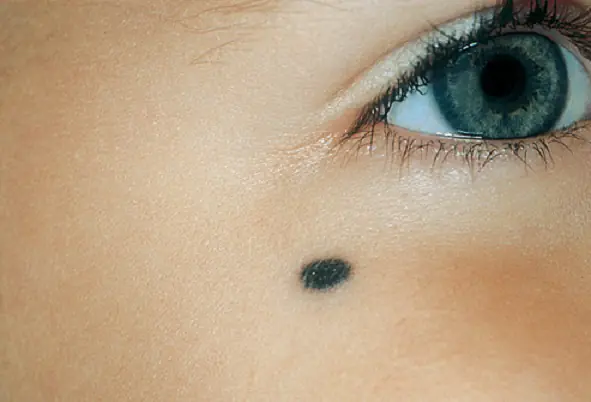Every year, every person must undergo a medical examination, during which a visit to an oncologist is mandatory. First of all, this specialist examines the body for the presence of blackened moles, which can be dangerous to human health and in the future cause skin cancer - melanoma.
What is a birthmark and what sizes does it come in?
Moles are colored spots on human skin that form in melanin cells. They can be brown, black, red, blue, white.
In medical terminology, moles are called pigmented nevi. Their origin is associated with a large amount of melanin on a small cell, which forms a large or small bulge on the outer covering of a person.
Moles are classified according to size:
- small - from 0 to 15 mm;
- medium - their diameter can reach 10 cm, but not more;
- large and gigantic - localized in one area of the body and can completely cover an arm, leg, cheek, or neck.
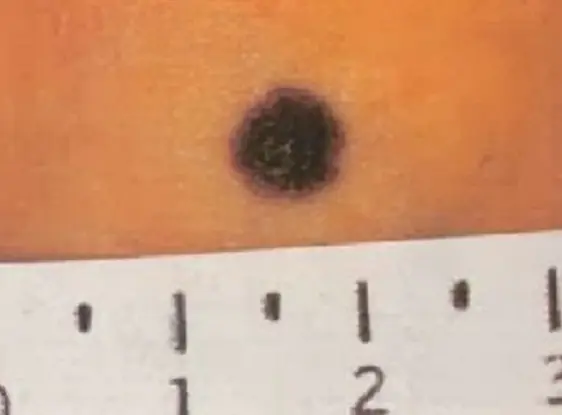
Forewarned is forearmed
You can find out whether moles are dangerous or not by carefully examining them. In most cases, ordinary stains do not pose a threat. Only 30% of blackened moles lead to the development of melanoma.
Benign spots have a neat appearance, they protrude slightly above the surface of the skin and are colored in light shades of brown, pink or black. If you examine a nevus through a magnifying glass, you can see that it has grooves characteristic of tissue cells. Safe moles do not cause discomfort, they do not hurt or itch. The size allowed is up to 6 mm in diameter, the shape of the spot is round or oval with smooth edges.
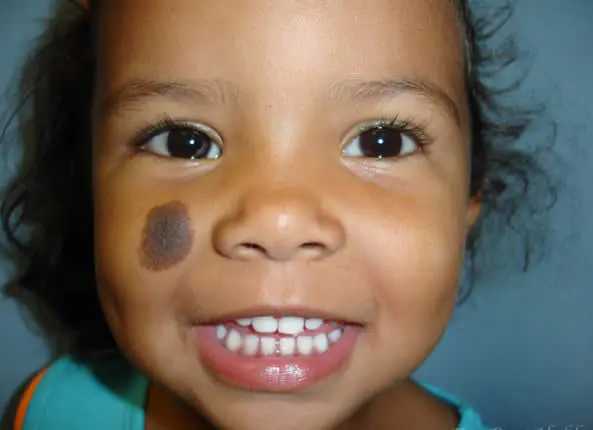
What to watch out for
- the formation has an unusual appearance, uneven edges, irregular shape;
- the mole has turned black and hurts;
- has a porous structure or looks like a dark polyp;
- began to change in size too quickly;
- cause discomfort - they itch, interfere with dressing, working, walking, constantly clinging and bleeding.
Another interesting observation: if a mole has changed color, but hair grows from it, then it is safe.
