Allergy in the hands to cold is a rather rare and not fully studied phenomenon, the exact causes of which have not yet been clarified. Doctors only know that the cause of this disease is the human body’s hypersensitivity to cryoglobulin (its own protein), which begins to change when exposed to low temperatures. This process causes the so-called cold urticaria.
Definition of the concept
Cold urticaria refers to an allergic reaction that manifests itself in exposed areas of the body. These are rashes in the form of red spots caused by exposure to low temperatures.
Although this disease is called an allergy, it has nothing to do with a true allergic reaction. Frost, dampness and cold are physical factors, and not a substance that increases the sensitivity of the body.
Causes of pathology
Doctors are confident that hand allergies to cold are not an independent pathology. This is only one of the symptoms of any physical disease. The reaction in the form of urticaria is manifested by an organism weakened by a latent and long-term course of the disease.
As mentioned above, the culprit that causes hand skin allergies to cold is a special protein (cryoglobulin), and the trigger is low temperature. The progress of the entire process is determined by various predisposing factors in the form of decreased immunity, as well as the presence of parasitic, colds and infectious diseases.
Another reason that a person is allergic to cold hands is problems with the digestive system in the form of cholecystitis, chronic gastritis or ulcers. But experts are confident that in addition to these, many other chronic ailments can cause the body to react to a decrease in ambient temperature.

Causes of urticaria
Allergy to cold on the hands (see photo below) has a rather complex mechanism of appearance and development, which modern medicine is not yet able to fully understand.
However, there are certain factors that provoke the manifestation of its symptoms. They are:
- contact with cold water that occurs in everyday life while washing dishes or when cleaning, as well as when swimming in natural bodies of water;
- a sudden transition of a person from an environment with normal temperature conditions to a windy environment with low air temperature;
- Drinking food or drinks that are too cold.
All these factors work only if the human body has a weakened immune system.
Symptoms of pathology
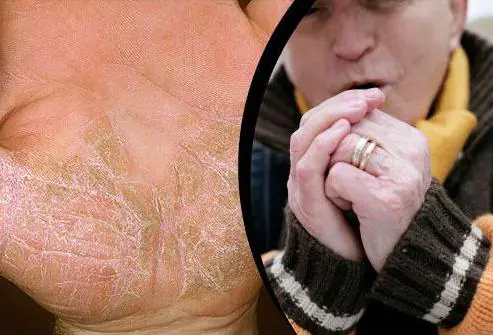
Allergies in the hands to cold are often disguised as dermatitis. That is why it can be very difficult to distinguish it from this disease. An allergy to cold on the hands (see photo below) begins with simple scratching of the skin. Then your hands become dry. The skin on them becomes rough and covered with small cracks. Next, rashes like urticaria appear. After this, the hands swell.
The body may also exhibit more intense reactions. This occurs when cold rain or snow hits the surface of the skin. In this case, the hands become covered with red, swollen blisters filled with clear liquid.
All these symptoms become pronounced immediately after warming the cooled areas of the skin. Then they gradually disappear, and after 30-60 minutes the skin becomes clear. In some cases, the rash lasts for a week, and sometimes longer.
Also, a person predisposed to allergies to cold begins to sneeze after going out into the cold. At the same time, he develops a runny nose. Such symptoms are associated with damage to the mucous membrane. All this causes difficulty in breathing.
The body's reaction to low temperatures sometimes manifests itself as an allergy to cold on the hands and eyes. At the same time, the organs of vision turn red, starting to tear and itch. At the same time, swelling of the area around the eyes and eyelids appears. It often becomes painful for a person to watch. He experiences pain in the eyes and other uncomfortable sensations, which intensify in bright daylight.
Cold allergies in the hands are also determined by some additional signs. These include:
Such manifestations bring great discomfort to a person and contribute to the appearance of irritability, and also reduce performance.
Cold urticaria in children
Redness of a baby's hands when going outside may well be a natural reaction of the body. Cold urticaria can only be distinguished if the child complains of itching that torments him in the area of the rash. But in any case, you will need to consult an allergist.
Children react to cold:
- during walks in cold seasons;
- when swimming in the pool;
- when in contact with cold water, as well as when eating ice cream.
