Causes of osteophytes. Symptoms of bone tissue growth on the spine, joints, heel, diagnosis. Conservative and surgical treatment, preventive measures.
The content of the article:- Reasons for appearance
- Symptoms of osteophytes
- Diagnostic methods
- Treatment options
- Medicines
- Surgical intervention
- Physiotherapeutic procedures
- Prevention
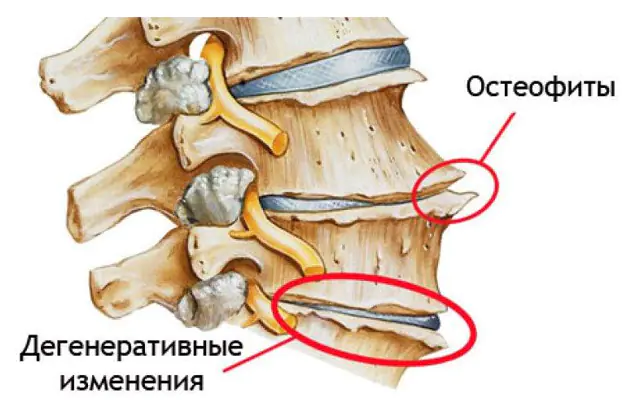
Osteophytes are pathological growths on the tissues of bones and joints that appear and grow as a person grows older. In most cases, growths do not bother people and are detected by chance during examination of other organs. But sometimes they cause acute pain and limit physical activity.
Causes of osteophytes
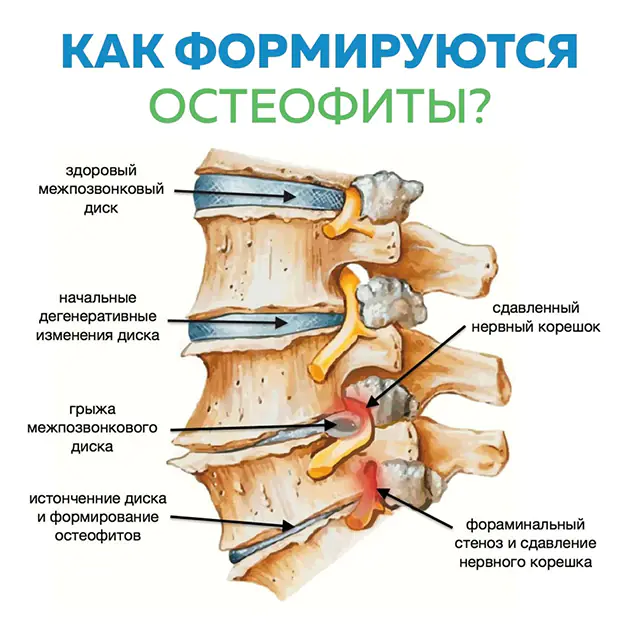
The proliferation of osteophytes is a natural compensatory reaction of the body. With age, spinal discs and cartilage tissue become thinner. To prevent pinching of nerve endings and destruction of bones, growths appear in the joints. They limit their activity, thereby saving them from complete destruction. But without treatment, the growths themselves become a source of pain.
At a young age, the following groups of diseases cause the appearance of osteophytes:
- Deterioration of metabolism. Thus, in diabetes mellitus there is a metabolic disorder involving calcium. Mineral salts are deposited in the joints and after some time form growths.
- Autoimmune processes. Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases affect connective tissue. Without treatment, osteophytes appear on the joints.
- Inflammatory processes in the bones. Brucellosis, osteomyelitis, and tuberculosis of bone tissue cause changes in its structure. Bone osteophytes are a common complication of these diseases.
- Oncological diseases. Cancerous tumors on the bones or joints cause degenerative processes in the tissues. The body responds with the same reaction to the spread of metastases.
- Mechanical damage. Injuries, fractures, and bruises of the periosteum require a long period of rest for normal bone healing. If during the rehabilitation period an autoimmune or inflammatory process appears in the body, the risk of osteophytes increases.
At a young age, osteophytes form in people with excessive stress on the joints. The reasons are flat feet, excess weight, curvature of the spine, heavy physical labor, and professional sports.
Based on the characteristics of their cellular structure, the following types of growths are distinguished:
- marginal osteophytes (on the elbows, shoulders, thighs, phalanges of the fingers);
- osteochondral (on the femur, knee joint);
- bone-spongy (on the spine, foot, heel);
After an inflammatory, infectious process, bruise, fracture, a malfunction appears in the cellular composition of osteochondral tissue. As a result, growths appear.
Symptoms of osteophyte development
In the initial stages of osteophyte formation, a person does not feel pain or discomfort. During this period, growths are diagnosed by chance on x-rays of injuries. In the later stages, the patient experiences difficulty maintaining usual physical activity.
Symptoms of cervical osteophytes appear after the nerve roots of this part of the spine are compressed. At the same time, a person feels:
- pain in the back of the head, radiating to the shoulder;
- decreased visual acuity;
- hearing impairment;
- frequent dizziness;
- pain when turning the head sharply.
Osteophytes of the thoracic spine do not manifest themselves until they grow to an extreme degree. Due to limited mobility in this part of the body, a person does not notice the disease until the nerve roots begin to suffer from compression by growths. After this, the patient feels pain during deep breathing, sneezing, coughing, turning and bending the body.
The lumbar spine is subject to the greatest stress. Therefore, bone growths appear there most often. Signs of osteophyte proliferation:
- dull pain in the lower back, radiating to the leg;
- decreased sensitivity of the lower extremities;
- numbness and tingling of the toes.
In the later stages of the disease, the pathological process can affect the internal organs of the small pelvis. The patient suffers from urination problems, intestinal disorders, and sexual dysfunction.
Osteophyte of the foot is manifested by pain and crunching during movement. By the end of the day, the patient feels very tired and limited mobility of the legs. The skin at the site where the growths appear becomes red and hot to the touch. Due to swelling and curvature of the foot, the gait changes, and difficulties arise with choosing shoes.
If the symptoms are ignored, the growths damage neighboring tissues, leading to inflammation and infection. Osteophytes of the lumbar and other parts of the spine, without treatment, begin to compress nerve fibers, causing disruption of the brain and spinal cord. The most dangerous consequence of the disease is complete immobility of the torso and limbs.
Methods for diagnosing osteophytes
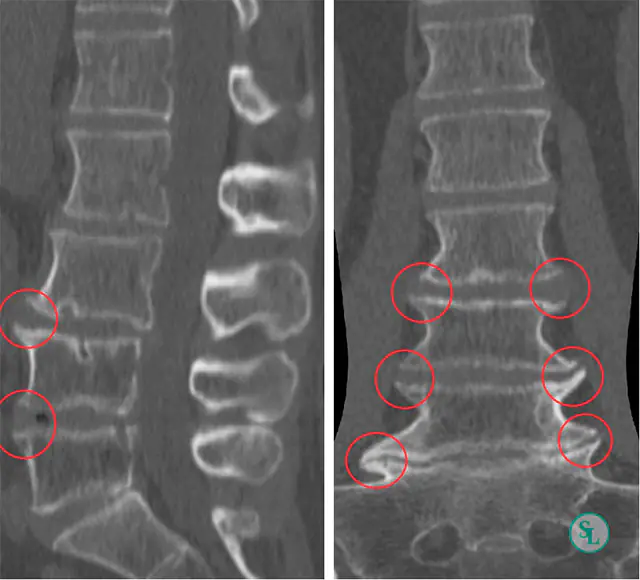
Osteophytes are not an independent disease, but symptoms or complications of diseases of the musculoskeletal system and metabolism. Therefore, it is important for the doctor to identify not only the location of the growths, but also the cause of their appearance. During the preliminary examination, he studies the patient’s medical history, asks about his work and lifestyle, and palpates the sore spot.
Next, he directs the patient to a series of diagnostic tests. To identify osteophytes, one of these methods is used:
- Radiography. This method allows you to see even small (2-3 mm) bone growths. It is usually performed when osteophytes are suspected in the joints of the limbs. To carry out the procedure, a person removes clothes and jewelry from the sore spot, places the arm/leg on the table on top of a special film. In this case, healthy parts of the body are covered with a protective apron. The doctor takes a photo and gives it to the patient a few minutes later.
- CT scan. To assess the condition of hard structures and identify the root cause of osteophyte formation, CT is prescribed. This method also involves the use of X-rays. But unlike X-rays, the doctor can evaluate the results using a series of layer-by-layer images. To do this, the patient is positioned inside a machine that rotates around his body and photographs him.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. The main difference between an MRI study is the use of electromagnetic waves that are safe for humans. When they come into contact with fabric, they give a unique response, which is captured in the form of photographs. Doctors believe that CT is more suitable for evaluating hard structures, while MRI is more suitable for soft tissue. Both procedures are safe and informative.
After studying the test results, the doctor finds out the reason for the growth of bone tissue, tells how to get rid of osteophytes, and how to cure the underlying disease.
Methods for treating osteophytes
Treatment of osteophytes is carried out in a comprehensive manner. Conservative therapy helps relieve inflammation and pain. With the help of surgery, growths are removed and joints are replaced. Traditional medicine helps to recover after surgery.
Medicines for the treatment of osteophytes
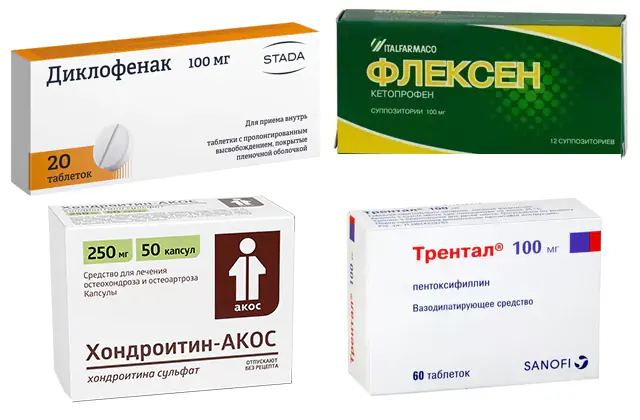
Osteophytes of the vertebrae and joints often manifest as acute pain. To improve well-being and quality of life, the doctor prescribes medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Medicines relieve pain, relieve swelling, and extinguish the inflammatory process. The drugs are produced in the form of tablets for internal use and ointments for external use. The price of Diclofenac is 25 rubles in Russia (11 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 30 tablets. Analogues - Ketoprofen, Flexen.
- Chondroprotectors. The drugs stimulate the production of substances that nourish joint tissues, prevent the destruction of structures, activate the synthesis of synovial fluid, and have an anti-inflammatory effect. The price of Chondroitin is 580 rubles in Russia (229 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 60 capsules. Analogues - Rumalon, Glucosamine.
- Drugs to increase blood circulation. Medicines reduce blood viscosity, have a slight vasodilating effect, and improve microcirculation in areas of impaired blood circulation. The price of Trental is 610 rubles in Russia (215 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 5 ampoules. Analogues - Pentoxifylline, Latren.
- Vitamin complexes. The drugs prevent deficiency of vitamins, which are necessary for the synthesis of synovial fluid and other components of bones and joints. Remember, the body reacts especially sharply to a lack of B vitamins. The price of Kalcemin is 80 rubles in Russia (30 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 30 tablets. Analogues - Complivit, ArtriVit.
Surgical intervention in the treatment of osteophytes
Removal of osteophytes is indicated in cases of complete destruction of the joint, severe pain during movement, and compression of the nerve roots in the spine.
Osteophytes on the hip or other joint limit a person’s mobility. Without treatment, they grow and cause irreversible processes of tissue destruction. In this case, the doctor prescribes an endoprosthetics procedure.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon cuts the skin and muscle tissue, removes the destroyed joint, and installs an artificial prosthesis. Metal alloys, ceramics, and polymers are used as materials for the implant. Thanks to this, the endoprosthesis lasts 15-20 years.
Pinched nerve roots of the spine require surgery to remove osteophytes. Surgery is performed under general anesthesia. In this case, the doctor must have high skill so as not to sever the nerves and not touch the blood vessels supplying the spinal cord. The rehabilitation period lasts 20-30 days.
Late-stage calcaneal osteophyte is also treated with surgery. The operation is performed endoscopically. During this procedure, the doctor makes small holes in the heel area, where he inserts instruments and a video camera. Next, he cuts the plantar tendon, saws off and removes the growth.
Physiotherapeutic procedures for osteophytes
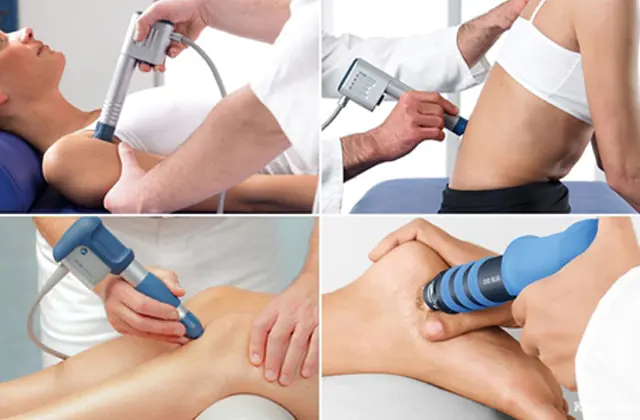
Pictured is shock wave therapy
You can stop the growth of osteophytes not only with the help of folk remedies and medications, but also through the use of physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Electrophoresis with Novocaine. A napkin moistened with the drug is applied to the patient’s sore joint. A device attachment is installed on top that gives electrical impulses. They help the drug components penetrate into deep tissues.
- Diadynamic therapy. The procedure has an analgesic effect, as current waves block nerve impulses. In addition, during the session, blood circulation and lymph flow in the sore spot increases. As a result, the activity of the spine or joint improves.
- Shock wave therapy. During the session, osteophytes soften and decrease in size. In addition, the crushing of calcium salts into small particles is noted. As a result, pain is relieved, swelling is reduced, and the patient’s well-being improves.
Complex treatment of osteophytes involves physical therapy exercises, massage, manual therapy, and wearing special orthopedic devices.
Prevention of osteophytes

Follow the principles of healthy eating. Include foods with calcium and other minerals in your diet, and take vitamin complexes annually. Watch your weight and prevent the development of obesity.
Do exercises, walk and bike rides. Remember, during moderate physical activity, blood circulation in the bones and joints increases. Thanks to this, they receive more oxygen and nutrients.
Take care of your joints while playing sports. During training, use professional clothing, shoes, attributes, and equipment. Before the main load, warm up your muscles with a warm-up, and after it do stretching exercises.
Don't skip medical examinations. Identify diseases in a timely manner and follow all doctor’s instructions for their treatment. Do not change the dosage of medications or the duration of physiotherapeutic procedures on your own. Do not allow complications of diseases to develop.
What are osteophytes - watch the video:



