
Hives – an allergic skin condition, manifested in the form of redness, itching and characterized by the appearance of blisters or papules.
Generalized urticaria (ICD10 code L50) differs from the usual large area of distribution of the rash - the rash often fills the entire body of the patient.
Symptoms and manifestations
Symptoms of generalized urticaria is similar to the symptoms of any other form of urticaria, but is characterized by increased severity and the presence of general malaise of the patient:
- A rash in the form of blisters (swellings) on the skin of pink or red (usually burgundy) color, surrounded by an inflamed, reddened area. The rashes are usually round or oval in shape, can reach up to 15 centimeters in length, are often itchy, vary in size, they can merge into larger areas, thus spreading urticaria throughout the body in an adult or child;
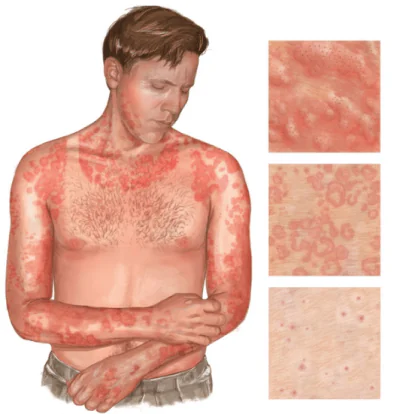
- Tissue swelling or acute Quincke's edema in the mucous membranes (throat, tongue, lips), in the stomach, in the brain;

- Dizziness;
- Burning and pain of the skin in the area of edema;
- Feeling of tightness in the chest;
- Anaphylactic shock, fainting or fainting are symptoms of acute generalized urticaria;
- Decrease in systolic pressure;
- Difficulty breathing.
Severe manifestations Generalized urticaria lasts about 2-3 days, in the absence of treatment - up to a week, then the disease goes into remission.
To know about all stages and symptoms of urticaria can be seen on video:
You can see more clearly what it looks like generalized urticaria all over the body, on photo:
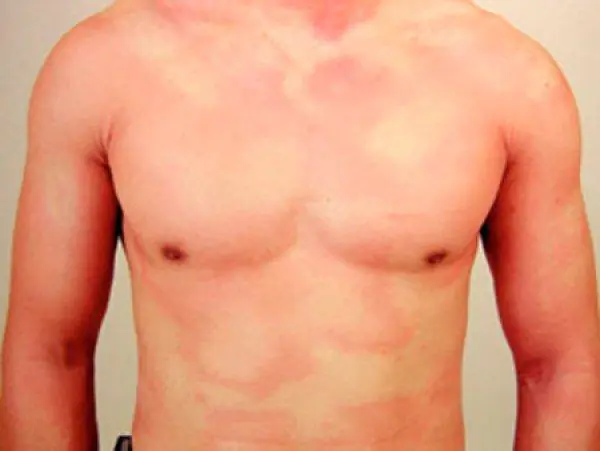
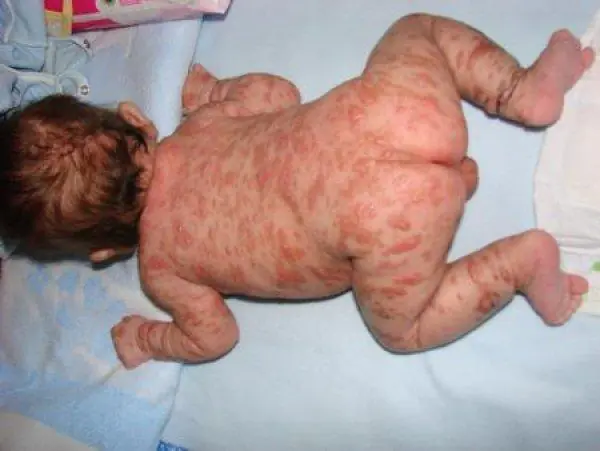
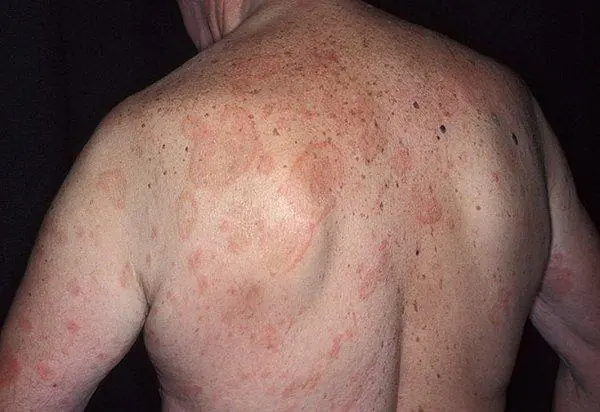
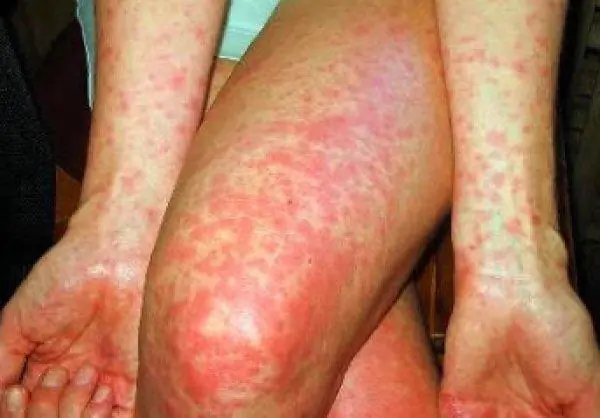
Causes
Generalized urticaria - This is an advanced form of ordinary allergic urticaria.
