Nevi (moles) are found on the body of almost every person and in most cases are not dangerous. What is a birthmark and is it dangerous? Only some types of this formation are dangerous because they can become malignant, i.e. transformation into melanoma. Therefore, it is important to monitor every mole on your body.
What are nevi and what do they look like?
Many people do not know about the nature of moles and, due to the fact that these formations do not bother them throughout their lives, they do not even remember their existence. What is a nevus from a medical point of view? This is an accumulation of pigment cells on the surface or layer of the skin, which can be congenital or acquired. Congenital spots can be of different sizes - from 0.5 to 10 cm in diameter. The location on the body and the size of these formations are initially embedded in human DNA and are already present in a newborn, but are not visible until a certain age.
Causes of nevi
Acquired nevus - what is it and what causes moles? Pigment cells located between the epidermis and dermis can accumulate for the following reasons:
- ultraviolet radiation – provokes excessive production of melanin by skin cells;
- hormonal changes – due to hormonal changes in the body, new moles may appear and old moles may disappear;
- different types of radiation, injuries can cause migration of pigmented cells;
- heredity - the amount, type, location of congenital pigmentation is determined genetically.
Types of moles
Pigment formations can be classified according to their origin, size, color and location on the skin. Congenital birthmarks come in different shapes, colors, and some can reach 10 cm in diameter. Depending on the location on the body, they may have hair on the surface (Becker's spot). By their nature, there are the following types of nevi:
- vascular - arise due to atypical growth of capillaries (hemangioma, anemic);
- pigmented - due to an excess of melanin in the skin.
Pigmented nevi have a number of varieties:
- by location - borderline (on the palms, feet, genitals), nevus of Ota (pigmentation on the face);
- by color, nature of distribution - blue (cyan), brown, violet and pink spots, Setton's nevus or halonevus (spot surrounded by white non-pigmented skin), linear (several nodules in a chain);
- in shape - flat and convex, papillomatous, warty, fibroepithelial, verrucous;
- by the nature of the forming cells - melanoform, melanocytic, sebaceous glands;
- by location in the layers of the skin - dermal, intradermal, intradermal, dysplastic, superficial.
Congenital nevus
Birthmark (ICD name - congenital non-tumor) or congenital nevus - what is it? In the photo on the Internet you can see congenital skin formations of enormous size, which can be located on any part of the body and have different colors. Congenital pigmentation of a certain area is genetically determined with which a person is born. More often it does not pose a threat, but many factors, external and internal, can provoke the growth and transformation of cells that can form melanoma - the most dangerous type of human malignant tumor.
Acquired moles
Melanoform nevi, which consist of cells with melanin, are most often congenital, but can also appear during life. Acquired moles are often melanocytic - with different types of cells, incl. and pigmented. During life, under the influence of many environmental factors, a person can develop a formation of any nature. Such acquired skin tumors must be monitored to avoid the risk of their malignancy (transformation into a malignant formation).
What is a histological examination of a mole?
Histology of nevus - what is it? This is an examination of a mole to determine the risk of melanoma arising from it. Any birthmark carries a potential threat; under the influence of various factors it can develop into a malignant formation - melanoma. This type of cancer is considered the most dangerous due to the lack of response from the body. Melanoma can develop on any part of the skin, on the mucous membrane and even on the retina of the eye. Therefore, it is important to have your moles checked at least once a year by a dermatologist.
Melanocytic nevus
Due to the appearance of neoplasms, they are divided into melanocytic and melanoform. Melanocytic spots can form from three types of cells. Thus, melanocytic neoplasms, often benign, are:
- epidermal;
- dermal (intradermal);
- mixed origin.
Epidermal moles are dark in color, often flat and small in size. Sometimes they have hair. If epidermal spots protrude above the surface of the skin and become papillomatous, this may indicate a risk of developing melanoma from them, so it is important to carry out histology on time. Melanoform spots are formed from cells with melanin, so they are brown in color, are congenital, harmless, and can appear in a child during adolescence.
What are nevi on the skin that are not melanoma dangerous?
The concept of a melanoma-hazardous and melanoma-non-hazardous mole implies that there is a risk of melanoma forming from it. Only a doctor can tell exactly which mole is dangerous after a histological examination. However, there are medical statistics that show that some types of spots have a pronounced risk of forming melanoma and these include nevi: pigmented borderline, giant congenital, blue, nevus of Ota, Spitz, Dubreuil. Descriptions and photos of dangerous spots are easy to find on the Internet, but only a doctor can tell about the danger of a particular formation.
Diagnosis of nevi
The type and danger of spots on the skin are determined by the following methods:
- fluorescence microscopy - a special device, a dermatoscope, illuminates the skin to identify the cells that make up the mole, at what depth they are located and how they are formed;
- computer diagnostics – multiple magnification of a pigmented spot, measuring it and identifying its structure;
- histology – laboratory determination of tumor markers.