Types of allergies to low temperature
Cold urticaria can be:
1. Acute or chronic. This form of pathology begins with intense itching of exposed skin, sometimes spreading to the entire body. Further, swelling occurs in the affected areas, manifesting itself in the form of blisters. In acute pathology, individual areas of the skin become covered with intense red rashes, similar to a nettle sting. Severe forms of the disease are accompanied by general malaise, pain in muscles and joints, increased heart rate and severe weakness. Such exacerbations last for several weeks, and sometimes can bother a person throughout the cold period.
2. Recurrent. This form appears only in autumn, winter and early spring. At other times, it worsens when the skin comes into contact with cold water.
3. Reflex. This form of allergy is a local or general reaction of the body to cold. Its manifestations are a rash that occurs in the area of direct contact with low temperatures.
4. Family. This is a rare form of allergy that is passed down through the family. This pathology is characterized by a maculopapular rash, accompanied by a burning sensation. This reaction occurs 0.5-3 hours after contact with cold. Symptoms of familial urticaria include joint pain and chills, as well as occasional fever.
5. Cold erythema. The manifestation of this type of pathology is accompanied by redness of the skin with pronounced painful sensations in the affected areas.
6. Cold dermatitis. The skin with this form of the disease is very flaky and itchy. As the pathology worsens, swelling is also observed.
Cold urticaria test
All of the above symptoms should not be confused with the body’s natural protection from wind and cold, which do not cause much discomfort to a person and quickly go away in a warm room. But at the same time, it is important for both the patient and the doctor to promptly determine what the nature of the reaction to cold is. To do this, you can undergo a complex examination that uses special equipment. But there are also simple methods that can be used even at home.

So, you can apply a piece of ice to the crook of your elbow for 10-15 minutes. If urticaria appears, this indicates the body’s predisposition to cold allergies. But if you have any doubts, it is still better to consult a doctor. After all, to accurately determine allergies, you will need a blood test.
Treatment
What should those who have allergies to the skin on their hands do? The symptoms and treatment are well known to specialists. However, the answer that doctors give does not always suit patients. Doctors will recommend completely eliminating exposure to the allergen, that is, frost and cold. And it is almost impossible to do this. But in any case, those who suffer from winter allergies will need to wear warm clothes made from natural fabrics when going outside and try to avoid hypothermia.

You should also take into account the fact that the degree of sensitivity in each person is an individual indicator. Some suffer from an allergic reaction already at minus 8-10 degrees, while others suffer at minus 24-28. There are also people whose skin becomes red when they wash their face with cool water. In addition to precautions, there are many remedies, the use of which will significantly reduce the consequences of pathology.
Use of drugs
If a person is allergic to cold on their hands, the treatment of this disease will be similar to eliminating a true allergy. Among medications, antihistamines such as Claritin, Tavegil and Suprastin are prescribed. It is worth keeping in mind that some medications produce a hypnotic effect, and, therefore, they should not be used before performing work that requires quick reaction or concentration. In severe cases, the doctor may prescribe some immunosuppressants, as well as plasmapheresis to cleanse the blood of glucocorticosteroids and cryoglobulins.
Often, cold allergy is a manifestation of chronic infection with sinusitis or bronchitis, tonsillitis or pyelonephritis. Diseased teeth can also provoke its manifestation. In this case, the doctor should prescribe appropriate medications to eliminate these ailments.
People with impaired intestinal and liver function are predisposed to allergies, including cold allergies. In these cases, treatment of the underlying disease will eliminate the unpleasant symptoms.
It is also worth remembering that those who have allergies to the skin on their hands (symptoms and treatment of pathology are the subject of our attention) should be under constant medical supervision, since the body’s reaction is individual for each patient.
Use of ointments
When diagnosing “cold allergy,” creams sold in pharmacies are sometimes used. However, their use will require prior consultation with a specialist.
How to treat allergies to cold on hands? To eliminate unpleasant symptoms, you should pay attention to antihistamines for external use. These include “Gistan N” ointment for cold allergies on the hands, as well as “Skin Cap”. You should only take into account the fact that these products contain a hormonal substance.

When solving the question “How to cure allergies to cold on your hands?” Don’t forget about auxiliary products that will save your skin from irritation.
Treatment of children
For kids, cold allergies cause great discomfort. The red spots and rashes that appear on their hands after a winter walk are itchy and may even become inflamed. Such a child should be taken out for walks less often in cold weather, and when visiting the street, dress him properly and lubricate his hands with baby cream.
