervical myositis. A dull pain appears on one side of the neck, sometimes radiating to the back of the head. A person often notices shooting pains from the ear to the shoulder. Pain in the temples and forehead area is also possible. Less often, unpleasant sensations - pain and numbness - are experienced by the hands to the fingertips. There is usually no restriction of movement in the neck, but it can be caused by pain. The danger of muscle inflammation in the cervical spine without proper treatment is the progression of the disease and the involvement of neighboring tissues in the pathological process, including the muscles of the larynx, diaphragm, and pharynx. Thus, the appearance of shortness of breath and cough can be an alarm bell and a reason to urgently go to the hospital so as not to lead to suffocation.
- Lumbar myositis. This pathology very often causes pain in the lumbar region. However, the pain is not very intense and is aching in nature. But at the same time they are felt constantly, even at rest. And upon palpation and during physical activity they noticeably intensify. Sometimes unpleasant sensations appear in the joints.
- Inflammation of the shoulder muscles. It is the result of fractures, dislocations, bruises and sprains. This type is more typical for people involved in sports. A distinctive feature is the appearance of symptoms 15-20 days after the injury.
- Inflammation of the muscles of the limbs. This type of disease occurs as a result of professional activity, for example, in drivers, machinists, seamstresses, musicians, who have poor physical activity and a long stay in a forced position.
- Inflammation of the masticatory muscles. Also myositis. The disease is characterized by severe tension in the masticatory muscle tissue, which sometimes leads to difficulty speaking and even the inability to eat.
- Polymyositis. Included in both classifications - due to the appearance and localization of the inflammatory process.
Types of myositis according to the nature of the disease:
- Spicy. Occurs due to hypothermia, excessive physical exertion and against the background of certain injuries. The onset of the disease is abrupt, the symptoms are quite pronounced. The patient has a high chance of a quick recovery, subject to timely and adequate treatment.
- Primary chronic. This condition is typical for toxic and infectious myositis. The onset of the disease is gradual. Symptoms are increasing.
- Chronic. Develops from acute or primary chronic in the absence of proper therapy. Exacerbations occur in waves. Sometimes the symptoms subside, but with prolonged exercise or other provoking factors, the pain returns, and persistent muscle weakness and limitation of motor activity gradually develop.
Diagnosis of myositis is made not only based on existing symptoms, because the symptoms are similar to some other diseases, for example, osteochondrosis, spinal hernia, kidney pathologies. To make a diagnosis, an MRI, X-ray or computed tomography is often performed, which will assess the structure of the tissues and determine the nature of the changes. Blood and urine tests, ultrasound examination of the kidneys are prescribed for lumbar myositis. In addition, the blood is examined for phosphorus and calcium content, the acidity of phosphatase, urea level, myoglobin, creatine kinase, etc. are determined. If there is a suspicion of an infectious nature, then a virological and bacteriological study is carried out, blood is taken for immunological samples, and PCR is also performed -diagnostics.
Methods for treating myositis
Myositis is an insidious and quite dangerous disease. In many ways, this pathology of the musculoskeletal system is similar in symptoms to osteochondrosis. Many people often self-diagnose and use over-the-counter ointments for treatment to relieve pain and inflammation. Due to such tactics, time is wasted, and the chances of a full recovery are gradually reduced. It is very important to undergo a timely diagnosis and begin adequate comprehensive treatment prescribed by a qualified medical specialist. Next, we will consider in more detail the treatment options for myositis.
Medicines for the treatment of myositis

Viprosal for the treatment of myositis
Many methods have been developed for the treatment of skeletal muscle inflammation. An extensive list of therapeutic measures is associated with the presence of a large number of possible causes of the disease. Therefore, the choice of one or another treatment option depends on the etiology of the disease. It is extremely important not just to eliminate the symptoms, but to eradicate the causes of myositis.
Thus, in case of infectious origin, antiviral, antibacterial or antiparasitic drugs are prescribed, respectively. If there is purulent inflammation of the tissue, then the abscess is opened and washed with further antiseptic treatment and the application of medications to fight the infection and restore tissue. Accordingly, if myositis was caused by a malfunction of the immune system, then drugs are indicated to suppress immune reactions and further correct the functioning of the immune system, which allows eliminating the inflammatory process.
Note! An important principle in the treatment of inflammatory processes in skeletal muscles is to provide the affected muscle tissue with maximum rest.The most obvious symptom of myositis is pain of varying intensity. It is this that primarily causes discomfort and significantly worsens the quality of life. Therefore, it is very important to eliminate this manifestation.
Medicines to combat the symptoms of myositis:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. This group of medications includes a wide list of medications, among which the most popular are Diclofenac, Ketoprofen, Ibuprofen, Voltaren, Nimesulide, Meloxicam and others. All of them perform several functions: neutralize the inflammatory process, eliminate pain, relieve swelling and act as an antipyretic. The high effectiveness of NSAIDs allows them to be prescribed to both adults and children. Among the side effects of incorrect dosage or excessive sensitivity of the body are the risk of bleeding and a detrimental effect on the liver.
- Angioprotectors. Their functions include normalizing capillary permeability and improving metabolic processes, which has a beneficial effect on the functioning of muscle tissue. Drugs in this group include Pentoxifylline, Curantil, etc. The drugs have a number of contraindications and side effects, so they should be prescribed taking into account possible restrictions.
- Antispasmodics. Drugs such as Viprosal, Vipratox, Apizartron contain bee or snake venom. They act as local irritants and relieve pain well.
- B vitamins. They are often prescribed in the form of intramuscular injections. Vitamins of this group have a positive effect on the entire body. And with myositis, their beneficial effect is expressed in the normalization of nervous processes and metabolism.
- Warming ointments. Used for external use in the affected area. The active ingredients quickly penetrate the soft tissues, have a warming and relaxing effect, and also eliminate pain. Menovazin solution, which is made on an alcohol base with the addition of menthol and novocaine, can also be used.
For myositis, traditional medicine drugs produce a fairly quick effect, unlike folk remedies. Their effectiveness is much higher, but each option has its own list of contraindications, which must be taken into account.
Physiotherapeutic procedures for myositis
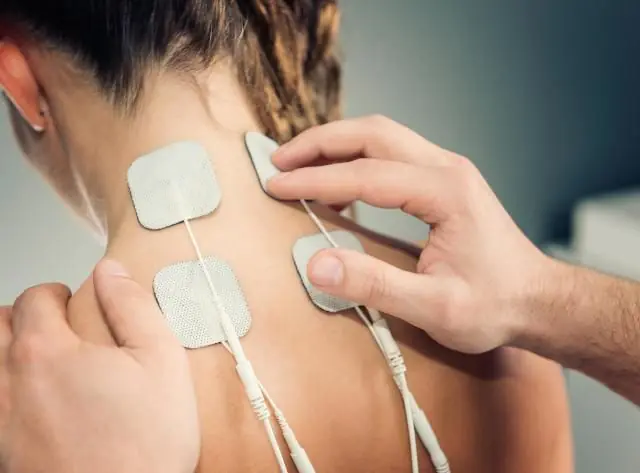
Electrophoresis for the treatment of myositis
If medications do not give the desired result for myositis, then it is necessary to undergo a course of physiotherapy that will help stop the pathological process and relieve the person from the symptoms of the disease. They are carried out within a medical institution, have a minimum of restrictions and fairly high effectiveness.
Physiotherapeutic treatment for myositis includes:
- Medicinal electrophoresis with novocaine. With the help of electrical impulses, the delivery of the drug to the affected tissue is accelerated, thereby enhancing the therapeutic effect. Typically, 12 sessions are performed and it is recommended to avoid strenuous physical activity for 3 weeks after treatment.
- Thermal treatments. They provide maximum muscle relaxation with subsequent relief from pain. By eliminating excessive tension in muscle tissue, metabolic processes are normalized, which speeds up recovery. Within the framework of this technique, 8-10 sessions of paraffin therapy, ozokerite, and UHF can be performed.
- Ultrasound. Treatment is carried out through the mechanical, physico-chemical and thermal effects of ultrasound. In the first case, a vibration massage is performed, in the second - mechanical resonance, accelerating the movement of molecules and changing the isoelectric state, in the third - an increase in local temperature. Ultrasound stimulates biochemical and physicochemical processes at the local level, accelerating metabolism.
- Acupuncture. In other words - acupuncture. Its functions include normalizing muscle tone, eliminating inflammation and pain. A timely procedure allows you to avoid progression of the disease and eliminate relapse. The course of treatment is 2-5 sessions.
- Massage. Usually carried out after a preliminary compress or warming up, this enhances its beneficial effects. Of course, it is better when it is carried out by a qualified specialist, but you can perform relaxing stroking, kneading and rubbing at home on your own or with the help of relatives. You can enhance the positive effect of massage for myositis with the help of aromatic oils of lavender, cinnamon, sandalwood, and rose. The method is not used for purulent lesions.
- Physiotherapy. Depending on the location of inflammation and the intensity of the pathological process, a set of moderate physical exercises is indicated, which are designed to restore the performance of skeletal muscles, speed up metabolism, improve blood circulation and increase endurance.
Folk remedies against myositis

Turpentine for myositis
Traditional medicine has many recipes based on improvised means that can reduce the manifestations of myositis without harmful effects on the body. A significant disadvantage of using such treatment is that people refuse qualified medical care in the hope of an easy recovery. This excludes the possibility of making an accurate diagnosis, which leads to frequent relapses and a significant deterioration in well-being.
The use of folk remedies in the treatment of inflammatory processes of skeletal muscles is acceptable after consultation with the attending physician and in combination with methods of traditional medicine.Traditional medicine to eliminate signs of myositis:
- Potato. This root vegetable must be boiled in its skin and then mashed. Apply 3-4 layers of cloth to the affected area and place potatoes on top of it. Then wrap it with a bandage and leave it until it cools completely. After removing the compress, the affected area is rubbed with vodka and wrapped in woolen cloth. During the procedure, you must adhere to bed rest.
- Cabbage. Whole leaves of fresh vegetables are used. Each leaf should be dipped in a solution made from water and baby soap, then sprinkled with a small amount of soda and applied to the sore area, fixing it securely. Exposure time is from 1 to 8 hours.
- Horsetail. Dried horsetail grass in a ratio of 1 to 4 is mixed with butter. This mixture is used to treat the sore area for pain relief.
- Turpentine. Based on it, you can make a good anti-inflammatory agent that can also eliminate pain. To do this, take three ingredients in equal quantities - turpentine, egg yolk and apple cider vinegar. Mix everything until a homogeneous mass is obtained and apply it as an ointment for myositis on diseased areas.
- Badyaga. Badyagi powder in an amount of 3 g is mixed with 1 tsp. butter. Next, rub into the affected area and wrap for 30-50 minutes.
How to treat myositis - watch the video:
You can seek help from many specialists if inflammation occurs in muscle tissue; it is important to correctly determine the cause of the disease. Initially, you need to visit a therapist, who will prescribe diagnostic procedures and subsequently refer you to a specialist, for example, a traumatologist, infectious disease specialist, surgeon, parasitologist, neurologist.