Treatment of moles
If pigmented areas of the skin do not bother you throughout your life and look normal, then most likely they do not pose any danger, but this does not mean that you can not monitor their condition. Timely diagnosis of changes will help to treat or remove the pigmented area in time to avoid its malignancy. How to treat moles that have caused suspicion? Today, surgical methods are used to remove suspicious formations on the skin.
Surgical removal of nevus
If the danger of a pigmented spot is identified, the doctor makes a decision regarding its removal. There are several surgical methods that are used depending on the type, location and nature of the tumor:
- resection – removal of the nevus surgically (excision) with a scalpel. Disadvantages – pain, scars remain;
- targeted irradiation of pigmentation with low doses of radiation;
- electrocoagulation – a bloodless method of removal with sealing of vessels;
- laser removal is quick, bloodless and painless, leaving no scars;
- cryotherapy – cauterization with dry ice or liquid nitrogen (not suitable for treating intradermal spots).
Treatment of nevi with folk remedies
Many people, having noticed new spots on their body, immediately begin to look for information from photos on the Internet, and then ways to treat them. There are many recipes for traditional treatment of moles on the Internet, but how effective are they? Among the existing recipes are the following:
- Treatment with vinegar. In folk recipes it is advised to apply directly to the affected skin. Such treatment can be dangerous due to burns.
- Mixtures based on lemon juice. Lemon is known for its ability to whiten the skin, so using such recipes can only change the color of the skin, and not cure it. Lemon juice helps fight seasonal pigmentation on the face and neck.
- Chalk mixtures that lighten the skin.
- Lapis pencil. This remedy has been mistakenly attributed to methods of combating moles, but it is effective only against warts.
Based on these recipes, we can conclude that it is simply dangerous to take on the treatment of skin pigmentation of any kind on your own. Intradermal, papillomatous and other neoplasms can only be diagnosed and treated by a doctor. A dermatologist or oncologist will be able to identify the nature of the formation on the skin, the degree of its danger and methods of treatment. Do not self-medicate so as not to injure your health and avoid the consequences of dangerous methods.
A skin nevus is a benign formation that appears on its surface. It can be congenital (from birth) or acquired (appear at a certain stage of life) in nature. Popularly, such growths are called birthmarks. In medical practice, they are all similar in their structure and mechanisms of formation.
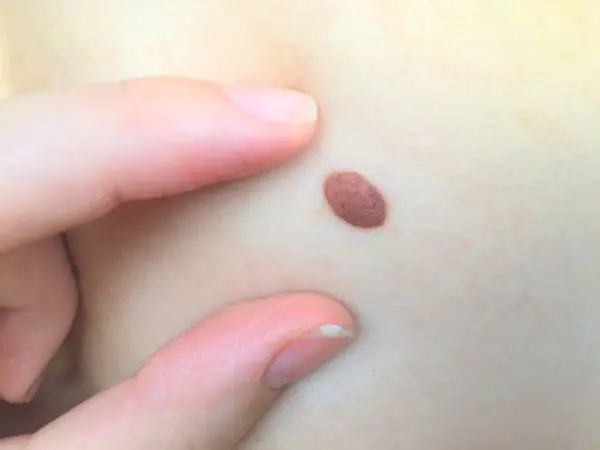
In the lion's share of clinical situations, nevus does not require a therapeutic process, since it does not have any effect on the quality of human life. However, doctors remove some types of moles because they believe that they run the risk of developing into an oncological condition. By the way, this is their key negative consequence.
Causes of moles
Nevus is a growth of the skin consisting of cellular structures. It looks like a growth or noticeable thickening on the skin surface. Includes an impressive amount of melanin, which makes it darker. This substance is produced with the participation of appropriate cells as a response to UV radiation. It acts as a stimulating factor for the production of excess pigment. Along with it, other provocateurs act, affecting many systems and organs in the body.
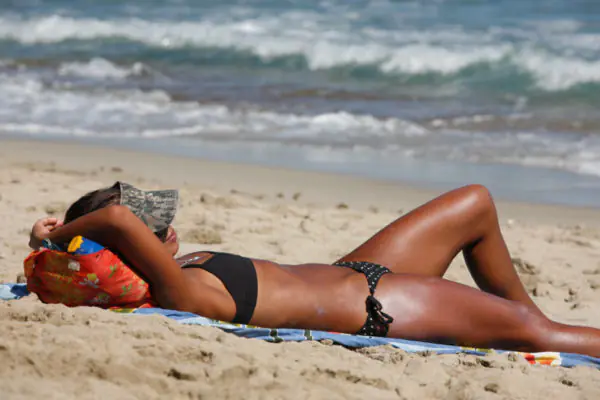

The formation of a nevus is the result of uncontrolled cell division. Within a certain stage of the progression of the condition, the number of cells turns out to be excessive, which is fraught with the appearance of a growth. Compared to a cancerous tumor, a nevus is not prone to rapid growth. A large proportion of its varieties are congenital spots that grow and develop along with the body. It turns out that at the end of the body’s growth (at about 20-25 years), the growth of spots stops or significantly slows down. Moles are traditionally formed under the influence of several pathogenic factors.
