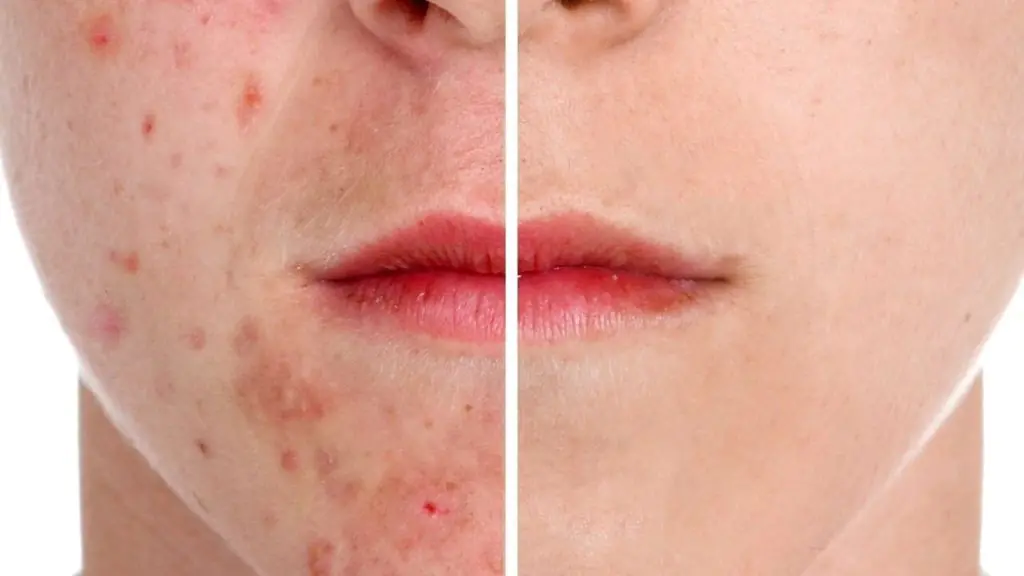
Acne vulgaris causes a lot of inconvenience to a person. They spoil your appearance and force you to hide your face from the direct rays of the sun and camera lenses. Acne like this is difficult to treat, but there are many methods that can make one of the main problems of puberty less noticeable.
What is acne vulgaris?
The word “vulgar” comes from the Latin “vulgus”, which means “people”. Acne began to be called “vulgar” centuries ago, among the common people who did not particularly care about their hygiene. Acne received such a specific name also because it most actively occurs during periods when hormones are “playing” in a person, and this not only causes cosmetic problems, but also affects behavior and lifestyle.
Acne vulgaris – These are acne that occur due to a general hormonal imbalance in the body. They occur more often in women during puberty (13-17 years), during sexual activity or, conversely, in its absence at a more mature age. You can read more about acne in teenagers in our article at the link: The mechanism of formation of such acne is standard - excess sebum, abundantly produced by the sebaceous glands, dead skin particles, cosmetics, and dust accumulate in the hair follicles. In this fertile environment for bacteria, infiltrates arise caused by the colonization of staphylococci, streptococci and other harmful microorganisms. The pores become enlarged, sebum is not removed from them, but accumulates. The sebaceous plug provokes inflammation, which can grow into a pimple of varying severity:
- first stage – the easiest, usually this is mild redness and thickening, which passes without developing into an abscess, or a small abscess that is superficial, quickly and independently opens, and does not leave behind a stain or scar;
- second stage – this is a large pimple that develops into an abscess, with redness and thickening of nearby tissues;
- third stage - These are deep pimples that may not go away for weeks, with severe redness, swelling and repeated suppuration.
Acne of the second and third stages leaves behind spots and scars, which then, even if the period of “blooming” with acne vulgaris has ended, greatly spoils a person’s appearance, and it is necessary to treat post-acne using laser, ultraviolet rays and other methods.
Types of acne:
- non-inflammatory acne is comedones or fat plugs into which infection has not yet penetrated:
- white comedones - the hair follicle is closed and narrowed at the top;
- black comedones - the follicle is open and dirt accumulates there, which gives it a dark color;
The more weakened the body as a whole, the more actively bacteria attach to the skin.
In the video, a dermatologist-oncologist talks about acne vulgaris, the reasons for its appearance and the characteristics of the disease:
Acne vulgaris and dermatovenereology
If a person is tormented by acne vulgaris, then you need to consult a specialist. A beauty salon and standard cosmetic procedures performed by experts for acne will not be enough. Treating yourself at home, trying various folk recipes and medications without consulting a doctor is also a mistake.
