The eyes have long been called the mirror of the soul, which has been sung by many great poets.
But what if an ugly stain appears on this clean and transparent surface that cannot be washed off? Why does it appear and is it a sign of a serious illness?
The answers to these, as well as other questions regarding the formation of moles on the eyeball or conjunctiva, will be given in this article.
Why does such a tumor appear?
Today, the main cause of nevus on the conjunctiva and eyeball, as well as on other parts of the body, is a large amount of melanin accumulating on a small fragment of skin and is responsible for the shade of the eyes, skin and hair. Nevi can also form under the influence of other factors, but the main one is disruption of the functioning of the endocrine system and hormonal fluctuations.
Today, there are a number of factors that provoke the occurrence of conjunctival nevi. These include:
- pregnancy (especially in later stages);
- stress and nervous disorders;
- exposure to various radiations on the body (including UV rays);
- infectious diseases;
- menopause;
- natural aging of tissues;
- taking contraceptives;
- inflammatory processes on the skin.
Forms of the disease
Modern experts distinguish two types of ocular nevi:
- conjunctival moles;
- nevi of the eyeball.
Conjunctival nevi
The conjunctiva (iris) of the eye is the transparent mucous tissue.
Neoplasms on it can arise both from the outside and from the inside.
Depending on which cells take part in the formation and growth of the nevus, iris pathologies are divided into:
- Vascular. They occur in places where small blood vessels accumulate on the mucous membrane and have a red or pink tint.
- Pigmented. This form of pathology is characterized by a dark color, which is explained by the large amount of melanin in the tissues.
- Cyst neviAs a rule, they are colorless and in appearance they resemble small air bubbles. Cyst-like moles appear in places where lymphatic vessels connect.
Sometimes moles on the iris can change under the influence of hormones. In addition, some nevi may lighten over time and even fade completely.
Moles on the eyeball
Just like moles of the iris, nevi of the eyeball can be divided into several types depending on their variability:
- Stationary. This type of mole does not change its color or size. As a rule, no serious problems arise with such neoplasms. They are not dangerous to health and do not require surgical intervention, although examinations by an ophthalmologist should not be ignored.
- Progressive. This group of moles has the ability to change their shape, shade and size. Progressive nevi have a yellow border, which in some cases can cause worsening vision or a decrease in viewing angle.
Localization and appearance
Nevi can be located on both the external and internal sides. Most often they are localized at the edge of the inner eyelid in the corner of the eye, at the border of the conjunctiva, in the area of the lacrimal caruncle, or in the semilunar fold.
In some exceptional cases, moles appear on the inside of the eyelid or near the pupil, but they do not affect vision.
New growths on the eye can have different shapes and colors. There are flat and convex moles in shape. The hue of nevi can vary from light pink or yellow to blue-black. The color of the mole directly depends on the number and type of cells from which the nevus is formed.
Sometimes colorless neoplasms occur. This is explained by the fact that the cells that form it do not contain pigmentation. As a rule, a conjunctival nevus has clearly defined boundaries, a flat shape and a velvety surface.
Symptoms
Iris nevus usually begins to appear in the first 10-20 days of life. At this stage, local irritation or small pigment spots are observed.
Single, maximally limited, flat or slightly convex epithelial neoplasms appear, which move without problems along the surface of the sclera. Quite often at this stage, cystic cavities form within the boundaries of the nevus.
Depending on the individual characteristics of the body pigment spots can have different shades, and in some nevi, pigmentation may be completely absent.
Pigmentation color ranges from light brown and tan to dark chocolate and blue-black. In adolescence, the nevus may change in size and become more pronounced.
A malignant neoplasm on the conjunctiva has the following clinical manifestations:
- unusual location of the formation: the border of the eyelid or the arches of the iris.
- Pigmentation extending to the cornea.
- Sharp growth and change in the shade of pigment spots.
- The appearance and development of vascularization (with the exception of puberty).
How is it diagnosed?
During the initial examination of the nevus of the iris and the eyeball (the white of the eye), the specialist must pay attention to the following complaints of the patient:
- constant discomfort and sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the eye.
- Cosmetic changes (defects).
- A feeling of “sand” poured into the eyes, which does not leave the patient for a long time.
- Hemorrhage into the mucous membrane.
After listening to the patient’s complaints, the ophthalmologist must examine the eye. He studies the condition of the iris, cornea and mucous membrane. Then, using a special slit lamp, he checks the transparency of the shells.
At the second stage of diagnosing the disease, the following instrumental techniques are used:
- Ophthalmoscopy - a method of studying the retina, small vessels and the state of the optic nerve by reflecting light from the fundus of the eye. This procedure is carried out using an ophthalmoscope on a dilated pupil.
- Ultrasound of the eye makes it possible to study the state of the deep components of the eye structure. This technique is used to control the growth of nevus.
- Duplex color scanning allows you to study the structure of the eye and its general blood circulation.
- Angiography, which helps determine the presence of retinal angioma. During the procedure, a fluorescent dye is used, which accumulates in the places where moles appear.
In addition, if necessary, the attending physician may additionally prescribe CT and MRI. Thanks to these diagnostic methods, the malignancy of the neoplasm is confirmed or refuted.
Forecast
With timely treatment of nevus, the prognosis given by specialists is almost always favorable. This is explained by the fact that in modern medicine there are many ways to prevent the degeneration of a nevus into melanoma.
Treatment
If the neoplasm is stationary, then treatment is not required. The main thing is to visit an ophthalmologist once a year, to exclude the growth and development of nevus. If the mole begins to grow and change color, treatment must be started immediately. Today, medicine uses several methods for treating nevus. These include:
- microsurgery;
- laser therapy;
- cryodestruction;
- brachytherapy.
Microsurgical removal
This treatment method is suitable for treating all types of nevus. Most often used to combat large and malignant tumors. If a mole creates discomfort, pain occurs, and experts suspect melanoma, then it is recommended to remove the nevus surgically.
During the operation, local anesthesia is used, so there is no need to be afraid of pain. The main advantage of this treatment method is its relatively low cost, compared to other methods of combating nevi.
Laser therapy
Quite often, neoplasms on the eye are associated exclusively with cosmetic defects. But at the same time, everyone forgets that such a pathology can cause loss of vision, and, consequently, significantly worsen the quality of life.
It is for this reason that before surgery it is necessary to undergo a complete eye examination and consult with an oncologist. And if necessary, make a histology of the contents of the nevus. Laser therapy allows treatment without plastic surgery or sutures.
Using a laser, excision of the tumor is carried out within tissues not affected by pathology.
Cryodestruction
Today, a very popular method for removing nevi using liquid nitrogen is cryodestruction. The method is based on exposing moles to extreme cold, so that it is enough to completely destroy any organic matter.
Brachytherapy
This method of removing nevi is very simple, but safe. After the brachytherapy procedure, the patient does not feel pain, and it has no consequences or complications.
The main advantage of this procedure is that in one session the body is exposed to several types of radio waves that remove nevi and trigger tissue regeneration. Today, brachytherapy is used as part of a comprehensive treatment or as an independent procedure.
Prevention
If moles appear on the eye (both outside and inside), You need to pay special attention to protecting your eyes from the aggressive effects of the scorching sun. To do this, you need to use special glasses and lenses with a UV filter, as well as regularly visit an ophthalmologist and monitor the condition of your eyes.
Conclusion
The main task of all modern ophthalmologists is to save and preserve human vision. Therefore, at the first suspicion of a pathology of the iris and eyeball or the slightest discomfort in the eye, it is necessary to consult a specialist, undergo an examination and begin treatment.
The formation of moles on the eye is rare, but it is possible. They are formed due to accumulations of melanin and are created on any anatomical areas, including in the eye. The formation is of exactly the same nature as on the shoulder or arm. However, this area causes reasonable concern and concern, so it needs to be monitored and observed by a doctor.
Causes
A mole can appear in infants, adults and the elderly. In this case, the ocular nevus can be localized on the iris, on the white or on the cornea. In some cases, the mole is not visible and can only be detected using an ophthalmological microscope.
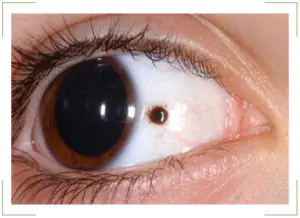
As a rule, a birthmark is visible from the side. It has a darker pigment composition. Therefore, the nevus is very noticeable in people with light eyes. To understand why it is dangerous, you need to understand the reasons for the formation:
Congenital feature
Then the pupil and white will have a nevus from the first days of the child’s life. In newborns, this spot is often small in size. But over time, the eye changes color and it grows. Moreover, its increase is very intense.
| Congenital nevus does not pose a threat to vision. It does not interfere with visual function and does not affect the functioning of capillaries. |
Acquired nevus
In this case, the mole appears throughout life. And this can happen at any moment. After all, the conjunctiva and the eye are exposed to different influences throughout life. Moreover, such effects can be directed not only directly to the conjunctival region. This is caused by severe stress, hormonal changes, pregnancy, and so on. In any of the above cases, there is a possibility of a birthmark appearing on the eye.
Types of moles in the eye
Typical nevus
Located on the iris of the eye. This area is also called the conjunctiva. Such moles are small spots with a diameter of several centimeters. As a rule, they have a clear shape and edges. The color of the nevus is often brown. 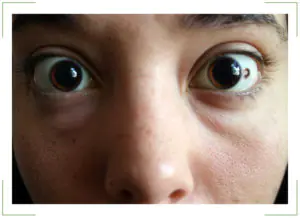
Atypical nevus
It may be colorless and located on the inner surface of the iris, where it is not visible. Accordingly, it is invisible from the outside. The initial nevus is also small in size. At the same time, they may not change during a person’s life. But when the mole enlarges, the subsequent stage is expressed by a more extensive nevus. It begins to take up a lot of space and switches to protein.
Conjunctival nevus
Covers the previous two types. Since this is the iris of the eye, the moles that are located on it are conjunctival nevi. This type of spots is further divided into cystic and vascular.
Thus, cyst-shaped ones do not have a pronounced color and are honeycomb-like formations. Meanwhile, capillary ones are created from small blood vessels. That's why they have a pale pink or red color.
Choroidal nevus
It is located inside the eye and is invisible to others. Actually, the choroid is a collection of vessels located on the inner surface of the eyeball. Therefore, a nevus can only be noticed during an examination. Such formations may have a constant shape and size, but there are times when they change.
Stationary and progressive nevus
| The appearance of a mole in the eye does not mean a risk of developing cancer. This sign can be completely safe. Moreover, the nevus does not affect visual acuity or eye function in any way. |
Nevus is not considered a disease. This is an education that every person has. It’s just that moles are usually located in other anatomical areas. For example, on the back, arms, and so on.
In this case, the nevus can grow over time. Such formations are called progressive. They change size and shape, gradually increasing. Often, growth occurs at a very rapid pace. So, in one year a mole doubles in size.
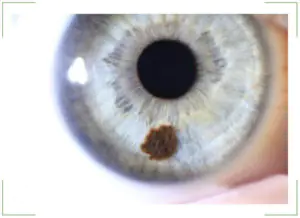
If any other spot begins to grow, this indicates a potential cancer threat. But this principle does not work regarding nevus in the eye. It is important to clarify the situation. An increase in the size of the spot does not mean that the mole is turning into a malignant formation. The risk of developing cancer remains throughout the entire period of existence of the nevus in the eye. Therefore, when a mole appears, it is necessary to consult a doctor, undergo an examination and monitor the dynamics of its condition.
What is the danger of pigmented nevi in the eye?
As stated above, education does not pose serious consequences for vision. They do not obstruct vision, do not narrow the field of vision, or impair its sharpness. At the same time, birthmarks do not cause any discomfort to a person.
The only threat is the likely development of the nevus into a malignant cancer. Therefore, many consider it necessary to treat and remove moles in the eye.
Symptoms of nevi
The main sign is that the stain is noticeable to others and to the person himself. The nevus can be located around the entire perimeter of the eye, this does not play any role.
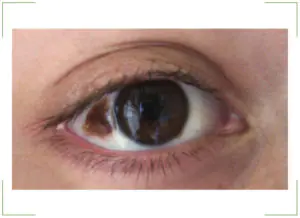
The only symptom of a birthmark is a change in corneal pigmentation or protein. The appearance of small spots and clusters in the form of bubbles indicates the initial stage of the nevus. If such formation causes concern, you should contact an ophthalmologist and undergo an examination. It is impossible to be sure in any other way what type of nevus it is.
Diagnosis of formations
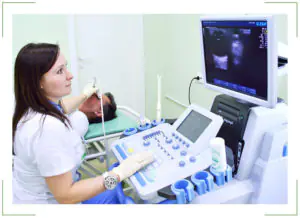
Detection of a birthmark is carried out using special equipment. After all, it is necessary not only to study the cornea or pupil. The doctor must look inside the eyeball, examine the fundus, and so on. Therefore, various techniques are used:
Ultrasound diagnostics
It is a well-known ultrasound examination. Only the patient's eye is the object. Using this technique, it is possible to identify accumulations of melanin in certain parts of the eye. This test is very accurate and provides a complete picture of what is happening inside the visual organs. There will be no hidden areas, which is very important for further treatment of nevus;
Angiography
This is a type of x-ray examination. It is necessary for studying and assessing the condition of blood vessels. As stated above, a nevus can form directly on a collection of blood vessels in the eye.
During the examination, it is recommended to use both methods. They complement each other perfectly and give an accurate picture of the development of the birthmark. A lot of information can be obtained by studying the nevus over several years.
Treatment methods
This phenomenon is not a disease. This is a condition of the eye in which there is an accumulation of pigmented formations. They form a nevus. It cannot be affected by medications or physiotherapeutic methods. The mole will not disappear from this.
Only birthmark removal is used. It can be removed using laser technologies, with local anesthesia, without placing the patient in a hospital.
| Such technology is safe and does not involve the risk of worsening the patient’s condition. |
Forecast
In the vast majority of cases, even if a mole grows, it remains safe and does not affect health. However, it can always be removed using a laser, thus eliminating the risks.
Can a nevus turn into cancer?
Theoretically, any mole can turn into cancer. And nevus is no exception. However, it is not a disease in itself. But in order to eliminate the risk, the formation should be removed.
Prevention of cancerous transformation of eye nevi
It is impossible to predict the growth of a nevus into a cancerous tumor. There is such a risk, although it is extremely insignificant. It is impossible to exclude such a case with the help of medicines, drops or traditional medicine potions. Therefore, the only option is to remove the nevus immediately after detection.
Moles (nevi) on the human body are a common occurrence, since everyone has them. Usually they are not paid attention to until the formations cause discomfort. But the appearance of a birthmark on the eye is cause for concern, since few people experience such a pathology.

Causes
Moles on the organs of vision appear due to an increased concentration of melanin. This is a pigment responsible for a certain color of hair, skin, eyes. The nevus is formed during the prenatal development of the child, begins to color during puberty, and acquires its brightest color after 30 years. But in 20% it is not pigmented at all, and is only discovered randomly during an ophthalmological examination. It manifests itself especially actively under the influence of certain factors. These include:
- intense exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- hormonal instability;
- injuries to the mucous membrane of the eye;
- inflammatory, infectious processes;
- genetic predisposition.

Nevi can be located in various ocular structures. The method of their detection and treatment depends on this.
Birthmark on the conjunctival membrane
Moles occur on the conjunctiva in 5% of cases. They can appear both outside the shell and inside. In some cases they are flat, in others they are convex. Localized in the area of the eyeball, cartilage, lacrimal caruncle.
Birthmark on the choroid
A nevus of the choroid of the eye is a formation that resembles a mole in appearance. But it is located in the depths of the organs of vision, and not on the skin. This type is detected in 2-10% of people. A very dangerous type of nevus that can degenerate into an aggressive malignant tumor. Formed from the cellular material of the supravascular plate. It is located behind the wide part of the eye, but sometimes forms in the equator area. The danger lies in its ability to malignize, which means degeneration into a malignant and rapidly growing formation, which sometimes leads to irreversible serious visual defects.

Depending on their tendency to enlarge, nevi are of the following types:
- Stationary.The birthmark can be flat or convex in shape, grayish or gray-greenish. It is evenly colored. This type of nevus does not have a negative effect on visual function. Usually its edges are smooth, but sometimes they can be visualized as slightly blurred. Stationary moles for the most part do not become malignant.
- Progressive. The nevus is prone to growth, during which its boundaries lose sharp outlines, its size changes, as well as the uniformity of coloring. A very dangerous type of birthmark, which leads to complications such as impaired visual perception, compression of choroidal vessels, degeneration into a cancerous tumor, and retinal detachment. A progressive pigmented nevus is detected only dynamically, tracking changes in the neoplasm over several months. During this time, the person undergoes several ophthalmological examinations, during which an increase in the size of the nevus is detected, a violation of the clarity of its boundaries, a change in color (it becomes heterogeneous, a yellowish shadow forms around the birthmark).
If an atypical mole develops, then a lighter choroid can be seen near it, as well as degenerative areas within the formation itself. Any changes in the nevus should alert the ophthalmologist and think about prompt treatment.
Based on the cells that make up the nevus, the following types of neoplasms are distinguished:
- Vascular. Formed from capillary clusters. The spot has a pinkish or reddish color.
- Pigmented. Neoplasms are formed from a large number of melantocyte cells. They have different shades, even black.
- Cyst-shaped. They are formed from the cells of several fused lymph vessels. In appearance they resemble a honeycomb.
The danger of nevi in the eye
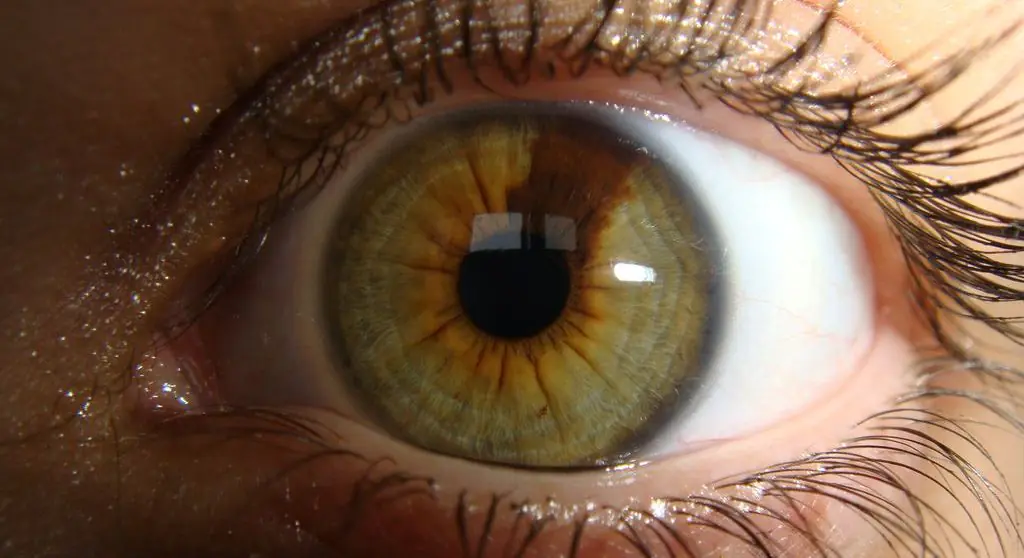
For some people, moles on the eye do not bother them throughout their lives. But sometimes they begin to transform, that is, they degenerate into a cancerous tumor, especially under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Fortunately, according to statistics, only 1 case out of 500 occurs when a nevus transforms into cancer.
You should contact an ophthalmologist in the following cases:
- the birthmark has changed color and size;
- vision has deteriorated or the visual fields have narrowed;
- the presence of a foreign object is felt.

Symptoms
The signs of nevus of the choroid and conjunctiva are almost identical. An ordinary birthmark does not manifest itself in any way. Such a neoplasm is discovered during an ophthalmological examination completely by accident.
Progressive nevus has its own symptoms:
- impaired quality of vision;
- distortion of visible objects;
- sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the eye;
- limited fields of vision.
If you have such symptoms, you should consult a doctor to prevent dangerous consequences.
Diagnostics
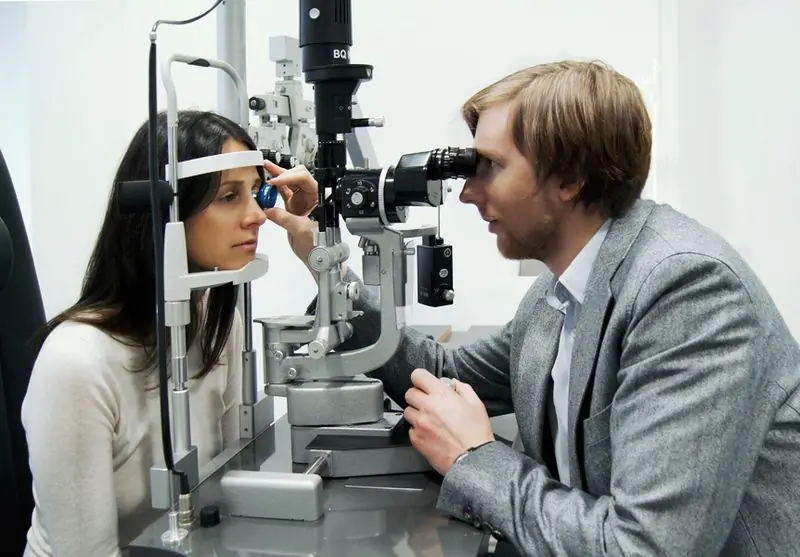

Initially, the doctor collects an anamnesis, asking the patient about the time the nevus appeared in the eye and whether it causes any discomfort. After this, he examines the mucous membrane and carries out instrumental diagnostic measures.
- Ophthalmoscopy. Examines the condition of small vessels of the retina and optic nerve using an ophthalmoscope with a dilated pupil. When examining the eye using a red filter, the tumor can be clearly seen. When using a green filter in an ophthalmoscope, a specialist sees negative changes in the ocular structures that occur with a progressive nevus.
- Echography. Using the procedure, the focus of pigmentation is identified.
- Ultrasound of the eye. Study the deep structures of the eye. The technique is necessary to control the progression of nevus.
- Fluorescein angiography. It is used to identify retinal angiomas. During the procedure, a contrast agent (fluorescein) is injected into the eye, which highlights areas with pathological changes.
Treatment methods
In cases where the birthmark turns out to be a benign formation and does not cause discomfort to the person, treatment is not carried out. Progressive nevus requires constant monitoring. Control checks are carried out every six months. If there is an increase in formation, then treatment is prescribed. The therapeutic technique is selected depending on the location of the birthmark and its size.
The progressive form requires surgical intervention. An atypical mole requires urgent treatment, since it has the highest risk of degeneration into a malignant form and a large cell nevus in the area of the optic nerve (choroidal melanocytoma).
There are several types of surgical removal of moles in the eyes:
- Electroexcision. A method for removing a nevus in the eye using an electric scalpel. It is used to remove large malignant tumors followed by plastic surgery.
- Laser therapy. The birthmark is removed with a laser beam without suturing or plastic surgery. Healthy tissues are practically not affected. Nevus removal with a laser is often used when the formations are located in a hard-to-reach place.
- Cryodestruction. A popular way to remove a mole is using liquid nitrogen. Cryodestruction is used to completely destroy any organic matter.
- Brachytherapy. A simple and fairly safe way to remove a mole in the eye. In just one session, nevi in the eye are removed using radio waves of various frequencies, which not only eliminate birthmarks, but also trigger regenerative processes in the tissues of the eye. Brachytherapy is used as an independent procedure and as part of a comprehensive treatment.
Prevention and prognosis
A stationary type of birthmark on the eye has a good prognosis, since the risk of transformation is minimized, as well as a timely detected and treated progressive nevus. Atypical moles are considered dangerous, as they can become malignant over time.
Preventive measures to prevent malignancy of moles in the eye are:
- protecting eyes from the aggressive effects of ultraviolet rays;
- visit an ophthalmologist once a year.
A birthmark on the eye is not a very common pathology that requires increased attention in any case. If it is detected, you should immediately consult a doctor for examination and, if necessary, treatment.



