- Causes
- Kinds
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis of folliculitis
- Treatment
- Complications of folliculitis
- Prevention
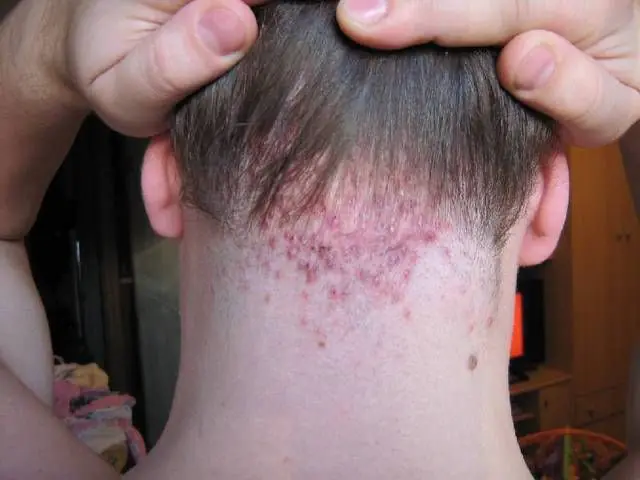
Folliculitis is a form of pyoderma, an infectious purulent disease that affects hair follicles. Characteristic manifestations of the disease: in places where the hair follicle grows, pustules (multiple or single) appear, through which the hair passes. With severe damage, pustules form ulcers that leave scars after healing.
Causes of folliculitis
The photo shows folliculitis on the face
The disease occurs for various reasons: virus, parasites, bacteria, fungus. Let's look at the main ones:
- Fungal skin infections can be caused by dermatophyte or candidiasis.
- Parasites, for example, mites cause demodicosis.
- Virus - herpes simplex or herpes zoster can develop.
- Pruritic dermatosis: eczema, allergic and atopic dermatitis.
- Increased sweating.
- Diseases that reduce immunity: HIV, diabetes.
One of the most common causes is microtrauma of the skin combined with poor hygiene. For example, socially disadvantaged sections of the population living in unsanitary conditions, as well as in hot countries, have a high risk of developing folliculitis, since their climate contributes to the spread of infection.
Types of folliculitis
Photos of different types of folliculitis
- Staphylococcal folliculitis mainly affects men due to careless shaving. Inflamed areas appear in the area where stubble grows: on the chin and around the mouth. See photos of staphylococcal folliculitis and how to treat it.
- Syphilide acne, appears against the background of syphilis, has a pale red color. Folliculitis treatment begins with the underlying pathology. The rash will not go away until syphilis is treated.
- Inflammation caused by dermatophytes. The inflammatory process begins with inflammation of the epidermis (the upper stratum corneum of the skin), then the hair follicle (follicles and hair shaft) is affected. If folliculitis is not treated, the hair roots become deformed and cutaneous folliculitis begins to develop on the scalp.
- Candidal folliculitis occurs with prolonged lying down with the application of occlusive dressings and prolonged fevers.
- Pseudomonas - occurs after taking a bath with insufficiently chlorinated water. Poor disinfection provokes the entry of staphylococci and other pathogens into the body.
- Impetigo Bockhart - the disease causes hyperhidrosis when using warm compresses. Abscesses appear 2-5 mm.
- Occupational - Affects people who come into contact with hazardous chemicals without skin protection. The disease forms on the back of the hand.
- Tick-borne is a dangerous species and difficult to treat. Specific intensive therapy is required.
- Gonorrheal is a rare variety. Inflammatory areas appear as insufficient treatment of gonorrhea or complications after it. When analyzed, a high level of gonococci is diagnosed in the rash. Ulcers are localized on the genitals of both sexes: in men in the foreskin area, in women - on the perineum.
- Eosinophilic folliculitis is a consequence of HIV infection. A rash is one of the symptoms of HIV. Blood test results revealed a high level of eosinophils. Pustules are localized on the face, limbs, and torso.
- Depilation is a common type of disease among men who live in the tropics. Pustules with pus are symmetrically localized on the legs. After treatment, scars remain.
- Gram-negative - the cause is weak immunity. Mostly occurs after taking antibiotics.
- Fungal - spreads at high temperatures and humidity. Rashes appear on the shoulders, neck, and face.
Symptoms of folliculitis
Visually, folliculitis appears as red nodules on the skin measuring about 1 cm in diameter. The formation is localized in the hair growth area. If the disease affects the face, then pustules form on the forehead, nose, and cheekbones. On the head, pustules form with a red rim. To determine the treatment of folliculitis, we learn the main characteristic symptoms of the disease:
- Redness of the skin.
- Purulent pimples are spherical or cone-shaped.
- Itching.
- After opening the vesicle and removing the pus, a red spot remains.
Rarely, the lymph nodes near the affected area become inflamed. Scars and pigmentation may remain on the skin after folliculitis. During the bacterial process, the blisters become filled with bloody, yellow or white contents. With fungal folliculitis, flat areas with a border form where white plaques accumulate.
The rash is painful, which causes poor sleep in children, since contact with bedding causes discomfort. Often, babies' body temperature rises. In babies, the buttocks, groin and external genitalia are often affected. Less commonly, the neck, back and legs are affected.
Diagnosis of folliculitis
If you suspect the development of folliculitis, the dermatologist must:
- Establish the etiology of the disease.
- Examine the rash.
- Examine the hair follicle.
- Identify the pathogen.
- Detect concomitant diseases that may lead to the development of infection.
- Carry out a dermatoscopy to determine the extent of the lesion.
- Refer the patient for analysis of discharge from pustules. It will be required for testing for fungi, microsporia, bacteriological culture and testing for Treponema pallidum.
- To avoid confusing follicles with syphilis and gonorrhea, prescribe an RPR test and PRC.
If this skin infection has been identified, then proceed to the paragraph below “How to treat folliculitis.”
Treatment of folliculitis
Treatment of folliculitis should begin as early as possible so that the disease does not develop into a chronic and acute inflammatory process. Therapy must be appropriate to the etiology of the disease. When the first rash appears, treatment with solutions of aniline dyes is sufficient: brilliant green, fucarcin, iodine, methylene blue. To prevent the rash from spreading, healthy areas of the skin are treated with salicylic/boric alcohol or other antiseptics. You should not squeeze out pus with your nails so as not to worsen the disease.
How to treat folliculitis with pharmaceutical drugs. For fungal origin, antifungal drugs (fungicidal creams) are prescribed, bacterial - ointments and creams with antibiotics, herpetic - Acyclovir.
If the disease relapses, UV irradiation is performed. In case of deep relapse, systemic therapy is used.
For staphylococcal infections, Cephalexin, Dicloxacillin or Erythromycin are prescribed orally; for pseudomonas infections, they are treated with Ciprofloxacin; for dermatophytes, Terbinafine is prescribed; for candidiasis, Itraconazole and Fluconazole are used.
Simultaneously with the treatment of folliculitis, treatment is carried out for concomitant diseases: diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency.
Complications of folliculitis
Having identified the symptoms of folliculitis, it is necessary to begin treatment on time, otherwise complications may develop:
- Boils on the skin (boils).
- Inflammation of the skin (carbuncle).
- Abscess.
- Infectious diseases of the scalp.
- Formation of scars at the site of the rash.
Prevention of folliculitis
For preventive purposes, it is recommended to follow the rules of personal hygiene and skin care. General recommendations are a healthy lifestyle, healthy eating and regular exercise.
Video about what folliculitis is:
- Related article: Tea tree oil for treating folliculitis