Local developmental defects
This condition primarily affects innate cellular structures. Sometimes they make themselves felt due to disturbances in the division process in the later stages of fetal formation and development. Such damage is insignificant in size and not noticeable. Due to this, formations are detected only in the 2-3rd year of a child’s life in the process of a significant increase in the skin surface. Doctors have found that about 60% of birthmarks are of this nature.
Heredity and genetics
There is a widespread belief that growths are transmitted along a genetic line, and this fact was discovered many centuries ago. In reality, such phenomena function like this. Tumors or pigment spots are subject to coding through a gene chain within the DNA molecule. During the process of material transfer, it is transferred together with the chromosome from the mother or father to the child/children. A mole is the result of the interpretation of genes during the development of a child’s body. The probability of transmission is 50% if the parents also have a hereditary type of formation.

UV radiation
The neoplasm can occur both at birth and during life. UV radiation is the reason for stimulating the functioning of melanocytes in the basal layer of the skin. In order for the pigment to be produced as intensively as possible, the body begins to produce a lot of melanotropic hormone. If the rays continue their impact on the skin, the cells multiply. As a result, instead of proper tanning, a pathological process develops, consisting in the proliferation of skin cellular structures. In this situation, representatives of the fair sex over the age of 30 are susceptible to moles.
Injuries
Skin damage of a mechanical type - wounds, scratches, bites - are also harbingers of the formation of melanin spots. Due to their influence, an inflammatory reaction occurs, affecting various layers of the skin. This provokes the production of biologically active media capable of stimulating the growth of cellular structures. This is a minor factor that rarely affects the process of nevus formation.
Hormonal factors
Statistical med. Studies have proven the effect of hormones on the formation of growths. Provoking factors include puberty, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and menopause. Pathological conditions include disorders of the adrenal cortex and endocrine system. Restructuring of this type has a serious impact on the functioning of the pituitary gland. But moles formed as a result of the influence of this factor rarely become malignant.
Viral and bacterial agents
Infectious processes, where the main players are viruses and bacteria, also provoke the appearance of new spots. The mechanism of formation of moles has many similarities with traumatism. A role in such phenomena is played by the widespread inflammatory process that occurs against the background of these infections.

Modern medical practice is ready to identify several groups of people exposed to risk factors for the occurrence of these formations:
- those who perform work duties under excessive UV radiation;
- people who regularly stay in southern latitudes and near the equator;
- persons working in the chemical industry and complex production;
- citizens who have been using hormonal drugs as therapy for a long time;
- persons with reduced immune defense factor;
- patients suffering from chronic endocrine pathologies;
- people with an impressive number of congenital birthmarks;
- relatives of individuals who have been formally diagnosed with skin cancer.
Development can start with each of these conditions, so you should be alert and constantly monitor the skin changes that occur.
Types of formations
The extensive classification of moles is due to the variety of their external manifestations.
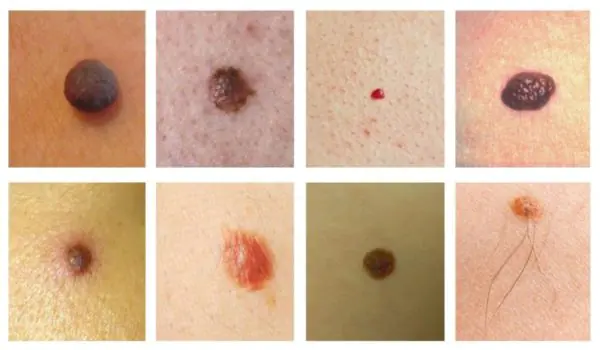
Pigmentless (basal)
It has an oval shape, a whitish tint, and has clearly visible boundaries that cannot protrude above the skin. The longer an individual is exposed to the sun's rays, the more noticeable darkening is formed. Growths are detected in childhood and remain unchanged for a long time. Based on the zone of localization of cellular structures, it is customary to distinguish:
- hypodermal appearance (in the hypodermis and practically invisible externally);
- borderline type (accumulation of melanin made itself felt between the dermis and epidermis);
- epidermal (localization zone - the epidermis itself);
- intradermal (dermis).
Intradermal
The dermal (intradermal) type of neoplasm is benign and stands out against the background of the skin surface. There is no pain on palpation, and the surface of the growth is soft. May have a pinkish, brownish and even black (rare) tone.
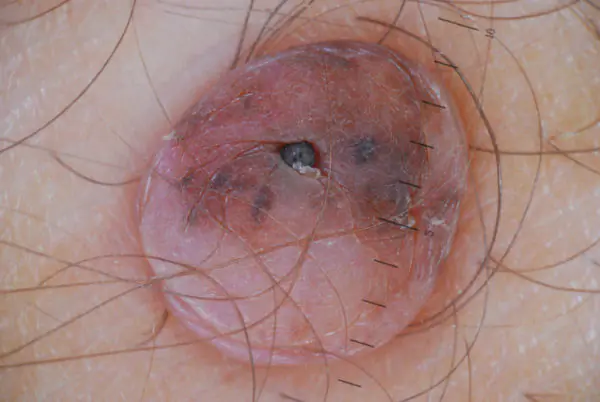
The dermal type of moles is divided into the following medical (clinical) areas:
Warty
In practice it is called verrucous. In appearance it is a dark brown growth. It has a bumpy surface. It protrudes above the skin and is noticeable. Education has a congenital form and manifests itself predominantly in females. The mole is of a benign nature and does not cause anything other than an aesthetic defect. If the discovery occurred in a relatively mature age period, it is necessary to examine it for malignancy.
Noncellular
Birthmarks of this category predominate on the face and neck. The patient sees them in the form of a brown lump. The percentage probability of formations degenerating into melanoma is small. Removal is carried out in situations where the mole entails the formation of a purely cosmetic defect.
Pigmentary
Nevus implies a high concentration of melanin, which indicates the formation of a clear color. Over time, the color does not change, but does not lose its brightness. Shapes, dimensions, surface characteristics are variable. Neoplasms appear in hard-to-reach areas (groin, armpits, mammary glands).
Linear
A linear growth is represented by a group of formations of medium-dark color, located in one line. Due to the resulting configuration, it easily lends itself to the diagnostic process.
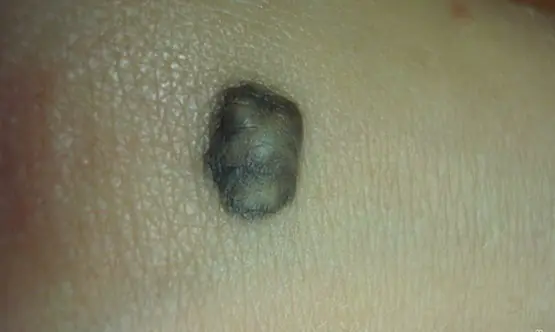
Blue
This is a Jadassohn-Tiche formation, acting as a type of melanocytic growth (pigmented). The difference is an uncharacteristic shade for birthmarks, which varies from light blue to dark blue and even purple. Blue growths are benign in nature. Rebirths are rare in practice.
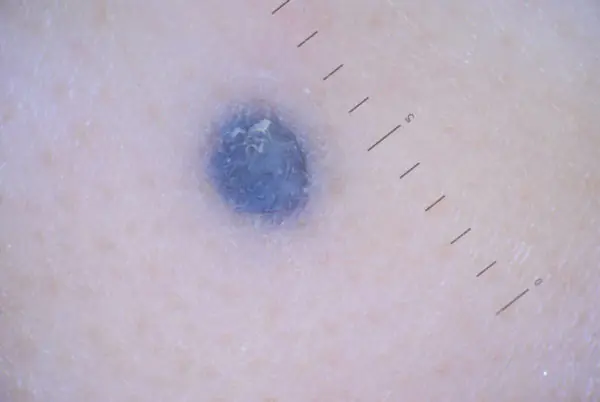
Dysplastic
These are non-standard moles (in terms of external and internal characteristics). Due to their unusual nature, it is necessary to maintain a special attitude towards them throughout the entire time they are present on the body. This is due to the high risk of developing into a cancerous tumor of the skin. The clinical manifestations of the neoplasm are as follows:
- impressive size indicator;
- color formed unevenly;
- elevation above the skin (not always);
- formation of black hairs on the surface.
Becker
It primarily affects males during puberty. This is due to the release of an impressive amount of androgens into the blood fluid. As a result, several previously insignificant spots increase in size, which provokes their merging. A growth with equal edges is formed. The total size can reach 20 cm. Traditionally it occurs in the area of the shoulders, back, and pelvis. The color intensity is average, decreasing with age.
Sebaceous glands
This is a nodular spot of a benign nature, resulting from a defect in the functioning of the sebaceous glands. Traditionally, it has a congenital form and appears in the first years of a child’s life. Affects both boys and girls with equal frequency and intensity. Affects the scalp.
Setton
A type of pigment growth when a white area of skin appears around the birthmark. Gender and age characteristics do not affect the risk of developing the disease. But scientists are used to linking it with autoimmune lesions and vitiligo.
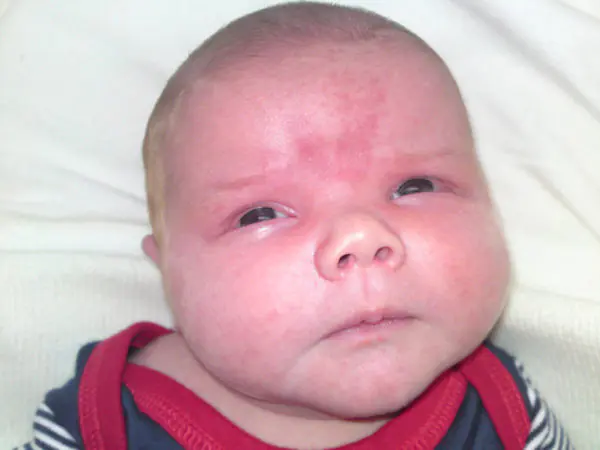
Otherwise known as “wine stain”, “angel’s kiss”. It has a congenital form, is localized on the face, neck, and acts as a consequence of a defect in the cardiovascular function. The spot increases in size along with the baby's growth.
Mongolian spot
A single growth or a group of them, localized in the area of the sacrum, gluteal muscle structures, thigh areas, and back. Appears in newborns and has a variety of colors with a smooth surface.
A single spot (or group of spots) on the skin. The location is predominantly in the cheek area, area around the eyes, nose, upper lip. This is an obvious precancerous condition, since the tendency for degeneration is impressive.
Outwardly similar to the previous one, the variability concerns only the localization zone: it is formed on the neck, scapula, collarbone, deltoid muscle.
Dysplastic
The condition is otherwise called Clark's nevus. A single spot (or group), presented in the shape of a circle, oval, colored in a red, brown, red tone. There is a slight protruding area in the center, the total size is 6 mm. This group includes birthmarks that have at least one of the following characteristics:
- asymmetry (uneven contours, crooked structure);
- uneven edges;
- lack of ideal color distribution;
- size indicator from 6 mm;
- lack of similarity with other spots.
Due to a number of factors, the formations resemble melanoma, but practically do not turn into cancer.
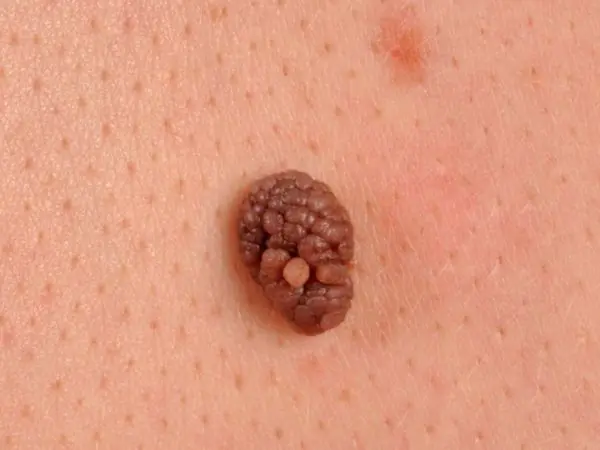
Papillomatous
This is a type of classic epidermal type mole. Its surface is formed on the basis of irregularities and growths, similar in external factors to cauliflower. The physician and the patient may detect a raised area above the surface of the skin and individual bumps that are brown or pinkish in color. Despite their unattractive appearance, such growths are safe for health and life, since they have zero chance of degenerating into cancer. However, the external parameters of a mole can easily be confused with a malignant growth.
Fibroepithelial
This dermal growth is common and is represented by a classic mole with an impressive number of connective tissue particles. The shape is convex (circle), the sizes are variable, the color is red or pink, sometimes light brown. Safety is explained by the minimal likelihood of degeneration into a cancerous tumor.
Melanocytic
This is a type of pink lesion presented in the form of a classic epidermal mole with variable color. They are typical for those with light skin tone, as they produce pink pigment.
Reed's nevus is a benign tumor from a histological point of view. There are similarities with melanoma in a number of parameters, which leads to a number of difficulties in the diagnostic process. In a number of situations, education exists from early childhood, and sometimes makes itself felt throughout life. Reed's mole is rarely dangerous. The types in medicine are diverse, and this is only a part of the varieties of such formations.

Diagnostic complex
A doctor performing diagnostic procedures undertakes to set a set of goals:
- establishing the type and class of mole;
- identifying treatment options;
- timely recognition of the onset of cancer;
- identification of indications for additional implementation. examination methods;
- taking measures of the therapeutic process.
During the initial examination, the medical specialist undertakes to establish several answers to the most important questions:
- at what time the growth appeared;
- it is present from birth or from any age;
- how has he behaved over the past days, weeks, months;
- whether there were changes in dimensional indicators;
- whether the color characteristics and contour parameters have changed;
- whether diagnostics were carried out;
- whether healing measures were taken.
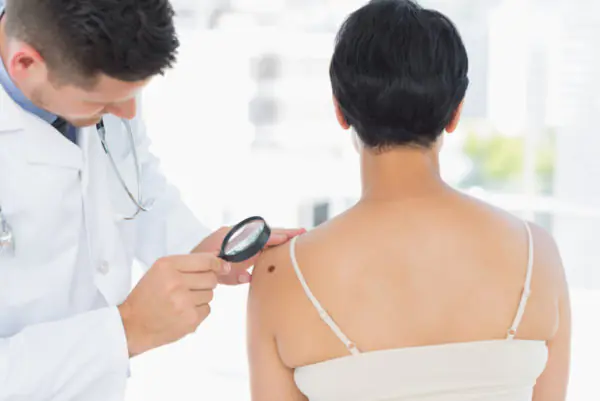

So, the first stage is communication with the patient. This is followed by an examination, during which the physician assesses the shape, size, and location. If the diagnostic goal is not achieved, auxiliary measures are prescribed:
- smear from the surface (subsequent examination of the material through a microscope) with results obtained the next day;
- examination on the patient’s body (a microscope is used, a smear is not taken, the procedure is performed directly on the body);
- computer diagnostics (provides an image of a pigment spot saved on a computer; it is expensive, but effective);
- laboratory examination (determines the fact of degeneration into melanoma);
- histology (shows the structure of the formation, reveals the degree of its danger and stage of development);
- biopsy (an impressive examination in all directions, making it clear what should be done for the further therapeutic process).
Therapeutic process
Treatment is carried out in various ways. Surgery is common. The practice of removal by other means is used. Indications for choosing one or another option are determined by the treating specialist. Several key factors are taken into account.
- Key features of age spots. These include its type, size, and risks of transformation into cancer.
- Availability of the necessary equipment in the clinic. Many establishments use only a scalpel and do not use other methods due to lack of equipment.
- Individual characteristics of the body. Some patients cannot bear the pain, so painless techniques are preferred. The degree of sensitivity of the skin is also taken into account.
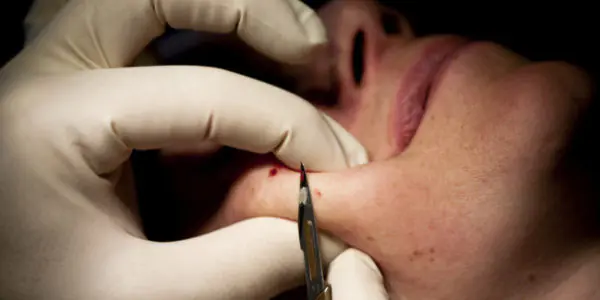
Surgical excision
The main tool of a doctor is a scalpel. Due to the undemanding nature of the technique, the method is considered the most common. Doctors give it preference when it is necessary to remove large growths. The disadvantages are in the following aspects:
- presence of scars after surgery;
- the need to remove not only the spot itself, but also the surrounding skin in the area of 3-5 cm);
- the need for anesthesia (local in adults and mainly general in children).
Recently, this type of excision is rarely used, because there is a possibility of the spot degenerating into a tumor process. Along with surgical techniques, there are other common types of birthmark removal.
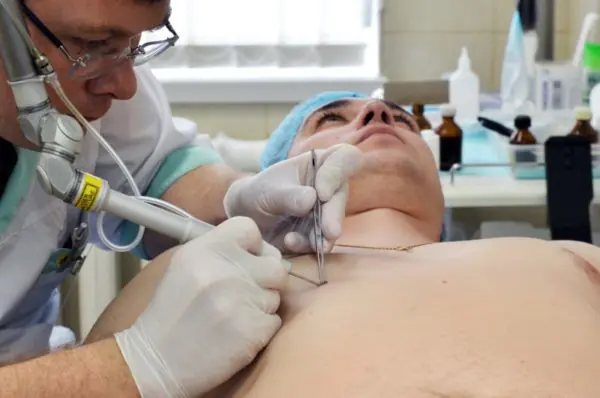
- A liquid nitrogen. Provides treatment for nevus through freezing. Low temperatures cause the spot to die, which then turns into a scab. After healing, natural skin begins to grow in its place. There are no scars or cicatrices, no pain.
- Electrocoagulation. The method is the opposite of the previous one, since high temperatures are used for excision. Compared to the classical operation, the method has a number of advantages: no blood, no need to remove large areas. But the method is not used for excision of large moles.
- Laser removal. The technique has become widespread in modern cosmetology salons. It helps to instantly remove small-sized moles on the face and neck. The laser penetrates deeply, and there are no scars or burn consequences. The patient does not feel pain.
- Radiotherapy. Has good recommendations within the framework of modern world medicine. The essence is to use a special knife capable of generating a beam of radiation concentrated in the area of the pathology.
If there is a suspicion of a malignant nature of the process, surgical intervention is traditionally used. In this case, surrounding tissue is removed to avoid subsequent growth of the tumor process.
Prevention of degeneration
There are no specific measures, but there are a number of rules that will help avoid complications.
- Avoiding sun rays during the most active hours (from 11 a.m. to 5 p.m.).
- Use of special creams and lotions.
- Constantly working to improve immune function.
- Refusal to visit the solarium.
- See a doctor if you notice changes in a mole.
Thus, a nevus is a benign growth that has every chance of turning into cancer. To avoid complications, it is necessary to monitor its changes and show it to a doctor.
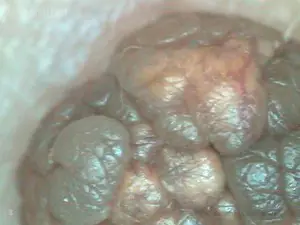
Pigmented spot on the body, melanocytic nevus, pigmented nevus, intradermal nevus - all these benign neoplasms are, as a rule, congenital defects of the skin. Reasons: in a certain place of the skin, a cluster of cells appears - nevocytes, which contain a large amount of melanin.
Melanocytes, where pathological changes occur, are called nevocytes. In the normal state, melanocytes give the skin color and synthesize melanin. By and large, mole and nevus are synonymous words; nevus comes from naevus, which means “birthmark” in Latin.
Melanin and melanocytes
Melanin is a natural pigment dye that is found in human skin, retina, iris, hair and even in the brain. Weak or intense skin color depends precisely on the number of melanocytes. The same applies to eye color. An effect such as tanning is also due to the presence of melanin.
There are three types of melanin:
- neuromelanin is a special type of melanin that is found in the brain;
- eumelanin - black or brown color - melanocytic nevus;
- pheomelanin is yellow.
In the body, melanin appears in melanocytes. These are special cells that have many processes. They take the hormone thyroxine from the blood, which is secreted by the thyroid gland. After undergoing an oxidation procedure, thyroxine is converted into melanin. Then, along the processes of melanocytes, the newly formed melanin passes to the skin cells. This is where it is deposited.
In addition to pigmentation, melanin also has in the body many other functions:
- increases the body's resistance to stress;
- it is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from the negative effects of radioactive radiation and toxins;
- actively participates in the normalization of sleep and wakefulness;
- prevents excessive emotionality and stabilizes the emotional background.
Albino people have colorless eyes, white or light red hair, and completely white skin. Their body is completely devoid of melanin. These people are weakly resistant to various types of diseases and often die young.
Reasons for the formation of nevi
Melanocytic nevus
Usually these are hormonal changes in the body. Often this appears in adolescence, but there are others:
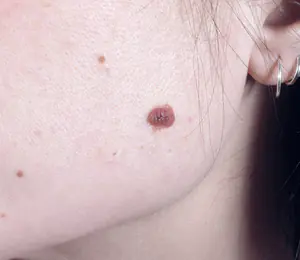
During pregnancy, a change in sex hormones occurs in the female body.- Inflammatory and allergic skin diseases.
- Exposure of skin to ultraviolet radiation. Frequent solariums and sunbathing provoke activation of age spots.
- Menopause.
- Use of contraceptives.
Dysplastic nevus
Today, most dermatologists are inclined to think that many pigmented nevi, even those that appear in adulthood, are congenital malformations of the body. These disorders, after which the nevus appears, are already present in the embryonic state.
The factors responsible for the appearance of dysplastic nevi have not yet been fully elucidated. But there is main reasons for the development of the process:
- infection of the genitourinary system of a pregnant woman;
- changes in sex hormones (estrogens, progesterones);
- genetic disorders;
- the effect of negative factors on the body of the expectant mother (toxic substances, radiation).
Under the influence of all or certain factors, the development of melanoblasts—tissues that form melanocytes—is disrupted. As a result, melanoblasts accumulate in certain areas of the skin and transform into nevocytes.
There are two features that distinguish melanocytes from neocytes:
- Dysplastic nevi on the skin weakly obey regulatory processes in the body, but have not completely lost this ability, which cannot be said about cancer cells.
- Neocytes do not have processes along which the pigment could move to other skin tissues.
It is believed that new nevi do not appear with age. It’s just that they were completely invisible before and showed themselves only after a while.
Symptoms and classification of nevi
Hemangiomas are characteristic vascular tumors. The most common is “strawberry nevus”, which has a red tint. These neoplasms appear in many newborns and disappear within a month of the baby’s life.
Melanocytic nevi vary greatly in shape, color and size. Today, there is no consensus among dermatologists as to what formations are classified as nevi. Therefore, nevi are often called benign tumors that do not contain melanin.
Anemic nevus - This is one of the types of vascular nevus. This is a part of the skin with poorly developed blood vessels, so its color is very light.
Congenital nevi in children include teratomas; this is essentially a congenital tumor. They contain leather, as well as all other tissues.
Nevi of the sebaceous glands are sometimes found in the scalp area. They also do not have melanin.
Types of nevi
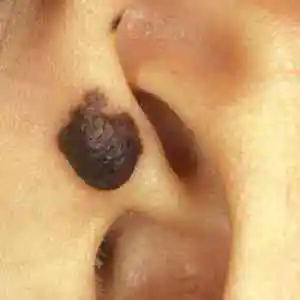
Intradermal nevus is considered the most common type of melanoform nevus. It is so called because the accumulation of melanocytes occurs in the dermis - the middle layer of the skin.
Noncellular border nevus - This is a simple, non-protruding spot above the skin area. In some cases, the border nevus stands out slightly above the surface. This species has strictly defined contours and a brown color. The size and location of the nevus on the body can vary greatly. This type of melanoform nevus is characterized by an accumulation of melanocytes between the dermis and epidermis.
Intradermal nevus slightly convex, but differs in that it has an uneven and bumpy surface. It is almost always found on the head or neck, but sometimes it can be seen on the torso. The critical age for the manifestation of such a skin infection is 15-35 years. Over time, the intradermal nevus seems to move away from the body and is supported only by a thin stalk.
As a rule, it turns into a papillomatous or otherwise warty nevus, however, warts are growths that are slightly different in appearance. A large number of irregularities and cracks form in them, where dead epithelial cells accumulate. This is an excellent environment for the emergence of pathogens, which later lead to dangerous infections.
A complex pigmented nevus has the shape of a mole, and it is this that defines the concept of a “mole.” As a rule, it rises above the skin and has a variety of complex colors: from black to light brown. Often there are coarse hairs on the mole. The surface of the mole is smooth, and it can be located anywhere on the body.
Basal nevus also looks like a regular mole, but there is usually no pigmentation here. The standard color is flesh.

Blue nevus has a characteristic color because it is associated directly with melanin deposits under the skin. Residents of Asian countries usually have these moles. Moles rise slightly above the body, have a smooth surface, are hard to the touch, and in rare cases, hair grows on them. The diameter of the neoplasm is usually no more than 6 mm.
Halo nevus or seton nevus - an unusual type of dermal nevus, in this case, on the contour of the pigment spot there is a light rim of skin, completely devoid of pigmentation. This type of neoplasm has not yet been fully studied. These spots are often adjacent to melanomas and vitiligo. Often there is slight skin inflammation in the area of the halo nevus.
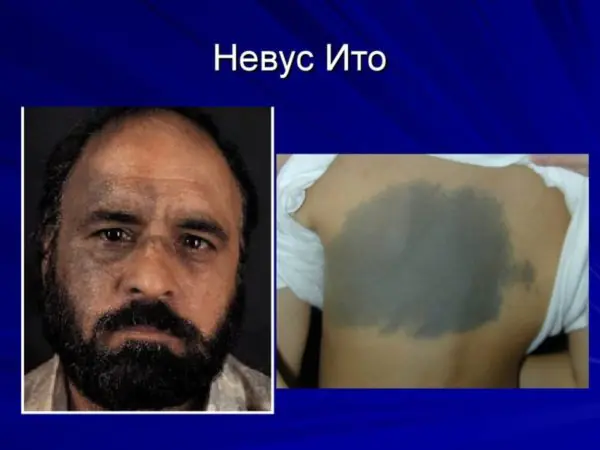
Nevus Ota. Localized on the face in the form of “dirty” spots.
Nevus Ita is localized under the collarbone in the area of the shoulder blade, neck and chest.
Becker's nevus or epidermal pilar nevus, usually formed in young men and adolescents, is completely different from the nevus of Ota. Initially, several small spots appear on the body, which are light brown or brown in color. They are crowded together, but after a certain time they unite, creating large spots (up to 25 cm) with uneven contours. In this case, the spots get a warty surface, with a hair growth.
Papilomatous or warty nevus is characterized by its large diameter. As a rule, it is localized on the neck or surface of the head, but in some cases it can be seen in other places. In appearance it looks like a wart, hence the name. The surface of the tumor is usually covered with hair.
A nevus of the eye is located on the iris. This is a clearly visible spot that comes in a variety of shapes and sizes. The tumor can also be located in the retina, and it can only be determined through a thorough examination by an ophthalmologist.
Linear nevus - this growth forms on the human body from birth. It can consist of a whole group of small nodes of various shades: from black to light flesh. They are located on the body in the form of a chain. This growth can cover several centimeters of skin, or can completely occupy the surface of the arms or legs. Hairs often form on it.
Separation of nevi by size:
- small ones have a diameter of 0.6-1.6 cm;
- average neurodermal their size is 1.6-11 cm;
- large pigment ones, their diameter is more than 11 cm;
- gigantic, found over most of the body.
As the body grows, the appearance of the growths also changes. Their number can also change, and not only in the direction of increase.
Giant nevi of infants have a large danger of transformation into melanoma.
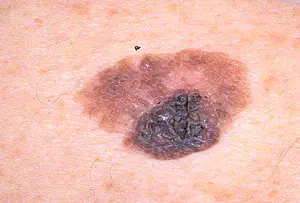
Dermal nevi can be found in 85% of adolescents aged 10-16 years.- In people 20-25 years old, up to 40 birthmarks can be observed on the body.
- After 35 years, a person has only 20-25 moles on his body.
- In people over 85 years of age, nevi are almost impossible to detect.
This dynamics is explained changes in hormonal levelswhich occurs throughout a person’s life.
So, we have examined a large number of nevi, and only one thing becomes completely clear - to determine the growth, its classification and name, naturally, perhaps, paying attention to the size, color, appearance and other characteristics, but how correct is this definition, if today the number of varieties Are there already hundreds of nevi? Is it really possible that any of us, without special education, can establish an accurate diagnosis and determine the danger in advance?
Therefore, we recommend that you consult a doctor if you have any concerns about tumors. Moreover, an experienced doctor can not only define a growth, but will also tell you why it formed on the head or arm, what are the reasons why an ordinary pigmented nevus, which is called a mole, manifests itself incomprehensibly, will tell you what a congenital neoplasm is and what – acquired. This information received from the doctor will make it possible to assess the situation and determine whether it is necessary to remove an ordinary mole, how to do it, and how to care for the place on the body after removing the growth.