A dermatovenerologist is a doctor who treats skin and venereal diseases and identifies the relationship between these diseases and the general condition of the body. It is a destructive and widespread belief that these doctors treat exclusively sexually transmitted diseases. If you are concerned about acne vulgaris, which is accompanied by disruptions in the menstrual cycle in women, and with urological problems in men, then be sure to visit a dermatovenerologist. He will prescribe a comprehensive examination that will reveal the underlying causes of the rash. Scraping, blood testing for allergens and harmful microorganisms, dermatoscopy, culture and smear - there are many methods for studying.
Causes
Acne occurs due to excess sebum production, clogged pores and slower regeneration and exfoliation processes. Causes of acne vulgaris:
- hormonal changes in the body during puberty;
- hormonal imbalances at any age, due to gynecological diseases, stress, decreased immunity, exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- PMS and menopause in women;
- unhealthy diet with a predominance of flour, fatty, spicy and sweet foods, consumption of sweet carbonated drinks and fast food;
- frequent use of cosmetics, insufficient cleansing of the facial skin.
Photo of acne vulgaris
Treatment with medications
Acne vulgaris is treated with medication. Doctors usually prescribe the following drugs:
- Antibiotics. They are prescribed for the third, most severe, stage of acne. Antibiotics fight inflammation and infection; they need to be taken in a course and together with drugs that support the intestinal microflora.
- Hormonal medications, usually birth control pills. They even out hormonal levels, the main cause of acne vulgaris.
- Ointments, gels and mash containing hormones, various antimicrobial agents, wound healing, promoting exfoliation and regeneration, drawing out pus. For example, zinc ointment, balsamic liniment according to Vishnevsky, “Zinerit”, “Baziron AS”, “Skinoren”.
- Drugs whose active substance is isotretinoin. It actively reduces sebum production, affecting hormonal levels.
Traditional methods
Acne vulgaris is often treated with traditional methods. If the form of the disease is severe, they are usually not enough. But in mild and moderate stages, especially at the beginning of the disease, traditional medicine will really help cope with the disease, subject to systematic treatment:
- Masks. They can be very different, depending on the skin type and rashes. Clay masks help a lot; they tighten pores, mattify, and cleanse the skin. You can add calendula tincture or a few drops of essential oil of tea tree, rosemary, lemon, mint to this mask. Good reviews about masks made from raw potatoes and grated carrots and cranberries.
- Lotions based on herbal infusions, with and without alcohol. Aloe juice, lemon juice, and chamomile infusion help well.
Before using any essential oil for the first time, be sure to conduct a sensitivity test. Mix a couple of drops in vegetable or olive oil, apply the mixture to the area under the elbow or next to the palm.
Acne vulgaris can and should be treated. The main thing is to carry out treatment under the supervision of a specialist and regularly cleanse the skin.
Acne vulgaris is an inflammatory process characterized by inflammation of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles. The main cause of the pathology is staphylococcus. Most often, this unpleasant phenomenon develops on the skin of adolescents from 10 to 19 years of age (during puberty). It is more severe in guys than in females.
Types of acne
The pathology can be both inflammatory and non-inflammatory in nature. Its course depends on the activity and role of bacteria in inflammation. There is a mild, moderate and severe phase of the disease. Acne vulgaris itself is divided into the following types:
- Comedones. They are non-infectious in nature and are fatty plugs that clog the pores of the follicles. They can be black (if dirt and dust have reached its surface) and white. White subcutaneous pimples on the forehead are easily palpable; their diameter varies from one to three millimeters. Black comedones have the same appearance, only with a black head.
- Papules are pimples that occur during an inflammatory process when fatty acids irritate the walls of the follicle.
- Pustules begin when there is inflammation inside the hair follicle.
- When fatty acids enter the tissue or the follicle ruptures and the inflammatory process begins, nodules and cysts form.
- Globular acne. This form of the disease is considered the most severe. Males are often exposed to it. Symptoms: frequent abscesses, the appearance of sinuses, scars on the skin. Localized on the back, chest, limbs, head and buttocks.
- Acne is lightning fast. These are sharply formed acne, with abscesses often merging into one affected area. Symptoms of the disease include swelling of soft tissues, joint pain and leukocytosis.
