Description and causes of pterygium of the eye. Main symptoms and diagnosis. Treatment methods include medications, surgery and folk remedies. Prevention.
The content of the article:- What are pterygium eyes?
- Reasons for development
- Symptoms and diagnosis
- Treatment options
- Medicines
- Surgical intervention
- Folk remedies
- Prevention
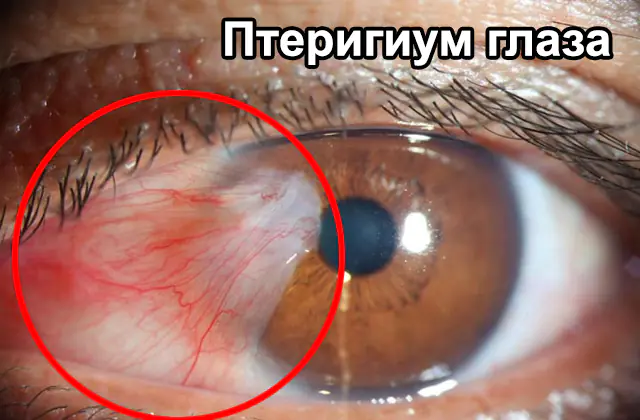
Pterygium of the eye (formation of the pterygoid hymen) is a pathological process in which the conjunctiva grows on the cornea. Such ingrowths have a triangular shape and extend all the way to the surface layer of the horny tissue. The disease is not accompanied by severe symptoms; in most cases, patients turn to an ophthalmologist due to psychological discomfort and cosmetic imperfections. Surgical therapy is performed only if the disease provokes discomfort and subjective complaints.
What are pterygium eyes?
In the photo there is a pterygium of the eye
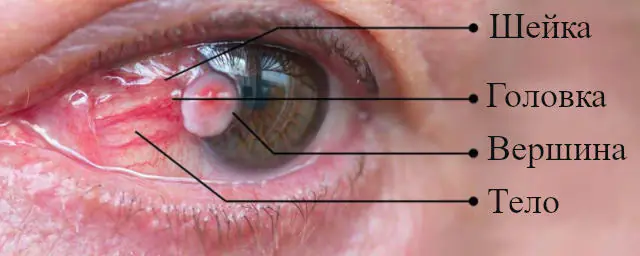
Pterygium of the eye is a pathological conjunctival fold growing on the corneal tissue. It consists of a head, neck and body, which can grow towards the inner corners of the eye, and the head and neck are often fused.
The pterygoid hymen is easy to detect for the average person without the use of additional ophthalmic instruments. It is a triangular film of gray color, the sharp edge of which is directed towards the pupil. It can affect one or both eyes, and is more often formed on the part of the olfactory organs.
Residents living in southern countries, as well as people who often spend a lot of time in the fresh air, are at risk of developing eye pterygium. The disease is more often observed in men over 45 years of age.
A predisposing factor that can provoke a disorder is a repeated inflammatory process affecting the conjunctiva. It can also develop due to a hereditary predisposition.
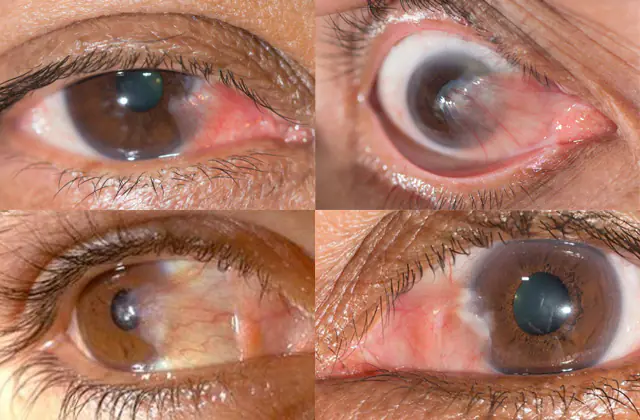
The disease has several forms. With progressive tumors, the tumor increases over time, with stationary tumors it remains unchanged.
The following main degrees of pterygium are distinguished:
- the pterygoid hymens are transparent, the vessels are easily visible through them;
- the hymen is translucent, the vessels are not completely visible;
- a highly active, opaque pterygium through which the vessels cannot be seen.
Even after surgical intervention, repeated relapses of pterygium and its complications are observed:
- symblepharon - fusion of the conjunctiva of the eyeballs with the conjunctiva of the eyelids;
- fusion of the eyelids or corneal cataract;
- impaired mobility of the organs of vision with the subsequent development of convergent strabismus.
Pterygium can lead to complications: the formation of scar tissue in the cornea, impaired mobility of the eyeballs, strabismus, and with a regular inflammatory process - malignant degeneration.
Reasons for the development of pterygium
Among the main reasons for the development of pterygium are regular exposure to an irritating factor on the cornea of the eyes:
- Increased ultraviolet or infrared radiation, which leads to dry eye syndrome;
- Prolonged stay in the open air or in a dusty room, which provokes inflammatory processes in the cornea, agricultural workers, fishermen, hunters, carpenters, joiners, plasterers are at risk;
- Spending a long time at the computer and insufficient hydration of the eyes, which leads to dryness;
- Predisposition to the development of allergic conjunctivitis;
- Regular overstrain of the visual organs;
- Exposure to dry air;
- Traumatic damage to the organs of vision.
The described factors lead to damage to epithelial cells, the development of inflammatory reactions, and a decrease in local immunity. Microcirculation is disrupted, and the process of formation of new vessels starts. All this leads to the formation of pterygium - abnormal deposition of collagen and elastin in the intercellular space.
Symptoms and diagnosis of pterygium of the eye
In the initial stages, pterygium disease is asymptomatic. The patient feels the growth of the film and may detect a visible cosmetic imperfection - a gray film. The pathology negatively affects the quality of tear films with the subsequent development of irritation, which over time transforms into an inflammatory process.
As the pathological process progresses, pterygium provokes:
- feeling of dryness;
- eye irritation;
- increased lacrimation;
- sensation of foreign bodies in the eyes.
When the conjunctival area becomes inflamed, swelling forms, redness and itching are observed.
When the pupils are blocked, visual acuity decreases. Pterygium can change the shape of the cornea, causing astigmatism, and periodically becomes inflamed.
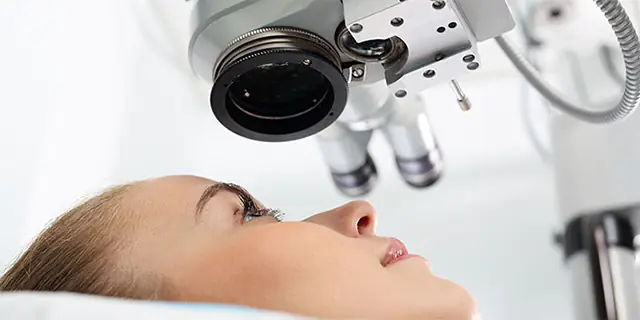
Making a diagnosis is not difficult for an experienced ophthalmologist. The golden method for diagnosing pterygium is biomicroscopy using a slit lamp. With the help of this medicine, the doctor specifically examines the conjunctival region, the anterior chamber of the eye, the lens, the vitreous body, the irises and corneas.
In order to visualize the fundus, special three-mirror Goldmann lenses are used. Biological microscopy is a painless procedure that helps identify pathological changes of an inflammatory and traumatic nature, structural anomalies, clouding of optical spheres, and possible hemorrhages.
In order to identify the degree of progression of pterygium, additional testing is prescribed:
- ophthalmoscopy, with the help of which the fundus of the eye is examined in detail and visually assessed how transparent the optical media of the organs of vision are;
- keratotopography, with the help of which the degree and form of the disease are revealed;
- morphological studies of tissues to identify vascular disorders;
- refractometry, which determines the refractive power of the organs of vision;
- visometry is a non-invasive technique that evaluates visual acuity using a special table with letters of different sizes.
For a detailed study of the pterygoid hymen, lacrimal function is examined to obtain a prognosis regarding the degree of growth and possible relapses after surgery.
Methods for treating pterygium of the eye
A small pterygium does not require specific therapy. If the pathological process spreads, surgery is performed. During therapy, cytostatics are also used, which inhibit the functioning of the immune system and prevent tissue rejection. If pterygium reoccurs after surgery, consultation with an ophthalmologist is required. Patients are also recommended to wear protective glasses with UV filters.
Medications for pterygium of the eye
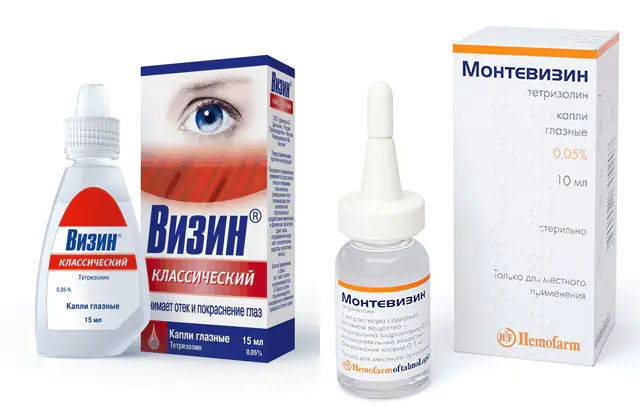
To prevent the progression of the disease, at the first signs of a disorder, it is recommended to consult a doctor. The treatment regimen is selected depending on the stage of pterygium and the extent of spread of the pathological process.
To reduce discomfort, the ophthalmologist recommends drops to patients with pterygium. The drug Visin reduces redness and irritation, eliminates itching and dry eyes. This is a Canadian-made drug from the group of alpha-adrenergic agonists. Price - 350 rub. (140 UAH). Analogues: Montevisin, Octilia, ViiOptic.
Visine is indicated for patients with swelling and hyperemia of the conjunctiva caused by an allergic reaction, chemical and physical factors - smoke, dust, chlorinated water, light, cosmetics, contact lenses.
It is recommended to instill 1-2 drops into each eye up to 3 times a day. The manufacturer does not recommend continuous use of the medication for more than 72 hours.
Visine is well tolerated. In rare cases, itching, burning, redness and tingling in the eyes, irritation of the conjunctiva, and dilated pupils have been reported.
Important! If the symptoms of pterygium do not go away, it is necessary to reconsider your lifestyle, working conditions, and use eye protection.Surgical intervention for pterygium of the eye
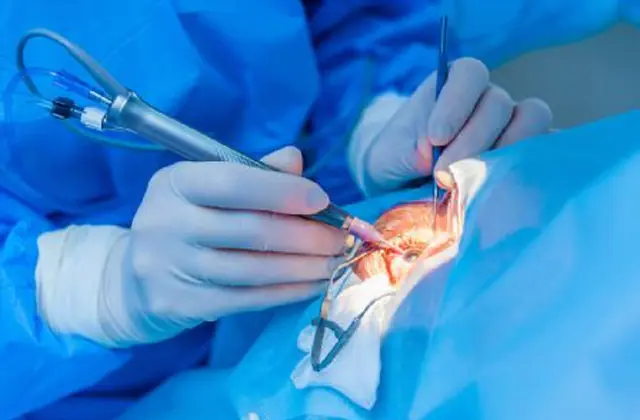
The main method of treating pathology is surgical removal of pterygium, which is carried out according to indications:
- cosmetic imperfection that provokes psychological discomfort in the patient;
- damage to the optical parts of the cornea.
During the operation, the doctor separates the pterygium from the cornea, after which he performs eye surgery using displaced flaps.
Despite the fact that the doctor removes degenerative tissue, such a procedure leads to recurrence of pterygium in more than 75% of cases. To prevent the re-development of more aggressive growths, the doctor may recommend the use of dosed irradiation using beta radiation, photodynamic therapy, and cryotherapy.
To replace defective tissues, the use of conjunctival autografts and special amniotic membranes is indicated. They are attached using seams or glue. This procedure reduces the likelihood of relapse of the pathology to 8-12%. Surgical treatment of pterygium is carried out using local anesthetics.
After surgery, complications may develop: infection, failure of conjunctival grafts, corneal scarring. In rare cases, there are complaints of perforation of the eyeballs, retinal detachment, and hemophthalmos. Beta radiation can cause thinning of the sclera and corneas.
Folk remedies against pterygium of the eye

The disease cannot be completely cured using traditional medicine. Traditional treatment for pterygium is used as an addition to basic therapy recommended by a doctor.
Effective folk recipes for pterygium of the eye:
- Aloe vera leaves are washed with water, a small piece is cut off, and the gel is extracted. Pass through a double piece of gauze until a liquid substance is obtained. Chamomile is poured with boiling water and left for 15 minutes. Next, it is recommended to wash your hands thoroughly and apply 1 drop of aloe vera to the affected eye with a sterile pipette. Then rinse it with chilled chamomile infusion. The procedure is carried out in the morning, for 30 days. Next they take a break. The course of therapy can be repeated several times a year.
- To reduce inflammation in the eyes, use tea leaves. It is necessary to brew strong black tea, generously moisten a cotton pad with the resulting drink and apply it to the affected eye. Regular use of tea leaves reduces the inflammatory reaction and restores visual acuity.
- To reduce the inflammatory reaction, a decoction of chamomile is also used: 3 tablespoons of dried raw materials are poured with boiling water (250 g). Infuse for several hours, filter, and use to prepare compresses.
- To reduce the symptoms of pterygium, it is recommended to use fucus seaweed. 4 tablespoons of dried seaweed are placed in a thermos, filled with water and left for 15-20 hours. The resulting product is poured into ice molds and sent to the freezer. It is recommended to wipe your eyes with fucus-based cubes daily, before going to bed. The course of treatment is up to 15 days, after which a break is taken.
- To prepare phytodrops, you need to prepare cumin seeds, cornflowers and plantain in advance. All substances are mixed in equal proportions, ground in a coffee grinder, poured with boiling water and filtered. Pour into a dark glass container and store on the refrigerator door. Before use, the drops must be warmed in the palms of your hands. Instill 1-3 drops three times a day. The course of treatment is 20 days.
Prevention of pterygium of the eye
To prevent pterygium disease, it is recommended:
- qualitatively protect the organs of vision from irritating factors - dust, dry air, chemicals;
- promptly treat inflammatory pathologies of the visual organs under the supervision of an experienced ophthalmologist;
- use sunglasses with a high degree of protection against UVA/UVB sunlight;
- If your eyes are dry and uncomfortable, use moisturizing drops recommended by your doctor;
- When working on a computer or other gadgets for a long time, take a break every 40-60 minutes.
At the first manifestations of ophthalmological disorders, it is recommended to refrain from self-medication and seek advice from a doctor. Timely, high-quality therapy improves the prognosis and prevents the development of complications.
Video about what pterygium of the eye is and how to treat it:



