A person is sensitive to his health, and in particular to the condition of his skin. Any irritation, inflammation or ulcer may cause suspicion and be a reason to visit a doctor. Among skin diseases, folliculitis is common - an inflammatory process at the location of the hair follicle. Timely diagnosis and treatment of such a diagnosis will help avoid complications.
Features of the diagnosis of folliculitis and its symptoms
Folliculitis - This infectious skin disease, affecting the hair follicle. It is characterized by purulent inflammation first of the superficial area of the follicle, and with further development of the process - damage to the deeper layers.
The infection penetrates the skin when it is scratched, through cracks, small wounds, and cuts. This disease manifests itself in the form of one or more purulent pimples, which, when opened, turn into ulcers. Most often they form in places where hair grows on almost any part of the body:
- in the armpits;
- in the groin area;
- on foot;
- on the skin of the face or scalp.
After healing, the ulcers leave virtually no traces; only in the case of deep skin damage, scars may remain.
The main symptoms of folliculitis:
- redness of the affected area;
- itching and pain;
- the presence of pimples on the skin - pustules with whitish purulent contents, often they appear in the place of hair growth;
- after opening the pustules, bleeding ulcers appear, which after a while become covered with a crust.
In regions with a hot climate, the prevalence of this disease is much higher than in cold countries.
Causes of the disease
There are several reasons for this diagnosis:
- fungal infection - the causative agent can be dermatophytes, the genus Pityrosporum and Candida;
- viral infection - herpes or molluscum contagiosum;
- bacterial inflammation - staphylococcus bacteria, gonorrhea or syphilis pathogens are involved;
- The causative agent of the disease is parasites, for example, ticks.
Additional factors for the development of this disease may include:
- increased sweating;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- wearing clothes that are too tight;
- the presence of diseases associated with itching and constant scratching of the skin;
- diabetes mellitus, anemia and liver disease;
- malnutrition;
- decreased immunity and the presence of immunodeficiency states;
- prolonged skin contact with certain ointments or chemical liquids - technical oils, kerosene.
To prevent any kind of skin diseases, including folliculitis, it is important to follow the rules of personal hygiene when shaving, depilation and other similar procedures, as well as when visiting public places - swimming pools, gyms, baths and saunas.
Classifications of folliculitis
There are several classifications of such an unpleasant skin disease:
- For reasons of appearance - depending on the type of pathogen:
- viral;
- syphilitic;
- bacterial;
- fungal;
- parasitic.
- By degree of damage:
- surface – it is characterized by redness of the skin, small pustules - up to 5 mm, absence or mild itching and soreness;
- deep – characterized by inflamed areas of the skin, painful, dense red pustules up to 10 mm in size.
- According to the course of the disease:
- uncomplicated – passes without complications – the pustules open, and ulcers form in their place, healing after a few days;
- complicated – damage to the deep layers of the skin and the spread of the inflammatory process.
There are a large number of varieties of folliculitis, sometimes similar in appearance to other skin diseases. Therefore, it is better not to self-medicate, but to entrust the doctor with making an accurate diagnosis and prescribing therapeutic measures.
This type of inflammation of the hair follicles is characterized by purulent rashes on the skin caused by a fungal infection - yeast-like fungi of the genus Cand />
The main symptoms are redness of the skin in the area of the hair follicle, in place of which a pustule is formed, which subsequently opens, forming a wound or ulcer. In most cases, with timely treatment, the rash goes away in about 2 weeks.
This type of folliculitis is the result of a disease such as syphilis. A distinctive feature of this diagnosis is the presence of groups of damaged areas of the skin - inflamed follicular sacs, usually pale red in color.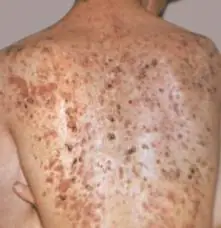
Treatment of syphilide is possible only after getting rid of the main cause of its occurrence - the diagnosis of syphilis.
The name staphylococcal folliculitis speaks for itself. Its causative agent is staphylococcus, the most dangerous of which is aureus. The disease can affect adults and children, and the method of infection is usually airborne or contact.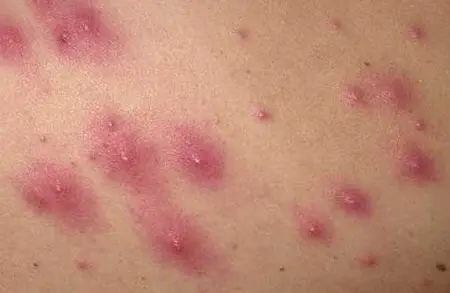
Symptoms of this disease are the appearance of a purulent rash on the skin, which can be chronic. In childhood, an increase in body temperature, weakness and deterioration in general health are possible. As a treatment, in addition to medical intervention, personal hygiene and nutritional correction may be recommended.
This pathology usually develops on the scalp and may be accompanied by damage to the hair shafts. It is caused by infection with dermatophytes - molds.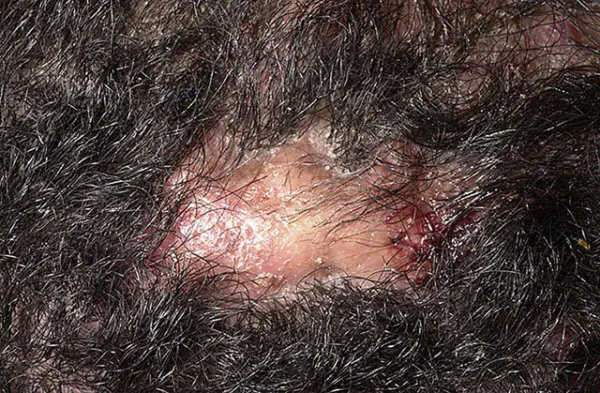
The disease in question is quite unpleasant. It is characterized by inflammation of the epidermis in the area of the hair follicles with the formation of purulent pustules, which subsequently turn into ulcers - bleeding or with a crust formed.
This type of folliculitis is associated with exposure to dirty, contaminated water - most often these are public places - swimming pools, beaches. The infection from the water gets onto the skin, and through minor damage, cracks, and wounds it enters the body, forming inflamed areas and purulent pustules, usually round in size and red in color. They cause an unpleasant itching sensation in a person.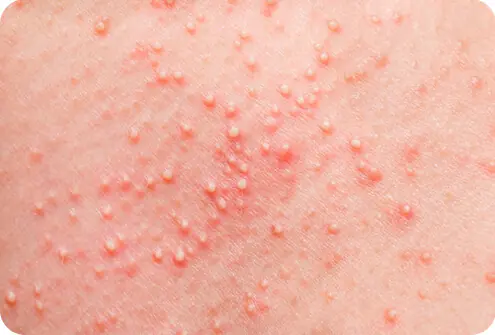
In most cases, the rash disappears within 7-10 days. Additional treatment is prescribed by the doctor after taking the patient’s medical history.
This type of folliculitis is associated with professional activity and the specifics of certain professions - working with chemicals, gasoline, technical oils and lubricants. Prolonged contact of such substances with the skin causes irritation, redness and the formation of inflammatory foci.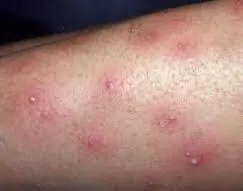
Most often, the disease spreads to the back of the hands and the outer part of the forearms. One of the treatment options, in addition to therapy, may be to avoid working with specific chemicals.
A type of folliculitis that can occur after being bitten by insects such as ticks. Its symptoms in most cases are similar to the standard signs of such a diagnosis. Treatment for this disease will be prescribed after studying the specifics of the insect and getting rid of the consequences of the bite.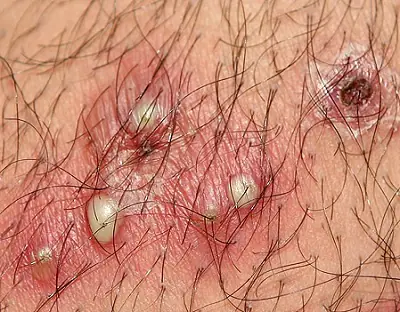
As a rule, tick-borne folliculitis takes much longer to cure than other types of similar diseases.
Gonorrheal folliculitis is a consequence of an untreated or complex, long-term disease - gonorrhea. The causative agent in this case will be gonococci.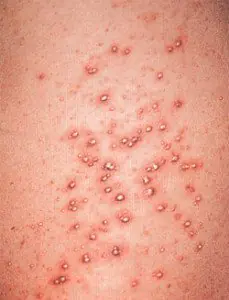
This rare disease, as a rule, affects the perineal area in women, and the foreskin in men and manifests itself in the form of rashes in these areas. Treatment of the disease in question will be fruitful after getting rid of gonorrhea.
Folliculitis caused by a fungal infection does not have any special symptoms. It manifests itself in the form of a purulent red rash accompanied by the appearance of ulcers. To clarify the diagnosis and treatment methods, laboratory testing is required to identify the source of the disease.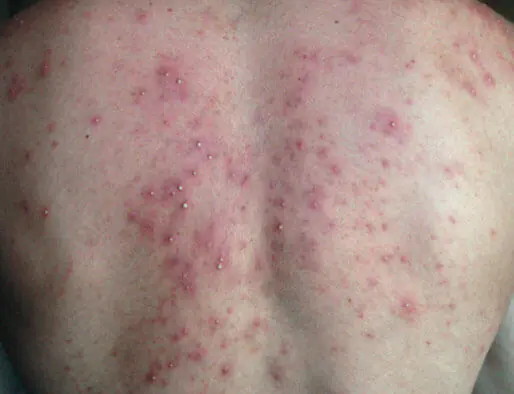
Antifungal ointments and similar drugs are most often prescribed as therapeutic measures.
The cause of the development of such a disease is weakened human immunity. In most cases, an additional factor may be the use of antibiotics or hormonal drugs. A distinctive feature of the disease is its rapid development - the appearance of a purulent rash on the face and, in rare cases, on the chest and arms.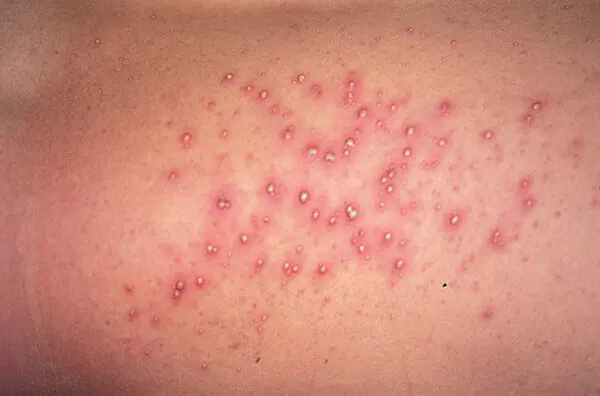
Depending on the severity of the disease, gram-negative folliculitis is divided into deep and superficial. Its treatment will depend on the severity of the disease and the general health of the patient.
The disease in question usually affects men. The affected area is the lower limbs. The main symptoms are the formation of purulent inflammations on the skin of the legs, both single and group. Their distinctive feature is symmetry.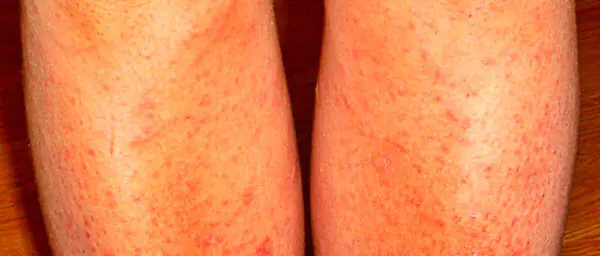
An additional factor provoking this diagnosis may be a hot climate and high air temperature.
The causes of this disease are not fully understood. According to some data, the main one is the presence of immune system cells - eosinophils in the skin near the hair follicle. To identify such a disease, a biopsy and blood test are performed, based on the results of which treatment is prescribed.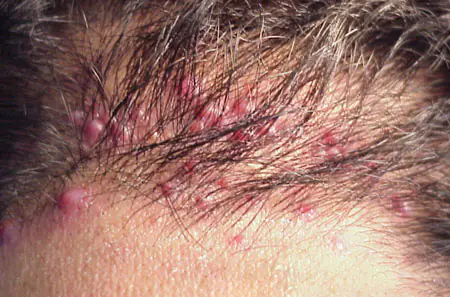
Symptoms of eosinophilic folliculitis include redness of the skin in the area of inflammation, the presence of itching and purulent pustules of varying sizes on the face, scalp, back, and arms. The disease is observed in both adults and children.
The peculiarity of this disease is the presence of hemispherical pustules of different sizes on the surface of the skin. As a rule, they are not solitary, but spread in groups.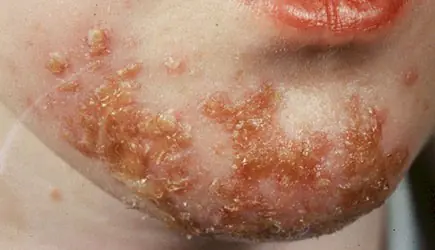
The main reasons for the appearance of Impetigo Bockhart are maceration of the skin - a violation of its integrity, as well as excessive sweating. Often, an additional factor for the development of such a disease can be the use of warm compresses.
Read a detailed article about impetigo disease, its symptoms and treatment.
Most often, this disease occurs in middle-aged men and is accompanied by the formation of pustules, fistulas and nodules on the top of the head. The chronic course of the disease may be accompanied by the appearance of scars.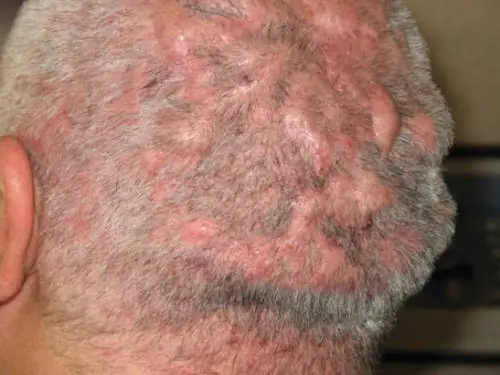
The causes of the disease may be acne, decreased immunity or its unusual reaction to external influences, or a bacterial infection. Antibacterial drugs or corticosteroids may be prescribed as treatment; in rare cases, surgery is indicated.
The causes of the disease in question have not been fully established; perhaps they are related to the characteristics of the patient’s body. This type of folliculitis is characterized by a chronic course, the appearance of papules and pustules, as well as the subsequent formation of scars at the site of inflammation.
Affected areas: scalp, groin area, armpits.
Timely diagnosis of the disease
The patient can detect the first symptoms of folliculitis himself - the formation of pustules, ulcers, and itching of the skin. When visiting a doctor, the primary diagnostic method is an external examination of the patient - the symptoms of this disease are most often quite characteristic, which makes it possible to establish a diagnosis and select treatment methods.
In addition to the inspection, the following procedures are carried out:
- collection of anamnesis - medical history with a description of symptoms, complaints, dates of identification of signs of the disease;
- general blood test and determination of glucose levels;
- bacteriological culture and microscopic analysis of samples taken;
- biopsy;
- dermatoscopy;
- in some cases an immunogram may be required.
A similar series of procedures is necessary to establish the cause of folliculitis and differentiate it from other similar diseases - different types of lichen, acne, keratosis pilaris, prickly heat.
How to cure folliculitis
If an accurate diagnosis is made - folliculitis You must follow your doctor's orders. They will depend on the nature of the disease:
- bacterial folliculitis is treated with antibacterial ointments - Erythramecin or tablets intended for oral administration - Cephalexin and Dicloxacillin;
- fungal - antifungal agents, as a rule, such drugs include Flucanazole, Intraconazole and Bifonazole 1%;
- in the case of a gram-negative type of disease, attention should be paid to restoring immunity;
- in the presence of diabetes mellitus, special treatment methods are considered - a therapeutic diet, special medications.
For the treatment of folliculitis, brilliant green, fucarcin, salicylic acid, special lotions and creams from the Klerasil series can be prescribed. In case of severe forms of the disease, antibiotics from the “sulfonamide” group and compresses with ichthyol ointment may be prescribed.
In some cases, the state of health is reflected in a person’s skin, and, despite the fact that folliculitis is infectious in nature, its development can be facilitated by malfunctions of any body systems. Therefore, it is important to promptly consult a doctor if you have suspicious symptoms, which will make it possible to maintain the health and aesthetic appeal of the skin.
The site provides reference information for informational purposes only. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. All drugs have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required!
Concept. Definition
Folliculitis refers to skin diseases and is a form of superficial pyoderma.
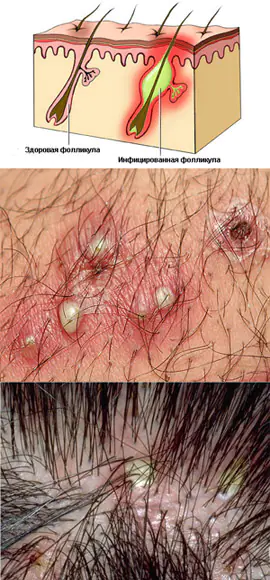
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the upper parts of the hair follicles. The inflammation that occurs with folliculitis is infectious. The mechanism of development of the disease is that first a papule is formed at the mouth of the follicle, then a pustule is formed, which is penetrated by hair in the center. The next stage is the formation of a crust in the follicle area. If the inflammatory process goes deeper and affects the entire follicle, and not just its upper section, then the disease is called sycosis. The disease has its favorite localization sites, which include parts of the body with an abundance of vellus hair. In this regard, folliculitis most often affects the extensor surfaces of the legs and arms, and the scalp.
Epidemiology. Statistical data
Folliculitis most often occurs in hot countries, where the climate is favorable for the development of inflammatory skin diseases. Also, this disease occurs more often in socially disadvantaged sections of society, which is facilitated by unsanitary living conditions.
Folliculitis is often of an occupational nature and is observed in people whose work involves constant exposure to reactive agents: gasoline, kerosene, tar, lubricating oils, etc.
Accurate statistics are not provided, since in most cases such patients rarely seek medical help, preferring to self-medicate. Doctors most often come to the attention of patients who have developed complications due to folliculitis: phlegmon, abscess or lymphadenitis.
Clinical symptoms of folliculitis
In the initial stage of the disease, redness of the skin in the area of the inflamed follicles and moderate pain are noted. Simply put, pustules form on the skin around the hair. In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, the inflammatory process progresses and causes the formation of an infiltrate in the affected area. The surface of the skin in the area of the inflamed follicle takes on a cone-shaped or spherical shape and has a yellowish color, which is associated with the accumulation of pus. After removing the covering of the pustule, pus is determined, after removal of which, an area of saturated red color is visible.
The number of folliculitis can vary: from 1-2 to a huge number. In some cases, patients complain of severe itching in the area of folliculitis. In severe cases, when the number of inflamed follicles is very large, the patient may experience an increase in lymph nodes (local).
Features of different types of folliculitis
Pseudomonas folliculitis is caused by the pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This type of folliculitis is also known by another name - “hot bath” folliculitis, because it usually occurs after taking a bath in hot water that has not been sufficiently chlorinated. Gram-negative folliculitis develops in immunocompromised patients who have been taking antibacterial medications for a long time due to acne. It is characterized by the fact that the patient’s condition worsens sharply, which manifests itself in increased acne. Abscesses may form. Folliculitis caused by dermatophytes. This infection typically begins with the upper layer of the epidermis, after which the inflammatory process seizes the mouths of the follicles, and then the hair shafts. A complication in this case is dermatophytosis of the scalp. Folliculitis, caused by fungi belonging to the genus Pityrosporum, is characteristic of tropical and subtropical climates. It is characterized by an itchy rash of a monomorphic nature (papules and pustules), which is located at the mouths of the follicles. In such patients, scratching is found localized in the shoulders, back, face and neck. Depilatory folliculitis of smooth skin is another type of disease that occurs mainly in hot countries. Middle-aged men are more susceptible to the disease. Also, this type of folliculitis is characterized by symmetry of the lesion. Inflamed follicles appear evenly on the skin of the lower extremities. After eliminating folliculitis, characteristic follicular scars remain on the skin. Gonorrheal folliculitis is the most rare compared to other types of this disease. Its location is the foreskin in men and the perineal area in women. Occurs with long-term and untreated gonorrhea. When examining the contents of pustules in such patients, gonococci are found in large quantities. Occupational folliculitis develops in people of certain professions and is associated with exposure to irritating chemicals on the skin. With this type of disease, rashes are usually localized on the back of the hands, as well as on the extensor surfaces of the forearms. Impetigo Bockhardt, despite its name, nevertheless belongs to the group of folliculitis. In this case, hemispherical, superficial pustules appear, which can range in size from a poppy seed to a lentil. The pustules are permeated with vellus hair and are arranged in groups. The reason for the development of this folliculitis is increased sweating and maceration of the skin, which is a consequence of the use of warm compresses. Tick-borne folliculitis. Develops after ticks, lasts longer than other varieties, requires specific treatment of the underlying disease (if the tick poses an epidemiological danger). Eosinophilic folliculitis. Observed only in an isolated group of patientsClassification
Folliculitis is classified according to various criteria. The classification below is based on the immediate cause that led to the development of this disease:
- Bacterial (staphylococcal, pseudomonas folliculitis, gram-negative);
- Fungal (candidiasis caused by dermatophytes, folliculitis caused by Malassezia furfur);
- Syphilitic;
- Parasitic (Demodex folliculorum mite);
- Viral (caused by herpes zoster and herpes simplex viruses, molluscum contagiosum virus).
According to the degree of damage, folliculitis is divided into:
- Superficial. This type is characterized by small pustules (2-5 mm in diameter). The pustules have a hemispherical or conical shape, are penetrated by hair in the central part, and are connected directly to the mouths of the hair funnels. Around the pustules there is a small inflammatory rim, colored pinkish-red. Pain may be completely absent or minimal. The duration of the disease is 2-3 days, after which the contents of the pustules turn into a brown crust. After the crust is rejected, areas of pigmentation and peeling may remain.
Based on the number of inflamed follicles, the disease is classified into:
- Single folliculitis;
- Multiple folliculitis.
According to the course, folliculitis is classified into:
- Complicated;
- Uncomplicated.
Causes of folliculitis
Folliculitis is an infectious disease, therefore it can be caused by pathogens of various kinds: bacteria, herpes viruses, fungi. Despite the fact that folliculitis is caused by certain pathogens, many other factors and concomitant diseases also play an important role. They are divided into two groups:
Exogenous (external) factors:
- Skin microtraumas;
- Skin contamination;
- Incorrect or untimely application of occlusive dressings;
- Climatic conditions (high humidity and ambient temperature);
- Habit of wearing tight or tight synthetic clothing;
- Hypothermia.
Endogenous (internal) factors:
- Anemia;
- Diabetes;
- Lack of adequate nutrition;
- Liver diseases;
- Treatment with drugs from the group of immunosuppressants;
- The use of glucocorticosteroids locally, especially under an occlusive dressing.
There are also a number of disorders in the body that indirectly contribute to the development of folliculitis. These include :
- Periodontal disease;
- Gingivitis;
- Caries;
- Chronic tonsillitis;
- Chronic pharyngitis;
- Obesity.
All these conditions are characterized by the fact that they weaken the body’s immune defense, which becomes unable to provide adequate resistance to skin infections.
Complications of folliculitis
In most cases, folliculitis is mild and does not pose a real threat to human life. In some cases, complications may develop. As a rule, complications develop in the absence of adequate treatment, non-compliance with personal hygiene rules and insufficient immune response of the body.
Complications of folliculitis include:
- Furuncle (and this in turn can lead to the development of lymphadenitis and hidradenitis);
- Carbuncle;
- Abscess;
- Dermatophytosis of the scalp (with folliculitis caused by dermatophytes);
- Formation of follicular scars.
In isolated cases, such severe complications due to folliculitis as nephritis, meningitis and severe forms of pneumonia have been described.
Diagnostics
In diagnosing folliculitis, an important role is played by examining the patient. The rash with folliculitis is quite characteristic and allows you to reliably establish the diagnosis. Additional examinations make it possible to establish the cause that led to the development of the disease.
Nature of the rash
Papules or pustules are characterized by the fact that they are located at the mouths of the hair follicles. There are rims of hyperemia around them. Most often, the inflamed follicles are located close to each other in a disorderly manner.
Anamnesis (information about the onset of the disease, predisposing and preceding factors) also plays a role in making a diagnosis.
To establish the nature of the disease, a microscopic analysis of the Gram smear and bacteriological culture of the contents of the pustules are performed. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed.
A blood test is also required to determine blood sugar levels in order to rule out undetected diabetes mellitus, which can also be the cause of the disease.
Differential diagnosis
- Inflammation of the hair follicles of a non-infectious nature;
- Rosacea;
- Acne vulgaris;
- Exposure to chemicals (chlorine);
- Toxicoderma of medicinal origin (lithium, corticosteroids, bromine preparations);
- Kirle's disease.
- Follicular keratosis;
- Diffuse neurodermatitis;
- Ingrown hairs;
- Vitamin deficiencies C and A;
- Devergie's disease;
- Lichen planus (follicular form);
- Discoid lupus erythematosus;
- Prickly heat;
- Necrotic acne;
- Scurvy;
- Grover's disease.
Treatment
In the initial form of the disease, fairly simple but effective methods of treating folliculitis are used. Treatment of pustules is carried out with 2% camphor or salicylic alcohol, 2% solution of brilliant green, fucorcin or a solution of methylene blue. Remember, you can only use 1% and 2% salicylic alcohol, high concentrations are excluded. Salicylic acid is part of the Klerasil series creams, gels and lotions specially created for the skin.
In cases where the folliculitis is deep and the accumulation of pus is significant, it is recommended to open the pustules, remove the pus, followed by treatment with one of the listed solutions.
For deep forms of folliculitis, it is recommended to apply compresses with ichthyol 1-2 times a day.
Chronic recurrent forms of folliculitis require the use of stronger medications. In these cases, drugs from the sulfonamide group and antibiotics are prescribed. In this form, immunostimulating therapy is also indicated.
When using local remedies, it is not recommended to squeeze the affected area or try to squeeze out pustules, as this increases the risk of developing a boil, and in severe cases, phlegmon.
Ultraviolet irradiation has proven itself as a non-drug therapy for folliculitis. Suberythemal doses are prescribed every other day or daily. The general course is 6-10 exposures.
If folliculitis develops against the background of diabetes mellitus, then a corrective diet is additionally prescribed. When carbohydrate metabolism is normalized, the risk of relapse of the disease is greatly reduced.
Mupirocin ointment is prescribed locally 2 times a day. Cephalexin, dicloxacillin, erythromycin or methicillin are prescribed orally. The antibiotic is selected based on the body’s specific sensitivity to antibacterial agents.
Pseudomonas folliculitis
In severe cases, ciprofloxacin is prescribed.
Folliculitis caused by gram-negative bacteria
Antibiotics should be discontinued. Local therapy with benzoyl peroxide is prescribed.
Fungal folliculitis
Locally specific antifungal agents are prescribed. It is recommended to take itracanozole, terbinafine, and fluconazole orally.
Herpetic folliculitis
The drug acyclovir is prescribed orally.
In the treatment of folliculitis, a huge role is given to traditional methods of treatment, which have successfully proven themselves and are recognized by official medicine.
Let's look at some of the most common and effective traditional medicine recipes.
- Decoction of viburnum and rose hips
The decoction contains: viburnum berries - 200 grams, rose hips - 200 grams, dried nettles - 100 grams. Here we also add nut shells, always green - 10 grams, fresh homemade cottage cheese - 50 grams, bee honey - 50 grams, water - 2 cups.
How to prepare a healing infusion? We take ripened and washed viburnum berries, as well as rose hips, and combine them with nettles and nut shells. Pour boiling water over the dry mixture and simmer on low heat for 10 minutes. After this, the mixture should sit for 24 hours, then filter it. We have prepared the basis for future applications. When we begin treatment, we make a mixture of fresh cottage cheese and honey and add two tablespoons of decoction to them. Place the mixture of vorog with viburnum decoction on the affected area of the skin 3 times a day for 20 minutes. - Chamomile decoction
Chamomile is a magician for relieving inflammation. Wash with its decoction, prepared in accordance with the instructions on the medicine box, at least three times a day. The same decoction can be applied to any other areas of the skin that show signs of folliculitis. Chamomile will remove inflammation from the skin and dry it. - Hot towel
To prevent staphylococcal folliculitis, use the old and proven folk method, it will help prevent the onset of the disease. After shaving, apply a damp, hot towel to your face for just a minute. - Dandelion officinalis
This herbal infusion is drunk internally. It is prepared from the roots, or together with the leaves.
Pour one glass of boiling water into two, level teaspoons of small and well-dried leaves and boil for 10 minutes. Strain the broth and take 50 ml 4 times a day. - spinyleaf
We use thorny leaves as an effective external folk remedy. Take 50 g of root and cook in half a liter of water for 30 minutes. Remove the broth from the heat and continue to steep for one hour, do not forget to strain. Used by patients for compresses, baths and soothing dressings. - Cleavers
Here we use flowers, that is, the above-ground part of the plant, as raw materials. Sprinkle the dried powder from the plant onto the sore spot under a medicinal bandage. - woodruff
Everything is very simple here: fresh, just prepared pulp from the leaves is applied topically under a medicinal bandage to the site of the abscess. Be sure to change the bandage 2 times a day. - Tatarnik prickly
This plant is also called thistle. As in the previous recipe, we use it topically, make a fresh paste from the leaves of the plant and apply it to the affected area. - Burdock
We drink the decoction internally. To do this, boil chopped burdock root (1 tablespoon) in 500 ml of water for 10 minutes, leave for 1 hour, filter. Take 50 ml 2 times a day.
Forecast
For folliculitis, the prognosis is considered favorable. With a significant depth of the lesion, foci of pigmentation may remain after the crust falls off. Complicated folliculitis is rare, but it is successfully treated by doctors.
Under favorable conditions, the pustule dries into a crust, which soon falls off, the infiltrate gradually resolves, and after 6-7 days only pigmentation or, with a significant depth of the lesion, a scar remains in place of the former folliculitis.
Folliculitis means “inflammation of the hair follicle.” This process accompanies a group of skin diseases caused by staphylococcal infection. Folliculitis belongs to pyodermatitis - pustular skin diseases, the most common of dermatoses.
Pyoderma accounts for half of the cases of temporary disability due to skin diseases. A considerable proportion of them belong to folliculitis. They can occur in different people, but most often they affect representatives of certain professions - miners, builders, metallurgists, and transport workers. In this regard, pyodermatitis and folliculitis in particular are socially significant diseases, in the fight against which both the state and employers in the most dangerous industries from the point of view of dermatological morbidity should participate.
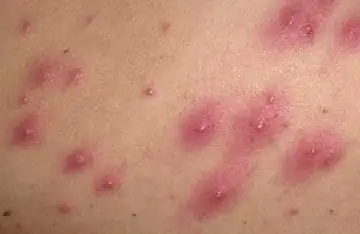
What it is?
Folliculitis is an infectious disease characterized by purulent inflammation that affects the hair follicles of the middle and deep sections. The disease has different causes: parasitic, viral, fungal and bacterial. Characteristic manifestations of folliculitis are multiple or single pustules appearing in places where hair grows, through which the hair passes.
Reasons for development
Inflammation of the hair follicles is initiated by pathogenic microorganisms: fungi, mites, viruses and bacteria. It becomes a place of residence for these organisms due to external factors or due to human health problems.
Thus, the causes of folliculitis are conventionally divided into:
- exogenous (external circumstances);
- endogenous (diseases that create optimal conditions for the life of pathogenic organisms).
Among the endogenous factors are:
- liver diseases;
- obesity;
- low hemoglobin;
- diabetes;
- malnutrition, due to which the body experiences a deficiency of certain substances.
Exogenous causes include:
- high ambient temperatures;
- hypothermia of the body;
- skin injuries (cracks or microcracks);
- incorrectly selected clothing (made from “non-breathable” and (or) synthetic materials, tight);
- skin contamination caused by poor hygiene or specific human work (work on the ground, activities requiring contact with certain reagents, chemicals (locksmith, car service employee, etc.).
Sometimes folliculitis is initiated by strange, not at first glance, reasons: caries, tonsillitis, gingivitis, pharyngitis, periodontal disease.
It would seem, how can a hair follicle on the arm become inflamed due to a sore mouth or throat? The point here is pathogenic microorganisms localized in the mouth and throat. They are carried by the blood throughout the body, without even passing through the hands. A weakened immune system is unable to put up a reliable barrier around healthy organs: bacteria (viruses) reach the hair follicles and settle there.
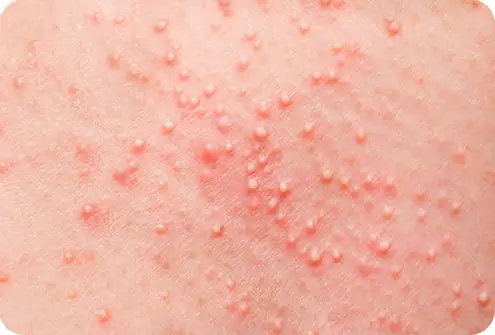
Folliculitis symptoms
The symptoms of folliculitis will depend on the type of folliculitis you develop. For example, with the superficial type, pustules can reach sizes up to 0.5 mm in diameter and be painless to the touch. As a rule, there is a pink inflammatory area around them, sometimes with a reddish tint to the skin. Approximately on the third day, the ulcers dry out and become covered with a brownish crust, leaving a slight peeling behind. The appearance of pigmentation on the skin may also be present.
The deep form of folliculitis is manifested by more severe damage to the hair follicle. Reddish nodules up to 1 cm in diameter may appear on the skin and are painful. On their surface there is an abscess, which is penetrated by a hair. The abscess can usually open within a few days, become covered with a crust, and the inflammatory nodule disappears over time.
The main complaints of a patient with folliculitis are pain and itching. In some cases, there may be enlargement of the lymph nodes that are located near the area of inflammation. The patient may also be concerned about a cosmetic defect on the skin that remains after folliculitis. This could be excess pigmentation or scars.
Staphylococcal folliculitis manifests itself in the initial period as a process of inflammation around the hair, beginning the development of ostiofolliculitis, or staphylococcal impetigo. These are small-shaped and sized pustules with dense walls, which are pierced in the center by a hair. After a few days, the pustule dries out, forming a cone-shaped yellow crust, which is quickly rejected.
If conditions are not good for the patient, painful sensations occur in the affected area, which especially bothers the patient if there is a large number of folliculitis; in this case, a pronounced infiltrate appears. Due to the involvement of the tissue surrounding the follicle in the inflammatory process and the fusion of specific elements of the rash, deeper, long-lasting varieties of staphyloderma, carbuncle, furuncle, etc. appear.
In diagnosing a disease such as folliculitis, an important role is played by examining the patient. Rashes with folliculitis are very characteristic and allow a correct diagnosis. Additional examination measures will help to accurately identify the cause that could lead to the development of the disease.
Features of different types of folliculitis
There are many types of folliculitis, and therefore, from a practical point of view, it is advisable to consider separately the characteristics of each of them.
- Herpetic. Just like staphylococcal, it is more common in men who shave in the area of the nasolabial triangle and on the chin.
- Kleshchevoy. It develops after a tick bite, lasts longer than other varieties, and requires specific treatment of the underlying disease (if the tick poses an epidemiological danger).
- Eosinophilic. It is observed only in an isolated group of patients (HIV-infected).
- Candida. This type of folliculitis usually occurs under occlusive dressings. The risk of developing folliculitis increases with topical use of drugs from the group of corticosteroids under a bandage. Also, the risk of the disease is higher in bedridden patients and long-term feverish patients.
- Staphylococcal. Characteristic of areas where bristly hair grows (nasolabial triangle, chin). It occurs mainly in men who shave. In severe cases, when the death of hair follicles occurs, after the end of the inflammatory process, connective tissue scars are formed.
- Acne. This type of folliculitis is a consequence of syphilis. It is characterized by the fact that the inflamed follicles acquire a faded red color and, in some cases, are located in groups. Elimination of this pathology is possible only by treating the underlying disease with specific agents.
- Gram negative. Develops in patients with weakened immune systems who have been taking antibacterial medications for a long time due to acne. It is characterized by the fact that the patient’s condition worsens sharply, which manifests itself in increased acne. Abscesses may form.
- Pseudomonas. Caused by the pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This type of folliculitis is also known by another name - “hot bath” folliculitis, because it usually occurs after taking a bath in hot water that has not been sufficiently chlorinated.
- Folliculitis, caused by fungi belonging to the genus Pityrosporum, is characteristic of tropical and subtropical climates. It is characterized by an itchy rash of a monomorphic nature (papules and pustules), which is located at the mouths of the follicles. In such patients, scratching is found localized in the shoulders, back, face and neck.
- Folliculitis caused by dermatophytes. This infection typically begins with the upper layer of the epidermis, after which the inflammatory process seizes the mouths of the follicles, and then the hair shafts. A complication in this case is dermatophytosis of the scalp.
- Gonorrheal. It is most rare compared to other types of this disease. Its location is the foreskin in men and the perineal area in women. Occurs with long-term and untreated gonorrhea. When examining the contents of pustules in such patients, gonococci are found in large quantities.
- Professional. It develops in people of certain professions and is associated with exposure to irritating chemicals on the skin. With this type of disease, rashes are usually localized on the back of the hands, as well as on the extensor surfaces of the forearms.
- Impetigo Bockhardt, despite its name, nevertheless belongs to the group of folliculitis. In this case, hemispherical, superficial pustules appear, which can range in size from a poppy seed to a lentil. The pustules are permeated with vellus hair and are arranged in groups. The reason for the development of this folliculitis is increased sweating and maceration of the skin, which is a consequence of the use of warm compresses.
- Depilatory folliculitis of smooth skin is another type of disease that occurs mainly in hot countries. Middle-aged men are more susceptible to the disease. Also, this type of folliculitis is characterized by symmetry of the lesion. Inflamed follicles appear evenly on the skin of the lower extremities. After eliminating folliculitis, characteristic follicular scars remain on the skin.
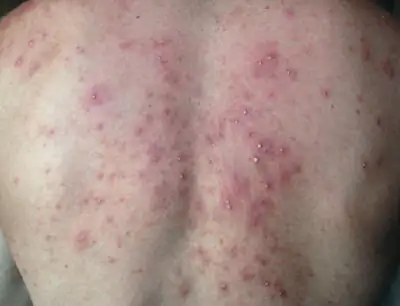
What folliculitis looks like: photo
The photo below shows how the disease manifests itself in humans.
Diagnostics
Dermatologists must examine the rash and conduct a dermatoscopy, which will show the depth of the lesion. The specialist can also refer the patient to donate discharge from the pustules, which will be required for:
- microsporia;
- research on fungi;
- bacteriological culture;
- tests for Treponema pallidum.
There is also a need for differential diagnosis. Folliculitis should be distinguished from pathologies such as syphilis and gonorrhea. In this case, the doctor prescribes:
If necessary, the specialist will prescribe blood sugar testing and an immunogram. In addition to gonorrhea and syphilis, the disease should be differentiated from the following:
- phrynoderma;
- streptococcal impetigo;
- Hoffmann's perifolliculitis;
- drug toxicoderma;
- furunculosis;
- pink lichen of Zhiber;
- nodular cystic acne.
The treatment required for hair folliculitis, as well as ailments on the legs, pubis, face, back, and skin, is described below.
Complications
In most cases, this disease does not cause serious consequences for human life and health. But if there is no proper treatment, the infection penetrates deeply and the disease becomes more complicated. The situation is aggravated if the patient neglects the rules of hygiene, and also if he has a significant weakening of the immune system.
Complications of the disease include the following:
- furunculosis and carbuncles;
- dermatophytosis;
- formation of scar tissue;
- tissue decay.
Scars and cicatrices are formed as a result of attempts to squeeze out pus from inflammatory elements.
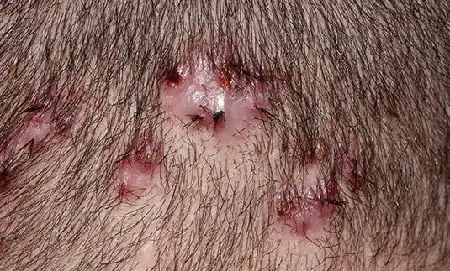
How to treat folliculitis?
Single ostiofolliculitis can go away on its own, without additional treatment. To avoid complications, you can use antiseptic skin hygiene products.
In more severe cases, the following drugs are used:
- Bactericidal ointments and solutions dry the skin and relieve inflammation: Methyluracil, Betadine, Miramistin, zinc ointment. Apply 1-3 times a day;
- Antibiotics topically twice a day - effect on staphylococcus (erythromycin, syntomycin ointments, Levomekol)
- Wiping the skin with alcohol solutions (boric, salicylic, camphor alcohol, brilliant green, methylene blue);
- Antiallergic drugs to reduce itching - Suprastin, Claritin, Lomilan;
- Pure ichthyol is applied in a thin layer to large folliculitis, and an antiseptic bandage is applied on top (change once a day);
- Physiotherapy: UV irradiation, UHF, laser therapy.
Proven methods and recipes of traditional medicine:
- Compresses, soothing bandages with thorny leaves. Boil 50 g of root in 0.5 liters of water for half an hour. After an hour, strain. Use the decoction daily.
- Chamomile decoction is a valuable remedy for inflammation. Per liter of water - 1 tbsp. l. colors. Steam, let it brew for 30 minutes, strain. Carry out the procedure in the morning, afternoon and before bed.
- Tatarnik prickly. Excellent relieves inflammation. Grind the leaves, grind them, apply the paste to the rash areas. Keep for 30 minutes.
- Headbands with woodruff. Cover the ulcers with a paste of fresh leaves. Carry out the procedure 2 times a day.
- Dandelion infusion. Wash roots, leaves, chop, 2 tbsp. l. raw materials pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, boil for 10–15 minutes. Strain the infusion that has been steeped for half an hour. Drink a quarter glass 3 times a day.
- Burdock decoction. Pour a spoonful of crushed root into 0.5 liters of water. Boil for 10 minutes, let sit for an hour, strain. Take the healing infusion twice a day before meals.
- Effective applications. Prepare a decoction: pour 2 tbsp. water 200 g of rose hips, the same amount of viburnum, add 100 g of nettle, 10 g of green walnut shells. Simmer on fire for 10 minutes. The decoction is infused for a day. Mix 50 g of fresh cottage cheese and honey. Dilute the curd-honey mixture with a decoction, apply it 3 times during the day for 15–20 minutes.
If the lesion is large, then oral antimicrobial drugs are prescribed - Erythromycin, Azithromycin, Cephalexin, Amoxicillin. Before using any of these remedies, consult your doctor!
During treatment, avoid contact with water and do not visit the sauna, swimming pool or shower.
Nutrition
Diet is not necessary when folliculitis occurs. But there are concomitant diseases for which dietary adjustments are necessary. Patients who are obese or have diabetes should follow a low-carbohydrate diet.
It is important to adhere to the following dietary rules:
- The consumption of animal fats should be limited.
- Eliminate flour products, spices, chocolate, sweets, alcohol, strong coffee and tea from your diet.
- Eat as many fresh vegetables as possible to provide your body with the required amount of fiber. You can also eat bran.
- You should include a sufficient amount of protein in your diet, including animal protein. Preference should be given to lean meats such as veal, chicken and turkey.
- It is worth eating more foods rich in vitamins. Carrots, beets, rose hips, and blueberries will be especially useful.
Prevention
Prevention of folliculitis consists of the need to eliminate factors that can provoke the disease. Also, for prevention purposes, you should use soap with an antiseptic effect and regularly treat the skin with benzoyl peroxide, which has excellent disinfecting and keratolytic properties.