As for antihistamines, they can be given to a child only as prescribed by a doctor. In this case, the baby needs not only to be treated, but also to strengthen his immunity.
The use of folk remedies
Nature has given us many natural products that can help eliminate allergies to cold hands (symptoms). And treatment in adults (as well as in children) will be safe and quite effective.
So, raspberries are an excellent folk remedy. Its dry and crushed roots in the amount of 50 g should be poured with 0.5 liters of water, and then simmered for 30-40 minutes over low heat. The decoction thus obtained is cooled and filtered. You should drink the drug 2 tbsp. spoons in the morning, in the afternoon and before bed. The course of treatment with raspberries is two months. This decoction can also be used for prophylactic purposes. In this case, it should be drunk two months before the onset of cold weather.
Red beets and sunflower seeds help against allergies. These products must be eaten in winter in any quantity and in all types. Freshly squeezed beet juice is effective against illness. It should be drunk three times a day, half a glass. Freshly squeezed celery juice will also help with allergies. It is taken 0.5 teaspoon three times a day before meals.
A solution prepared from 1 g of mumiyo and 1 liter of boiling water is an excellent remedy for the symptoms of cold allergies. The raw material, dissolved in water without sediment, is recommended for adults 100 ml in the morning, for children 50 ml, and for primary schoolchildren 70 ml. The same drug, only of higher concentration (1 g per 100 ml), is recommended as an external remedy. They lubricate the skin of the hands.

In order to eliminate dryness, flaking, itching and redness of the skin in children due to cold allergies, prepare a solution from pine shoots in vegetable oil. For this, raw materials are pre-prepared. Pine shoots should only be young. They are taken in a 1:1 ratio to vegetable oil and the mixture is infused for five months in a dark place. The resulting drug is rubbed into the child’s skin.
Allergic swelling is perfectly eliminated by drinking birch sap. This drink is an excellent general tonic, which also regulates water-salt metabolism in the body, while producing a mild diuretic effect. You can consume juice in any quantity, but for an adult it should not exceed one liter per day, and for children - from 200 to 500 ml (depending on age).
If, when returning from a cold street to a warm room, a person is haunted by severe itching, the cause of which is a cold allergy, then hands and other parts of the body can be gently wiped with juice obtained from lemongrass.
Cold allergy is one of many types of negative responses of the body to various external stimuli. The very name of this allergy suggests that an allergic reaction occurs under the influence of cold temperatures.
Until recently, medicine rejected such a diagnosis, since there is no allergen that provokes a specific reaction of the body as such, there is only a physical effect - cold. No allergen means no allergies.
But when exposed to cold air, some sensitive people experience a significant release of histamine, which causes reactions similar to other types of allergies - the development of swelling, vasodilation, redness and itching of the skin and mucous membranes. This is a response to a decrease in the temperature of the skin's thermal receptors.
Causes of cold allergies
Why does cold allergy occur? Medicine does not yet know the exact answer to this question, but with the following factors, particularly sensitive people may experience this strange type of allergy:
- When there is a sharp change in a person’s presence in an environment with normal air temperature to an environment with low temperature - in winter, especially in windy weather
- In contact with cold water - in everyday life when washing dishes, cleaning, swimming in open water
- When drinking very cold drinks or cold food
Allergy to cold often develops after severe illness and long-term treatment with antibiotics; it is believed that it has a genetic predisposition; it can occur against the background of infectious diseases (for example, tuberculosis) or parasitic diseases (roundworms in children, adults, pinworms in children, giardiasis. 
In a strong, hardened organism with a strong immune system, such temperature changes do not cause any reactions.
However, in the event of a decrease in protective forces, systemic disorders, serious illnesses, or metabolic disorders in the body, this type of allergy may occur. Stress, as we know, is the most important risk factor for immune failure, so stress-resistant people tend to get sick less often and have good health.
Provoking factors for the development of cold allergies
- The presence of allergic reactions to other irritants - food, pollen (allergy to poplar fluff), household allergies
- Some infectious diseases - mumps, measles (see symptoms of measles in adults), mycoplasma pneumonia, rubella
- Thyroid diseases, systemic lupus erythematosus, cancer
- The presence of chronic diseases - sinusitis, sinusitis, various worm infections, intestinal dysbiosis
- Recurrent skin diseases – neurodermatitis, eczema, psoriasis
- Hereditary factor
There are cases when such a reaction is hereditary in nature, that is, it is inherited and most often it is the body’s reaction to windy weather than to cold. The symptom of such an allergy is a burning sensation, not itching of the skin.
How does an allergy to cold manifest itself?
How does an allergy to cold manifest itself? Symptoms of such an allergy can have various forms of manifestation - from mild symptoms that disappear some time after contact with a cold environment, to serious recurrent skin rashes.
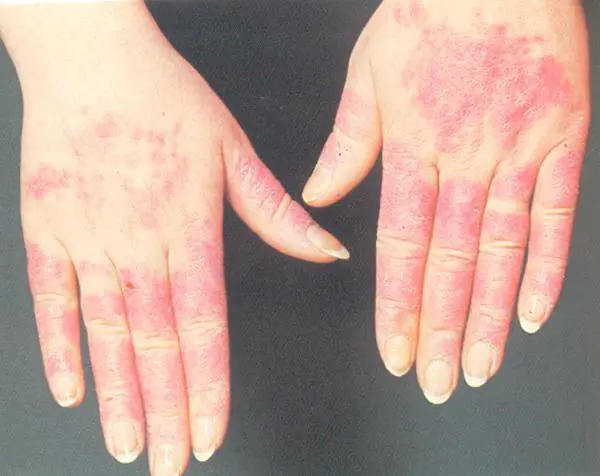
Skin manifestations are the most common signs. These include redness, swelling, itching of open areas of the body that have come into contact with a cold environment. After some time, the skin begins to hurt, itch, and may become blistered, similar to hives.
Cold allergies in children can even affect the inner surface of the legs, thighs, knees and manifest themselves in the form of hives. The rash is pink, dense, itchy, but goes away within a few hours. There are cases when, after a cold, the skin not only turns red and itches, but also becomes covered with a layer that begins to peel off, as with dermatitis. Sometimes bruises appear at the site of the allergy over time.
Most often, cold allergies occur on the face and hands, since these places are more exposed to the external environment, they are always open and more vulnerable.
General malaise - increased blood pressure, shortness of breath, headache and weakness.
Allergic rhinitis - the appearance of a runny nose, sneezing when going out into cold air. Swelling of the mucous membranes of the nose can either greatly complicate nasal breathing or completely block it, and upon returning to a warm room, all allergy symptoms disappear.
Signs of allergic conjunctivitis are tearing, swelling around the eyes, swelling of the eyelids, pain in the eyes. Hypersensitivity to bright light also occurs. To differentiate the diagnosis, you should definitely consult an ophthalmologist and dermatologist, since if profuse lacrimation occurs in the cold, this may be a sign of tick-borne infection (demodex) or fungus, etc.
Diagnosis of cold allergies
If you experience similar symptoms, then first of all you need to visit a therapist and an immunologist - an allergist. After a set of diagnostic and laboratory tests, it will be possible to accurately determine the cause of the allergic reaction. Cold allergies, the symptoms of which are similar to other types of allergic reactions, should be differentiated from a number of other diseases.
- Sometimes in small children of preschool age, cold allergies on the face are similar to atopic dermatitis, neurodermatitis.
- Often similar allergic symptoms occur with idiopathic dermatosis. With this disease, heat and cold skin receptors are deregulated. Swelling, lacrimation, sneezing, and difficulty breathing occur in both cold and heat.
- Intolerance to the fur of some animals - rabbits, mink, chinchillas, woolen fabrics, sheep's wool - can also be confused with an allergy to cold. When putting on clothes and going out into the cold, a person returns with a rash and swelling of the nasopharynx; as a result, this can be assessed as a reaction to the cold, and not an allergy to wool or fur.
- The situation is similar with perfume products. Typically, perfume is applied to the forearm, neck, face, and an allergic rash can be caused by cosmetics and perfumes, and not by cold.
When symptoms appear, it is important to make a correct diagnosis, and only after differentiating the signs of allergy can a doctor confirm this disease. Then, the question arises: is an allergy to cold treatable?
How to treat allergies to cold
The inability to eliminate an allergen such as cold makes the fight against such an illness quite difficult. If the patient is diagnosed with an allergy to cold, treatment in this case is purely symptomatic. It is only possible with the help of antihistamines to slightly reduce its manifestations, or to protect exposed areas of the body as much as possible from exposure to negative temperatures. You can reduce the occurrence of allergic reactions if:
- Before going out into the cold, lubricate your face and hands with baby cream, for adults, with any rich cream. Lips should be lubricated with hygienic lipstick. This will partially protect uncovered areas of skin from cold air.
- Badger fat has a very good effect; it is rich in unsaturated fatty acids and vitamins B and A, which have only a positive effect on the skin. 20 minutes before going out into the cold, you can lubricate exposed areas of the skin with badger fat (lips, cheeks, nose, hands); if there is no serious liver damage, then you can consume it orally 40 minutes before. before breakfast, 1 tbsp. a spoonful of fat.
- Long warm gloves, preferably waterproof mittens for children, warm scarves, it is preferable to have hoods in outerwear - this will effectively protect from the wind and better retain heat.
- Medicinal herbs, if there is no allergy to them, can also help with the development of urticaria, which appears as an allergy to cold. Burdock root, tricolor violet and walnut leaves are very useful. To collect, mix the raw materials in equal proportions, 2 s. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water, leave for 1 hour, strain, consume the resulting broth 60 ml 3 times a day.
- Pine cones (see pine cones for stroke) or spruce cones also have beneficial properties; 4 cones are required to prepare the decoction; they should be ground in a mill or meat grinder, poured with water and simmered over low heat for half an hour. After straining the broth, you can wipe it on chapped and rough skin every evening.
- If you have a cold allergy, the symptoms of which are minor, then gradual hardening and rubbing can strengthen the immune system and reduce the body's reaction. But for young children and people with intense symptoms, hardening is contraindicated, as it is fraught with the development of complications in the form of anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema, and laryngeal edema.
- During the cold season, you can use antihistamines (A complete list of all allergy pills is in our article.)
| A drug | Price, rub.) | |
| Antihistamines in tablets | Tavegil | 170-250 |
| Zyrtec | 250-300 | |
| Zodak | 130-200 | |
| Tsetrin | 160-240 | |
| Claritin | 180-240 | |
| Suprastin | 120-140 | |
| Levocetrizine | 170-300 | |
| Cetirizine | 90-100 | |
| Fexofast | 160-200 | |
| Parlazin | 130-140 | |
| Antihistamines creams, ointments (ointments for dermatitis) | Skin cap, Gistan N contains a hormonal substance (list of all hormonal creams and ointments) | 150-160 |
| Gistan, La-kri - contain extracts of medicinal herbs, use it if you are not allergic to them | 170-190 | |
| Auxiliary products for skin irritation | Panthenol spray and cream foam | 200-300 |
| Dexpanthenol cream | 140 | |
| Bepanten | 470 | |
| Antihistamine drops in the nose (For rhinitis from the cold, 20 minutes before going out into the cold) | Allergodil | 280-300 |
| Fenistil | 280-300 | |
| Parlazin | 280-300 |
Hands are one of the most exposed areas of the human body. It should not be surprising if during the cold season the skin on the back of the palms turns red, peels and even cracks. To avoid the development of such symptoms, we wear gloves and mittens, and use protective fatty creams. In order to protect yourself from local (local) hypothermia and, in fact, frostbite, these measures are enough - however, an allergy to cold on the hands requires additional actions. It is a rare pathology that causes significant discomfort to patients due to the rapid development of a reaction to low temperatures. It is characterized by various symptoms on the skin of the palms, hands and forearms, and can be combined with other types of cold sensitivity - damage to the eyes, the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract. If you suspect that you suffer from individual intolerance to low temperatures, it is worth finding out what to do to prevent repeated episodes (relapses) of the disease.
Can rashes on the hands be considered an allergy?
The presence on the skin of such elements as spots, blisters, blisters, nodules (papules) is often caused by reactions of an immunological nature, which are based on individual specific sensitivity to any irritant (sensitization). However, in some cases there are other reasons:
- Infection (erysipelas, scabies, herpes, papillomavirus).
- Insect bites (mosquitoes, bedbugs, fleas, etc.).
- Contact with poisonous plants (nettle, ivy).
- Frostbite or burn with deep skin damage and blistering.
- Autoimmune process (psoriasis).
A rash from cold on the hands is considered to be a pseudo-allergic reaction.
The exact reason for its development is still unknown, but there is a well-founded assumption about the pathogenesis (mechanism of formation) of manifestations. Low temperature is not a classic irritant and cannot represent an antigen - a foreign substance to which the immune system reacts. However, under its influence, in a sensitive person, special pathological proteins called “cryoglobulins” accumulate in the body; they become the target of protective complexes (antibodies) and provoke symptoms of cold intolerance.
Predisposing factors
Although the reasons for the development of sensitivity to low temperatures are still being studied, it is known that allergies to frost on the hands are often secondary (acquired) in nature and can be associated with:
- with the presence of infectious diseases (hepatitis, mononucleosis, chronic bronchitis, tonsillitis);
- with cold thermal injury to the skin (frostbite of the palms, hands, even the first degree of severity, when there are no blisters or necrosis);
- with bronchial asthma, hay fever and other allergic pathologies;
- with taking medications (in particular, hormonal contraceptives, antibiotics).
The hereditary factor plays a significant role; if close family members have a cold allergy on their hands, this increases the risk of developing the disease in the patient. In addition, there is a genetic syndrome that causes sensitivity to low temperatures. It is manifested not only by skin damage, but also by deterioration of hearing, inflammatory reactions in the eyes, urinary system, and musculoskeletal system.
Symptoms
Hands are often exposed to external influences at any time of the year, and pathological changes in the area of the palms, hands or forearms, as a rule, do not go unnoticed. If you are intolerant to cold, the skin begins to itch and break out in a rash immediately after contact or after some time, for example, at intervals of 1-3 hours. The disturbances disappear after warming up, although in some patients a sharp change in temperature conditions (transition from frost to a warm room) causes a deterioration of the condition, which soon stops.
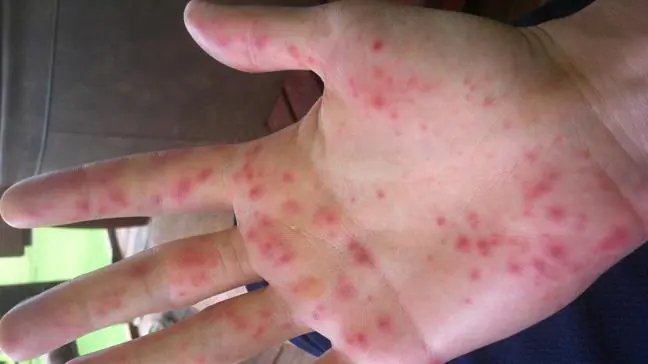
Hives
Allergy to the hands from cold with this variant of pathology is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Itching, unpleasant burning sensation.
- Redness of the contact area.
- The appearance of pronounced edema.
- The appearance of a rash in the form of blisters.
The reaction develops within a few minutes after contact with the provoking factor, is characterized by an increase in symptoms over two to three hours, after which it stops on its own, especially if the patient is warm. Sometimes the so-called “reflex form” is observed, in which the rash surrounds the contact area, but does not directly affect its area.
It is not always limited to only damage to the hands; it is possible that the skin of the face, neck and entire torso may be involved in the pathological process; there is a risk of developing Quincke's edema (dense swelling of the lips, cheeks, mucous membranes) and general symptoms: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, weakness.
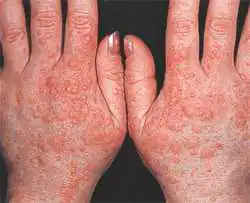
Dermatitis
It is characterized by such manifestations as:
- redness;
- edema;
- itching;
- feeling of tightness;
- dry skin;
- peeling.
Sometimes a small rash appears on the back of the palms and hands, represented by spots, blisters, and nodules. In some patients, an allergy to cold does not immediately spread to the hands, but first affects other contact areas of the lips and cheeks. Often the process also occurs in isolation, it can be one-sided, for example, if the patient in the past only had frostbite on one palm, it will become the epicenter of the manifestation of disorders.
When allergic to cold, the skin of the hands not only peels off, but also cracks; this is accompanied by a decrease in local immune defense and a disruption of the barrier function of the epidermis, which leads to an increased risk of infection.
Patients may suffer from various forms of microbial and viral pathologies, in particular, they complain of the appearance of warts and crusts. It is worth distinguishing irritation from cold on the hands from allergies; it occurs only with prolonged exposure to strong physical factors (ice water, gusty wind, snow), is not characterized by a rash or swelling, and can be prevented by lubrication with protective creams.
Treatment
If, even after short contact with cold, the skin can turn red and blistered, swells and flakes, you need to contact an allergist to find out the reasons for the sensitivity. After a comprehensive diagnosis, the doctor will select the most effective methods of therapy.
Cold protection
Includes measures aimed at breaking contact with the provocateur of the development of a sensitivity reaction by low temperature. To do this you need:
- Wash dishes, bathe and swim only in warm water.
- Dress appropriately for the weather and always wear gloves that are heat-repellent and moisture-resistant.
- Avoid touching cold objects, even if it is a glass of drink with ice added to it.
To limit the effect of low temperatures on the skin of your hands as much as possible, you should use special cosmetics (Cold Cream, Barriederm), which can be purchased at the pharmacy. Knowing about sensitivity to cold, you should apply a protective agent not only to the palms and wrists, but also to other open areas of the face, forehead, and neck. For them you need to select a special option (lotions and balms). The undoubted advantage of anti-frost cosmetics is that it protects the skin from low temperatures and chemicals, and also has a healing, moisturizing and soothing effect.
Pharmacological drugs
How to treat cold allergies on your hands? The following tools are used for this:
- antihistamines (Cetrin, Erius, Zyrtec, Fenistil);
- cromones, antileukotriene drugs (Ketotifen, Montelukast);
- healing ointments (Bepanten);
- topical (local) glucocorticosteroids (Mometasone).
Medicines are not able to completely eliminate sensitivity to low temperatures, so they are used exclusively when the reaction worsens and the emphasis is placed on protective measures designed to prevent its development. Pharmacological drugs can be used only as prescribed and under the supervision of a physician, especially given the fact that many patients require individual selection of the dosage of the drug.
Traditional methods
Home medicine remains relevant and is often used to eliminate the consequences of a reaction to cold. Unfortunately, it cannot influence the causes of sensitivity and permanently rid the patient of allergies. To improve the condition, it is recommended:
- Rinse your hands with chamomile infusion. To do this, use dry raw materials (a bag or a teaspoon per 200 ml of hot water), which is poured with boiling water and covered with a lid for 30 minutes. After cooling to a comfortable temperature, you can water and lubricate your previously washed hands with the resulting warm liquid. Repeat 3-5 times a day.
- There are vegetables, fruits, butter, cottage cheese and other sources of nutrients. It is especially important to regularly consume dairy products, a variety of fish, meat, cereals seasoned with oatmeal, corn, and buckwheat butter. In winter, it is worth supplementing your diet with vitamin teas.
- Drink rosehip decoction. Traditional healers believe that this remedy strengthens the immune system and thereby helps to reduce the symptoms of local cold sensitivity on the hands. To prepare it, you will need 20 g of dried fruits, which are poured with 500 ml of water and boiled for about 10 minutes, then left under a lid and a towel for up to 3 hours. Drink fresh, warm, 0.5 cups three times a day.
If you have acquired intolerance to low temperatures, it is important not to forget about the likelihood of a primary cause, for example, a source of chronic infection. Treatment aimed at its sanitation can give very successful results in relation to cold allergies.
Prevention and useful tips
To prevent low temperatures from harming health, a sensitive person needs to:
- If possible, avoid contact with ice and snow;
- always heat water for bathing, washing dishes, and cleaning;
- treat caries, diseases of the tonsils, and gastrointestinal tract in a timely manner;
- ensure that the diet is balanced;
- do not use soap, replacing it with less aggressive gels with a neutral pH;
- Always wear or carry warm, waterproof gloves.
Knowing about intolerance to low temperatures, carry ointment against cold allergies in your bag, jacket or coat pocket; apply it to sensitive areas on your hands, repeat the procedure as necessary, do not rub until completely absorbed.
Your doctor can choose a suitable barrier product that will protect and care for your skin. Distribute the ointment evenly; without intensive massage, it will be enough if it covers the entire area of likely contact with the cold.