- Pyoderma. The pathology most often affects women and is characterized by rosacea on the face. The disease is characterized by damage to the cheeks, nose, forehead and chin area.
Painful sensations are caused only by cystic formations on the skin; other varieties cause only psychological suffering.
What is the difference between pustules and papules? They have a similar appearance. These are points that resemble a cone, their size varies from two to five millimeters. The accumulation of lymphocytes and neutrophils occurs in the epithelium. After the epithelium ruptures, a pronounced inflammatory process in the dermis begins. Papules become very inflamed, but do not affect the deeper layers of the skin.
The nodules are denser in consistency than papules, similar to cysts, but have a different structure. Cysts are filled with pus and can become infected and form abscesses. After this form of the disease, unevenness occurs, the surface of the skin in some areas may sink. Only a specialist can diagnose the disease using laboratory tests.
Acne vulgaris and causes of the disease
Only every fifth teenager treats the disease; the rest of the parents let everything take its course, believing that acne vulgaris will go away on its own. People try to disguise them or squeeze out emerging pimples. Such decisions are a temporary measure that aggravates the situation.
Causes of acne vulgaris:
- Problems with the functioning of the sebaceous glands (increased sebum production or changes in its viscosity);
- Hereditary predisposition;
- The sebaceous glands atrophy;
- Hormonal imbalance.
With the beginning of the body's adjustment to puberty, the child's body changes: the production of the gonads increases, the condition of the skin changes, the glands secrete more sebum. Fat changes viscosity, pores become clogged, followed by inflammation. The skin is “decorated” by acne vulgaris.
They can be caused by a number of other reasons:
- Unbalanced diet;
- Constant stress;
- Increased sweating;
- In women, acne can cause premenstrual syndrome
Acne treatment
Remember that acne leads to boils if left untreated for a long time. There are two directions for treatment:
- Internal (treatment with drugs).
- External (ointments, skin care procedures, treatments using special devices).
Often, vulgar facial acne is a sign of other diseases of the body (failure in the endocrine system, pathology of the gastrointestinal tract). Before starting treatment, you should be examined by a gynecologist, gastroenterologist, or endocrinologist. If other diseases are identified, then an integrated approach is necessary. The main goal of treatment is to normalize the patient's sebum production. To do this, it is recommended to treat the skin with drying cosmetics and pharmaceutical products.
Nutrition against acne vulgaris
Doctors recommend reviewing your diet. Good reviews from recovered patients about vegetarianism. It quickly brings the skin back to normal. It is best to eat something that has a positive effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. These are greens added to dishes; porridge; fruits and vegetables.
Therapeutic methods
The most commonly used methods for treating pathology:
- Skin cleansing. This technique works well when the patient has a mild stage of the disease.
- Herbal tinctures. Treats acne with calendula, celandine, chamomile. They have a strong bactericidal effect.
- Treatment with a course of physiotherapy. These procedures are performed only by a doctor. The patient is prescribed quartz radiation, autohemotherapy and other treatment methods.
- A course of antibiotics. Used in severe stages of the disease, when it becomes chronic. These are ointments, creams, tablets and even injections.
- A course of procedures with a cosmetologist. This includes laser treatment, peeling, and skin cleansing.
- Facial volumization in the salon helps a lot.
- An erbium laser can help with a more gentle method.
Monotherapy
If the patient has a mild degree of the disease, then treatment is aimed at eliminating comedones. If pustules or papules have formed, the doctor will prescribe the use of antibiotics, tretinoin, and peroxide. Course: from 6 weeks until symptoms disappear completely. Comedones are treated with tretinoin with increasing concentrations. If you are allergic to it, treatment with tazarotene, products with azelaic acid, salicylic acid, and propylene glycol is used.
Antibiotics
For moderate severity of the disease, the doctor prescribes tetracycline and minocycline. Course: 3 months. Gradually the dose of medication is reduced. If the disease is complicated or poorly treated, then the dosage of the drug may be increased. To avoid relapses, prophylaxis with medications should be carried out.
Before using antibiotics, you should be aware of the side effects. The patient may be concerned about problems with bowel movements and gastrointestinal tract function. And the use of antibiotics during long-term treatment provokes thrush in female representatives. If the patient has a severe inflammatory process, but it is necessary to avoid antibiotics, doctors recommend using isotretinoin. It is taken once a day for 4–5 weeks; if the drug is poorly tolerated, the dose of the medication is reduced.