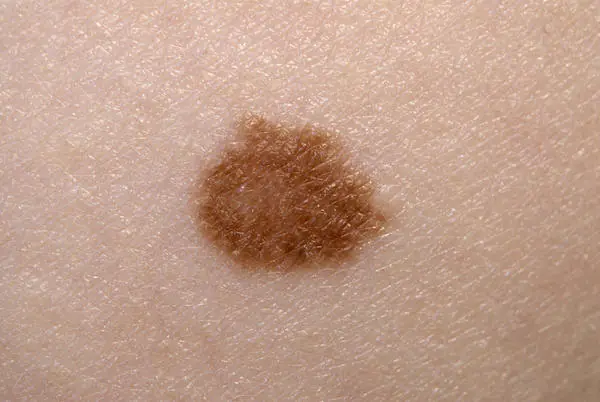
Reasons for appearance
All age spots appear on the body under the influence of external factors. Nevi do not degenerate on their own. In order for them to grow or multiply, the following factors must contribute to this:
- injuries;
- hormonal changes, menopause, pregnancy;
- ultraviolet.
Sunbathing in large doses is one of the primary factors influencing the blackening of moles and their growth. If you have a lot of such spots on your body and face, then sunbathing is contraindicated for you. People with pale skin are not recommended to stay in the sun for long periods of time or visit solariums.
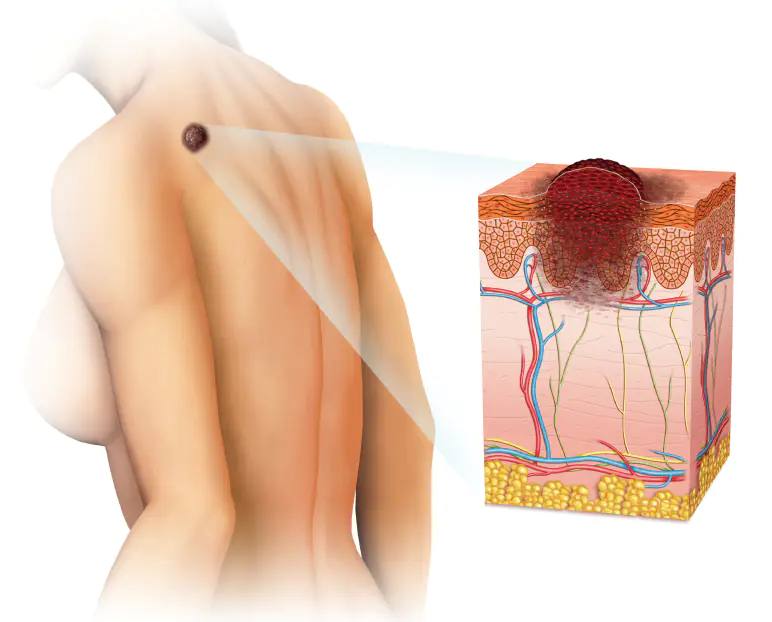
Potential danger
If you notice that you have black spots or moles of the same color on your body, then monitor them. Measure them once a week and keep a record. Observe whether they cause discomfort. What causes potential danger:
- spots whose diameter exceeds 1 cm;
- if the tumor protrudes too high above the skin;
- a dark nodule is visible;
- giant neoplasms larger than 20 cm2;
- flat spots with a loose structure of flaky skin;
- blue spots;
- senile pigment spots protruding on the face and having a loose structure and irregular shape;
- merging of several moles into one;
- neoplasms in which fluid accumulates.
System for identifying dangerous moles AKORD
To find out whether moles are dangerous or not, scientists from American universities suggest using the ABCD method. In our country there is also a domestic analogue called AKORD:
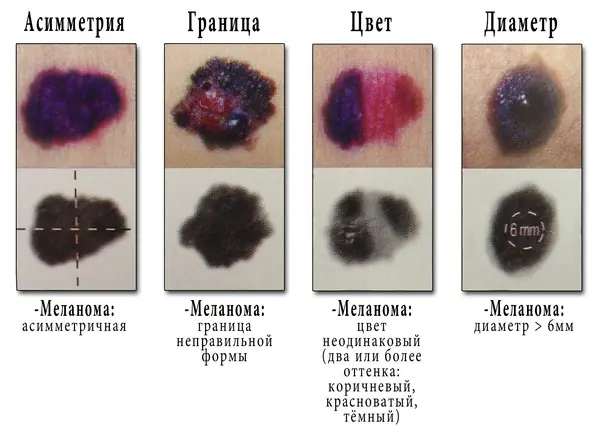
A - asymmetry. If a mole on a finger or any other place has an asymmetrical shape, then it can be dangerous. You can check symmetry if you conditionally divide the spot with a line into two parts and compare them.
K - edges. A dangerous formation has blurred, unclear boundaries. It may be that the mole has turned black and the edges have become red or burgundy.
O - coloring. This is the next factor indicating the degree of risk. If the color is light and uniform, everything is safe, otherwise you need to consult a specialist.
R - size. All moles with a diameter greater than 0.6 cm are dangerous.
D - dynamics. If you notice that the spot has changed within a week or a month, this is a very bad sign.
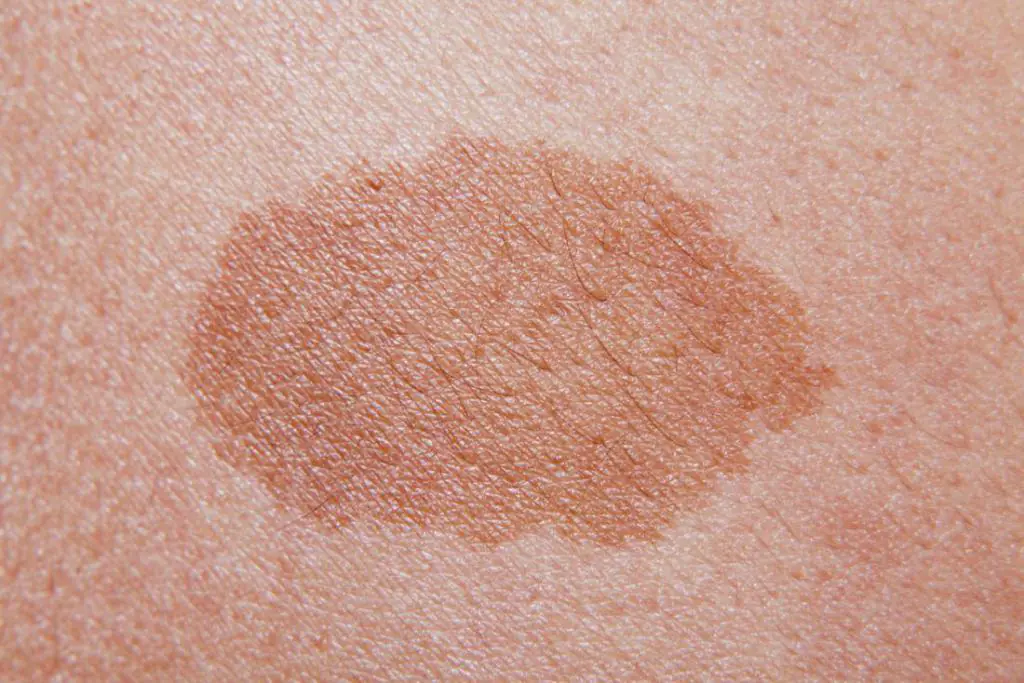
Methods for diagnosing dangerous and non-dangerous moles
If you suspect that a mole is malignant, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. The first inspection is carried out in the usual way, using a magnifying glass. The specialist will examine the entire body, regardless of where the mole is located - on a finger, on the face, on a leg or in another place.
Next, you should scan the tumor using a flaw detector. This is a special device that allows you to look inside the nevus. It increases the size of the cell several times, so you can see the structure of the mole. And after this, the doctor will assess the patient’s condition and send for further studies, if necessary.
If a mole has turned black, then you can find out reliably about its nature by doing a biopsy. This is the most reliable and 100% test option that will tell you whether there is cancer in it or not. But a biopsy is possible only after the nevus is completely removed from the body.
Treatment
There is only one method of getting rid of the disease - complete removal. At the same time, another small piece of healthy tissue is captured. If a mole has changed color and is causing concern, it is better to get rid of it immediately. Early diagnosis and prevention of further growth of nevus is the way to protect yourself from melanoma. Moreover, the procedure is absolutely painless.
Methods for removing blackened moles:
- classic - surgical removal with a scalpel is suitable for very large stains;
- laser - the point is evaporated with a laser, and the procedure is absolutely safe and does not cause discomfort; several moles can be removed at once;
- cryodestruction - flat formations are removed with liquid nitrogen through freezing;
- electrocoagulation - pedunculated moles are cauterized with electric current at the site of their growth;
- radio wave removal is another method that is now rarely used, but is suitable for all moles; removal is carried out using a powerful radio wave frequency.
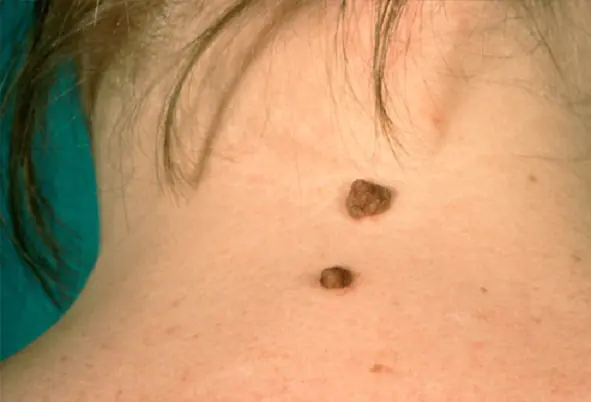
Which moles cannot be removed
If a stain on the body does not cause discomfort or interfere, it is better not to remove it. Nevi with the following characteristics are considered safe:
- the diameter of the point on the body does not exceed 5 mm;
- when examined under a magnifying glass, tissue grooves are visible;
- smooth, clear round edges;
- hairs are visible that grow from the mole;
- if it looks like a pigment spot that protrudes slightly above the skin;
- does not hurt or itch;
- does not grow or change color.
Experts recommend removing safe moles if they can be injured in everyday life, for example, at the junction of clothing, on the palms of the hands, in the armpit, on the finger, neck and other similar places. Nevi on the face are often removed to give beauty to delicate skin.
It is very easy to catch a mole and damage it while shaving, dressing, combing hair, or bathing. Frequent injuries can lead to hardening of the skin in this area and have dangerous consequences.
You should not remove red moles. Contrary to general fear, these types of spots are absolutely safe if they have signs of safe nevi. Small, neat red spots do not need to be removed.
Precautionary measures
Moles should be checked annually by visiting a specialist. Additionally, you need to do this at home, especially during the summer holidays. It is advisable to evaluate the condition of each of the spots before and after the end of the solar period. If you notice growth or a mole has turned black, you need to go to an oncologist.
The most dangerous time to be in the sun is from eleven in the morning to fifteen o'clock. Be aware that sunscreens do not protect against the harmful effects of ultraviolet rays. Dark spots attract the sun's rays much more than light areas of skin. Try to spend this time indoors or in the shade.
Summer clothes should be light and natural. Give preference to cotton fabrics.
If there are raised moles on the body that cause discomfort, or they have been injured, then you should not cover them with a band-aid. Under the sticker, the skin will not breathe and a greenhouse effect will occur. This is a very dangerous condition for the skin and can lead to further damage.
Go for sunbathing in the morning before 11.00 o'clock and in the evening, after four o'clock in the afternoon. Keep children away from the sun and avoid getting burned.
- children under five years old;
- in the presence of large or giant birthmarks;
- if there are a large number of moles on the body.
Try to plan a trip to particularly hot countries in the autumn. It’s not for nothing that September is called the “velvet season.” At this time, the sun is no longer so hot, but at the same time warm air and pleasant sea temperatures remain. Young children should avoid traveling to hot countries such as Egypt, Tunisia, Cuba, and Spain. And, of course, always keep an eye on your kids and don’t let them sleep in the sun without protective umbrellas. Be sure to use sunscreen on the beach.
Melanoma is a malignant neoplasm that develops from pigment cells. The cause of melanoma can be an ordinary mole, which gradually, increasing in size and causing pain, provokes skin cancer. Not all patients can discern malignant transformation in the early period, which makes treatment of the disease more complicated. Read our next article to learn how to recognize the symptoms of melanoma moles.
General information about moles
A mole (birthmark) is a defect in the development of the skin, which can be either congenital or acquired during life. Scientifically, these formations are called “nevi.” They are benign tumors that, under the influence of various factors, can turn into malignant ones. This occurs after the skin cells are overfilled with the pigment melanin. As a result of this, they degenerate and turn into melanocytes.
Many experts talk about the danger posed by a large number of such formations on the body. You need to be especially attentive to those that in everyday life are often subject to mechanical stress (friction and pressure from clothing). This is very dangerous for human health and most often such a mole is simply removed.
What to do if a mole grows? Any changes in the size, shape or color of such formations require immediate consultation with a doctor. They also turn to a specialist if the nevus hurts or itches for no apparent reason.
Types of moles
There are many varieties of such formations. They are:
- light and dark in color;
- protruding above the surface of the skin and flat;
- deeply embedded in the thickness of the skin and superficial.
Often small moles give a special zest to its owner, but there are times when large formations on the face simply disfigure a person’s appearance.
All types of nevi are conventionally divided into 2 types:
- vascular, which include papillomatous formations and angiomas;
- pigmented, among which are freckles and lentigo (a uniformly pigmented flat spot of brown or black color).
Causes of painful nevi
Many people are sure that if a mole hurts, then this is the first sign of its oncological degeneration. In fact, painful sensations in the area where the nevus is localized do not always indicate the development of any complication and can be associated with the following objective reasons:
- Injury to the surface of the nevus. Impacts, injections, and incisions in the epidermis at the location of the nevus are not uncommon, but one of the most pressing issues is the situation in which the patient tore off a mole. We will consider what to do in this case below, however, mechanical damage to the pigmented tissue of the nevus is one of the leading etiotropic factors causing pain.
- Burn of any nature. Thermal shock can cause intense pain in the epidermis, which is especially pronounced in areas where moles and age spots are located.
- Hyper- or hypothermia. Increased or decreased body temperature may be accompanied by a feeling of soreness in the skin, especially in places where moles are located.
- Malignant transformation. Evidence of the onset of the oncological process may be pain, which is associated with the fact that the mole is inflamed. What to do in this situation can only be suggested by a specialist in the field of oncodermatology, who will not only perform a visual examination of the inflamed area of the epidermis, but will also prescribe a number of diagnostic measures to identify the prerequisites for the development of melanoma. After receiving the research results, the doctor will determine the most rational concept of therapy or recommend removing the inflamed nevus.
The last factor is by far the most dangerous, as it is associated with uncontrolled division of skin cells, which leads to cancer.
This is due to mechanical trauma to surrounding cells during tissue proliferation. Often this process is accompanied by an increase in the size of the pigmented formation. It is also important to note that sometimes during malignant transformation, a small white spot (halo) may form around the body of the mole, which is caused by a reflex vasospasm.
Which moles are dangerous?
But not all nevi are prone to malignancy. In medicine, moles are divided into melanoma-hazardous and melanoma-non-hazardous. The first group includes five types of nevi.
Considered very dangerous giant mole – it degenerates into a malignant tumor in 50% of cases. This is a huge bumpy formation that can occupy a significant part of the body, such as the back or chest. In appearance it resembles a gray or brown wart. A giant mole grows throughout life.
Borderline mole It is a dark or black uniformly colored small spot up to 1 cm in diameter with a smooth, dry surface. It does not grow or change color, and is not affected by solar radiation. As a rule, border nevus is located on the soles, palms, and in the intimate area. Degenerates into a malignant formation in 10% of cases.
Blue nevus - a small (usually about 1 cm) dense round mole of blue, grayish or black-blue color, rising above the skin and well-defined. Localized on the head and neck, hands, feet, buttocks. As a rule, such moles are single, that is, a person has one in the singular. It becomes malignant quite rarely.
Nevus Ota - this is a rather large birthmark of a bluish-brown or bluish-gray color, located on the face, auricle, and mucous membrane of the mouth in the cheek area. It has an uneven shape and uneven color. Often congenital or appears during the first 20 years, mainly in representatives of the Mongoloid race. It rarely develops into melanoma.
Dubreuil's melanosis It is a small, light brown to black, irregularly shaped spot with well-defined borders. The stain is unevenly colored and sometimes resembles a black blot on a brown background. It develops mainly on the face, most often in people with fair skin exposed to solar insolation, usually in women after 50-55 years. It grows slowly. It is considered a precancerous condition and degenerates into melanoma, according to various sources, in 45-75% of cases.
What contributes to the degeneration of a mole into melanoma?
Risk factors for malignancy of moles include:
- intense ultraviolet irradiation;
- damage to a mole;
- hereditary predisposition.
What to do when a mole grows
If you notice that one of the moles on your body is growing, you should, of course, consult a doctor who will help you understand the reasons and, if necessary, take some tissue for analysis.
Most often, doctors will suggest that you remove the mole to stop its growth. Don’t be afraid, in modern clinics this procedure does not cause pain, and the recovery period is minimal. With the right approach, you won't even have a scar.
There are also traditional methods for removing moles. For example, before the advent of medicine in its modern format, moles were removed with garlic juice, which was smeared on the formations 3-4 times a day. The celandine method was also popular, when celandine juice was squeezed onto a mole for 10 days.
If you notice an enlargement of a mole on vacation and there is no opportunity to see a doctor right now, take a small amount of baking soda and add a couple of drops of castor oil. Apply the resulting mixture to the mole at night, and also completely limit the contact of the mole with the sun.
What is melanoma
Melanoma is a particularly aggressive type of skin cancer. Typically, melanoma originates from skin cells that produce the pigment that colors tanned skin, birthmarks, or freckles. These cells are called melanocytes, hence the name melanoma. The incidence of melanoma is about 8 cases per 100 thousand population among men and about 12 cases per 100 thousand population among women. Unlike other forms of cancer (malignant diseases), melanoma most often affects young people (15-40 years old). In the structure of mortality from cancer among women, melanoma ranks second (in first place is cervical cancer), and among men - sixth (after lung cancer, prostate cancer, stomach cancer, colon cancer, pancreatic cancer).
Signs of melanoma
It’s clear that you can’t touch them - tear them off, pull them with threads, or injure them. You need to be careful if the mole is constantly touched - by clothes, belts, handbags. All your moles need to be examined from time to time, because melanoma often develops from an inconspicuous small mole. Atypical cells begin to multiply there, and even a small malignant tumor on the skin can metastasize and kill a person.
A so-called ABCD test has been developed to help identify “wrong” moles.y:
- A - asymmetry. If a beautiful round mole becomes asymmetrical, as if “creeping” across the skin, changing shape, this should be a signal to immediately consult a doctor.
- B - from the English word “border”, which means “edge”. When fuzzy, jagged or blurry edges of a mole appear, this is also a suspicious symptom.
- C - from the English “colour” - “color”. A normal mole has a uniform color - light or dark bronze. If several colors appear (red, white, purple, black), the mole loses the enzyme and becomes heterogeneous - this is also one of the factors that should alert you.
- And finally, D is the diameter. If the diameter of the nevus exceeds six millimeters, it is advisable to see a doctor. In general, if any sign is clearly visible, it is advisable to do a biopsy of the mole - take a small part of it for analysis to identify malignant cells.
It is possible to identify factors that provoke the degeneration of a benign mole into a malignant tumor. And first of all, genetic. If close, blood relatives have had cancer or precancerous conditions, the risk of getting melanoma increases 15 times! Such people need to watch their moles especially carefully, and visit an oncodermatologist every six months so that he can literally examine them from head to toe. Another provocative factor is solar radiation.
Some moles appear at birth, while others appear over the years. There are those that appear and disappear. These are genetically predetermined processes. And some moles are destroyed by the body itself, recognizing them as a foreign body. In this case, a white spot may remain at the site of the mole. In general, moles can be very different - flat, convex... - this is not a determining factor in the development of melanoma. Skin cancer can arise even from a small, flat mole. But if hair grows on a mole, according to experts, this is good, although it does not look very beautiful.
Why is melanoma dangerous?
Melanoma is the most aggressive form of cancer known today. This tumor quickly metastasizes (even at very small sizes) which within a few months can affect the main vital organs (brain, lungs, bones). Once metastases are detected, melanoma is considered virtually incurable.
Who is at risk of getting melanoma?
There is now a proven connection between various types of skin cancer and solar radiation. This principle also applies to melanoma. Solar radiation is the main cause of the development of this type of tumor. In some people, however, the sensitivity of the skin to solar radiation is higher due to the presence of certain predisposing factors: a large number of freckles on the body, the presence of benign skin tumors, the presence of atypical nevi, light skin sensitive to the sun, working in open sunlight.
Where does melanoma come from?
As we said above, the source of melanoma development are pigment cells that synthesize the biological pigment melanin, which colors the skin and age spots on the skin. There are a lot of such cells (melanocytes) in birthmarks, freckles, and nevi. For early diagnosis of melanoma, it is very important to know the characteristics of the structure and all pigment formations of the skin. Very often, when visiting a doctor, it turns out that the patient does not know what a healthy mole should look like and how it differs from an atypical nevus or a malignant melanoma tumor.
Below we give brief descriptions of skin pigment formations:
Freckles – pigment spots of small size, usually round or oval in shape, not protruding above the surface of the skin. Most often, freckles cover the skin of the face, but they can appear on almost the entire surface of the skin. Freckles fade in winter and reappear in spring and summer.
Moles (birthmarks, nevi) – pigment formations of medium size (up to 1 cm in diameter), usually dark and evenly colored; however, lightly colored flesh-colored moles are found. The surface of the mole may only rise slightly above the surface of the skin. The edges of moles are smooth. Atypical nevi – large pigmented skin formations with uneven edges and uneven coloring. Some atypical nevi can be considered precancerous formations. Malignant melanoma – a pigmented skin formation that arises from moles or on “clean skin” with uneven edges, a bumpy surface, and uneven color of varying intensity. The edges of melanoma are often surrounded by an inflammatory rim (a bright red stripe).Additional signs for diagnosing melanoma
- An increase in the size of the mole is more than 7 mm;
- The appearance of a zone of inflammation along the edges of pigmented skin formations;
- Bleeding and itching of pigmented skin formations.
When diagnosing melanoma, it is important to take into account the fact that in men this tumor is most often located on the back, and in women on the lower leg. Regardless, all areas of the skin should be checked, including the scalp and nail beds (melanoma may appear as a black spot under the nail). If these signs are detected, you should immediately consult a dermatologist. The earlier melanoma is detected, the greater the chance of successful treatment.
What types of melanoma are there?
From a clinical point of view, there are several types of melanoma:
- Superficial melanoma This is the most common type of skin cancer. Superficial melanoma is located in the upper layers of the skin, and its surface does not protrude much above the surface of healthy skin. This type of melanoma is most easily confused with a regular mole or an atypical nevus.
- Nodular melanoma occurs in a quarter of all patients with melanoma. This is the most aggressive form of skin cancer. Nodular melanoma has the appearance of a dark-colored nodule of various sizes, raised above the surface of the skin.
- Lentigo melanoma – found on the head and neck of older people. The surface of this tumor is slightly raised above the surface of the skin.
- Subungual melanoma occurs in every tenth patient with melanoma. Most often, the tumor forms under the nails of the big toes.
What is the Breslow index
The Breslow index (Breslow thickness) determines the thickness to which melanoma cells have penetrated deep into the skin.
If the Breslow index is more than 0.5 mm, the patient must be referred to a dermatologist for removal of the formation.
Melanoma and other skin cancers
In addition to melanoma, there are other types of skin cancer (squamous cell skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma), however, unlike melanoma, they are much less aggressive and are more treatable. Basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma of the skin appears as a long-term non-healing crack or wound, which is usually located on the face, neck, or back of the hand.
Treatment of melanoma and other skin cancers
The type of treatment for melanoma and its effectiveness depends on the stage of its development. The earlier melanoma is detected, the greater the chance of a full recovery. If the diagnosis of melanoma or another form of skin cancer is confirmed, surgical removal of the tumor is performed. Usually the operation is performed under local anesthesia. The surgical intervention itself does not pose any danger to the patient. In some cases, surgical treatment is combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy. The appearance of metastases significantly reduces the patient’s chances of survival, however, recently there have been reports of the invention of new ways to combat cancer, in particular melanoma, for example, using monoclonal antibodies that can defeat the disease even at the stage of metastasis.
How to protect yourself from melanoma
Because melanoma is extremely dangerous, people who are at high risk of developing the disease (such as people who spend a lot of time outdoors) are advised to take certain precautions to prevent melanoma and other skin cancers. To protect yourself from skin cancer:
- Try to limit your time in the sun as much as possible, especially during lunch hours.
- If sun exposure is unavoidable, protect exposed skin from direct sunlight: wear a long-sleeved T-shirt, a wide-brimmed hat, and pants.
- When exposed to direct sunlight, be sure to use sunscreen. The protection factor of the cream should be at least 15. • Study all the main and minor signs of melanoma and, if possible, discuss them with your doctor. Make sure you know exactly what melanoma can look like and how to distinguish it from a regular mole.
- Check the entire surface of your skin regularly. Your back and scalp should be examined by a friend or relative.
- Consult a doctor if you notice any skin element that makes you suspicious.
Nevi are skin cells where a lot of pigment accumulates. Birthmarks are brown in color, but they come in red, blue, black and colorless. It is impossible to understand which shade is dangerous without examining a doctor.
Much depends on the hereditary factor and the degree of ultraviolet radiation. But if a mole changes color and suddenly becomes lighter or darker, this is an alarming signal; it may indicate its degeneration into malignant melanoma.
Factors contributing to changes in nevus color
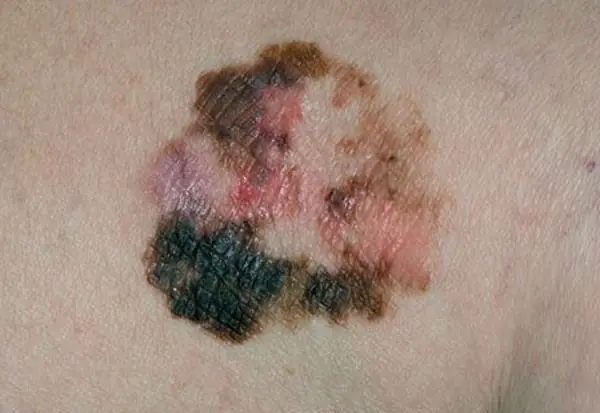
There are many reasons that influence the darkening or lightening of a mole. The leading factor is genetics. Neoplasms are often congenital. If relatives have malignant ones, then there is a high risk that the child will also develop melanoma.
Another reason why a mole becomes light is due to exposure to ultraviolet radiation. People with many moles on their body should not stay in the open sun for a long time or visit a solarium.
Regardless of the reason for the appearance of a nevus, any changes in it indicate the development of a certain process in the skin, and how dangerous it is should be determined by a doctor.
Changes in the color of a mole also occur for other reasons:
- Exposure to chemicals. If the nevus is constantly exposed to toxic agents, this leads to its modification and irritation.
- Damage. Banal scratches, scratches, wounds or insect bites lead to the degeneration of birthmarks. This causes inflammation of the skin and leads to the production of substances that increase cell growth.
- Hormonal imbalances. A nevus may acquire a heterogeneous consistency, change size and shade due to hormonal imbalance. Most often, dysfunction occurs in pregnant women, adolescents and people with diseases of the endocrine system.
Reasons why education brightens

If the mole has changed color to light, then the stain may be resolving. During life, many nevi disappear and the change in color of the mole is not dangerous.
A light nevus indicates a malfunction in the functioning of pigment-producing cells. First, an area appears around the tumor where there is no pigment. Then the shade disappears at the mole itself.
Such changes may indicate the initial stage of vitiligo development. Despite the fact that this pathology does not pose a mortal danger and is not accompanied by painful symptoms, it brings psychological discomfort to its owner.
The tendency to vitiligo is hereditary, but the determining factors in the development of the disease are disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system and nervous tension.
The third reason why the mole has become smaller and lighter is a decrease in the concentration of sex hormones. Often, violations occur during menopause.
Factors leading to darkening of nevi
A dark nevus may be a consequence of a number of changes occurring in the body:
- infection;
- excess of sex hormones;
- injuries (rubbing, scratching, damage to a birthmark);
- increased exposure to ultraviolet radiation (the skin darkens and nevi on the body also become more saturated in color).
Danger signs requiring medical advice

When a mole changes color, the worst consequence is the development of melanoma. This is a cancerous tumor that develops from nevi or epidermal cells. The exact causes of malignancy have not yet been established. It is known that birthmarks of heterogeneous color degenerate on the lower extremities in women and on the torso in men.
In order to promptly identify melanoma and seek medical help, you need to know what dangerous signs indicate the initial stage of its development. Symptoms that should alert you:
- the mole has changed in size;
- suppuration;
- the nevus has become lighter or darker;
- ichor or blood is released from the formation;
- change in shape.
If all these signs are combined with the appearance of unpleasant sensations (itching, pain, burning and tingling) - this is another significant evidence of the development of a cancerous tumor. Melanoma is indicated by an uneven shade, peeling of the skin near the mole and its thickening. Often the necrotic area near the malignant nevus is sprinkled with small papillomas, which is a visible sign of cancer.
It is impossible to independently diagnose and determine the benignity of a mole. Treatment for melanoma at an advanced stage may not produce results, leading to death.
A flesh-colored mole that gradually changes color is considered benign. Typically, such changes occur under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. But the risk of malignant degeneration is still present and it is better to consult a dermatologist.
Treatment and prevention
If, in addition to lightening, no other changes occur in the nevus, then no special treatment is required. Therapy is limited to procedures that improve skin condition. This includes physical therapy and taking vitamins.
But when pathological processes develop in a mole that contribute to its darkening or lightening, complex treatment is prescribed. To identify the nature of the neoplasm, the doctor performs a puncture of the skin. If, under the influence of processes that have changed the mole, it has become malignant, external treatment is not carried out. After excision of a nevus, the risk of relapse and dangerous complications increases.
Medical statistics say that malignant degeneration of a mole occurs in 13% of cases, mainly in women.
A favorable prognosis for treatment of a cancerous tumor is possible only under the supervision of an experienced doctor. The doctor performs a histological analysis. It makes it possible to determine the degree of malignancy of the mole and prescribe the optimal course of therapy.
If the dermatologist decides that a mole that has changed color to dark or light requires removal, then the procedure is carried out using one of the leading methods:
- Electrocoagulation (exposure to high-frequency current).
- Laser therapy (painless and safe procedure that does not leave scars on the skin).
- Radio wave method (removal occurs using high-frequency radio waves).
- Surgery (used to excise large moles).
- Cryodestruction (used to remove flat nevi using liquid nitrogen).
If a mole changes color to dark after laser hair removal, an urgent consultation with an oncologist is necessary.
There are a number of preventive measures to prevent the development of cancer. So, you should not stay in the sun for a long time or abuse the solarium. It is recommended to use products that protect against ultraviolet radiation.
After taking water procedures, the surface of the skin must be thoroughly wiped. In summer, it is advisable to wear clothes made from natural fabrics (cotton or linen). Those with fair skin are allowed to sunbathe before 11 a.m. and after 4 p.m., and during the heat of the day, all parts of the body must be covered with clothing made from breathable fabrics.
So, if a birthmark has changed color, then to exclude its malignant degeneration, you need to contact a dermatologist. Moreover, it is necessary to insist on conducting a thorough examination of the nevus, which will make it possible to determine the condition of the birthmarks and, if cancer is detected, to carry out effective and timely treatment.