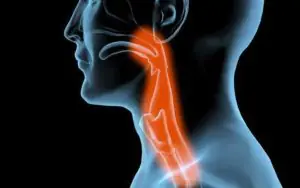
The throat is particularly sensitive, and even the slightest injury causes discomfort and pain. With a serious burn to the throat, not only the surface of the mucous membranes can be damaged, but also tissues and organs that lie deeper. Children and careless or very quick people are especially at risk for this type of burn. To avoid injuries of this kind, you should follow simple safety rules, be careful and avoid haste in everyday activities. For example, you can easily get, although not significant, but still an unpleasant throat injury in the morning, rushing to work in a hurry to take a large sip of tea that has not cooled down to a safe temperature. The food gets burned precisely because of the rush. Chemicals and their vapors can also cause this disease. Such dangerous things should be stored out of the reach of children, in securely closed containers that should be signed. It is better to treat minor burns of the throat mucosa under the supervision of a physician. It would be a good idea to know what to do if you have a throat burn.
Distinctive characteristics
The throat is most vulnerable to various types of injuries, including burns, since its delicate tissue structure is highly sensitive and can be easily damaged.
A burn in the throat is different in that it is internal and affects the larynx, palate and esophagus. The extent of damage depends on the severity of the injury. The burned area cannot be covered with a bandage, and the injured areas are difficult to reach for treatment. With this type of damage, the swallowing reflex may disappear for a long time, which will make it impossible to eat food naturally.
With such damage, the following are felt: Acute pain, increased salivation, increased body temperature, the affected area of the throat burns, the person may feel sick, dry cough, hoarseness, swelling of the affected area, swollen lymph nodes, lack of oxygen.
In very dangerous stages, bleeding wounds, blisters appear, the upper layers of tissue are severely damaged, painful shock and respiratory collapse may occur.
Causes
Thermal burn affects the throat when ingesting hot food or drink, and chemical burn when the throat is exposed to medications, alcohol, acids or chemicals.
The main causes of this type of damage are negligence and carelessness when interacting with hot liquids, food, as well as chemicals, alcohol-containing liquids and medications of a certain group.
Alcohol and alcohol. The risk group primarily includes socially vulnerable citizens suffering from addiction, who consume alcohol-containing liquids and low-quality alcoholic beverages for other purposes.
Damage from alcohol-containing liquids occurs if the alcohol concentration in them is more than 70 percent. This is the easiest type of lesion, since a membrane forms on the mucous membrane that does not allow alcohol to penetrate deep into the surface layer of the epithelium. If alcohol penetrates into the esophagus, a white coating of dead tissue cells appears on its internal surfaces.
The injury is accompanied by the following manifestations: pain in the chest and cervical region, weakness appears in the stomach, and the sensitivity of taste buds is dulled.
Hospitalization, if the esophagus is not damaged, is not required and after some time the tissue cells will recover on their own.
Hot food and liquid. Most often, the throat is burned by hot tea or food, as well as by inhalation of hot steam. Thermal burn of the throat occurs in most cases and does not pose a great danger if it does not penetrate into the deep layers of the mucous membrane. But it all depends on the temperature of the food, steam or drink ingested and on the time of action of the hot agent.
Children are most susceptible to these types of injuries. Therefore, to prevent a child from getting a burn on the palate from hot food, you should always check the temperature of the food served on the table.
There are three degrees of burn injury:
- First degree. Acute pain, the mucous membrane turns red.
- Second degree. The appearance of a gray-white plaque with liquid blisters.
- Third degree. Tissue death is observed.
The first and second degrees of severity are the most common and with proper treatment, regeneration of damaged areas occurs quickly. Grade 3 is very rare, it is the most difficult and can only be treated in a hospital.
Burn of the larynx by gastric juice. In diseases accompanied by the release of bile, you can get injury to the larynx caused by gastric juice.
Symptoms of damage: sharp pain, irritation of the mucous membrane, a feeling of chest compression, gag reflex, heartburn, increased formation of bile after eating heavy food.
Chemical burn and its signs
Chemicals such as acids and alkalis, as well as their vapors, if they enter through the oral cavity or nasopharynx, cause this type of injury. You should also be very careful with medications, for example, iodine or Lugol, which can cause chemical damage.
Chemical injuries are more dangerous than thermal ones, since after ingestion they have a destructive effect on tissue cells for a long time. The general symptoms of the chemical type are basically the same as for thermal injury: acute pain, the mucous membrane becomes red, and a strong burning sensation is felt.
When lubricating the throat during inflammation of the tonsils, there is a chance of getting a throat burn with Lugol if it is highly concentrated.
During radiotherapy of the mucous membrane, if the dosage of the drugs is not observed, a burn from electrophoresis is possible. To prevent this from happening, you must know the list of contraindications for this procedure.
A burn of the larynx by gastric juice also refers to a chemical type of injury, but is classified as a separate type.
First aid for burns of the trachea and throat
It is advisable for every person to know the procedure for emergency actions in case of a throat burn and what to do in such cases, as well as how and how to treat it.
Providing first aid consists, first of all, of quickly and competently providing it, a lot depends on it. The more quickly it is provided, the faster and easier the treatment will be.
First of all, the patient must be given cool water to drink. Afterwards you need to treat the affected area with an anesthetic.
If the injury is caused by acid, then you need to dilute 2 grams of baking soda in a liter of water and give this solution to the injured person to drink.
In case of damage due to exposure to alkali, for oral administration you need to dilute 3 grams of acetic or citric acid in a liter of water
First aid for a throat burned by iodine is simple. It is enough to rinse for 15 minutes with boiled water at a temperature of 16-18 degrees, and then apply a sugar solution to the damaged area.
In the room, you need to open a window to let air in and call an ambulance.
Further treatment
Treatment at home. Treatment of such ailments in a mild form can be carried out at home, since there is no threat to the life and health of the victim, and the treatment is not complicated.
1st and 2nd degree burn injuries to the throat are not very dangerous and can be easily treated at home. It can be treated both with the use of medications and by resorting to folk remedies. Typically, rosehip oil is used, and when gargling, soothing, healing herbs are used. But still, before treating a burn in the throat, it is strongly recommended to consult a doctor.
Means for treating a burn of the larynx with boiling water.
In this case, drugs of the following types are used: almagel, phosphalugel, de-nol, rennie, methyluracil, motilium, gaviscon, vitamins A and E, lanza and nolpaza.
All these drugs are available, but consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Hospital treatment. The most dangerous injuries of this type are classified as third degree and are treated only under the close supervision of doctors and only in a hospital.
A throat burn is an injury to the mucous membrane of the throat caused by the destructive effects of chemical or thermal factors. The main cause of the pathology is simple carelessness. Burns occur accidentally in domestic or industrial conditions, as well as intentionally - during a suicide attempt. Industrial burns occur when inhaling vapors of chemical compounds while working without personal protective equipment, for example, without a respirator. Children are most susceptible to throat burns as a result of insufficient control over them, but they often occur in adults.
A burn of the larynx is a lesion of the epithelium, and in severe cases of deep-lying tissues: muscles, ligaments, cartilage. The consequences of such pathologies are very dangerous for humans.
Chemical or thermal damage to the larynx causes immediate pain and requires immediate medical attention and adequate correction.
Minor burns may not be treated, since the epithelium of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract has the ability to quickly repair itself. Severe injuries can lead to disability and even death.
Depending on the type of etiopathogenetic factor involved, throat burns are classified into chemical and thermal. Symptoms and methods of providing first aid for these ailments are somewhat different.
Etiology
The causes of burns to the throat mucosa are divided into two large groups: chemical and thermal.
- Chemical burn to the throat - a serious problem, the main cause of which in domestic conditions is alcohol or certain medications. Treatment of tonsillitis with iodine solution or alcohol tinctures can lead to a chemical burn of the throat mucosa. Iodine is an aggressive chemical that can cause serious tissue burns. "Lugol", "Yox" - medicines prepared on the basis of iodine. The use of these drugs in the presence of severe pharyngitis or tonsillitis can result in a burn of the mucous membrane. Specific substances that cause chemical burns include: citric acid, vinegar, ammonia, soda, acetone, acids and alkalis, ethyl alcohol. A burn of the larynx, accompanied by pain and burning, can be caused by the reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus during gastritis with high acidity. Acids cause coagulation of muscle proteins and the formation of a dry scab, which is an obstacle to further penetration of the chemical. Alkalis have a more aggressive effect on the laryngeal mucosa. They dissolve proteins. In this case, wet necrosis develops, allowing chemicals to penetrate inside.
- Thermal burn of the larynx occurs when consuming hot food and boiling water, as well as when inhaling hot air, for example, during fires. Many burn blisters appear on the oral mucosa. At the same time, the victim develops vision problems, general health worsens, and the functioning of internal organs is disrupted. This is a milder form of pathology compared to chemical damage to the laryngeal mucosa, which is associated with short-term exposure to hot substances and their rapid neutralization with cool water.
Symptoms
A burn to the throat is manifested by intense and excruciating pain when swallowing, burning and painful sensations in the nasopharynx, profuse salivation, dyspeptic disorders, fever, swelling and redness of the mucous membrane, the appearance of blisters and areas of whitening on it, enlarged and painful lymph nodes, changes in the timbre of the voice, cough , shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat.
Burn injuries often spread from the larynx to the lower parts of the respiratory system: the trachea and bronchi. At the same time, the general condition of the patients worsens significantly. Trauma to the esophagus is manifested by excruciating pain in the chest and epigastrium, prolonged hiccups, belching and heartburn. Simultaneous irritation of a large number of nerve endings leads to serious consequences - reflex cessation of breathing. In cases of severe burns, toxic shock occurs.
A local burn of the pharynx is manifested by internal discomfort and goes away on its own within a week. More serious injuries require consultation with a doctor and comprehensive treatment.
- Thermal burn of the larynx occurs when drinking hot liquid, food or inhaling hot air. A burn from boiling water cannot be isolated. It usually spreads to the mucous membrane of the mouth, esophagus, and trachea. The symptoms of the pathology develop rapidly and cause a lot of trouble. The victim experiences sharp and excruciating pain, hypersalivation, reflex vomiting and other characteristic clinical signs.
- Chemical burns are less common than thermal burns. but it is much more severe and less responsive to therapy. Throat burns from various chemicals are very dangerous for humans. Clinically, they manifest themselves with the same symptoms as thermal ones. When a chemical enters the respiratory tract, dysphagia and dysphonia occur, and respiratory functions are disrupted.
Based on the severity and severity of tissue damage, there are three types of throat burns:
- 1st degree burn It is characterized by damage to the surface epithelium, on which whitened areas appear, and after 2-3 days they begin to separate. Patients feel a burning sensation and slight pain in the throat.
- 2nd degree burn characterized by more serious tissue damage and the formation of blisters with gray films on the mucosa. By the end of the second week, the plaque separates, the blisters burst, and erosions appear in their place - sores. They heal with the formation of small superficial scars that do not cause organ dysfunction. Intoxication is added to the pain syndrome.
- 3rd degree burn manifested by severe intoxication of the body and abundant purulent sputum caused by the death of inflamed tissues. Scabs appear on the mucous membrane, which over time are rejected to form large and deep bleeding ulcers. After they heal, a scar remains, disrupting the swallowing process.
Second- and third-degree throat burns are dangerous injuries. In the absence of timely medical care, the victim may die due to suffocation or intoxication.
Urgent Care
The prognosis of the disease depends on the quality and speed of emergency care. First, it is necessary to establish the damage factor by inspecting the scene of the incident and interviewing witnesses. Then they move on to inspecting the affected area. With acid burns, there is a dry scab on the mucous membrane, and with alkaline burns, there is a wet, jelly-like scab.
- First aid for thermal burns involves drinking cool water, crushed ice, or gargling with anesthetic solutions.. Cold water will stop the burn from spreading into the tissue. You need to drink it in small sips, holding the water longer near the damaged area. Pieces of ice must be dissolved in the mouth. To reduce pain, you can take a solution of novocaine or lidocaine.
- In case of a chemical burn, first aid is aimed at neutralizing acids and alkalis that have entered the body. For acid burns, use a solution of soda, and for alkaline burns, use a solution of citric or acetic acid. The patient should rinse the stomach, give a glass of milk and a little vegetable oil, and then call an ambulance.
To alleviate the patient’s condition, it is necessary to ensure an influx of fresh air, maintain a quiet regime, and exclude from the diet foods that irritate the affected mucous membrane and interfere with regeneration.
Treatment
It is necessary to treat 2nd and 3rd degree throat burns in a hospital setting. First degree burns are treated at home under medical supervision.
In the hospital, patients are prescribed the following groups of drugs:
- Painkillers – “Lidocaine”, “Trimecaine”, “Analgin”, painkillers pastes, narcotic analgesics “Fentanyl”, “Naltrexone”, “Promedol”.
- Sedatives – “Relanium”, “Persen”, “Valoserdin”, “Afobazol”.
- Detoxification therapy is carried out for deep burns - intravenous administration of glucose-saline solutions, Ringer's solution, Lasix.
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics and sulfonamides are used to prevent secondary infection. Typically, patients are prescribed drugs from the group of fluoroquinolones, macrolides, and the latest generation cephalosporins.
- Glucocorticosteroids to reduce swelling and relieve shock - Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone.
- Antiseptic solutions for rinsing - “Anestezin”, “Miramistin”, “Tantum Verde”, “Aqualor”.
- Antihistamines - Diphenhydramine, Calcium Chloride, Suprastin.
- Drugs that accelerate epithelization and tissue regeneration - “Aaevit”, “Retinol”, “Aekol”, “Solcoseryl”, “Methyluracil”.
Experts transfer patients with a burn to the larynx to a gentle diet and recommend eating only soft, cool food in pureed form.
For the treatment of burns first degree They use traditional medicine, topical medications, and physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Gargling with decoctions of medicinal herbs,
- Cold compresses on the neck,
- Irrigation of affected tissues with peach or rosehip oil,
- Oil inhalations,
- Lubricating a sore throat with olive or sea buckthorn oil.
In severe cases, surgical methods are used to treat burns. Operations are performed when scars, ulcers, or serious deformities form, which lead to dysfunction of the affected organ.
Treatment of local burns gives a good result: the mucous membrane quickly regenerates. With 2nd and 3rd degree burns, tragic consequences may develop that can lead to disability and death of the victim.
Prevention
It is known that burn diseases of the larynx are usually the result of simple carelessness. To prevent this, you need to pay a lot of attention to preventive measures, be vigilant and extremely attentive.
- Small children should not be left unattended. Before giving your babies a bottle of formula, you need to try it. Do not leave hot drinks, household chemicals and other chemicals within reach.
- Hazardous substances should be stored in specially designated areas out of the reach of children.
- People who are interested in alternative medicine can use prescriptions only after consultation with a specialist.
- It is necessary to follow safety precautions and know the rules of first aid.
A throat burn is damage to the epithelial and underlying tissues of the mucous membrane of the throat, provoked by the action of high temperature or chemical reagents. This can be an industrial or domestic injury, and the main reason is ordinary negligence and a violation of safety regulations.
Superficial burns are not dangerous to health, while severe damage can cause disability and even death and require adequate, timely drug therapy. Let's find out what to do in case of a throat burn: how to immediately help the victim and how to treat the injury.
General information
Children often receive household throat burns due to inattention and insufficient parental control. Adults are more often injured at work - during an accident or due to violation of safety rules (for example, when working with aggressive chemicals without a respirator).
At the same time as the throat, the mucous membranes lining the oral cavity and the tissues of the tongue are injured. In severe situations, damage affects the larynx and trachea, bronchi and lungs, and esophagus. In this case, not only the epithelium is destroyed, but also the underlying muscle structures.
With mild burns, healing of the mucous membranes occurs quite quickly even without special treatment. However, a deep burn of the larynx and throat causes unbearable pain and requires immediate adequate treatment. In another situation, the injury can cause disability or even death of the victim.
Depending on the type of damaging agent, a throat burn can be thermal or chemical.
Thermal injuries include:
- burn of the throat with boiling water (in case of accidental swallowing of hot liquid);
- hot steam (in case of violation of the rules of inhalation, during an industrial accident);
- hot air (in case of fire).
Chemical burns to the throat are caused by exposure to:
- alcohol;
- pharmacological agents (iodine, hydrogen peroxide);
- acids, alkalis and other aggressive chemicals (acetone, saturated solutions of ammonia, soda, citric and acetic acid).
Alcohol burns to the throat are caused by the consumption of ethyl alcohol (70 or 96%). Such injuries are diagnosed mainly in people suffering from chronic alcoholism, who instead of high-quality alcohol drink medical or industrial alcohol or tinctures based on it.
Of the pharmacological drugs, iodine often provokes injury. One of the well-known methods of treating pharyngitis and tonsillitis is gargling with iodine solution or preparations based on it (Yoks, Lugol). But if you gargle with an overly concentrated solution or use the drugs more often than the manufacturer recommends in the instructions, it is easy to get a throat burn from iodine.