The rash can be caused by physical factors such as heat, cold, exercise, sunlight, stress, constant pressure on an area of skin (such as from a belt), a sudden increase in body temperature (from a fever or hot bath or shower), or from contact with irritating chemical, detergent, cosmetics or soap.
The rash may be symptom systemic allergic reaction:
- Pollen, animal hair, mold;
- Insect bites, especially bee stings, hornet stings;
- Allergies to food (tree nuts, fish and shellfish, fatty dairy products, legumes, peanuts), food additives;
- Allergy to medications, penicillin or aspirin.
Causes hives also include:
- Stress, depression, strong feelings;
- Overwork;
- Disruptions in the endocrine system;
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Fungal diseases.
Diagnostics
Allergist or the dermatologist will ask about the history of allergic reactions, as well as recent exposure of the patient's skin and body to pets, plants, insects, or new foods or medications.
During physical examination The doctor will measure the pressure, examine the patient's skin, measure its temperature, and perform several skin tests (skin testing with a blunt object for dermographism, ice test for cold urticaria, exercise bike test for cholinergic urticaria).
Specialist also may appoint:
- Complete blood count and allergen test;
- Analysis of urine;
- Analysis of stool for dysbacteriosis and analysis of worms;
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal cavity.
Treatment
First aid
As first aid the patient can:
- Eliminate exposure to the allergen (if it can be identified);
- In case of Quincke's edema, immediately call an ambulance, the patient will be given an injection of Prednisolone;
- A single dose of an antihistamine (Suprastin, Tavegil) before visiting a doctor;
- At the first symptoms of anaphylactic shock, call an ambulance immediately. Before her arrival, place the patient on a horizontal surface, with his legs slightly higher than his head.
Providing first aid for Quincke's edema on video:
Drug therapy
For relax for simple manifestations of urticaria, the doctor will prescribe:
- Anti-itch body lotion (such as Calamine lotion);
- Cream or ointment (Fenistil-gel, Gistan-N, Asmanex, Mometasone, Uniderm);
- Antihistamine drug Tavegil, Suprastin, Tavist or Benadryl 2 times a day in the morning and evening.
If these drugs are not effective, the specialist will prescribe sedative antihistamines: Cyproheptadine, Azatadine or Atarax.
The initial appointment is scheduled for the evening due to its calming effect, as well as hormonal ointments: Advantan, Prednisolone ointment, Elokom, Soderm.
For persons with significant side effects from these medications, non-sedating antihistamines may be used, including Claritin, Zyrtec, or Allegra.
In cases where the patient is resistant to such treatment, urticaria is added to the treatment. H2 receptor blockers. These include Zantac, Axid, Tagamet.
If the patient does not respond to antihistamine therapy, the doctor prescribes:
- Glucocorticosteroids to suppress the immune system in chronic generalized urticaria;
- Laxatives and diuretics;
- Bronchodilators and oxygen therapy (in the presence of bronchospasms).
At severe symptoms For generalized urticaria, your doctor may prescribe:
Reception leukotriene receptor antagonists - a type of medication that will help reduce redness and swelling of the skin.
Side effects antagonists are rare and relatively insignificant compared to taking glucocorticosteroids. These drugs include Cyclosporine, which has proven effective in treating hives by suppressing the harmful effects of the immune system, and Omaluzimab, which is given by injection and reduces the antibodies that cause generalized hives.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is aimed to eliminate symptoms mild (to moderate) form of generalized urticaria, against the background of a severe/acute form, traditional medicine will be powerless.
- Wipe your skin menthol lotion, previously applied to a cotton pad. This will help reduce itching;
- Drink more water, it is advisable to drink Borjomi;
- 400 g oat flakes Grind in a blender and add to a warm bath, take it for 30 minutes. A colloidal solution of oats will reduce itching and relieve inflammation;
- Mix valerian tincture And hawthorn (they can be purchased at the pharmacy), drink 35 drops of the mixture at night every day, wash it down with clean boiled water, this will calm the nerves, relieve itching and inflammation caused by hives;

- Pour 1 dessert spoon yarrow herbs a glass of boiling water (250 ml), leave for 45 minutes, drink 3 times a day before meals for 2 weeks;
- 250 g marjoram pour boiling water (4 liters), leave for 30 minutes, add the resulting composition to a pre-drawn warm bath, duration of the procedure is 15 minutes, course of treatment is 10 days.
Diet
Antihistamine diet includes the following principles:

Avoid or reduce your consumption of canned foods;- Avoid consuming fermented foods (blue cheeses, alcoholic beverages, foods containing yeast);
- Histamine levels in foods vary depending on how ripe they are;
- Eat only fresh fruits and vegetables;
- Eliminate red meat and sweets from your diet.
Add in the diet:
- Chicken and turkey;
- Fresh Fruits – With the exception of strawberries, most fresh fruits are low in histamine levels;
- Fresh vegetables - excluding tomatoes;
- Grains - rice noodles, rye bread, oats, puffed rice, crackers, millet flour, pasta (from corn or durum wheat);
- Fresh pasteurized milk and skim dairy products;
- Milk substitutes - coconut milk, rice milk;
- Cream cheese, butter;
- Most leafy herbs;
- Herbal teas.
Learn more about methods of treatment and prevention of urticaria Can on video:
Finally, Generalized urticaria should not be left to chance. Against the background of this disease, it is important to seek medical help.
Doctor only can prescribe adequate treatment for the disease, which will completely relieve the patient of symptoms and discomfort.
Urticaria in adults is common. This problem has occurred at least once in 20% of the world's population. Despite the fact that the causes of the pathology may vary, the symptoms and treatment methods are largely the same. Next - about the different manifestations of urticaria in adults, photos of symptoms and treatment.
Photo of Urticaria in adults 8 pieces with description
Causes and triggers of urticaria in adults
The causes of hives in adults vary. Identifying provoking factors is not an easy task even for experienced specialists.
In the vast majority of circumstances, the disease is formed on the basis of one of the pathologies. Among them:
- endocrine disorders;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract (especially gastritis and ulcers of various types);
- Liver diseases and gallbladder pathologies;
- dysbacteriosis;
- lupus erythematosus (and other systemic diseases);
- cancerous tumors;
- parasite damage (a common cause of urticaria in adults);
- allergic response of the body to an intolerable component;
- advanced infectious diseases (or bacterial);
- prolonged stress;
- hypersensitivity to high and low temperatures, as well as to sunlight.
In addition, with urticaria in adults, the cause of the pathology can be blood transfusions.
All of the above provokes weakening and improper functioning of the immune system. As a result, the body cannot cope with the load and reacts to this with rashes and swelling.
What causes urticaria in adults is not completely known even now. However, in a number of situations, the cause is precisely the functioning of the immune system.
Symptoms of urticaria in adults
Symptoms of urticaria in adults vary depending on the type of pathology. However, they are usually similar.
The general symptoms are as follows:
- intense itching (appears first);
- swelling of the skin (you can look at the photo of urticaria in adults);
- the formation of pink and reddish blisters on the skin (flat and with unclear outlines, can be different in size and localized in different areas of the body);
- weakness and malaise;
- temperature increase;
- chills;
- nausea and problems with stool;
- hyperemia.
What urticaria looks like in adults depends on the degree, nature and location of the disease:
- Urticarial vasculitis. There is inflammation of the capillary and vascular walls, which appears in the form of specific blisters. Symptoms persist for up to 5-6 days. It often appears on the face (photos of urticaria on the face of adults are available online).
- Papular form. Tissue swelling is observed. On the skin there is hyperpigmentation in the fold areas. The outer epidermal layer thickens and becomes rough. Photos of urticaria in adults on the body can be viewed online.
- Cholinergic urticaria. Appears due to the active release of a neurotransmitter. Pinkish blisters form on the skin of the entire body. May appear after stress and intense physical activity. Other symptoms include shortness of breath, heavy breathing and general weakness.
- Aquagenic type. An allergic response of the body to minerals in water. Blisters form on the epidermis. Often on your feet. Photos of urticaria on the legs of adults clearly demonstrate the situation. It passes quickly and does not have serious consequences.
- Adrenergic urticaria. A rare event. The reason is stress. A specific type of papules form on the skin surface.
- Contact type. The reason is contact with an allergen. Pinkish blisters appear on the skin, uniting into groups over time.
- Demographic. The reason is external effects on the skin. Appears as reddish blisters or straight stripes. More often - on the arms and back. Photos of urticaria on the hands of adults are also available on the Internet.
In some cases, urticaria may be complicated by other symptoms (due to a severe allergic reaction):
- severe nausea;
- developing swelling of the face and neck;
- a feeling of lack of oxygen (may be accompanied by Quincke's edema);
- loss of consciousness or faintness.
In these circumstances, you need to immediately call an ambulance, and provide first aid to the patient - administer instant anti-allergy medications inside.
The patient can also intensively comb the formations. This is fraught with infection and the appearance of pathologies such as furunculosis.
Treatment of urticaria in adults
Therapy is complex. Here's how to treat hives in an adult:
- Removing the allergen from the body. This is achieved by rinsing the stomach or nose, taking a cool shower, using eye drops, etc.
- Taking medications. The range of products includes anti-allergy drugs and general health-improving drugs.
- Taking vitamin complexes. It is an additional measure designed to improve immune function.
- For external use. The patient is prescribed ointments and gels that soothe the skin and fight inflammation (photos of urticaria symptoms in adults demonstrate the severity of the situation).
- Folk recipes. It is an additional and optional measure. Requires prior consultation with a doctor.
- Selection of diet. The allergen is excluded from the menu. More vegetables and proteins are added to the diet to strengthen the immune system.
In addition, ASIT therapy may be prescribed. The bottom line is that the immune system is gradually “accustomed” to the causative allergen. The patient is given a special drug containing a small amount of allergen. Over time, the body gets used to it and the intensity of the reaction to the provocateur decreases, gradually fading away. Therapy is carried out before contact with the allergen - about two months.
Only a doctor can tell you how to treat urticaria in adults. All remedies are prescribed in the hospital after studying the nature of the disease.
Treatment of urticaria in adults with medications
Treatment of urticaria in adults with medications includes a set of drugs from the following groups:
- Antihistamines. Designed to eliminate itching and alleviate the patient's condition. New generation drugs do not affect the central nervous system.
- Immunosuppressants. They weaken the immune response to a stimulus that is too strong.
- Glucocorticoids. Hormonal-based anti-inflammatory agents. They are characterized by the greatest effectiveness. However, they have a number of contraindications.
- Antipruritics. Usually - for external use. There are special soothing ointments for urticaria on the skin of adults.
- Immunoglobulins. Contains antibodies to the irritant. Reduces the manifestations of the disease.
- Vitamins. They have a beneficial effect on the immune system.
Medicines for urticaria in adults are used both internally (tablets) and externally (ointments and gels). As a rule - in a complex. Both have side effects. Therefore, all medications and dosages are prescribed by the doctor.
Treatment of urticaria in adults with folk remedies
For any type of urticaria, treatment in adults is possible with folk remedies. However, only in combination with taking medications.
- Potato compress. Raw potatoes are grated and the resulting mass is wrapped in sterile gauze. Apply to the affected area. Leave for 30 minutes and then rinse the area with clean water.
- Herbal baths. Made from a decoction of anti-inflammatory herbs. Plants such as chamomile (leaves and flowers), string and juniper are suitable. You can use oak bark. Any of the above is poured with water, put on gas and boiled over low heat for 2-3 minutes. Leave until the broth reaches a comfortable temperature and take a 20-minute bath. Do not wipe the skin - just blot it with napkins. The stronger the broth, the better.
- Valerian infusion. With the addition of hawthorn. Both tinctures are mixed in equal proportions. Take before bed by dissolving 30 drops in a glass of water.
- Celery root. Has a diuretic effect and eliminates swelling. The plant is grated and the juice is squeezed out through cheesecloth. Take the juice before meals 3 times a day. One tablespoon at a time. Useful for severe rashes (there is a photo of what urticaria looks like in adults in case of severe symptoms)
- Nettle infusion. Reduces the intensity of itching and strengthens the body. Take 50 grams of the plant and fill it with one bottle of vodka. Insist for 7 days in a dark place. Afterwards the mixture is filtered. Take: three times a day, one small spoon.
Only a competent specialist can tell you how to cure urticaria in adults. Therefore, before using any of the above recipes, you should consult a hospital.
Prevention of Urticaria in adults
For different types of urticaria in adults, the symptoms and treatment are often the same. The same applies to preventive measures.
To prevent the progression of pathology and possible relapses, it is necessary:
- avoid contact with the irritant;
- adhere to a competent diet with the exception of the provoking substance (or adding it in micro quantities);
- work on strengthening the immune system;
- eliminate bad habits;
- stop using aggressive household chemicals;
- do not wear uncomfortable clothes;
- avoid temperature changes;
- take medications strictly under medical supervision.
In most patients, acute pathology can be completely cured. If the disease is chronic, it is necessary to identify provoking factors and all treatment should be aimed at eliminating them. In the absence of proper therapy, the chronic form may not go away for years.
A type of rash is urticaria. It occurs at any age, but most often in children. This condition is characterized by the appearance of itchy elements on the body in the form of raised blisters. Very often, urticaria is combined with Quincke's edema.
Blisters as a type of rash
Almost everyone has experienced allergies. This condition is considered pathological, since a similar immune response does not occur in healthy people. Urticaria is a condition that combines various diseases. During life, it is detected in every third person.
This pathology was described by Hippocrates. The prevalence among the population reaches 20%. In 60% of cases, an acute form of urticaria is diagnosed. In every second patient, the rash is combined with angioedema.
The following types of urticaria are known:
- allergic;
- medicinal;
- urtical;
- idiopathic;
- physical.
The latter is divided into dermographic, cold, solar, vibration, aquagenic, cholinergic and provoked by physical effort. If the rash persists on the human body for more than 6 weeks, then we are talking about a chronic form of urticaria.
Causes and risk factors
Not everyone knows why blisters appear on the skin. The following factors play a role in the development of this pathology:
- taking medications;
- hypersensitivity to certain products;
- arthropod bites;
- contact with household chemicals;
- the presence of acute and chronic infectious diseases;
- exposure to cold;
- intense insolation;
- exposure to vibration;
- hard physical labor;
- mechanical irritation of the skin;
- autoimmune disorders;
- pathology of the nervous system;
- frequent stress;
- exposure to fungal allergens;
- hereditary predisposition.
In chronic urticaria, blisters may occur for unknown reasons. In most cases, this disease is caused by the development of an allergic reaction. Drugs often act as irritants. These may be vaccines, serums, immunoglobulins, NSAIDs, tetracyclines, sulfonamides and anti-tuberculosis drugs.
Sometimes itchy blisters form on the body after eating certain foods. The most hyperallergenic are nuts, citrus fruits, milk, fish, strawberries, eggs and seafood. In everyday life, the development of urticaria on the skin is possible due to contact with washing powder and cleaning products.
The cause may be either skin contact with an allergen or inhalation of vapors. The appearance of blisters is often observed when bitten by insects (mosquitoes, bees, wasps, hornets). The substances contained in their venom cause an acute allergic reaction. Swelling and anaphylactic shock are possible. The risk group includes adults and children who have the following diseases:
- helminthiases;
- protozoa;
- sinusitis;
- tonsillitis;
- tumors;
- mycoses;
- intestinal pathology;
- serum sickness;
- cryoglobulinemia;
- helicobacteriosis;
- lupus;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- pathology of the thyroid gland;
- hepatitis;
- diabetes;
- gastritis;
- herpetic infection.
Red spots similar to urticaria can form due to hormonal changes. This occurs during puberty, pregnancy, menopause and taking contraceptives.
Pathogenesis of disease development
Any attending physician should know the mechanism of development of urticaria. In most cases, the rash appears in response to exposure to an allergen. The mechanism of disease development can be immune or non-immune. In the first case, the appearance of blisters is based on 4 types of allergic reactions. In most cases, symptoms occur immediately after contact with the allergen.
In this situation we are talking about an immediate reaction. Symptoms of the disease appear only upon repeated contact with the allergen. When a substance first enters the body, immune, pathochemical and pathophysiological reactions develop. Protective immunoglobulins of class E are produced against a foreign substance.
Lymphocytes accumulate in tissues. Immune complexes are formed that attach to target cells. Upon repeated contact with the substance, the production of histamine, bradykinin, serotonin and heparin increases. A rash appears. There may be changes in the skin and mouth.
Hives are the result of dilation of blood vessels and release of fluid into the intercellular space.
Swelling of the papillary dermis develops. With the immediate type of response, symptoms appear within 5-30 minutes. A delayed type reaction is less common. The non-immune mechanism is simpler. In this situation, the irritant acts directly, affecting mast cells. The result is the production of inflammatory mediators (histamine, serotonin).
Clinical symptoms
The clinical manifestations of urticaria are very specific. It is difficult to confuse it with another skin pathology. The main symptoms are:
- rashes in the form of blisters;
- itching;
- swelling of tissues.
Like other diseases, urticaria can occur in mild and severe forms. In the latter case, the following symptoms appear:
- vomit;
- muscle and joint pain;
- headache;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness;
- dyspepsia;
- anxiety.
Not everyone knows what urticaria looks like. The rash consists of blisters. These are small, cavity formations about 5 mm in size. They are pale pink or red. The blisters are round in shape and rise above the skin. Their number can be in the tens and even hundreds. When you press on the skin in the area of the blisters, it turns pale for a while.
Elements of the rash are most often localized in the extremities, chest and abdomen. In children, the face is often affected. The blisters are located singly. They can merge, forming large lesions up to 15 cm in size. Signs of urticaria appear suddenly and disappear just as quickly. When elements of the rash become infected, complications in the form of suppuration are possible.
Different types of hives
Hives can manifest in different ways. Sometimes a dermographic form of the disease occurs. Its peculiarity is that blisters form in places of scratching and mechanical friction against the skin. They itch. The skin of the face, hands and other parts of the body may be affected. This pathology develops primarily upon contact with wool or chemicals.
Secondary urticaria sometimes occurs. It occurs against the background of serum sickness and mastocytosis. The main provoking factor is skin irritation. You need to know not only how urticaria manifests itself, but how to identify it. To make a diagnosis, the patient's skin is irritated with the blunt end of a spatula. The appearance of blisters indicates dermographic urticaria.
Sometimes a rash appears due to nervousness. Otherwise, such urticaria is called cholinergic. It can appear against the background of emotional stress. Most often, teenagers and young adults encounter it. If such urticaria is present, the symptoms are represented by blisters up to 5 mm in size with an area of redness. The rash itches.
The rarest form is adrenergic urticaria. It occurs under severe physical stress. The disease can manifest itself as wheezing, rash and a drop in blood pressure. With this form of urticaria, the rash quickly disappears. If symptoms occur in frosty weather or upon contact with ice water, then we are talking about a cold allergic reaction.
The main signs are rash, itching and tissue swelling. Blisters can become very itchy in the cold. After the person warms up, they disappear. Every third patient develops signs of Quincke's edema. These include an increase in the volume of the lips and cheeks, swelling of the eyelids and difficulty breathing. Some people develop aquagenic urticaria. With it, the elements of the rash are small and surrounded by red spots. Sometimes there are symptoms of urticaria without itching.
Possible negative consequences
If a sick person is not treated in a timely manner, the following complications are possible:
- swelling of the throat;
- asphyxia;
- swelling of the tongue;
- breathing problems;
- anaphylactic shock.
In 30% of cases, urticaria becomes chronic with periodic exacerbations.
A very dangerous condition is anaphylaxis. It disrupts the functioning of the heart, nervous system and respiratory organs. The following complications are possible:
- atrial fibrillation;
- extrasystole;
- collapse;
- heart attack;
- bronchospam;
- suffocation;
- convulsive syndrome;
- kidney damage;
- bronchial asthma.
If left untreated, hives can cause depression.
Patient examination plan
You need to know not only the symptoms and treatment of this disease, but also diagnostic methods. If you suspect urticaria, the following tests will be needed:
- skin allergy tests;
- application tests;
- dermatoscopy;
- general clinical tests;
- blood chemistry;
- antinuclear antibody test;
- dermographic test;
- exercise test;
- cold test;
- immunological study.
According to indications, a coprogram, analysis for parasites, ultrasound, FEGDS, electrocardiography, radiography and bacteriological analysis are performed. Sometimes liver function is assessed.
If urticaria is suspected, treatment should begin after determining its type. To do this, a dermographic study is performed, during which the doctor irritates the skin with line movements. If blisters appear after a few minutes, the diagnosis is confirmed.
An exercise test is performed to identify adrenergic urticaria. The patient is asked to run for 5-15 minutes, walk at a fast pace and take a hot bath. If blisters appear, as from nettles, then a cold reaction must be excluded. To do this, ice is applied to the human skin for 10-20 minutes. Then the body is warmed up. The presence of a reaction in the form of edema confirms the diagnosis. To identify contact urticaria, a potential allergen is rubbed into the patient's skin.
Methods of treating the disease
Sometimes this disease requires emergency help. It is necessary in case of development of anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema and lack of effect from taking antihistamines. For anaphylaxis you need:
- administration of Epinephrine, Prednisolone (Dexamethasone) and an antiallergic drug;
- resuscitation measures;
- ensuring airway patency;
- calling an ambulance.
If urticaria and shock develop due to an insect bite, then you need to remove the sting and apply a tourniquet. If the mouth swells and the person is unable to breathe, intubation or tracheotomy is performed. If there is no pulse, an indirect cardiac massage is performed. These are the basic rules for providing emergency care.
An important aspect of the treatment of patients with urticaria is the use of systemic antihistamines. These include Cetrin, Erius, Zodak, Zirtec, Loratadin, Kestin, Suprastin, Tavegil, Claritin, Fenistil, Telfast, Fexofast, Allegra, Dinox and Beksist-Sanovel. For urticaria, treatment is most often carried out with 2nd generation drugs.
For young children, syrups and drops for oral administration are best. Some drugs have a negative effect on the liver. The doctor should take this into account when prescribing medication. Leukotriene antagonists and mast cell membrane stabilizers are often included in the treatment regimen. These include Zaditen, Ketotifen and Daltifen.
If there is no effect, systemic corticosteroids are prescribed. The most commonly used are Dexamethasone and Prednisolone. Sometimes immunosuppressants (Cyclosporine) are included in the treatment regimen. You need to know not only what urticaria is and how it manifests itself, but also what ointments are prescribed for this pathology.
The most effective external medications are Fenistil and Psilo-Balm. They eliminate itching and signs of inflammation. In the treatment of urticaria, weak hormonal ointments (Sinaflan) are widely used. For skin irritation, auxiliary agents are often prescribed. These include Panthenol spray. When urticaria and rhinitis are combined, nasal drops are used.
Addition to the main treatment
Medicines alone are not enough for recovery. For urticaria, the symptoms and treatment should be known to every doctor. To get rid of this pathology, you need to:
- adhere to a hypoallergenic diet;
- do not overcool;
- do not stay in direct sunlight for a long time;
- use gloves when in contact with household chemicals;
- wipe dust regularly;
- do not walk near flowering plants;
- drink more fluids;
- wash your hands more often;
- Avoid contact with insects and ticks.
You need to know not only the reasons for the development of cold urticaria, what it is, but also how to get rid of it. People with increased sensitivity to low temperatures need to lubricate their face and other exposed areas of skin with cream before going outside in frosty weather, wear gloves and a scarf, do not wash their hands in ice water, do not swim in ice holes, harden themselves and take antihistamines for prevention.
It is important to avoid any pressure on the skin. No need to wear tight clothes. Patients with exercise urticaria should avoid strenuous work. You can't be stressed. Nutrition is an important aspect of treatment. If you have urticaria, you should exclude from the menu:
- fish;
- citrus;
- nuts;
- strawberries;
- seafood;
- cow's milk;
- spices;
- sauces;
- canned food;
- eggs;
- tomatoes;
- mushrooms;
- honey;
- sausages;
- carbonated drinks.
You cannot drink alcoholic beverages or smoke. With this pathology, you should avoid taking antibiotics and other drugs that cause a rash. Immunotherapy may be used for allergic urticaria. Such treatment is based on a gradual decrease in the body’s sensitivity to irritating substances. Such patients are given a potential allergen in diluted form. Gradually the response decreases. Thus, the appearance of urticaria is most often caused by allergies. If you have a rash, you should consult a doctor. Self-medication is the main reason for the disease to become chronic.



