It's hard not to be alarmed when baby's delicate skin suddenly becomes rough and rough. What happened, why did the skin become rough and is it dangerous? Should I go to the doctor or try to cope on my own?
In general, situations when you have to figure out why a child has rough skin can be divided into several fundamentally different groups:
When it's not a disease
Dry, rough skin in a child can appear either as a result of illness or simply under the influence of external factors: cold, wind, friction.
Friction
For example, the skin on a child's elbows may become rough, wrinkled and dark simply because they are often leaned on while lying down watching TV or playing with gadgets. The same rough brown or pinkish dry, rough patches may appear on the top of the foot if the child has a habit of sitting with one leg tucked under him, which constantly rubs against the upholstery of the chair.
Something similar can happen to the skin of the legs, or less often, it can appear on the hips if you wear woolen pants directly on the body. In this case, the rough red spots look like goose bumps. Actually, this is what it is, irritation appears due to the impact of coarse wool on children’s skin, which has become sensitive in the cold (however, similar problems also occur in adults).
Cold, wind
Children aged 7–10 years who begin to walk independently may develop pimples on their hands: the result of exposure to cold, moisture and wind (most often when walking in wet mittens or without mittens at all). Small rough bumps appear on the skin, it turns red and peels.
All these cases do not require medical intervention. It is enough to change the child’s habits so that the skin does not get injured again and again, and lubricate the areas of peeling with a rich, nourishing cream.
- This could be domestic hand cream with vitamin F, blue Nivea, Vaseline.
- One of the folk remedies is goose fat.
- It is not recommended to use oils in their pure form: any oil effectively moisturizes only after peeling, when keratinized particles of the epidermis have been removed. It is not worth scrubbing already irritated sensitive skin, so as not to further injure it.
In a newborn and a child up to one year old
In the first two weeks of life, dry, rough skin, fine peeling on the baby’s stomach and sides may be normal: this happens in about a third of babies. After removing the vernix, the skin becomes more sensitive to external influences and dry air in the room (especially in winter, when central heating is on) reduces the amount of moisture in the skin. No special measures are needed here: it is enough to bathe the baby regularly (provided that the umbilical wound has healed) and after bathing, lubricate the skin with baby oil or milk.
The skin of a healthy baby can dry out and peel if:
- too dry air in the house,
- excessive use of baby powder,
- bathing too often with soap or foam,
- adding string, chamomile, oak bark to the bath.
All this is quite easy to detect and eliminate.
Diaper dermatitis
Rough skin on the butt of an infant can become a manifestation of diaper dermatitis, when the skin begins to swell due to excess moisture or is injured by the diaper. In this case, in addition to peeling on the skin, red swollen areas appear that appear denser and seem to rise above the surface. The redness does not have clear outlines, gradually fades away, and is often covered with small papules (tubercles), which can spread beyond the area of redness. When the process begins to fade, the redness disappears, but peeling and sometimes rough skin remains. Diaper dermatitis is always limited to the diaper area, the spots are uneven, and “drips” around the elastic bands are often visible.
This situation can hardly be called a variant of the norm, but there is no reason to panic. If you take measures in a timely manner, preventing infection from occurring, you can cope with the problem without a doctor. The diaper must be changed at least once every 2 hours. The baby's skin should be kept clean; when changing a diaper, any remaining urine should be removed with wet wipes. Areas of inflammation are treated with zinc powder or zinc ointment. If the problem is limited to mild redness and peeling, you can use creams with a healing effect (Bepanten).
If, with regular care and timely diaper changes, the situation does not change within 5 days, you need to consult a doctor.
When rough skin is a disease
- Hives
- Atopic dermatitis
- Eczema
- Psoriasis
Other diseases that can cause dry and flaky skin include: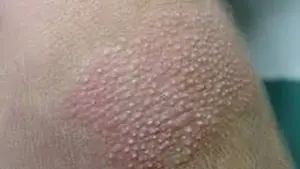
- follicular hyperkeratosis (goose bumps);
- congenital thyroid deficiency (hypothyroidism);
- congenital diabetes mellitus;
- a rare hereditary disease – ichthyosis;
And also some body conditions:
- lack of vitamins;
- helminthic infestation.
Allergic diseases
Allergy is one of the main problems of our time: according to WHO, a third of the population of developed countries already suffers from one or another of its manifestations, and in the future the number of such patients will increase. Proponents of the hygienic theory of allergies believe: the problem is that we live in a too clean, almost sterile world, and the immune system, due to the lack of real “enemies,” attacks the proteins of its own body.
