What is iridocyclitis, how to provide first aid? Methods of treating the disease: traditional therapy, physiotherapy, folk recipes.
The content of the article:- What is iridocyclitis
- First aid
- Treatment options
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Antibiotics
- Antiviral drugs
- Eye drops
- Other drugs
- Physiotherapy
- Folk recipes
Iridocyclitis is an inflammatory process in the iris and ciliary body. Pathology occurs as a complication after other more serious infectious diseases. Treatment is aimed at preserving vision and preventing complications.
What is iridocyclitis?
Iridocyclitis of the eye (from “iritis” - inflammation of the iris, “cyclitis” - a pathological process in the ciliary or ciliary body) is a disease that affects both parts of the eyeball. They are located nearby and connected by a single vascular network. The pathology is typical for persons from 20 to 40 years old.
The disease develops as a result of damage to the blood-ophthalmic barrier. This is a septum separating the eye vessels and the general blood flow. The task of a biological filter is to retain molecules and harmful microorganisms.
If there is an infection in the general bloodstream and the barrier does not work, antigens penetrate into the iris and ciliary body. An area of inflammation is formed. Due to swelling, the iris comes into contact with the lens. If inflammation occurs with the release of exudate (liquid emanating from the vessels during the inflammatory process), adhesions (synechia) form between the lens and the iris. They lead to pupil deformation and impair vision.
There are different classifications of ocular iridocyclitis depending on the factors taken as a basis. Based on the nature of inflammation, the disease is divided into the following types:
- Exudative. The pathology is non-infectious and develops with the formation of exudate. The patient quickly loses vision, and there is a risk of adhesions forming.
- Serous. With this form of the disease, serous fluid collects in the anterior part of the eyeball. Intraocular pressure increases, and there is a risk of developing glaucoma. Serous iridocyclitis is rare. More often diagnosed is fibrinous-serous, accompanied by swelling and redness of the iris.
- Fibrinous-plastic. This type begins acutely and is accompanied by pronounced symptoms: a decrease in intraocular pressure, clouding of the vitreous, a change in the shade of the iris, and fusion of individual zones of the pupil. Protein exudate accumulates in the anterior eye chamber. The resulting adhesions between the iris and the lens can lead to absolute fusion of these sections and complete loss of vision.
- Hemorrhagic. This form differs from others in that blood elements are present in the fluid accumulating in the anterior section.
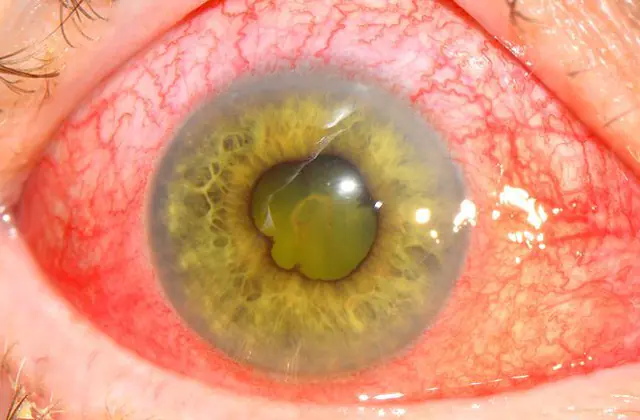
- Purulent. Develops against the background of bacterial infection. The disease makes itself felt within a few hours. The conjunctiva swells and turns red, the pupil becomes cloudy, the affected eye hurts greatly, intraocular pressure decreases, and the iris acquires a reddish or greenish tint.
Depending on the nature of the pathology, it can be:
- Acute. The disease develops quickly and is accompanied by well-defined symptoms: lacrimation, photophobia, constricted pupil, dilated blood vessels, pain in the eye, swelling of the iris. Vision in acute iridocyclitis deteriorates sharply.
- Subacute. It has less pronounced symptoms and develops more slowly. This form is intermediate between chronic and acute.
- Chronic. The disease progresses sluggishly, the symptoms are mild. However, against the background of this condition, complications quickly develop that can lead to complete loss of vision. Chronic iridocyclitis accounts for 70% of cases.
- Recurrent. Pathology manifests itself in the cold season. The rest of the time, symptoms of iridocyclitis are almost absent. The recurrent form of the pathology is usually combined with the chronic one.
Any of the listed forms of the disease is dangerous in its own way and threatens complete blindness, which is why it is so important to start treatment for iridocyclitis on time.
Depending on the cause, iridocyclitis is divided into several types:
- Infectious. The disease develops as a secondary one against the background of an inflammatory process that affects the entire body. Iridocyclitis is often diagnosed as a complication of measles, gonorrhea, tuberculosis, chlamydia and other infectious pathologies. The most common causes of the disease are staphylococci and streptococci. There are frequent cases of eye diseases after suffering from otitis, tonsillitis, caries.
- Allergic. Eye damage occurs due to an allergic reaction.
- Viral or herpes. Often the causative agent of the disease is the herpes virus. But there are cases when other types of viruses provoke iridocyclitis: influenza, hepatitis, etc.
- Metabolic. Pathology develops as a consequence of diseases with metabolic disorders in the body. These include rheumatoid diseases (rheumatism, ankylosing spondylitis, Sjogren's syndrome, etc.), diabetes mellitus, gout, metabolic disorders of unknown origin.
- Post-traumatic or traumatic. Damage to the eyeball as a result of trauma, injury, bruise or penetration of a foreign body provokes eye diseases, including iridocyclitis. The disease can develop after improperly performed surgery.
- Idiopathic. Pathology occurs for unknown reasons. Factors that indirectly provoke the disease include stress, hypothermia, excessive stress on the organ of vision, and deterioration of the immune system.
Having established the exact cause of the pathology, the doctor will be able to prescribe treatment. Sometimes, thanks to correct diagnosis, it is possible to completely restore vision.
First aid for iridocyclitis
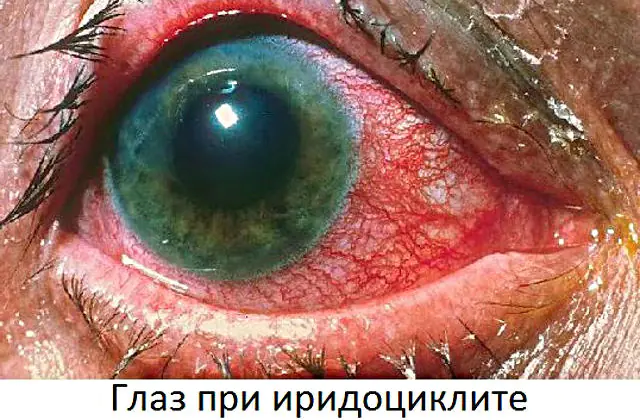
In the photo there is iridocyclitis of the eye
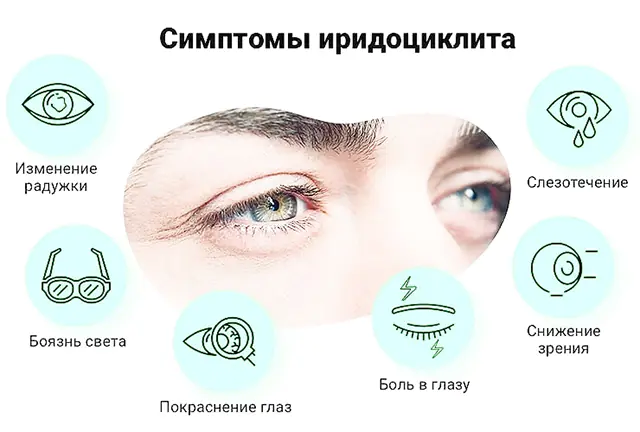
Before providing first aid for iridocyclitis, it is important to correctly recognize the disease. There are signs of iridocyclitis that are common to all forms of the disease. However, individual species differ in symptoms.
The pathology is characterized by:
- redness in the eyes;
- severe pain (the sensation intensifies when pressing on the eyeball);
- lacrimation;
- fear of light;
- change in pupil shape;
- blurred vision;
- formation of exudate with pus or blood in the anterior chamber of the eye;
- vitreous opacification;
- images appear blurry, as if in fog;
- change in iris shade;
- increase or decrease in intraocular pressure.
If a patient complains of pain in the eye, a sharp decrease in vision, lacrimation, it is important to correctly provide first aid for iridocyclitis. In acute or subacute forms of the pathology, drugs are used to relieve pain and prevent the formation of adhesions.
To dilate the pupils and prevent fusion with the lens, mydriatic medications are used. They break the synechiae, relaxing the eye muscles. Among the popular drugs: Midriacil, Cyclomed, Irifrin, Atropine.
The action of mydriatics lasts 3-5 hours. During this period, the patient may experience photophobia, lacrimation, and the appearance of farsightedness. Such conditions are side effects of medications that dilate the pupils.
Important! Frequent use of mydriatics harms the eyes, so first aid is to use them once. In the future, the need for these drugs is discussed with the attending physician.To relieve pain, painkillers are used: Naklofen, Lidocaine, Inocaine and others. The products are available in pharmacies without a prescription.
Methods for treating iridocyclitis
How to treat iridocyclitis depends on its etymology (origin), the identified pathogen and concomitant pathology. It is important to provide first aid correctly at the first symptoms of an acute illness. Then you need to urgently send the patient to an ophthalmologist.
Anti-inflammatory drugs for iridocyclitis
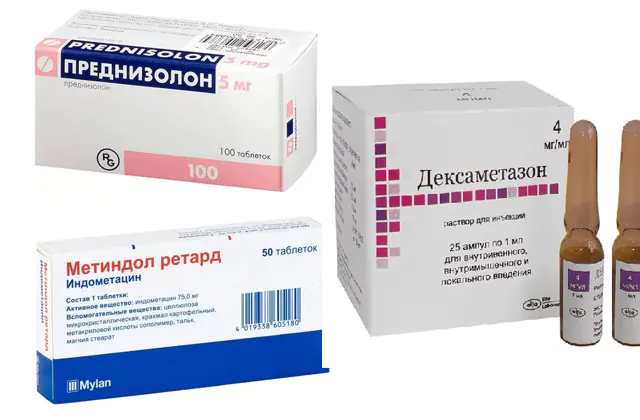
To relieve inflammation in iridocyclitis, hormonal and non-hormonal agents are used:
- Methindol. Contains indomethacin, a non-hormonal anti-inflammatory substance. It is obtained from indolylacetic acid. The medicine reduces body temperature, eliminates inflammation and pain. Traditionally, Methindol is prescribed for diseases of the musculoskeletal system. The tablets have an extended list of side effects. Price - 170-270 rubles or 60-100 hryvnia. Analogues - Indomethacin.
- Prednisolone. A hormonal drug related to corticosteroids. The product stabilizes cell membranes, reduces capillary permeability, and reduces the migration of leukocytes. The medicine is quickly absorbed and combines well with other medications. Price - 120 rubles or 50 hryvnia. Analogue - Hydrocortisone.
- Dexamethasone. A drug with a semi-synthetic hormone. The substance acts at the cellular level, relieves inflammation, activates glucose metabolism, and strengthens the immune system. Among the indications for the use of the drug are diseases of the organs of vision. The drug has a long list of side effects. Price - 225 rubles or 100 hryvnia. Analogues - Betamethasone, Betaspan, Depos.
Anti-inflammatory drugs do not fight the infection, but only prevent suppuration and further accumulation of exudate.
Antibiotics for the treatment of iridocyclitis
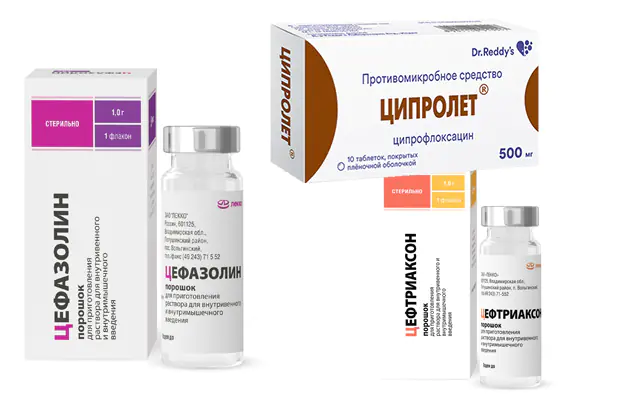
To treat eye iridocyclitis, antibacterial agents are used in the form of tablets, intravenous, intramuscular, and parabulbar (under the eyeball) injections. Among the popular drugs:
- Tsiprolet. A medicine with ciprofloxacin that affects the DNA of microorganisms. Within an hour after administration, the active substance reaches its maximum concentration in the body. The antibiotic has an extended spectrum of action and a minimum of contraindications. Also available in the form of eye drops. Price - from 50 to 120 rubles or 12-50 hryvnia. Analogues - Tsiprinol, Tsiprobaks, Ciprofloxacin, Tsifran.
- Cefazolin. Semi-synthetic antibiotic from the group of cephalosporins. It inhibits enzymes necessary for the formation of bacterial walls. The list of side effects of the medication is small, with a minimum of contraindications. Price - 50 rubles or 15 hryvnia. Analogues - Cesolin, Reflin, Cefamezin.
- Ceftriaxone. A drug from the cephalosporin group that inhibits cell wall synthesis. There are few contraindications, but the list of side effects is wide. Price - 24 rubles or 10 hryvnia. Analogs - Cefaxon, Cefogram.
- Gentamicin. An antibiotic from the aminoglycoside group. It is used in rare cases when pathogens are resistant to weaker drugs. The antibiotic has a wide list of contraindications and side effects. Price - 200 rubles or 90 hryvnia. Analogues - Amikacin.
Antiviral drugs for iridocyclitis

These drugs activate the production of interferons in the human body to fight the virus or contain their synthetic analogues. While antibiotics are prescribed when the causative agent is bacteria, antiviral drugs for the treatment of iridocyclitis help when the underlying cause is a virus.
Doctors often recommend:
- Anaferon. Homeopathic medicine used for herpes virus infection. The medicine contains human interferons. The medication has no contraindications; the only side effects are allergies. Price - 225 rubles or 100 hryvnia. There are no direct analogues.
- Gerpevir. A drug based on acyclovir, which exhibits the greatest activity against the herpes virus. The active substance has a minimum of contraindications and side effects. Price - 120 rubles or 50 hryvnia. Analogue - Acyclovir.
Antiviral drugs are prescribed orally or by injection.
Eye drops against iridocyclitis
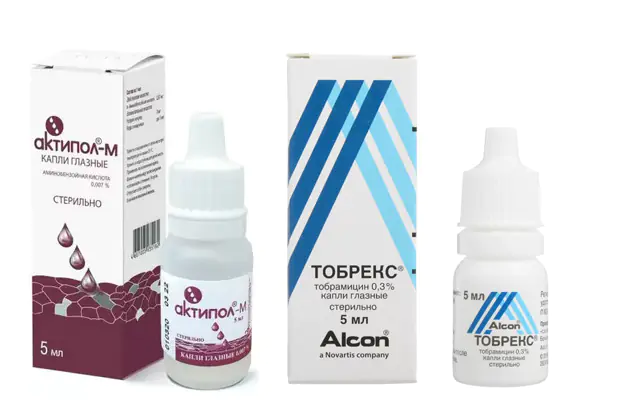
An important part of the therapeutic course are eye drops for iridocyclitis. Their choice is made depending on the cause of the disease. Drugs are divided into groups:
- Antibacterial. Along with antibiotic injections, ophthalmologists recommend topical medications in the form of drops. They act directly on the organs of vision and enhance the therapeutic effect. Medicines in this group include Tobrex, Okomistin, Gentamicin, Tsiprolet, Cefazolin, Floxal.
- Aktipol. Product based on para-aminobenzoic acid. The medicine activates the production of interferon in the body and strengthens the immune system. Indications for the drug include viral eye diseases. The medication has no contraindications or side effects. Price - 280 rubles or 130 hryvnia. There are no direct analogues.
- Antiviral. Medicines strengthen local immunity and are recommended when the cause of the disease is a virus. Medicines in this group include Poludan, Oftan Ida, Oftalmoferon.
- Anti-allergenic. When the cause of the disease is an allergic reaction (sometimes to toxins secreted by bacteria), Claritin, Citrine, Suprastin, Loratadine are prescribed.
Medicines are instilled into the corner of the eye 2-3 times a day in the dosage prescribed by the doctor.
Other drugs for iridocyclitis
Along with these medications, other medications are also used to speed up recovery and improve the patient’s condition with iridocyclitis:
- Vitamins and preparations to activate tissue regeneration: Taufon, Trypsin, Lidaza.
- Mydriatics for the resorption of adhesions: Atropine, Irifrin, Midriacil, Cyclomed.
- Enzymes for the resorption of synechiae: Fibrinolysin, Streptodecase, Lekozim and others.
- Means for reducing intraocular pressure: Betoftan, Fotil, Timolol.
Treatment of iridocyclitis takes place in a hospital under the supervision of doctors.
Physiotherapy for the treatment of iridocyclitis
To achieve a lasting effect of recovery from iridocyclitis, a number of physiotherapy procedures are used:
- Electrophoresis. Administration of drug ions using low current. The method is effective because it allows active substances to penetrate directly into the affected area.
- Magnetotherapy. Exposure of the painful area to a magnetic field. The physiotherapeutic method is used to activate blood flow and stimulate metabolism. Magnetic therapy relieves swelling, reduces inflammation and pain.
- Laser therapy. To eliminate inflammation, increase immunity and fight pathogens, low-intensity laser radiation is used. The method combines well with drug therapy, as it increases the body's sensitivity to drugs.
Along with physical procedures, autohemotherapy is becoming very popular - administering the patient’s own venous blood to activate local blood circulation.
Important! Surgeon intervention is necessary if dissection of adhesions is required. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Afterwards, a course of antibacterial therapy is prescribed. Surgical operations are performed if it is necessary to remove fluid from the vitreous body or eliminate complications resulting from the development of iridocyclitis (cataracts, glaucoma).Traditional recipes against iridocyclitis

Self-treatment of iridocyclitis is dangerous, since the disease can become severe or complications may arise. It is better to coordinate the use of traditional recipes with your doctor.
Most remedies are aimed at relieving inflammation and improving blood flow:
- Warm compress. Take a clean cloth bag and pour warm sand or salt into it. Apply to the sore eye for 10 minutes. Repeat the procedure 1-2 times a day.
- aloe leaves. Take 0.5 kg of aloe leaves. Grind them in a meat grinder and pour in 0.5 liters of cooled boiled water. Also pour 30 g of dry St. John's wort into 0.5 liters of boiling water. Boil the herb over low heat for half an hour and leave for another 40 minutes. Mix the prepared ingredients, add 0.5 kg of honey and 0.5 liters of white wine. Insist for a week. Take 1 tsp. 3 times a day for 5 days.
- Aspen bark. Place the prepared aspen bark in a container and fill it with water so that the liquid covers the solid ingredient. Boil and simmer for a quarter of an hour. Leave for 4 hours. Drink 1 tbsp. decoction per day.
Before using traditional recipes, check whether you are allergic to the components mentioned in them.
Note! With timely contact with an ophthalmologist and proper treatment, recovery occurs. In half of the cases, the pathology occasionally recurs, but its symptoms are erased. In advanced cases, the disease threatens with dangerous complications of iridocyclitis, including pupillary fusion, glaucoma, cataracts, retinal detachment, endophthalmitis, eyeball atrophy and others. With severe purulent inflammation and rapid loss of vision, blindness develops. In some cases, removal of the eye as an organ is required.To prevent iridocyclitis, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations by an ophthalmologist, treat underlying diseases, and in case of eye injuries, sanitation of inflamed and damaged areas.
How to treat iridocyclitis - watch the video:



