- Causes of oil folliculitis
- Symptoms of oily folliculitis
- Treatment of oil folliculitis
- Prevention of oil folliculitis
Oily folliculitis is a common skin infection caused by staphylococcus. It is an inflammation of the hair follicle (the upper part of the hair follicles). It develops against the background of sweating, scratching, dirt and irritation of the skin, and less often as a complication of scabies. The development mechanism is as follows: first, a papule is formed at the mouth of the follicle, and then a pustule is formed, the center of which is penetrated by hair. Then a crust forms on the affected area. If the inflammation penetrates deeper and affects not only the upper section, but the entire follicle, then the pathology is called sycosis.
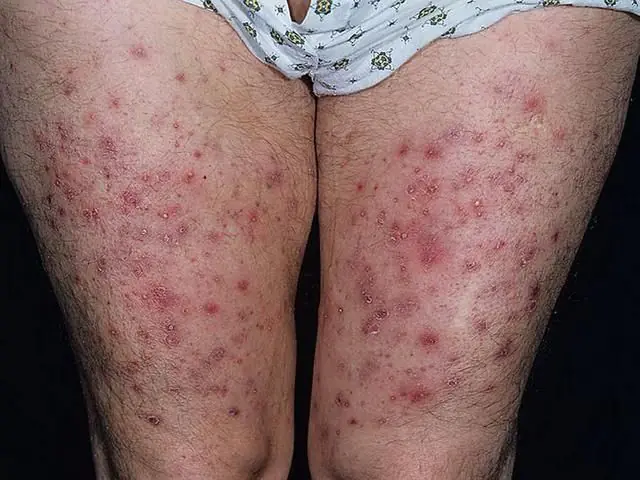
In what areas does oily folliculitis appear? The disease is localized on parts of the body with an abundance of vellus hair. It mainly affects the scalp, the surfaces of the legs, arms, forearms and the back of the hands in areas of extension, manifesting itself at the mouths of the hair follicles, where dense and dry nodules are formed. This disease is called oily (occupational) folliculitis.
Causes of oil folliculitis
Folliculitis most often affects people living in hot countries, where the climate is conducive to the development of inflammatory skin diseases. The disease is also often found in socially disadvantaged sections of society with unsanitary living conditions. Occupational folliculitis occurs in people of certain professions who work for a long time with chemicals that irritate the skin: mineral oils, coal and petroleum derivatives. People working in the field often suffer from it due to dust and the harmful effects of oils. Occupational factors also contribute to the disease: high air temperature, wet workwear, splashing and spraying of oils, insufficient experience of workers, poor sanitary and hygienic working conditions, etc.
Housewives and domestic workers often experience dermatitis from washing powders and synthetic detergents. In industrial conditions, the disease is provoked by contact with wool, washing tankers and cars, and the use of the new synthetic detergent sulfanol for degreasing metal products. Also, chemicals that contribute to the development of the disease include:
- pesticide;
- mineral fertilizers;
- fiberglass;
- epoxy and urea-formaldehyde resins;
- film varnish;
- synthetic fabrics;
- wet spun yarn;
- asphalt;
- pitch;
- rubber products;
- antiscale;
- liquid glass;
- cement, etc.
After eliminating the suspected allergen, the disease quickly passes, and prolonged contact with chemicals creates increased reactivity, which becomes the cause of occupational eczema.
Symptoms of oily folliculitis
In the photo, oil folliculitis in the abdominal area
The above reasons and harmful substances that contribute to the development of oil folliculitis cause hyperkeratosis and hyperplasia at the mouths of the follicles. In their place, horny plugs form. The disease is accompanied by acute inflammation and has the following clinical picture: flat, small acne appears, dry, with a dense consistency of reddish-lilac papules with a black dot in the center (horny acne). With horny acne, inflammation is very mild, and with oil folliculitis, an inflammatory corolla forms around the lesion, in the center of which a pustule forms. After opening, an ulcer appears, and subsequently a scar.
Most often, professional folliculitis develops on the extensor surfaces of the thighs, the back of the hands, buttocks, the anterior wall of the abdomen and forearms, where there are hair follicles. That is, the disease affects areas of the skin that are exposed to harmful drugs:
- Machine lubricating oil.
- Gasoline.
- Kerosene.
- Lubricating and cooling emulsions.
- Coal tar distillates, etc.
At the point of contact, the mouths of the hair follicles are filled with black plugs (comedones), which consist of oil, dust, and desquamated epidermis. Small nodules measuring 5 mm are formed at this site. When pressure is applied, sebum is released from the affected areas in the form of a rod or cylinder. It consists of horny scales, resinous substances, and epidermal cells. Over time, an inflammatory process begins around the affected areas, pustules and papules, the so-called purple corollas, appear.
- Read also about common symptoms of folliculitis
Treatment of oil folliculitis
In the photo are preparations for the treatment of oily folliculitis
Patients with occupational folliculitis are treated by washing the affected areas with hot water and soap. Apply 5% sulfur ointment to acne. The skin around the lesions is wiped 2 times a day with an alcohol solution of 2% (brilliant green, Pioctanin, Fukortsin, Castellani liquid, etc.). Prescribed externally by ultraviolet radiation. For deep folliculitis, pure ichthyol is applied to the entire element in the form of a cake, changing it 1-2 times a day. With the simultaneous appearance of a large number of deep acne, penicillin antibiotics and immunotherapy are prescribed, with chronic relapse - autohemotherapy, toxoid, staphylococcus, vitamin therapy (A, C).
Prevention of oil folliculitis
As a preventive measure, first of all, patients who have had oil folliculitis and come into contact with mineral oils should:
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- After your work shift, take a shower every day.
- When taking a shower, wash with laundry soap.
- Wear clean overalls every day.
- Follow safety regulations.
After the manifestation of dermatosis, patients are transferred to production without contact with hydrocarbons for a period of 2 months. If the disease relapses, they are transferred to dry and clean work on an ongoing basis. In the future, patients are advised to use mercury and tar ointment carefully, in particular for people with thick hair.
- Related article: how to make a compress to treat folliculitis at home