- What strains of HPV are there?
- Reasons for the degeneration of papillomas into cancer
- Main features
- Stages of degeneration of papilloma
- Diagnostic methods
- Prevention of degeneration of papillomas
The degeneration of papilloma is the process of malignancy of a growth caused by the active activity of HPV in the body. There are about 100 strains of the virus, and some of them are highly oncogenic. These types of pathogens can provoke the development of an oncological process.
What strains of HPV are there?
To date, it has been established that there are over 100 strains of papillomavirus. Only about 80 types of HPV have been thoroughly studied. Until the 80s of the last century, it was believed that papillomas on the body were an exclusively aesthetic problem and did not pose any threat to health. Later, clinical studies proved that many benign neoplasms of a viral nature on the skin and mucous membranes can degenerate into oncological tumors.
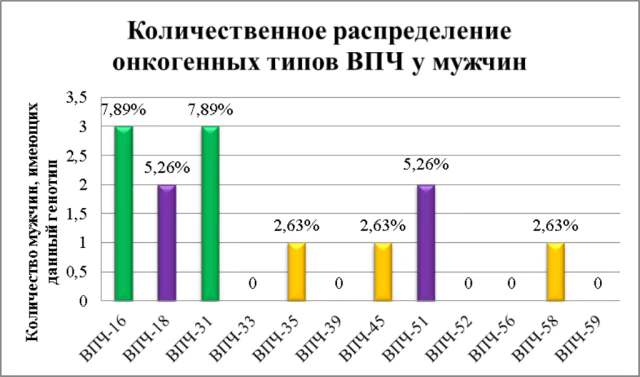
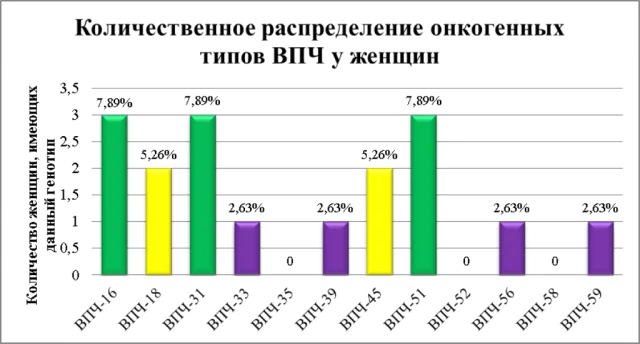
All papillomaviruses are conventionally divided into 3 categories:
- Non-oncogenic strains. These pathogens are not ways to provoke the appearance of potentially dangerous neoplasms. This group includes the following types: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 28, 49. They cause the appearance of flat and vulgar papillomas on the face, feet, and hands.
- Strains with low oncogenicity. We are talking about types 6, 11, 42, 43, 44. These pathogens can cause flat or pointed growths on the head, internal genital organs of women, respiratory organs, and neck.
- Strains with medium oncogenicity. This category includes viruses 31, 33, 35, 51, 52, 58. Under their influence, flat-shaped neoplasms are formed in the vaginal area, the walls of the uterus and its cervix, the penis, and the anogenital area of men and women.
- Strains with a high level of oncogenicity. Types included in this category are: 16, 18, 36, 45, 56, 66, 70. As a rule, such growths form on the internal and external genital organs, on the head, neck, open areas of the epidermis, and respiratory organs. In more than 50% of cases of papillomas, the causative agent is strains 16 and 18. They are considered the most common. They are responsible for cervical cancer.
It is worth noting that HPV is very common on the planet. And one person may well be infected with several strains of the virus at once. In this case, the risk of papilloma degenerating into cancer increases.
Reasons for the degeneration of papillomas into cancer
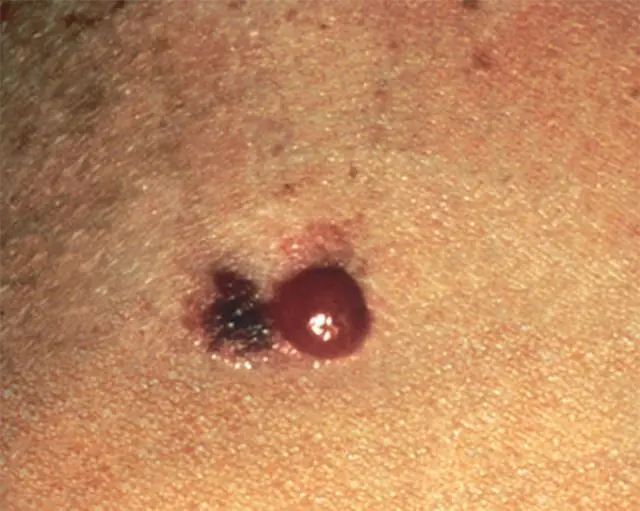
Photo of a potentially dangerous injured papilloma
It has been scientifically proven that papillomas and cancer can have a direct relationship. There are not too many highly oncogenic strains of the pathogen. Virus types with low and moderate oncogenicity may never lead to the development of malignant pathology in the absence of factors favorable to HPV.
It is worth noting that women are more easily and more likely to become infected with papillomavirus than men. This is due to the fact that they have high levels of estrogen in their bodies. This hormone is also a predisposing factor for the degeneration of papilloma into a malignant formation. Therefore, genital cancer occurs more often in women than in men. They also quite often develop oncology due to intraductal papillomas in the mammary glands.
In addition, the formation of an oncological tumor from a benign growth can begin under the following conditions:
- General decrease in the body's defenses;
- Genetic predisposition to cancer;
- Frequent injury to papilloma;
- Presence of chronic infectious diseases;
- Exposure to carcinogenic agents;
- Regular exposure to ultraviolet light and radiation;
- Chemical damage to the tumor.
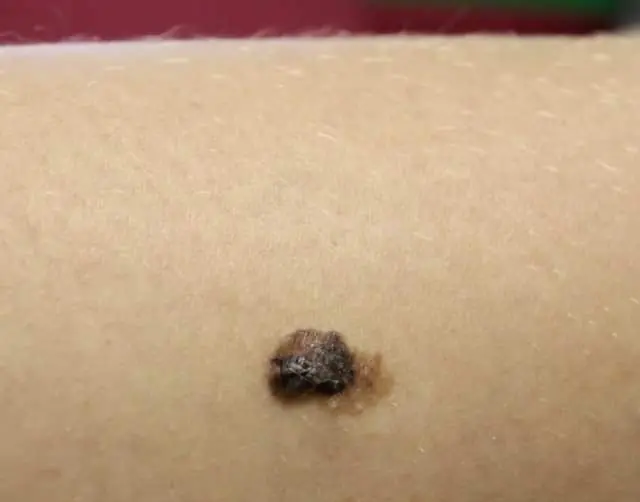
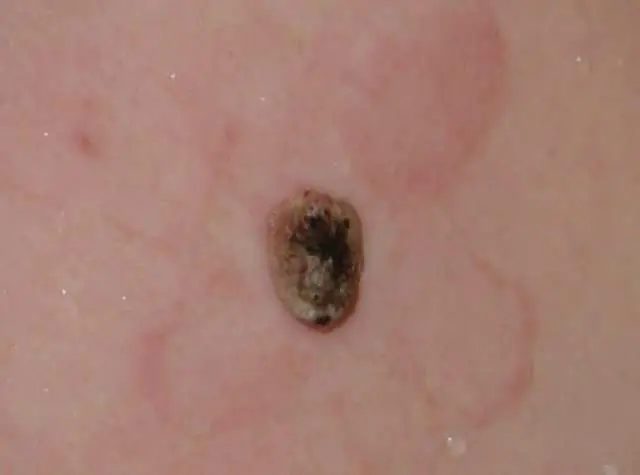
The photo shows the process of degeneration of papilloma into cancer
Hereditary predisposition to cancer consists of special mutations in the human body that are passed on from generation to generation. As a rule, they represent a defect in the functioning of the immune system, as a result of which it “does not respond” to abnormal cells and allows them to divide uncontrollably.
Deterioration of the immune system usually occurs under the influence of external factors. For example, radiation, poor environmental conditions, frequent stress. Also, the protective functions of the body can be weakened by improper unbalanced nutrition, alcohol abuse, smoking, and the development of focal infections. Often the provoking factor for the degeneration of papilloma into cancer is a sexually transmitted disease.
Mechanical damage to benign neoplasms also often causes their malignancy. For this reason, doctors recommend removing growths, especially in potentially dangerous places on the body, where they can often be injured, squeezed and rubbed.
The main signs of papilloma degeneration
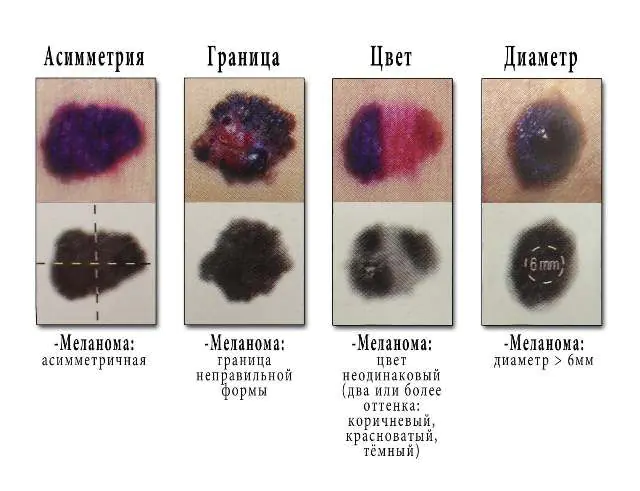
The photo shows signs of melanoma
Many people are interested in whether papilloma can develop into cancer? Most benign tumors remain as such and do not transform into cancerous tumors. However, it is impossible to know for sure which papilloma is safe and which carries a potential threat. Therefore, it is recommended to undergo a comprehensive examination and establish an accurate diagnosis. After this, treatment of the tumor should begin.
You should urgently contact a specialist if the following symptoms appear:
- Change in the color of the new growth, its darkening, blackening, discoloration, the appearance of dotted inclusions, multi-colored shades on one growth;
- Changing the contours of the growth, its rapid growth;
- Violation of the structure of the neoplasm and skin pattern;
- The appearance of painful wounds, cracks, ulcers in the area of the growth;
- Spontaneous rupture of papilloma with the release of ichor, pus, and blood from the neoplasm;
- Formation of a dense crust on the surface of the growth;
- Inflammation, redness, swelling in the papilloma area;
- Soreness, itching, burning of the growth.
If the papilloma is located in a place that is difficult to visualize, for example, on the internal genital organs or respiratory system, throat, then it is important to promptly pay attention to the accompanying symptoms. Thus, when papilloma degenerates into cancer in the throat and larynx, pain may occur when swallowing, chewing, and enlargement of regional lymph nodes. If papilloma on the genitals begins to become malignant, a burning sensation, itching in the vaginal area, vulva appears, and copious pathological discharge from the genitals begins.
The formation of a large number of new papillomas near the old one is not considered a direct sign of the degeneration of papilloma into a malignant formation. But this pathology is evidence that HPV has become more active. This phenomenon also indirectly indicates that a certain type of papillomas is prone to malignancy.
Only an oncologist can determine whether the papilloma has grown into cancer or not. He will evaluate the appearance of the tissues and, if necessary, refer you for a comprehensive examination.- Read also what cancerous papilloma looks like
Stages of degeneration of papilloma into malignant formation
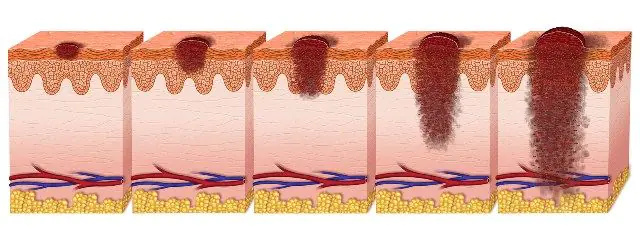
The photo shows the stages of degeneration of papilloma
The process of malignancy of a viral tumor is called malignancy. It begins with the formation of atypical cells in the papilloma. In this case, symptoms of cancer can already be noticed during the initial medical examination.
The initial stage of malignancy can last for months and years. The process of degeneration of papilloma has several stages:
- Initiation. At this stage, there are no external signs of malignancy of the neoplasm, but the process of division of atypical cells has already begun. It happens that at this stage, cancer cells die along with individual parts of the papilloma and the development of cancer stops.
- Promotion. Active division of pathological cells begins. Gradually they replace all healthy tissue. This process can fade or intensify. Visual symptoms of oncology may be mild or absent.
- Formation of cells without antigen receptors in papilloma. The human immune system is not able to fight them, since it does not see them as a threat. In parallel with this, stem lines of poorly differentiated cells are formed in the neoplasm. They divide rapidly and actively. This stage of malignancy is accompanied by visible changes in the growth - intensive degeneration of papilloma into cancer occurs.
- Tumor progress. It begins at the stage when malignant cells leave the original boundaries of the papilloma, and the oncological process invades neighboring healthy tissue. In this case, there is a high probability of the formation of metastases.
Methods for diagnosing malignant papillomas
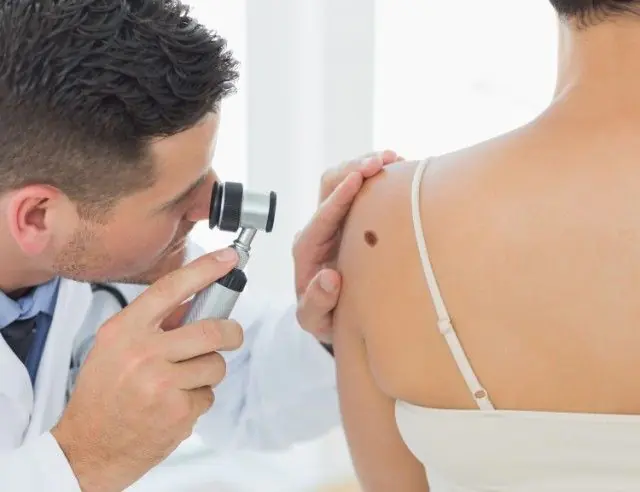
If a suspicious tumor is located on visible parts of the body, then diagnosis will not be difficult. Typically, the doctor conducts an initial examination and collects data for anamnesis.
Next, the patient is sent for tests:
- PCR blood test is a highly accurate test that helps determine the strain of the pathogen.
- The Digene blood test determines not only the type of virus, but also its concentration in the body;
- Cytological analysis or PAP test of epithelial cells of the genital organs.
If during these initial tests it turns out that the patient is infected with a highly oncogenic virus, and the neoplasm has signs of degeneration, then additional studies will be prescribed, including instrumental ones:
- Histological analysis of the growth to identify malignant cells;
- Blood test for tumor markers - if cancer is suspected, separate tests are performed for different organs;
- Ultrasound makes it possible to identify internal papillomas that have already degenerated into a malignant formation; it is prescribed for intraductal neoplasms, on the cervix, and in the respiratory organs;
- CT, MRI - informative examination in cases with the formation of tumors on internal organs.
Only after a comprehensive examination can we talk about an accurate diagnosis and prescription of the correct treatment.
Prevention of degeneration of papillomas
Pictured is Gardasil for HPV vaccination
If you do not want papilloma to develop into cancer, you should worry about prevention in advance. The development of the oncological process can be prevented by timely treatment of benign neoplasms, by removing or destroying them. Also, after treating papillomatosis, undergo tests that will make it possible to determine the risk of developing cancer.
In addition, it is important to prevent infection with papillomavirus. To do this, avoid unprotected sexual intercourse, try to increase your immunity and do not trigger chronic diseases.
Currently, vaccines have also been developed against some strains of the papilloma virus. For example, Gardasil (11, 16, 18 strains), Cervarix (16 and 18 strains). They work if a person is not yet infected with HPV. It is recommended to be vaccinated with them from the age of 9 and before entering into an intimate relationship. If infection with a certain high-gene strain of the virus has already occurred, then the vaccine is powerless. However, it may help prevent infection by other types of virus.
The degeneration of papilloma into cancer can also occur against the background of decreased immunity due to an unhealthy lifestyle and bad habits. By eliminating these factors from your life, you can significantly reduce your risks.
Can papilloma develop into cancer - watch the video:
Photos of the degeneration of papilloma into cancer can be found on the Internet. If you notice one or another symptom of an oncological process, immediately contact a specialist. Do not try to self-medicate or trigger the disease. This threatens the rapid and uncontrolled growth of malignant cells with a subsequent unfavorable prognosis for health and life.
- Related article: Why visit an oncologist for papillomas