Allergic reactions and diseases associated with excessive allergic readiness of the body often manifest themselves on the skin.
Hives
In appearance, this reaction is similar to traces of a nettle burn; the skin becomes rough, bumpy, swells, sometimes blisters appear (and sometimes the matter is limited to swelling). The rashes are itchy and may be painful to the touch. The skin and mucous membranes are affected, the rash can spread throughout the body, on the back and abdomen, or be located only in certain areas (for example, with increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation, solar urticaria appears only on open areas of the body).
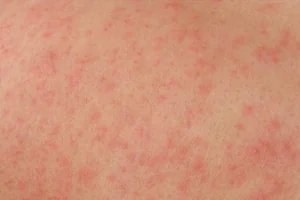
Hives can be triggered by food allergens (honey, citrus fruits), medications, insect bites, even cold and sun.
What distinguishes urticaria from skin diseases is the rapid appearance of many elements, while in skin diseases the rash begins with 1 - 2 elements and spreads over some time. Also, unlike skin diseases, rashes with hives last 1–2 hours, after which they disappear. The danger of this condition is that swelling of the mucous membrane can spread to the tissues of the larynx and impair breathing - this is called Quincke's edema. This condition requires immediate medical attention.
To treat urticaria, it is necessary to eliminate the allergen and take an antiallergic drug (loratadine, fexofenadine, cetrin). For food allergies, sorbents (Smecta, Polysorb, Enterosgel, Filtrum) are recommended; they will bind some of the allergens, preventing them from entering the blood. Fenistil can be used topically.
Atopic dermatitis
This is one of the most common causes of rough skin in a child. According to WHO, up to 15% of the world's population suffers from atopic dermatitis. Girls get sick more often than boys. The disease has a hereditary predisposition: if one of the parents has any allergies, the probability that the baby will develop atopic dermatitis is 20%; if both are allergic, the probability of the disease increases to 60%.
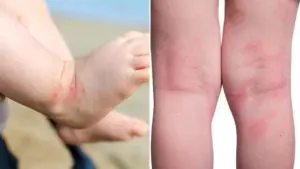
In essence, atopic dermatitis is an immune-dependent inflammation of the skin, during which the formation of the normal stratum corneum and lipid composition of the skin are disrupted. Speaking in Russian, due to inflammation caused by an allergic reaction, the skin produces too little fat and too many dead horn cells, which normally should protect it from external influences, but in atopic dermatitis, accumulating in excessive quantities, making the skin dry and rough.
Symptoms
The manifestations of atopic dermatitis depend on age. The disease usually appears at 1 year of age. In children (children aged 1–2 years), active inflammation predominates. Red, rough spots appear on the skin, covered with small nodules (papules) and small blisters that burst. forming weeping ulcers (erosions). Such rashes are located on the cheeks of a one-year-old child, less often on the forehead and chin, and on the hands.
As the child grows, the nature of the rashes and their prevalence change. Usually, after two years, the rough spots on a child’s skin become less bright, stop getting wet, and begin to peel off. And the skin itself becomes rough, its pattern intensifies and the lesions look wrinkled and may crack. The rash spreads to the neck and shoulders, elbow fossae, shins, popliteal fossae, gluteal folds, hands and feet. All these places actively itch, the child scratches them and can become infected. Then purulent crusts appear and the temperature rises.
Changes on the face are also possible: the eyelids darken, peel, and become wrinkled. Due to constant scratching, nails become smooth, shiny, and their edges wear down.
Usually the disease occurs as a series of exacerbations and remissions. Exacerbations occur more often in the cold season and are provoked not only by allergens, but also by stress and colds.
Treatment
Treatment of atopic dermatitis is complex and often unsuccessful. First of all, it is necessary minimize contact with allergens.
- A special diet is prescribed for this
Eggs, chocolate, citrus fruits, strawberries, factory juices, semi-finished products, and smoked meats are excluded from the diet. Sometimes this is not enough and you have to specifically identify foods that the child cannot tolerate, for example, cow's milk.
Let us dwell in more detail on nutrition for atopic dermatitis, because in children it is food allergens that most often provoke the disease. If the disease appeared before the introduction of complementary foods, the mother will have to take care of her diet, excluding the products mentioned above. An allergy can also occur to formula milk, then the problem should be discussed with a pediatrician who will help you choose a hypoallergenic product (alas, not a single hypoallergenic product actually guarantees the absence of a reaction.
If one or both parents are allergic, the baby is predisposed to atopic dermatitis. In this case, complementary foods should be introduced especially carefully: do not try to diversify tastes by adding one product once a week. Yes, the process will go slower, but it will be possible to track the baby’s reaction.
If the moment has already been missed, and at some stage of introducing complementary foods rashes appear, you will have to start all over again. For two weeks, the baby returns to exclusively breastfeeding. Then complementary feeding begins with minimal doses of one new product, gradually increasing the amount over two weeks. Only if it is well tolerated, the next one is added.
In older children, for whom mother's milk is no longer a necessity, but an addition to nutrition, it is necessary to use other schemes. First, almost everything is excluded from the diet. Only rice or buckwheat in water without oil or salt is allowed. Usually this stage is very difficult to survive: both the child and, especially, the grandmothers are indignant, trying to shove something “tasty” into their hands and accusing the young mother of abusing the child. Try to find an ally in the family who will take the fire.
After a week of such a strict diet, one new product is added. Further, new products are allowed every three days. Everything eaten and drunk during the day is carefully recorded in a food diary. Pay attention to hidden allergens: for example, eggs are often added to homemade cutlets.
- A change of scenery
If you have a baby at home with atopic dermatitis, you will have to change the environment. You need to remove carpets, drapes and other “dust containers” that harbor dust mites from your apartment. If there are feather pillows and duvets left in the house, you will have to remove them too. Check the bathroom for fungus: it often starts in hard-to-reach places, tile cracks. The fungus will also have to be removed regularly. Cleaning the house will have to be done every day: washing the floors can be replaced with a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter that does not allow small particles to pass through. A regular vacuum cleaner, on the contrary, only disperses allergens into the air. If finances allow, an air washer can be a good help, as it will maintain the desired level of humidity (which will have a beneficial effect on the skin of not only the baby, but also the mother), while simultaneously clearing the air of dust.
It is better to bathe your baby without soap and foam. You should not add potassium permanganate to the water - after the umbilical wound heals, the baby does not need sterility, and manganese dries out the skin. Herbs are also not useful - they themselves can become a powerful allergen. After bathing, you can lubricate your baby’s skin with special creams – emollients. Such creams are produced by many pharmaceutical cosmetics manufacturers. They can be used several times a day.
Drug therapy works in two main ways.
External therapy
Ointments with anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects are used.
- Doctors often prescribe ointments with hormones (for example, methylprednisolone acetate) - there is no need to be afraid of them, these drugs are indicated in clinical recommendations as first-line therapy. Modern ointments with glucocorticoids are safe for a short course (no more than a month). But the dosage must be strictly observed. A strip of cream covering the end phalanx of the index finger is enough to spread over the area of two adult palms. If the area of the rash is smaller, accordingly, you need to take minimal amounts of the product. Do not mix hormonal ointments with petroleum jelly or baby cream - this will reduce the concentration of the active substance and the effectiveness of the drug.
- As an alternative to hormonal ointments, you can recommend the drugs pimecrolimus (Elidel), approved from the age of three months, or tacrolimus (Protopic), permitted from the age of two. For frequent exacerbations, pimecrolimus or tacrolimus can be used for prophylaxis, applied twice a week - according to this regimen, they are allowed to be used for a year or more.
- Lesions in the hair are treated with shampoos containing zinc pyrithione.
- Tar as a folk remedy for treating atopic dermatitis is effective, but has a carcinogenic effect.
General therapy or systemic antiallergic drugs
Loratadine (Claritin), ebastine (Kestin), cetirizine (Zyrtec). They reduce itching, especially at night, and swelling of the skin.
Children over three years old with extensive skin manifestations benefit from ultraviolet radiation: if it is not possible to sunbathe, you can use special devices in the physiotherapy rooms of clinics.
If atopic dermatitis appears at 1 year of life, there is a 60% chance that it will disappear over time. In general, the later the disease occurs, the more likely it is to last into adolescence and adulthood.
Eczema
Another hereditary disease caused by an inadequate immune response. Often combined with problems of the gastrointestinal tract and biliary tract.
The area of skin becomes red and swollen, and small blisters appear on it and burst. leaving behind pinpoint weeping ulcers (erosions), which doctors call eczematous wells. Then crusts appear on them. As it dissolves, new elements appear nearby, so you can simultaneously see different manifestations - redness, blisters, erosions, crusts, peeling. The boundaries of the lesions are unclear.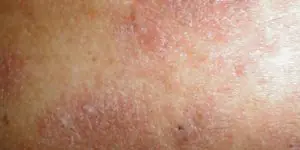
The rashes are symmetrical, the child has rough skin on the arms, legs, and face. Damaged areas alternate with clear skin, looking like an “archipelago of islands.” After the inflammation subsides, dense, darkened (or, conversely, pale) areas with rough, thick skin and an enhanced pattern remain, which gradually return to normal.
When the scalp is affected, seborrheic eczema occurs: yellowish or gray flaky and itchy crusts, yellowish-pink, swollen spots appear in the hair, behind the ears and on the neck, covered with greasy yellow flaky scales.
In children, the first signs of eczema usually appear between 3 and 6 months. Its manifestations are very similar to those of atopic dermatitis, the treatment is also similar: exclude all possible allergens, including food, ointments with glucocorticoids, oral antiallergic drugs, emollients several times a day to maintain the water-fat balance of the skin.
Psoriasis
Another disease in which skin changes are caused by an inadequate immune response. But unlike previous diseases, with psoriasis the trigger is infection: the disease often appears after chickenpox, tonsillitis, intestinal infections, or fungal infection. Most often this occurs between the ages of 4 and 8 years. The second peak incidence is adolescence.
If in adults psoriasis is rough, dry red scaly plaques, then in children it is most often red swollen spots, very reminiscent of diaper rash, but, unlike diaper rash, scaly. Such spots appear in the folds of the skin, on the genitals, face, and head. The plaques itch and flake off profusely. especially when combing, they often merge. About a third of children's nails change: indentations and transverse stripes appear in them. In adolescence, the elbows are often affected: groups of plaques with clearly defined boundaries gather around them, the skin is rough and red.
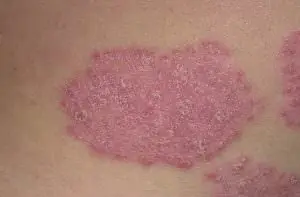
Just like atopic dermatitis or eczema, psoriasis gets worse. then goes into remission. The skin may clear completely, or a few “standby” plaques may remain. The duration of remission ranges from several weeks to tens of years.
Treatment of psoriasis begins with local therapy, the purpose of which is to remove peeling. To do this, use ointments based on salicylic acid, which soften the horny scales. The ointment is applied at night, washed off in the morning and the plaques are lubricated with ointments containing corticosteroids.
In severe cases, retinoids are prescribed orally - drugs based on active forms of vitamin A. But this is really a therapy for extreme conditions, which requires mandatory medical supervision.
Ultraviolet radiation helps well: it is useful for such children to sunbathe, and in winter to use artificial sources of ultraviolet radiation.
In the same way as with atopic dermatitis, a hypoallergenic diet is prescribed.
The manifestations of many skin diseases are very similar; it is difficult for a non-specialist to distinguish different types of rash from the descriptions. There is no need to try to diagnose and prescribe treatment on your own - there are dermatologists for that.
In the human body, the skin is one of the most important organs. It performs several functions at once: barrier, excretory, sensitive, thermoregulatory, storage and others. Therefore, parents should carefully monitor the condition of their baby’s skin from early childhood.
Normally, a child’s skin should be clean, smooth, without cracks or inflammation. If there are any changes on it (redness or roughness), parents should immediately pay attention to it. The child’s body signals that something has gone wrong.
If a child has dry skin, it means that the stratum corneum does not contain enough moisture. Its appearance changes - it becomes rough, wrinkled, sometimes even scaly, and loses elasticity. But that's not the worst thing. The danger lies in the fact that microcracks appear in dry skin, through which pathogenic bacteria easily penetrate into deeper layers and become the cause of the development of dermatological diseases.
Why does my baby have dry skin?
Dry skin in a child usually occurs in the first three years of life in the autumn-winter period or early spring. This phenomenon can be observed both on individual parts of the body (arms, legs, face) and on its entire surface. Children's skin is very sensitive to external factors, its protective function is just developing. Therefore, when dry spots or rashes appear on the body, it is important to determine which personal hygiene items can cause irritation to the epidermis, and exclude shampoos, soaps, gels, and washing powders to which the baby may be allergic. If your child has dry skin, you should choose only hypoallergenic hygiene and laundry products, preferably without a strong odor and bright color.
You should not bathe your baby in hot water, as it tends to dry the skin; the optimal temperature for this procedure is 37°C.
Sudden changes in temperature can also cause dry skin in a child. Severe frost and cold winds often cause irritation and redness on the face and hands. Therefore, before going outside, the baby needs to lubricate exposed areas of the body with a special cream.
Heating systems operating in winter dry out the air in apartments, so it is recommended to use special humidifiers during this period.
Dry skin in a child can be an allergic reaction of the body, so you should pay attention to food. Among them may be those that provoke allergies, in particular citrus fruits and chocolate.
Dry skin on a child's feet
Quite often, children have dry skin on their feet. Especially in the summer, it loses moisture to such an extent that it begins to crack and hurt. In this case, it is better to wear open shoes with maximum air access. To avoid dust and dirt getting into the cracks, you need to wear socks. Before going to bed, be sure to wash your baby’s feet with baby soap, wipe them dry and lubricate them with massaging movements with a special softening fortified cream.
Dry skin on a child's feet is highly susceptible to infections, which can lead to complications. The familiar heat rash, diaper dermatitis, and diaper rash spread quickly if not properly cared for, and a pustular rash can even form. To avoid complications, it is necessary to show the child to the doctor as soon as possible and begin treatment.
Treatment of dry skin in children
The epidermis in young children is not yet able to retain moisture in sufficient quantities, so it has to be replenished from the outside. The choice of moisturizer must be taken seriously, since the skin reacts sharply to external irritants. If the child has very dry skin, choose a product together with the pediatrician. Most often, in such cases, doctors recommend external preparations containing urea, in particular Excipial M lotion, as well as an additional course of vitamin A for a period of two months. It is better absorbed if you drop it on a small piece of black bread before eating. In some cases, if the baby’s skin is inflamed, vitamin E, calcium supplements, and fish oil are prescribed. The dose of medication is determined by the doctor.
It is better to bathe your child without foaming detergents at all. Herbal baths are very effective in such cases. You need to mix rose petals and chamomile flowers in equal proportions, pour boiling water over it and let it brew for 15-20 minutes. After this, strain and add to water. The procedure should last at least 10 minutes. A bath with flax oil is also effective (1 tablespoon will be enough).
After bathing, you can give your baby a massage, treating the skin with a cream containing vitamin A.
Dry skin of a child as a sign of the onset of the disease
Sometimes dry skin can indicate the onset of a disease. Therefore, if redness or irritation occurs, parents need to consult a doctor to make an accurate diagnosis, establish the cause and begin treatment. Dry skin in a child, mainly under the age of 1 year, often occurs with atopic dermatitis. Severely itchy, reddened areas are localized on the face, without affecting the nasolabial triangle.
Peeling and scaly formations on the elbows, knees, and cheeks may be signs of ichthyosis, a genetic disease in which the process of keratinization of cells in the body is disrupted.
If a child’s skin is very dry and peeling, most likely it is hypovitaminosis A and PP; treatment in the form of taking the necessary vitamins eliminates unpleasant symptoms.
It should be taken into account that dry skin can be caused by dehydration due to dyspeptic disorders (vomiting, diarrhea) and heavy sweating.
Dry spots on baby's skin
Dry spots on children's bodies often appear, and there is nothing unusual or scary about this, because she is very sensitive. But parents should be concerned if they do not go away for a long time. Firstly, the cause of such spots may be physiological, since in young children the fat glands are not yet fully functioning. Secondly, the condition of the skin is influenced by environmental factors (temperature and water hardness, air humidity, food, soap). At first, to soften the affected areas, you can use a product purchased at the pharmacy, for example, Panthenol. But if dry spots on the child’s skin do not disappear, you should consult a doctor, as they can be symptoms of serious diseases such as atopic dermatitis, eczema, and psoriasis.
Skin ailments are usually difficult to deal with, but a correct diagnosis made in time makes the task easier. If there are signs of a particular skin disease at an early age, it is very important to immediately take action and prevent its progression. Without proper treatment in a medical facility, it can become chronic.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Children's skin is like a litmus test: it instantly signals problems in the body and improper care. That is why it is so important to pay attention to any changes in her condition. Let's talk about how to develop an algorithm for caring for dry skin of babies.
- Main characteristics of healthy baby skin
- Causes of dry skin in children
- What does dry skin mean in a child?
- Dry skin on a child's feet
- How to eliminate dry skin
- Precautions for dry skin
- Rules for care at different times of the year
- Prevention measures
- Tools Overview
Main characteristics of healthy baby skin
Soft, delicate, velvety - this is how we usually talk about a baby’s skin. But even if the child is healthy, it does not become so immediately after birth.
Why? Explains Alexander Prokofiev, dermatovenerologist, medical expert at La Roche-Posay: “After the baby is born, his skin needs to adapt to the environment. In newborns, this process has not yet been completed, so their skin is more dry, more susceptible to irritation, redness, and easier to injure. These features disappear with age.”
Typically, by the age of two, the upper stratum corneum of the epidermis thickens, and the skin becomes more protected from external influences. The sebaceous and sweat glands begin to work more actively, and the process of thermoregulation gradually normalizes.”
Normally, a child’s skin should be pale pink and have good turgor, that is, be soft and elastic to the touch.
Bathing water should not be too hot © iStock
Causes of dry skin in children
“Children’s skin can become dry under the influence of both external and internal factors,” says Alexander Prokofiev. Let's list the external reasons.
Using detergents more than once a week, the water is too hard for bathing (it is better to pass it through a filter).
Exposure to the sun without protection
The baby’s skin is not able to resist the effects of UV rays, so children under one year old can be kept in the open sun for no more than five minutes a day, and even then “under the cover” of special baby creams with high SPF.
Dry indoor air and overheating
Overheated air is a test for a child’s imperfect thermoregulation system: the skin turns red, becomes hot, and irritation appears. The same thing happens if you wrap your baby up too much.
Cold air coming into contact with delicate baby skin can cause redness, dryness and irritation.
Internal factors may be due to:
poor nutrition, which is expressed in a lack of vitamins;
some diseases, primarily skin and endocrine;
What does dry skin mean in a child?
Very dry baby skin is a cause for concern. It is more vulnerable, easily injured, and damaged skin is more susceptible to infections, especially in infancy.
In addition, dryness may indicate the presence of:
ichthyosis (a disorder of keratinization of the skin, which manifests itself in the form of scale formation);
other diseases, including diabetes.
If dryness is a persistent feature of your child's skin, it makes sense to first consult with your pediatrician and then see a dermatologist for appropriate treatment.
Dry patches of skin on the child's face and body
Friction from shoes and clothing can also cause redness and flaking of baby's delicate skin. Sometimes the cause of hypersensitivity is the diseases mentioned above. In any case, choose clothes and shoes for your baby made from natural materials, and use children's hypoallergenic powders for washing. To prevent dry feet in summer, it is better to wear open-toed shoes.
How to eliminate dry skin
Use moisturizing creams, lotions or body milk made specifically for children's skin. On such products it is always written what age they are intended for.
The water for bathing the baby should not be hot. The optimal temperature for the bath is 36–37 degrees.
Bathe your child every day, but use detergents no more than once a week. Choose special delicate formulas for this.
Moisturize dry areas with baby cream, milk or lotion.
An important condition against dry skin in children is the drinking regime © iStock
Precautions for dry skin
Dry skin brings a lot of anxiety to a child. It itches, itches, flakes - all this causes moodiness and bad mood. What can parents do in this situation? First of all, eliminate any factors that provoke dry skin of the baby.
It is not advisable to use soap when bathing and washing your face; it dries out the skin.
Sponges made from rough materials are also harmful. Washing should be as gentle as possible.
Do not wrap your baby while walking to avoid sweating.
Do not self-medicate. If dry skin persists, consult a doctor.
Rules for care at different times of the year
A child's skin needs protection in both heat and cold.
Remember that you should not be in the sun during the hottest time, from 11 a.m. to 4 p.m. On the beach, be sure to wear a T-shirt and a Panama hat on your baby, and use children's sunscreen. When you return from a walk, wash off the SPF cream and apply a moisturizer to your skin.
Exposure to cold and dry indoor air contributes to excessive dryness of the skin. Install a humidifier in your home or regularly cover the radiators with a wet towel. Moisturize your baby's skin after bathing.
Prevention measures
To avoid dry skin, offer your child something to drink often. Make sure there are enough vitamins in his diet. Moisturize your baby's skin after bathing. In your care, use only hypoallergenic products tested by dermatologists.
The creams should include moisturizing and soothing components: panthenol, niacinamide, oils (shea, olive, wheat germ), zinc oxide, vitamins A, B, E, F, plant extracts (chamomile, calendula, string).
Tools Overview
Milk for very dry skin Lipikar Lait, La Roche-Posay
Formula with shea butter, thermal water and niacinamide nourishes the skin and restores its lipid barrier. Suitable for use in infants, children and adults.
Skin cleansing gel Lipikar Gel Lavant, La Roche-Posay
Contains shea butter and niacinamide and is free of fragrance and parabens. Has skin-soothing properties, suitable for the whole family.



