- Classification
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Drug treatment
- Treatment with traditional methods
- Decoctions and infusions for internal use
- Compresses for local use
Bacterial folliculitis is a bacterial staphylococcal infection of the hair follicles of the skin. It can be superficial and deep. The disease appears on any part of the skin, but mainly affects the surface of the arms, legs and chin. The main signs are papules and pustules, sometimes with a hair sticking out from the center. Bacterial folliculitis is a secondary infection, so the first thing you need to do is diagnose the cause, which could be allergies, demodicosis, endocrinopathy, etc.
Classification of bacterial folliculitis
The photo shows two types of bacterial folliculitis
The main common forms of bacterial folliculitis are:
- Staphylococcal folliculitis (Staphylococcus aureus). Caused by Staphylococcus aureus, depending on the severity of the lesion, it can be superficial (staphylococcal impetigo) or deep (sycosis). Progresses to the formation of a boil with frequent relapses.
- Pseudomonas folliculitis (Pseudomonas aeruginosa). This is “hot bath” folliculitis.
- Gram-negative folliculitis, which is caused by gram-negative flora.
Causes of bacterial folliculitis
Bacterial folliculitis is almost always secondary. Most often it develops secondary to demodicosis, allergies, and endocryopathy. If the underlying disease is not identified, folliculitis will develop and be accompanied by frequent relapses. The main reasons for the development of pyoderma:
- Ectoparasites (demodectic mange, sarcoptic mange).
- Endocrinopathies (imbalance of sex hormones).
- Allergic skin diseases (allergic dermatitis, food allergies).
- Immunosuppressive therapy (chemotherapeutic drugs).
- Dermatophysis (lichen).
- Trauma (bites, open wounds).
- Other skin diseases.
Bacterial folliculitis develops through the penetration of staphylococcal bacteria into the hair follicle through a break in the skin. It spreads to other areas of the skin when scratching the pustules. Also, the cause of the disease can be pseudomonas, which are detected after taking infected hot (hydromassage) baths.
Symptoms of bacterial folliculitis
The photo shows multiple bacterial folliculitis
Since bacterial folliculitis in humans develops secondary to the primary disease, the localization of ulcers and the degree of damage depend on the predisposing causes. If the factor of the disease is injury, then the infection is localized near it. With allergies and endocrinopathy, the torso is mainly affected. But regardless of the causes, the infection spreads throughout the body, especially with severe itching.
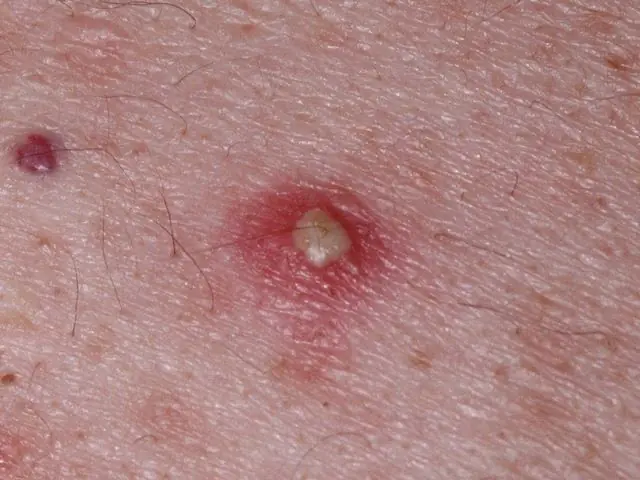
The primary features of bacterial folliculitis are the appearance on the body of small 1-2 mm white or yellowish-white bubbles surrounded by a thin red border. Initial lesions are often confused with urticaria. The hair follicle shaft passes through some abscesses. In areas of dense hair, the lesion can be diagnosed only after cutting. Inflammatory papules appear in small or large groups, accumulating in clusters. Pus with blood clots is often released from the abscesses.
Diagnosis of bacterial folliculitis
Culture smears can help make a diagnosis of bacterial folliculitis. Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and gram-negative bacteria (Klebsiella spp., Escherichia coli, Proteus spp.) can be cultured. For a fungal infection, Candida and dermatophytes are cultured; for a viral infection, viruses are cultured in cells or the herpes simplex virus. In case of chronic folliculitis, in order to establish Staphylococcus aureus, smears are taken for culture from the mucous membrane of the nose and anus.
Drug treatment of bacterial folliculitis
Typically, therapy for bacterial folliculitis in humans consists of treating the bacterial infection and eliminating the causes that provoked the disease. In the initial form of the diseaseTo prevent the spread of bacteria, the affected area is treated with alcohol solutions (Fukorcin, brilliant green, 2% camphor or salicylic alcohol). For fungal infections, antifungal agents are additionally prescribed (Itraconazole, Fluconazole, Terbinafine ointment), and for herpetic infections, antiviral drugs (Acyclovir).
For deep folliculitis with the accumulation of a large amount of pus, the pustules are opened, the pus is removed, and the affected area is treated with the alcohol solutions listed above. Next, antibacterial drugs are prescribed:
- Ointments Zenerit, Lincomycin, Erythromycin, Epiderm, Dalatsin-T - for topical use.
- Tablets Doxycycline, Erythromycin, Cephalosporin - for internal use.
Also at this stage of the disease, it is recommended to apply compresses of ichthyol ointment twice a day.
Chronic form of bacterial folliculitis requires treatment with antibiotics from the tetracycline group, which have a bacteriostatic effect (Oxycort). In this form, immunomodulators are prescribed (Immunal, Vitaferon, Timalin). A well-proven non-drug therapy is irradiation with ultraviolet rays, which is prescribed every other day or daily, in a general course of 6–10 times.
If treatment is started in a timely manner and correctly selected, then you can get rid of bacterial folliculitis within a week.
Treatment of bacterial folliculitis with traditional methods
Traditional medicine recipes have successfully proven themselves in the treatment of bacterial folliculitis. Let's look at the most common and effective ones.
Decoctions and infusions for internal use
- Pour 1 tbsp into 1 liter of boiling water. l. chamomile, leave for half an hour, filter and consume twice a day.
- Add 2 tbsp to 1 liter of water. l. burdock, boil for 10 minutes, leave for one hour, filter and consume 2 times a day.
- For 250 ml of boiling water take 2 tbsp. l. dandelion roots and leaves. Boil for 15 minutes, leave for half an hour and drink a glass three times a day.
- For 1 liter of water take 1 tbsp. l. crushed dry dandelion or large burdock roots. The broth is boiled for 10 minutes, left for 2 hours and drunk 50 ml 2 times a day.
Compresses for local use
- Fresh thistle leaves (another name is prickly tartar) are crushed to a pulp and applied to the affected areas.
- 50 g of spiny root are poured into 0.5 liters of water, boiled for 30 minutes, left for 1 hour and filtered. Used for compresses and soothing dressings.
- A paste is prepared from fresh leaves of woodruff, which is applied to the site of the abscess under a medicinal bandage 2 times a day.
If treatment is started in a timely manner and correctly selected, then you can get rid of bacterial folliculitis within a week.
- Read how to use Aloe vera to treat folliculitis