Traditional methods of treatment
Treatment of acne vulgaris with such remedies can be done at home using herbal raw materials. For lotions, rubs and masks, decoctions of calendula, aloe juice, infusions of St. John's wort, birch leaves and other plants are well suited.
Treatment with plant decoctions
To prepare these recipes, take 500 grams of boiling water, 4 teaspoons of vegetable raw materials, leave for an hour, and filter. Apply the decoction to clean, fat-free skin using cotton pads and gauze. Application to the skin is done with gentle movements. They should not injure the skin and remove vulgar acne.
We recommend lotions with aloe juice, a decoction of marshmallow roots, and infusion of celandine. Take a napkin soaked in the decoction (juice) and keep it on the skin for about half an hour. If the napkin dries quickly, then it needs to be moistened from time to time.
Compresses
This procedure is carried out once a day. If you have oily skin, the procedure is done using hot compresses. If the skin is dry, the compresses should be made warm so as not to irritate the damaged skin. Compresses are made using celandine, liquid honey or ammonia. Ammonia is diluted in the proportion of three drops per 250 grams of water.
Baths
Warm steam baths help open pores. They are done no more than once every 7 days. They use herbs with essential oils that have a disinfecting and disinfecting effect. Before the procedure, thoroughly cleanse the face without using rough peelings or scrubs.
- Take a wide container with a volume of at least half a liter. Place the plant material at the bottom, pour boiling water over it and let it brew for 10 minutes.
- Hot steam should not be used, as this will prevent the patient from damaging the skin.
- Recommended water temperature is about 43 degrees.
- We bend over the water and cover our heads with a towel. If the skin is dry, it will steam in 10 minutes. If oily, it will take 20 minutes.
- Don't lean too low into hot water. The optimal distance between water and a person’s face is 20–30 cm.
- Do not rub your face once the procedure is finished. Just blot it with a clean towel or paper napkin.
Yeast based mask
Acne vulgaris is afraid of masks by leaps and bounds. But this technique does not bring quick results. The course should be at least 20 procedures. Take 2 teaspoons of yeast, add warm water and stir to a paste. Apply to the face for 20-25 minutes, rinse it off the face with warm water.
Bodyagi-based mask
For white, black and inflamed acne vulgaris, use a mask with bodyaga. Mix bodyagu with water to a paste. Apply to inflamed areas for 7-10 minutes. If your skin burns too much, then this treatment method is not suitable for you due to increased skin sensitivity.
Infusion of walnut leaves
Take the nut leaves and fill them with vodka. Proportions are 1 to 10. Let it sit for several hours, wet the gauze and apply it to the affected areas of the skin. The method helps well with acne vulgaris on the back.
Acne vulgaris (aka acne) is a skin rash that occurs as a result of an inflammatory process in the sebaceous glands and hair follicles. This type of rash most often affects teenagers during active puberty and is less common in people over 30 years of age. Acne vulgaris itself is not dangerous, but it can become a serious cosmetic problem, and with severe inflammation it leaves scars and age spots on the skin.
Causes
The development of acne vulgaris is based on seborrhea - increased activity of the sebaceous glands, a decrease in the bactericidal effect of sebum and activation of pathogenic microbes. Streptococci, staphylococci, corynebacteria, as well as their metabolic products may be involved in the development of acne.
The main causes of acne vulgaris:
- hormonal activity (during puberty, pregnancy) or disorders due to pathologies of the endocrine system;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- demodicosis (a parasitic skin disease caused by acne mites);
- increased sweating;
- stress, nervous disorders, accompanied by increased production of hormones by the adrenal cortex;
- weakened immunity;
- avitaminosis;
- the use of certain medications (anabolic steroids, barbiturates, products containing halogens - fluorine, chlorine, iodine);
- improper skin care or lack thereof;
- unhealthy diet (abuse of fatty, spicy, smoked, chocolate, sweet carbonated drinks, coffee);
- bad habits;
- hereditary predisposition.
Development mechanism
The main reason for the appearance of acne vulgaris is still hormonal changes. Acne is provoked by male sex hormones: testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone.
Male sex hormones affect the functions of the sebaceous glands. If there is an excess:
- sebum production increases, cell division of the stratum corneum of the skin accelerates (hyperkeratosis);
- dying horn cells and sebaceous secretions mix, clog pores, clog the ducts of the sebaceous glands;
- in clogged ducts an optimal environment is created for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms;
- the active development of propionebacilli and coccal infection causes inflammation of the sebaceous gland.
During puberty, the production of male hormones increases in the body of both boys and girls. This is why teenagers most often suffer from acne. And in the presence of the listed provoking factors (one or more), the likelihood of acne increases, and inflammation occurs in a more severe form.
If in adolescence the appearance of acne is a physiological phenomenon caused by hormonal changes, then acne in adults is always a sign of certain disorders in the functioning of internal organs.
Localization
Acne vulgaris can appear on any part of the skin. Most often, the rashes are localized on the face, back, less often - on the chest, upper neck, and shoulders.
On the face
Inflammatory processes most often involve the skin of the face - thinner and more delicate, not protected by clothing, and more susceptible to negative external influences. On the face, most rashes are localized in the so-called T-zone (forehead, nose, chin), where many sebaceous glands are located. Less commonly, acne affects the cheekbones and skin around the lips.
On the back
The appearance of acne on the back is more common in men than in women. Usually the problem is caused by hormonal factors, disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, and excessive sweating. In some cases, the cause of inflammatory processes is intercostal neuralgia or allergies to synthetic fabrics, skin irritation caused by wearing too tight, constricting clothes.
On the neck
Inflammation of the skin on the neck, in addition to hormonal disorders, can occur due to excessive sweating, poor hygiene, irritation with hair or synthetic fabrics, as well as the body’s reaction to low-quality cosmetics or perfumes.
On the chest
There are quite a lot of sebaceous glands on the skin of the chest, as well as the back, they are located close to the surface, which increases the risk of inflammation, especially if hygiene is not observed or wearing tight and/or clothes made of synthetic fabrics.
Classification
Acne vulgaris is a general concept that unites various types of rashes, which can be inflamed or non-inflamed.
Types of acne vulgaris:
- Comedones. Non-inflamed elements resulting from blockage of the sebaceous gland ducts with sebum. They can be closed (white tubercles ranging in size from 1 to 3 mm that do not have access to the surface of the skin) and open (sebum moves through the gland duct to the surface of the skin, oxidizes, mixes with dust, which is why the sebaceous plug turns black).
- Papules. Inflamed elements in the form of dense reddish tubercles rising above the surface of the skin. As inflammation worsens, papular acne turns into pustules.
- Pustules. They are painful elements with purulent contents. Pustules up to 5 mm in size usually disappear without a trace, and larger formations often leave scar defects.
- Knots. Large (more than 5 mm) elements that arise when purulent-inflammatory processes spread into the deep structures of the skin (dermis, subcutaneous fatty tissue).
- Cysts. Cavity formations of a purplish-bluish color, filled with purulent contents.
Depending on the type of rash affecting the skin, there are 4 main forms of the disease:
- comedonal - non-inflamed open and closed comedones, localized mainly on the forehead, wings of the nose, chin, there are no inflamed elements;
- papulopustular – open and closed comedones, papules, a small number of pustules;
- pustular – a significant number of pustules on the face (more than 25 units), open and/or closed comedones;
- conglobate (confluent) acne - large nodes and cysts merge, forming a large affected area.
Conglobate acne is the most severe form of the disease, leading to the formation of scars on the skin.
Treatment
What is acne vulgaris, what type of acne affects the skin and how to treat the disease, a dermatologist will tell you. The specialist selects treatment in each case individually, taking into account the type of rash, the shape and severity of the inflammatory process, its location, gender and age of the patient.
Treatment of acne vulgaris is aimed at:
- suppression of sebum production by the sebaceous glands;
- cleansing and narrowing enlarged pores;
- reduction of inflammatory processes;
- suppression of pathogenic flora.
For these purposes, depending on the severity of the pathological processes, both local remedies and oral medications are used.
Local remedies
For mild acne, treatment is carried out only with external means. These are ointments, gels and creams based on benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, antibacterial components, and other medications with a drying, healing and antiseptic effect. For moderate inflammation, external retinoids are prescribed.
Based on benzoyl peroxide
Benzoyl peroxide has a pronounced keratolytic (promotes exfoliation of keratinized cells, slows down keratinization), comedolytic (dissolves sebaceous plugs, regulates oily skin), antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. The course of treatment with benzoyl peroxide-based products is 1-3 months.
The use of the drugs is contraindicated if the integrity of the skin is damaged (scratches, abrasions, cracks, cuts) and for people whose work involves constant exposure to the sun.
Sometimes after using the products, redness, peeling, and dry skin occur. These phenomena do not require discontinuation of therapy and disappear on their own a week after the start of treatment.
The most common drugs with benzoyl peroxide:
With azelaic acid
Products based on azelaic acid have a keratolytic and anti-inflammatory effect, tighten pores well, even out skin color, but do not affect sebum production. Recommended for the treatment of acne caused by the activity of propionic bacteria.
The drugs are not addictive and are used for a long time - at least 3 months.
Antibacterial
Commonly prescribed antibacterial medications for acne:
- Based on clindamycin. They have a bacteriostatic effect, especially effective against staphylococci and propionebacilli. They are used for a long time (up to six months), and do not cause the skin microflora to become addicted to the active substance. Available in the form of gels and solutions. Representatives: Zerkalin, Dalatsin, Klindovit.
- With erythromycin. The representative is Zinerit, which, in addition to the antibiotic, contains zinc. It has a bacteriostatic, regenerating and astringent effect, reduces sebum secretion. May be addictive and will be ineffective with subsequent use.
Topical retinoids
Retinoids are synthetic analogs of vitamin A. The drugs suppress the sebaceous glands, reduce skin oiliness, and normalize keratinization processes. They are highly effective in treating any form of acne, however, they can cause quite serious side effects. Must be used strictly as directed and under the supervision of a doctor.
- Isotretionine. Suppresses the activity of the sebaceous glands, relieves inflammation. It is used for a long time, from 16 to 24 weeks. Representatives - solution for external use Retasol, Retinoic ointment.
- Adapalene. It has anti-inflammatory, comedolytic and sebostatic effects, does not increase photosensitivity. Apply once a day, last up to 3 months. Very drying to the skin, suitable only for oily types. Release form: gel and cream. Analogues - Differin, Klenzit, Adaklin.
Retinoid drugs have a toxic effect on the fetus, therefore, during treatment with retinoids and for a year after the end of the therapeutic course, pregnancy should not be planned.
Other means
Other effective topical remedies to help get rid of acne vulgaris include:
- Preparations with zinc. They have an astringent, drying, antiseptic and adsorbing effect. Apply to acne spots 2-4 times a day. Representatives - Zinc ointment, Salicylic-zinc paste, Tsindol.
- Badyaga. Powder from the exoskeleton of freshwater sponges is produced in pure form for the preparation of a dosage form or is included in creams and gels for acne. Apply to inflamed areas for the time specified in the instructions, then wash off. Do not use if there is damage to the skin; it may cause allergies.
- Salicylic acid. Used in the form of a solution or ointment. It has a drying, keratolytic and antiseptic effect. Apply to problem areas three times a day.
- Curiosin. A product based on zinc oxide and hyaluronic acid has a drying, antiseptic and healing effect, and prevents the appearance of scars. Apply spot-on 2-4 times a day. Analog – Regetsin.
Preparations for oral administration
Treatment of severe forms of acne is carried out with drugs for internal use:
- antibiotics (Doxycycline, Clindamycin, Erythromycin) - used for a month, if there is no effect, they switch to therapy with synthetic analogues of vitamin A;
- retinoids (Roaccutane, Acnecutane, Sotret) - drugs affect all mechanisms of acne development (suppress the activity of the sebaceous glands, eliminate hyperkeratosis, suppress inflammation and the development of pathogenic flora), taken from 4 months to a year only as prescribed and under the supervision of a doctor;
- hormonal agents (Yarina, Jess, Diane, Janine) - prescribed to women if the appearance of vulgar acne is caused by an increased content of male sex hormones;
- sorbents (Polysorb, Polyphepan) - help cleanse the body of waste and toxins, are classified as auxiliary therapeutic agents, and are used in cases where acne develops against the background of disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
Acne vulgaris is quite difficult to treat, especially in severe forms of inflammatory processes, leading to the formation of gross scar defects. However, the modern choice of therapeutic methods and drugs can significantly alleviate the course of acne, achieve stable remission and prevent destructive changes in the skin.
It is important to understand that treatment of acne vulgaris is a long process, taking at least 4 months. And even if a noticeable improvement occurred earlier, therapy cannot be interrupted, otherwise a relapse may occur at any time.