- Stages of furunculosis
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Which doctor should I contact if a boil appears on the body?
- Treatment of furunculosis
- Drugs for the treatment of furunculosis
- Ointments for furunculosis
- Tablets for furunculosis
- Injections for furunculosis
- Prevention of furunculosis
Furunculosis is an infectious disease during which boils (boils) form on the body.
A boil is a purulent inflammation of a hair follicle; nearby tissues are also involved in this process. After the introduction of an infectious agent, which is staphylococcus, directly into the hair follicle, the inflammatory process begins.
- In most cases, furunculosis is provoked by Staphylococcus aureus, less often by white Staphylococcus. The main cause of the development of pathology is a bacterial infection, but the disease is not contagious for a healthy person. This is due to the fact that the skin is covered in a small amount of opportunistic flora, which are streptococci and staphylococci.
- Find out also what a purulent boil is
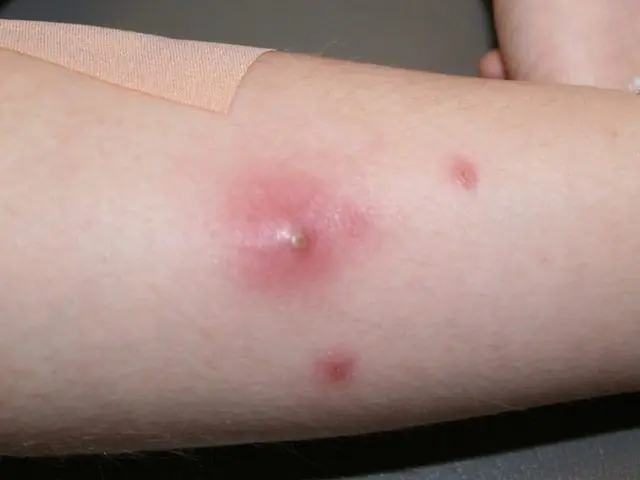
Stages of furunculosis
Before wondering how to treat furunculosis, first determine the stage of development of the disease:
- Mild degree – a boil is formed no more than twice a year, and only one always appears, and no intoxication of the body occurs.
- Average degree – there is a relapse up to three times a year, multiple inflammations appear, signs and intoxication are slightly expressed.
- Severe degree – furunculosis does not go away completely, constant intoxication is observed.
There are several stages of formation and development of this type of skin inflammation:
- infiltrates appear;
- necrosis, suppuration;
- healing.
Causes of furunculosis
The development of the disease is influenced by various factors, primarily the pathogenic properties of bacteria and the degree of their infectiousness. There are internal and external reasons:
- The primary form of pathology can develop on completely healthy skin.
- The secondary form becomes the result of complications of processes occurring as a result of superficial or deep staphyloderma.
Treatment and causes of boils are interrelated. Most often, the disease is provoked by the creation of a “gate” through which infection enters the body. For example, small cuts or other skin damage caused by strong friction of clothing, scratching, or traumatic injuries.
Internal factors also play an important role in the development of pathology, including:
- hypovitaminosis;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- anemia;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- alcoholism occurring in a chronic stage;
- pathology of the endocrine system;
- metabolic failures;
- treatment accompanied by long-term use of hormonal or antibacterial drugs, cytostatics;
- frequent overheating or hypothermia, which provokes a decrease in immune defense.
Regardless of how to treat a boil, if the cause that caused its appearance is not precisely established, the procedures will not bring the desired effect, and the pathology will become chronic.
Symptoms of furunculosis
The photo shows a large boil on the collarbone
The formation of a single boil is accompanied by painful sensations in the localized area. Redness and swelling of the affected part appears. If inflammation develops on the face, in the area of the lymph nodes, or the abscess is large, fever may appear, and a sharp deterioration in general condition is observed.
Before starting treatment for furunculosis, you first need to determine at what stage of development it is. This is quite easy to do, since at each stage specific signs appear:
- Formation of infiltrate – gradual inflammation occurs, the follicles located around the tissue become hard, red and swollen. When touched, there is severe pain. Treatment of boils started at this stage is most effective.
- Formation of necrosis – after about 3 days, inside the diseased follicle, around the hair, the process of forming a necrotic rod begins, consisting of pus and dead cells. An abscess with a black or white head becomes noticeable on the surface of the skin. Very quickly the abscess opens up on its own, after which the pus and the follicle shaft itself come out. Inflammation disappears, swelling subsides, and an open wound appears in place of the boil.
- Healing – if the abscess is small, after healing there are no marks left on the skin. However, in the case of extensive inflammation, the area of the opening of the abscess is similar to an ulcer, the healing of which takes a long time, leaving a scar on the skin.
Knowing what a boil is, it becomes clear how to properly treat it. In most cases, identifying a boil is not difficult, but there are situations when even a doctor needs to carry out additional tests necessary to make an accurate diagnosis.
For example, the treatment and causes of furunculosis on the buttocks are differentiated from inflammation of the sciatic nerve. If there is inflammation on the genitals, there is a possibility of infection with a disease that is transmitted during sexual intercourse. That is why, before looking for how to treat a boil, you should consult a dermatologist or surgeon. This is the main condition under which recovery can be achieved.
Diagnosis of furunculosis
To determine furunculosis, you need to undergo several procedures:
- Visual inspection.
- Dermatoscopy.
- The contents of the boil are sent for bacteriological examination.
In some cases, the use of additional diagnostic methods is required:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- Ultrasound;
- bacterial culture of urine;
- rhinoscopy;
- pharyngoscopy;
- radiography of the sinuses.
Such a thorough examination is required in the case of a severe chronic form of the disease in order to accurately establish the cause of its development. If furunculosis is not accompanied by complications, an external examination and blood test, culture of pus from the boil for sensitivity to antibiotics and flora is sufficient.
Which doctor should I contact if a boil appears on my body?
When diagnosing furunculosis, you need to visit several specialists:
- Dermatologist;
- Infectious disease specialist;
- Surgeon.
Treatment of furunculosis
How to cure a boil at home? First of all, it is necessary to strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene:
- Underwear and bed linen should be changed frequently and be sure to be ironed well.
- If cuts or scratches appear on the surface of the skin, pay special attention to their treatment, as it is in these areas that a boil may appear.
- Physiotherapy significantly speeds up the recovery process. The most commonly used are UV and UHF. These procedures can be used at different stages of boil development. If the boil is in its last stage, it is recommended to use ozone therapy.
- There must be a complete and balanced diet; the body needs a complex of proteins and vitamins. Pathology is most often associated with a lack of valuable microelements; a proper diet helps accelerate regeneration. It is necessary to completely avoid harmful foods - sweets, carbonated water, canned food, etc.
- During therapeutic therapy, it is recommended to limit bathing; the inflamed area should not be wetted too often. The use of medicinal baths is prescribed if the lesions are extensive and severe. In order for the solution to have disinfecting properties, it is recommended to add potassium permanganate to the water.
- You can wipe the affected areas with antiseptic solutions - for example, salicylic alcohol or furatsilin.
The following manipulations will be beneficial:
- Apply an antiseptic solution to the painful area (simple rubbing alcohol works great);
- the inflamed area is treated with Levomekol ointment;
- You can cauterize a boil with iodine;
- Warming up the boil with infrared rays is allowed.
If the abscess is large, at the infiltration stage, in a hospital setting, blockade with antibiotics can be carried out. Only a doctor should prescribe medications. When choosing antibiotics, the doctor takes into account the type of bacteria that caused the inflammation.
Only 10% of all known strains of staphylococcus can cause boils, while some of them are not sensitive to classical antibiotics. Antibiotics are prescribed during the treatment of multiple lesions or during surgery. The duration of antibiotic use in each case is determined on a strictly individual basis.
Drugs for the treatment of furunculosis
For single or multiple boils on the skin, therapy with antibacterial drugs is used. Several types of antibiotics are used, which are available in the form of tablets, injection solutions, ointments and suspensions.
Antibiotics against boils belonging to the penicillin series are the most popular, since for many years they have been actively fighting Staphylococcus aureus, including other strains of bacteria. If pathogens are resistant to penicillin, anthraglycosides, tetracyclines, macrolides and cephalosporins are prescribed.
Ointments for furunculosis
The photo shows ointments for furunculosis
After an opening or breakthrough of the abscess occurs, a bandage with antibacterial ointments is applied to the wound:
- Levomekol ointment – the most effective antibiotic for topical use. The active ingredient is chloramphenicol, which destroys a wide range of bacteria. Methyluracil accelerates the process of tissue regeneration. The drug is applied to a gauze pad, which is applied to the wound. The bandage is changed every day until the problem is completely eliminated. If the ointment is used for too long, there is a possibility of skin rashes. The cost of the drug is about 120 rubles.
- Bactroban ointment – an effective remedy for combating Staphylococcus aureus. The ointment has a pronounced antibacterial effect. It is allowed to apply a small amount to the area of infection 1-3 times a day. The duration of the therapeutic course is 7-10 days. An allergic reaction, headache or nausea may occur. The cost of the ointment is about 100 rubles.
Tablets for furunculosis
Pictured are tablets for furunculosis
For recurrent furunculosis, antibiotics are prescribed in tablet form. Drugs are selected after microbiological sensitivity testing, since many staphylococci are highly resistant to most antibacterial agents. The most commonly attributed technique is:
- Lincomycin Is an antibiotic that has a powerful bacteriostatic effect and helps in the fight against a wide range of bacteria. For an adult, 500 mg is prescribed 3 times a day before meals. An antibiotic may cause an increase in blood pressure or an allergic reaction. The duration of treatment cannot exceed 14 days. The cost of the drug is about 90 rubles.
- Cephalexin – this antibacterial agent belongs to the group of cephalosporins. It has a strong bactericidal effect on most strains of staphylococcus. The daily dosage is 1-4 g. It is important to take the tablets at regular intervals. Side effects may occur, such as disruption of the functioning of the intestines, stomach, hand tremors, and dizziness. The course of treatment can be 7-14 days. The cost of the drug is about 70 rubles.
For a boil on the face, the following antibacterial drugs are prescribed before opening the abscess:
- Doxycycline;
- Sumamed;
- Tsiprolet.
The following antibiotics are prescribed to treat inguinal furunculosis:
- Ceftriaxone;
- Fusidine sodium;
- Mupirocin.
Injections for furunculosis
Treatment for furunculosis with antibiotics can also be carried out using injections. Injections are given when therapy with other forms of drugs does not produce positive results. The most effective means in this form of release are:
- Levomycetin is an injection powder that contains the active ingredient antibiotic chloramphenicol. For the treatment of furunculosis in adults, intramuscular or intravenous use is prescribed, the daily dose is 1-3 g. The medicine is administered at a dose of 0.5-1 g twice a day. Therapy lasts 5-15 days. Adverse reactions may occur from the lymphatic, central nervous and peripheral systems. The cost of the product is about 50 rubles.
- Amoxicillin is a semi-synthetic antibiotic belonging to the penicillin series. Prescribed intravenously by drip and stream for furunculosis. The doctor selects the dosage individually. On average, the therapeutic course lasts 7-10 days. During treatment, side effects such as headache, tachycardia, dysbacteriosis, irritability, and dyspeptic symptoms may occur. The cost of the drug is approximately 150 rubles.
Prevention of furunculosis
To prevent the onset of the development of this pathology, simple preventive measures are required:
- strict personal hygiene at work and at home;
- complete rest;
- proper nutrition;
- hypothermia should not be allowed;
- treatment of wounds and injuries;
- regular medical examination.
Boils are not only a cosmetic defect. Treatment of this disease requires a systematic and correct approach. To prevent the onset of pathology, you need to monitor your health, strengthen your immune system, and avoid developing chronic diseases. Proper and nutritious nutrition is important, because a decrease in immunity occurs as a result of a lack of valuable microelements in the body.
Video about the causes and stages of furunculosis:
[media=https://youtu.be/vxzD6DRpdeg]