Description and causes of gastroduodenitis. Main symptoms and diagnosis. Methods of treatment, prevention.
The content of the article:- What is gastroduodenitis
- Reasons for development
- Main symptoms
- Treatment options
- Medicines
- Folk remedies
- Diet
Gastroduodenitis is a disease of inflammatory origin that affects the pyloric sections of the stomach and duodenum. Accompanied by weakness, pallor, weight loss, and pain. During therapy, they adhere to a diet and the basic principles of a healthy lifestyle, and use medications recommended by a gastroenterologist.
What is gastroduodenitis?
Gastroduodenitis is an inflammatory pathology that affects the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. The primary form of the disease is most often observed in schoolchildren and preschoolers, the secondary form - in young and middle-aged people. This is due to the peculiarities of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract at an early age.
Exacerbation of gastroduodenitis can be caused by exposure to irritating factors: unhealthy food, unfavorable external conditions, Helicobacter infection. The course of the disease is aggravated by eating unhealthy foods (sweetened carbonated drinks, crackers, chips).
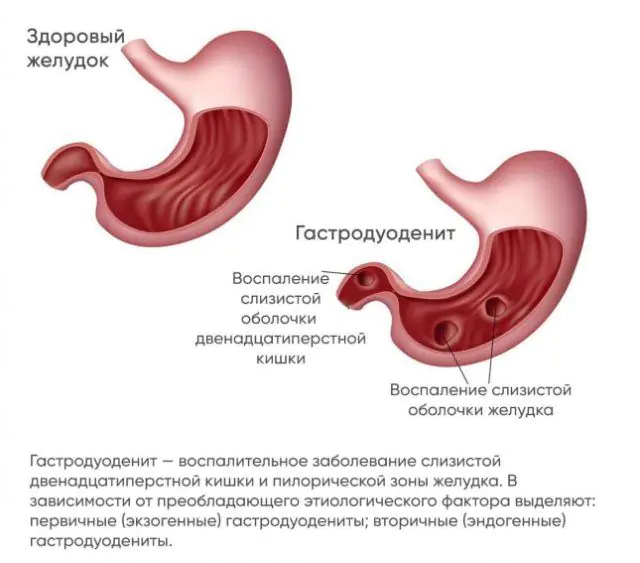
Doctors distinguish between acute and chronic gastroduodenitis. The inflammatory process leads to disruption of motility and the production of gastric juice, making normal digestion of food difficult. As a result of the penetration of bile acids into the stomach area, the formation of duodenogastric reflux is observed.
Gastroenterologists distinguish the following types of gastroduodenitis:
- Surface - leads to moderate inflammation of the mucous membrane, with no erosion.
- Hypertrophic - accompanied by a pronounced inflammatory reaction, due to which the structural elements of the mucous membrane change.
- Erosive - ulcers form on the surface of the mucous membrane.
- Atrophic - leads to thinning of the mucous membrane and disruption of the functioning of the glands that are located on it.
- Mixed - this diagnosis is made when several types of pathological process are combined.
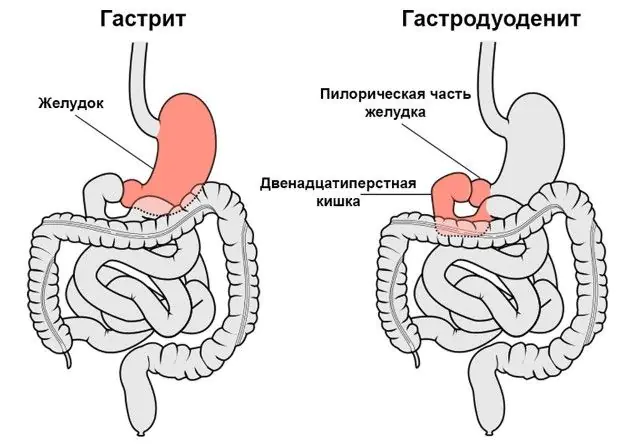
With autoimmune gastroduodenitis, the production of antibodies to the own tissues of the gastrointestinal tract is observed. This form of the disease occurs in no more than 3% of cases and is most often caused by exposure to the Epstein-Barr virus infection. The course of the disease is possible with high or low acidity.
The lack of high-quality, timely therapy leads to the transformation of gastroduodenitis into peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum.
Reasons for the development of gastroduodenitis
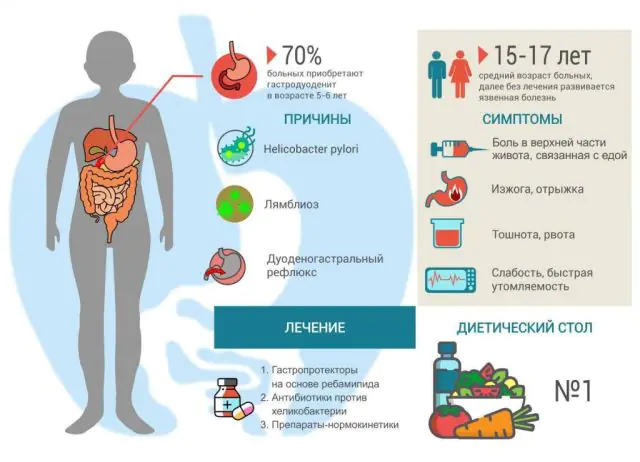
The causes of gastroduodenitis are associated with the influence of external and internal factors.
Among the external causes that can lead to the progression of the pathological process are exposure to bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse, caffeine), unhealthy diet (fatty, heavy, spicy, excessively cold or hot food), work in hazardous industries (constant interaction with metals, alkalis, acids, etc.).
The disease is also observed in patients who take long-term, uncontrolled use of certain groups of drugs: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, cardiac glycosides and other medications that cause damage to the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract.
Important! The main factor that leads to the development of the pathological process is exposure to the infectious pathogen Helicobacter pylori.Among the internal factors that can provoke gastroduodenitis are the effects of diseases of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, pituitary gland, hypoxia, hematogenous gastritis, allergies, and hormonal disorders. The disease can cause the contents of the duodenum to backflow into the stomach. The combination of bile acids with hydrochloric acid leads to the formation of compounds that damage the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract.
Main symptoms of gastroduodenitis
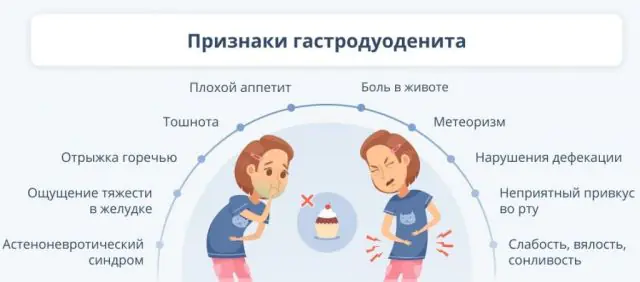
Symptoms of gastroduodenitis appear depending on the type of pathological process, the nature of the inflammation and its location, age and the presence of a history of concomitant disorders.
Acute gastroduodenitis begins suddenly, is accompanied by intense pain, defecation disorders, deterioration in general well-being, and increased body temperature. The main manifestation is pain in the abdominal area. They are diffuse in nature, affect the upper and middle parts of the abdomen, and occur immediately after a meal. The patient complains of a feeling of fullness and squeezing. Unpleasant sensations may increase if the patient stands or walks and decrease in a horizontal position. The pain in most cases is episodic, less intense than with gastric and duodenal ulcers.
If gastroduodenitis is accompanied by inflammation of the duodenum, pain occurs at night and 60-90 minutes after eating. A small snack reduces the severity of pain.
After eating food, there are complaints of heaviness, pressure and bloating in the abdomen. At the same time, the quantity and quality of food does not affect the symptom. This disorder is associated with an insufficient amount of enzymes that are necessary for normal digestion of food.
The clinical picture is often supplemented by nausea, bitter belching, loss of appetite, unpleasant taste in the mouth, and defecation disorders. Constipation alternates with diarrhea: in the first case, damage to the duodenum is observed, in the second, an inflammatory reaction in the stomach is triggered. In some cases, the need to defecate occurs during a meal or immediately after its completion.
If the disease is accompanied by flatulence, this may indicate the addition of pancreatitis. This sign of gastroduodenitis causes pain and bloating. There are complaints of a feeling of weakness, deterioration in general well-being, and decreased performance. The addition of astheno-neurotic syndrome leads to increased irritability and dysfunction of the cardiovascular system: arrhythmia, cardialgia, and decreased blood pressure.
Atrophic gastroduodenitis is accompanied by a sudden feeling of weakness, pallor, drowsiness, and increased sweating. The pathological process often involves surrounding organs, and the functioning of the pancreas is disrupted. This can cause disruption of the absorption of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. The clinical picture is complemented by copious stools with elements of undigested food, dry hair, swelling, and flatulence.
As a result, deficiency conditions develop: protein, fats, vitamins, microelements are below normal, all biochemical reactions in the body slow down. Body weight decreases sharply, anemia occurs, dry hair and nail plates occur, and the functioning of the immune and cardiovascular systems is disrupted.
The decision on how to treat gastroduodenitis is made by a gastroenterologist after an in-person examination of the patient and a comprehensive diagnosis. Laboratory tests include a breath test to identify Helicobacter, examination of stool, gastric juice, Helicobacter smear, biopsy, general and biochemical blood test.
Instrumental diagnostics of gastroduodenitis include antroduodenal myometrium, which allows to detect spasms in the duodenum, ultrasound examination of the peritoneum to confirm or exclude concomitant pathologies, intragastric pH-metry to determine acidity levels. Using fibrogastroduodenoscopy, the condition of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum is assessed.
Methods for treating gastroduodenitis
Treatment of the disease depends on the form of the pathological process and accompanying manifestations. Patients at any stage of gastroduodenitis are recommended to adhere to the basic principles of a healthy diet. This allows you to slow down the progression of the pathological process, makes you feel better, and has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract as a whole. They also take medications recommended by the doctor.
Medicines for gastroduodenitis
The treatment regimen for gastroduodenitis is selected individually for each patient, taking into account clinical manifestations, age, and the presence of concomitant disorders.
Therapy for gastroduodenitis includes the use of the following drugs:
- Festal - a complex medicine that exhibits choleretic, lipolytic properties, restores the functioning of the pancreas. Takes part in the digestion of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, ensuring their complete absorption in the small intestine. Thanks to bile extract, the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins is restored. Festal is not recommended to be taken simultaneously with antacids or antibiotics. Dragees are used 1-2 pcs. three times a day. A higher dose is possible only with prior agreement with your doctor. The price is 120 rubles. (50 UAH). The possibility of using Mezim, Pancreatin, Enzistal is being considered as analogues.
- Urdoxa - a drug from the group of hepatoprotectors with choleretic and immunomodulatory effects. Use 1 capsule 1 time per day, before going to bed. In childhood, the dosage is selected depending on the patient’s body weight. The duration of therapy is from 2 weeks to six months. According to indications, patients are recommended to take Urdoxa for several years. Cost - 750 rubles. (290 UAH). Analogs: Grinterol, Ursodez, Ursosan, Ursofalk.
- Spasmonet - a drug from the group of antispasmodics that reduces the severity of pain. The active substance helps reduce smooth muscle tone and peristalsis, and dilate blood vessels. Thanks to the described effects, the patient feels relief. The drug is taken 1-2 tablets up to 3 times a day. Price - 70 rub. (30 UAH). Analogues: Drotaverine, No-Shpa, Spakovin.
- Derinat - an immunomodulator that accelerates the regeneration process and exhibits wound-healing properties. Reduces the severity of inflammation, affects cells that are affected by pathogenic microorganisms, increases the protective properties of the body. Cost - 300 rubles. (120 UAH). The possibility of using Erbisol is being considered as an analogue.
- Novobismol - an antiulcer drug based on bismuth, which reduces inflammation and is active against the Helicobacter bacterium. Forms a protective film on the surface of the mucous membrane, protects against erosion and ulcerative lesions. Tablets are taken half an hour before meals, 1 piece. three times a day, washed down with a small amount of water. The duration of treatment is up to 2 months. Longer use of the product is not recommended. During therapy, stool may turn dark. The price is 500 rubles. (195 UAH). Analogs: De-Nol, Escape, Ulkavix.
- Normoflorin-B - a complex based on bifidobacteria, vitamins, microelements. A biologically active food supplement is used half an hour before meals, twice a day. The drug is diluted with water or juice and drunk immediately. To increase acidity, slightly alkaline non-carbonated mineral water is used as a solvent. The temperature of the liquid should not exceed 36.9 degrees. The drug increases local immunity, increases the body's resistance to infectious pathogens. The cost is 220 rubles. (85 UAH). Baktistatin is used as an analogue.
- Kvamatel is a drug that reduces the acidity of gastric juice and exhibits an antiulcer effect. During therapy, tablets are taken 20 mg twice a day, for prevention - a single dose of 20 mg of the drug. Price - 120 rub. (46 UAH). Analogue - Famotidine.
Folk remedies against gastroduodenitis

Aloe with honey for the treatment of gastroduodenitis
Treatment of gastroduodenitis with folk remedies is carried out as a supplement to medications and diet.
Effective folk recipes for the treatment of gastroduodenitis:
- One of the most effective remedies is a combination of honey and aloe juice. 3-5 large leaves are thoroughly washed, cut, and the pulp is extracted. Mix with honey in equal proportions, take 10 mg three times a day. The resulting product reduces the severity of the inflammatory process and restores acidity levels. This recipe is contraindicated for patients with erosive gastritis, as well as gastroduodenitis, which is accompanied by high acidity.
- 0.5 kg of chopped onion is mixed with the same amount of sugar until the juice is released. Place a small container with the onion-sugar mixture on low heat and heat for half an hour until the mixture turns a pleasant golden color. Take 2 tablespoons of this onion jam twice a day. To enhance the therapeutic effect, the onion mixture is combined with Omez or Omeprazole.
- Flax seeds have an astringent and soft enveloping effect, reduce the symptoms of the disease and the severity of inflammation. 5 tablespoons of raw materials are ground in a coffee grinder and poured with water in the evening. Boil over low heat for 10 minutes, then leave for 1.5 hours. Take 50 ml three times a day before meals. The duration of therapy is 30 days.
- To reduce the severity of the inflammatory reaction, light honey is mixed with melted butter, pre-soaked and dried walnuts, and grated fresh carrots. The resulting product is placed in a glass container and stored in the refrigerator. Take 20 mg twice a day before meals.
- If the patient is bothered by heartburn and periodic exacerbations of gastroduodenitis, drinking potato juice is indicated. The tubers of the plant are grated, 200 ml of warm water is drunk and after 10 minutes they are eaten with chopped potatoes. It is recommended to refrain from eating food for 60 minutes after taking the product. After an hour, you can take porridge with the addition of vegetable milk or water. The course of therapy is 14 days, after which a break is taken. The course can be repeated periodically.
- Egg white envelops the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, neutralizes the aggressive effects of gastric juice, regenerates damaged tissue, and helps increase local immunity in gastroduodenitis. Protein contains useful substances: from proteins, amino acids, vitamins and microelements to lysozyme - a natural antiseptic that is active against Helicobacter pylori infection. In order to prevent salmonellosis, the chicken egg is thoroughly washed and soaked beforehand. After thoroughly cleansing the product, it should be drunk half an hour to an hour before the main meal.
- Patients with gastroduodenitis are often offered the use of mint to provide an antispasmodic effect, restore digestion, and reduce the severity of the inflammatory reaction. A decoction of mint also exhibits a mild sedative effect and reduces the severity of psycho-emotional stress. To prepare the infusion, fresh or dried herbs must be brewed in a thermos and left to infuse for several hours, preferably overnight. The product is taken in the morning on an empty stomach (50 ml) and subsequently before meals throughout the day.
One of the most effective methods of treating the disease is drinking juices (cabbage, potato, sea buckthorn, aloe, plantain).
Important! If alternative treatment for gastroduodenitis does not exhibit the expected therapeutic effect and the patient’s well-being worsens, it is necessary to contact the attending physician again.Diet for gastroduodenitis

A diet for gastroduodenitis involves the use of soft food at a comfortable temperature, so as not to provoke mechanical and thermal damage. In the chronic form of the disease, split meals are indicated - up to 5 times a day. It allows you to restore normal synthesis of mucous secretions, as well as acidity levels.
The diet should be enriched with proteins, healthy fats, and carbohydrates. The menu includes broths based on lean chicken fillet, fruits, vegetables, and cereals.
Dairy products are used with extreme caution, observing the body's reaction.
Eating spicy and smoked foods is not allowed. Avoid fried foods, baked goods, alcohol, nicotine, rich meat and fish broths, soda, caffeine, spinach, and radishes.
Important! Therapeutic nutrition for gastroduodenitis is followed during periods of exacerbations.How to treat gastroduodenitis - watch the video:
To prevent gastroduodenitis, recommendations from doctors include maintaining a healthy lifestyle, stopping drinking alcohol and smoking. Moderate physical activity and restoration of the immune system are preferable. The diet includes fresh vegetables and fruits, protein, cereals, and whole grains. Even after stable remission has been achieved, it is recommended to adhere to the basic principles of a healthy lifestyle. If the pathological process worsens, you should refrain from self-medication and seek advice from a doctor.



