Dryness of the mucous membranes of the body is an unpleasant phenomenon that most often goes unnoticed, but in vain. This symptom is a signal from your body that a certain problem has arisen that requires elimination. However, in fairness, it is worth saying that dryness can also occur due to unfavorable climatic conditions and other incorrect actions of the person himself.
But whatever it is, this phenomenon can significantly complicate a person’s life, causing constant discomfort. Next, we’ll talk about dry mucous membranes of the body, the causes of its occurrence and methods of treatment.
Causes of dry mucous membranes
Perhaps, almost all of us have encountered this phenomenon - dry mucous membranes. Moreover, this is also the most common complaint that doctors hear.

Most often, this condition occurs with colds, acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, etc.
Just remember how this terrible dryness is added to a sore throat and nasal congestion, as if a whole desert had formed inside.
However, this is not the only reason for the development of this phenomenon. Since everything in our body is interconnected, the reason may be completely unexpected, as it seems to us, but quite logical in the opinion of our body.
Next, let's look at why the mucous membranes in the mouth and nose dry out.
Dry mouth
The medical name for this deviation is xerostomia., which is defined as dryness of the oral mucosa as a result of a decrease or cessation of the functioning of the glands that produce saliva.
Reference. If the phenomenon is chronic, then it is difficult for the patient to talk, eat, and taste, which turns ordinary everyday activities into hard labor.
Dry oral mucosa is characterized by the following distinctive features:
- strong feeling of thirst;
- feeling of “stickiness” in the mouth;
- a feeling of dryness not only in the mouth, but also in the throat;
- itching and burning, especially on the tongue;
- cracks on the lips and corners of the mouth;
- redness and dryness of the tongue, roughness;
- hoarseness of voice;
- halitosis.
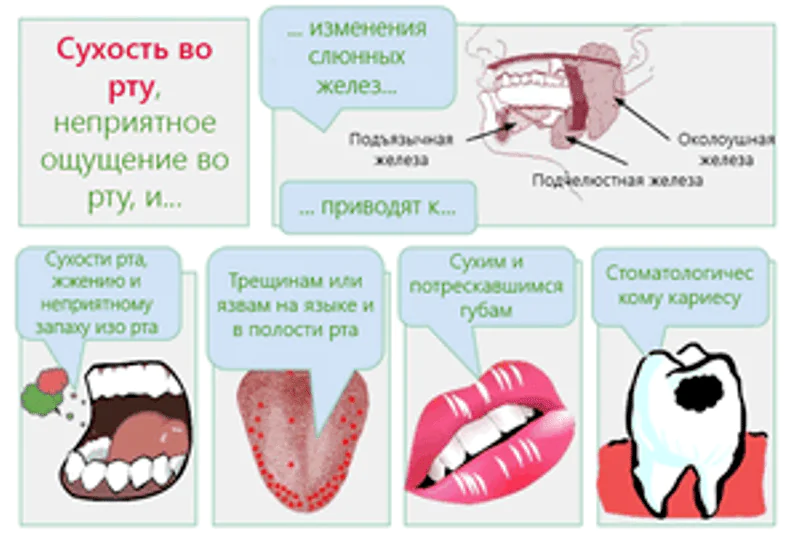
The oral mucosa primarily reflects the development of various pathologies and malfunctions in the functioning of many systems.
Therefore, below is a schematic list of the reasons that provoke the occurrence of this phenomenon. Due to the characteristics of the body, they can be associated both with ailments and as a result of the actions of the person himself.
| Drying factors not related to disease | Pathologies of which this phenomenon may be a symptom |
| Consumption of water in small quantities, especially in the hot season, and also when eating highly salted foods | Diseases of the salivary glands (mumps, Mikulicz's disease, sialolithiasis), characterized by impaired saliva formation, even before complete cessation |
| Use of drugs, the side effect of which is dry mouth | Infectious pathologies (flu, laryngitis, sore throat, pharyngitis, etc.) – this phenomenon develops due to a lack of water in the body due to high temperature, increased sweating |
| Mouth breathing (due to the inability to breathe through the nose due to polyps, deviated nasal septum, etc.) | Systemic diseases (Sjögren's disease, cystic fibrosis, systemic scleroderma) |
| Rinsing the mouth for no reason | Tumor formations in the oral cavity – salivary glands (parotid and submandibular) are often affected |
| Smoking | Endocrine diseases (thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus) |
| Alcohol intoxication | Anemia (lack of iron causes not only dry mouth, but tinnitus, dizziness, pale skin) |
| Menopause | Dehydration due to bleeding, burns, fever, vomiting, diarrhea |
In addition to the above factors, it is also possible to identify the following conditions that cause the development of such a condition:
- Lack of vitamin A.
- Injury to the salivary glands.
- Damage to various types of nerves (facial and glossopharyngeal).
- Strong psycho-emotional stress (excitement, stress).
Reference. The feeling of constant dryness in the mouth can cause the development of various gum pathologies (periodontitis, periodontal disease, gingivitis).
Dry nose

Dry nasal mucous membranes make breathing difficult and prevent them from performing their main purpose: filtering, warming and humidifying the inhaled air before it enters the lungs.
It follows that this phenomenon causes an almost 100% chance of “catching” any infection through airborne droplets, since the mucosal epithelium in such a situation is not able to retain pathogens.
Dry nose is characterized by the following symptoms:
- difficulty breathing;
- cracked skin on the nostrils;
- burning sensation and formation of dry crusts in the nose;
- sneezing;
- deterioration of sense of smell;
- headache;
- nosebleeds.
As for the factors for the development of dryness in the nasal cavity, they can be absolutely diverse. The most common ones are:
- Climate – winter frosts and too hot summers with low humidity are real tests for the respiratory system.
- Inappropriate indoor climate – this problem can be caused by dry air in the home, especially if it has an air conditioner.
- Harmful working conditions – chemicals, building materials or the constant presence of dust have a negative effect on the mucous membranes of the nose and respiratory system. Therefore, a respirator in this situation is a must.
- Long-term use of medications – excessive use of nasal vasoconstrictor drops, especially when the dosage is exceeded, causes the formation of dryness in the nose. In addition to local medications, this phenomenon can also be caused by systemic medications: hormonal and antihistamines.
- Pathological conditions - atrophic and hypertrophic rhinitis, rhinoscleroma, keratoconjunctivitis, Sjogren's disease and diabetes mellitus.
- Stressful situations and weak protective functions of the body – against the background of frequent or constant emotional overload, this condition may develop.
- Damage to the walls of the nasal passages – mechanical impact, burns, thermal effects.
In addition, deviations can provoke allergic reactions to various types of irritants (pollen, dust, animal hair) andexcessive passion for cleanliness of the nasal cavity (endless nose blowing and rinsing for no apparent reason).
Reference. Dryness can occur in older people (thinning of the mucous membrane) and in expectant mothers (hormonal changes).
Treatment of dry mucous membranes
First of all, in such a situation, treatment should begin with neutralizing the main cause of this deviation.
Reference. In case of pathologies of the respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, or diabetes mellitus, it is necessary to seek appropriate medical help.
Since this phenomenon can be a symptom of many systemic pathologies, and may also be a consequence of the influence of external factors, a person is not able to determine this on his own.
Thus, if possible, it is better to consult a doctor as soon as possible, where you will receive a full consultation and a plan of action in each specific case.

Treatment for dry mouth
Treatment of dry mouth is always carried out comprehensively, under the guidance of a physician and includes the following items that are mandatory for the patient to complete:
- therapy for the underlying disease (if any);
- complete cessation of bad habits (smoking, alcohol);
- if the reason is taking certain medications, then the doctor can either reduce the dose or select another remedy;
- reduce consumption of highly salted foods;
- consume enough fluid;
- Avoid alcohol-based mouthwashes;
- Peach, apricot, sunflower oil and honey applications will help reduce irritation of the mucous membrane;
- use drugs that replace saliva (at the discretion of a specialist).
In addition, it is necessary to maintain certain climatic conditions in the house: temperature and humidity. To do this, you need to frequently carry out wet cleaning and ventilation of the living space. Special devices will also help with humidification of the room.
Reference. Seasoning food with hot pepper also helps to activate salivation, but the main thing here is not to overdo it, so as not to cause problems with the digestive system.
Treatment for dry nose
The choice of therapeutic measures largely depends on the factors in the development of dryness. Only a doctor can select a complex of effective drugs.
However, the basis of treatment for this problem will always consist of local symptomatic treatment to moisturize the mucous membrane, reduce swelling and restore breathing.
To eliminate this condition, the following measures should be taken:
- Eliminate provoking factors – increase the humidity in the house (using humidifiers or wet towels and containers of water);
- Compliance with drinking regime – consume more water, decoctions, rose hips, tea.
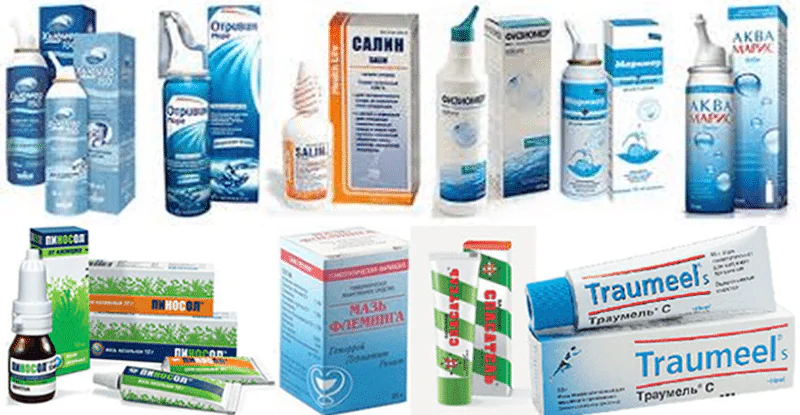
- The use of drugs to prevent dryness – drops and sprays from sea water (“Aquamaris”, “Humer”, “Salin”), as well as ointments (“Pinosol”, “Traumel S”) cope well with this.
- Inhalations – you can mitigate drying if you do inhalations using essential oils (sage, mint, eucalyptus) or herbal decoctions (calendula, chamomile).
- Application of solutions – you can instill sea buckthorn oil, olive oil, and also lubricate the nasal passages with cotton or gauze turundas (pre-impregnated).

The above measures will help alleviate a person’s condition while the underlying factor is identified and treated (if dryness is a symptom of the disease).
This problem can either arise or disappear on its own. However, if dryness torments you constantly or occurs with systemic frequency, then it is still worth paying attention to it.
A visit to the doctor may take a lot of time, and treatment of the problem itself may not take much time, but you will get rid of the unpleasant feeling, significantly increasing the quality of your life.
Dry skin and mucous membranes are due to insufficient hydration of their surface. Most often it is associated with a lack of secretion, which is responsible for hydration. For example, in the case of skin, this is sebum (fat).
This concept should not be confused with dehydration, although it, as a rule, is also accompanied by dry tissue. But dryness can occur without dehydration.
Usually dry skin (xerosis) does not indicate serious problems, but it can cause discomfort and sometimes lead to unpleasant complications.
Fortunately, most cases of xerosis are caused by external factors that are easy to control.
Separately, ichthyosis is a disease associated with extreme dry skin, which disfigures the patient and causes him physical and emotional suffering. Chronic and severe skin problems are a reason to consult a dermatologist.
Causes of dry skin
The main causes of xerosis include the influence of various environmental factors, as well as diseases that disrupt the functions of the skin.
Possible reasons include:
1. Climatic conditions. The skin becomes dry in winter when the temperature and humidity drop. Winter conditions contribute to the worsening of existing skin problems.
2. Central heating and air conditioning. Fireplaces, central heating, and air conditioners without humidification can cause dry skin.
3. Hot bath or shower. Frequently taking a hot bath, especially if a person likes to splash around in the water for a long time, can destroy the lipid barrier of the skin. It is also not recommended to swim in heavily chlorinated pools.
4. Harsh soaps and shower products. Many popular products contain aggressive surfactants (surfactants). These surfactants simply wash away the protective lipid membrane of the skin, causing dryness.
5. Sun rays. Like heat, the sun's rays dry out the skin. UV rays penetrate the epidermis, affecting the deep layer of skin - the dermis. They destroy collagen and elastin, leading to so-called solar elastosis.
6. Atopic dermatitis. This is one of the most common types of eczema and most often affects dry and sensitive skin.
7. Psoriasis. This skin disease is characterized by the rapid growth of rough, dry, dead skin scales, as well as itching.
8. Diseases of the thyroid gland. Hypothyroidism - insufficient thyroid function - reduces the activity of the sweat and sebaceous glands, which leads to dry skin.
Risk factors for dry skin
Dry skin can develop in any person, but the following groups are most susceptible to xerosis:
1. Elderly people.
2. Residents of countries with dry and cold climates.
3. People who like to take hot showers or baths often.
Symptoms of xerosis
Most often, dry skin is a temporary problem that only bothers you during a certain season, but it can last a lifetime. Symptoms of xerosis depend on your general health, age, where you live, and how much time you spend outdoors.
Possible symptoms include:
1. A feeling of tightness of the skin, especially after a bath.
2. Skin is wrinkled and dehydrated.
3. Skin looks rough instead of smooth.
4. The itching is bothersome, sometimes very intense.
5. Peeling of the skin - from slight to severe.
6. Skin cracks, sometimes bleeding and painful.
7. Redness of the skin, usually in limited areas.
In the following cases, it is recommended to consult a doctor:
1. The condition does not improve despite home measures.
2. Dry skin is accompanied by severe redness.
3. Dryness and itching interfere with normal sleep.
4. Ulcers and infected wounds form due to scratching.
5. The skin peels off in large areas.
Diagnosis of the causes of dry skin
Dry skin can accompany a number of skin and internal diseases, so your doctor will need to run some tests to make an accurate diagnosis. To determine some skin problems, sometimes a careful examination is enough, and to determine, say, thyroid deficiency, you need to analyze the level of thyroid hormones.
A list of skin conditions associated with xerosis includes:
1. Follicular keratosis. This condition causes small, acne-like pimples on the arms, legs and buttocks. Numerous pimples give the skin a rough, sandpaper-like appearance. Pimples are usually flesh-colored, but can also be red and inflamed.
2. Ichthyosis. In this unpleasant disease, skin cells form thick, dry scales that look like fish scales. The scales are small, multifaceted, from white to brown. Ichthyosis can cause deep, painful cracks in the palms and soles of the feet.
3. Xreotic eczema. This disease causes dry skin and numerous cracks in the skin. This characteristic skin appearance is described by some people as “dry riverbed” or “cracked porcelain”. The skin is inflamed, itchy and bleeding.
4. Psoriasis. The disease manifests itself as dry, flaking and itchy skin. The skin in the affected areas is reddish and covered with scales resembling dandruff. In severe cases, the disease may be complicated by infection.
Treatment of dry skin, useful tips
In most cases, dry skin can be treated with simple home remedies such as moisturizing after showering. For peeling skin, your doctor may recommend special creams that contain salicylic acid, lactic acid, or a combination of lactic acid and urea.
For more serious problems, such as atopic dermatitis or psoriasis, ointments and creams containing corticosteroids (Celestoderm B, Elokom, Advantan) can be used. If an infection occurs due to constant scratching or poor hygiene, the doctor may prescribe combination products that also contain antibiotics (Celestoderm B with Garamycin, Triderm).
If you are prone to dryness, it is not always possible to achieve flawless skin.
However, use these tips:
1. Moisturize your skin. There are many products that form a protective film that protects the skin from moisture loss. The simplest and most effective option is baby oil.
2. Limit hot baths and showers. Such procedures should last no more than 15 minutes, and the water should be used warm, not hot.
3. Avoid harsh soaps that dry out your skin. If you have sensitive skin, you cannot skimp on good soaps and shower gels. Use a gentle, oil-infused soap such as Neutrogena or Dove.
4. Use moisturizers immediately after swimming. After your bath, pat your skin gently with a towel to keep your body slightly damp. Immediately afterwards, apply baby oil or another moisturizer to your body.
5. Use a humidifier. If the cause of dry skin is dry air in the house, do not skimp on a humidifier (humidifier), at least a portable one for your room. Maintain your device regularly to prevent the humidifier from becoming a source of bacteria or fungi.
6. Choose appropriate clothing. Natural fibers such as silk and cotton allow your skin to breathe. Avoid fabrics with cheap dyes. When washing, do not use fragrances or other chemicals that may irritate the skin.
For itching and inflammation of the skin, American experts recommend limited use of a cream or ointment containing at least 1% hydrocortisone. This is a medium-strength corticosteroid hormone that copes well with inflammation, itching, and allergic reactions. In the United States, this drug is available without a prescription, but in most countries of the former USSR, hydrocortisone is prescribed by a doctor.
Before using such drugs, it would be a good idea to consult a dermatologist.
Possible complications of xerosis
For some people prone to eczema, dry skin can cause the following complications:
1. Atopic dermatitis.
2. Folliculitis (inflammation of hair follicles).
3. Cellulitis (bacterial infection of the subcutaneous tissue).
These complications usually occur in cases where the skin's protective mechanism is impaired. For example, severe dry skin causes cracks, which open the door to infection.