A burn from chemical reagents develops as a result of accidental or special (during a suicide attempt) ingestion of acid, alkali, or inhalation of fumes from their solutions. When exposed to acid, dehydration and destruction of cells occurs, as a result of which the burned tissues become covered with a dry crust (scab). This crust prevents the penetration of aggressive substances deep into the tissue. And when exposed to alkali, protein structures are destroyed, forming a gelatinous mass (wet scab), through which the aggressive reagent easily penetrates into the underlying tissue, destroying them, causing massive necrosis. This is why burns from alkalis are more dangerous than burns from acid.
Acid damage also includes a burn of the larynx from gastric juice. The stomach produces hydrochloric acid, which is necessary for normal digestion. With esophageal reflux disease, stomach contents reflux into the esophagus. The result is damage to the esophagus and adjacent walls of the larynx by hydrochloric acid.
According to statistics, of all types of chemical burns to the throat, alcohol damage is the most common.
Symptoms
A throat burn is accompanied by:
- burning in the nasopharynx;
- sore throat that gets worse when swallowing;
- excessive salivation;
- hyperemia (redness) and swelling of the mucous membranes of the pharynx and mouth;
- the formation of blisters and areas of necrosis (whitish plaque) on the mucous membranes of the mouth, throat, and when exposed to chemicals - dry or wet scab;
- inflammation of nearby lymph nodes, their enlargement, pain;
- change in voice (hoarseness, nasality, hoarseness).
A serious burn extending to the larynx and organs of the lower respiratory tract also manifests itself:
- rapid heartbeat;
- elevated temperature, fever;
- headache, dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- drowsiness;
- general malaise.
Depending on the type and location of the injury, in addition to the main symptoms, specific clinical manifestations may occur. So:
- a burn of the throat with alcohol is accompanied by dizziness, weakness, pain in the chest and stomach, loss of taste;
- the main symptoms of a chemical burn to the throat are often accompanied by the development of painful shock, disruption of the kidneys, liver, and heart;
- thermal damage due to fire or inhalation of hot steam is accompanied by redness of the conjunctiva of the eyes, lacrimation, blurred vision, which are caused by high temperature and smoke;
- with simultaneous damage to the walls of the esophagus, burning, unbearable pain behind the sternum and in the epigastric region, heartburn, nausea, and bloody vomiting are noted;
- combined damage to the larynx, trachea, and bronchi is manifested by chest pain, severe shortness of breath, respiratory distress, cyanosis of the skin (a sign of respiratory failure), cough, and audible wheezing in the lungs.
Degrees
Based on the depth of tissue damage and the severity of symptoms, 3 degrees of throat burns are distinguished.
- Damage to the surface epithelium with hyperemia of the mucous membrane, the appearance of whitish areas on its surface. The injury is accompanied only by a slight burning sensation and soreness in the throat.
- Damage to the epithelium and submucosal tissues, formation of grayish blisters on the surface. With a burn, in addition to local symptoms, signs of intoxication occur (fever, headache). The blisters burst 1-2 weeks after the injury, leaving open wounds - erosions - in their place. During healing, small scars form on the tissues, but the functions of the organ are not impaired in the future.
- Damage to deep structures leads to the formation of dry (with temperature and acid exposure) or wet (with alkali burns) scab. Massive necrosis (death) of tissue causes severe poisoning of the body with toxins. After the scab is rejected, deep bleeding wounds remain on the surface. The healing of ulcers and erosions is accompanied by the formation of large scars, which subsequently impair swallowing function.
A burn of the mucous membrane of the throat of the 2nd and 3rd degree is a dangerous injury, which, if not treated correctly and/or untimely, leads to death due to asphyxia (suffocation) or severe intoxication.
First aid
The prognosis for recovery from a throat burn is influenced by the quality and timeliness of first aid. To help the victim, you must:
- stop exposure to the damaging factor;
- provide access to fresh air;
- to relieve pain, give the victim any painkiller (for severe pain, you can administer an injection solution intramuscularly);
- call emergency help.
In case of thermal injury, cool water (drink in small sips) helps reduce pain and stop further tissue damage. In case of intense pain, the victim needs to gargle with a 0.25% anesthetic solution (Lidocaine, Novocaine).
To neutralize the aggressive effect of acid, gargle with a soda solution; for a burn with alkali, use a weak solution of citric acid or vinegar.
Treatment
Treatment of superficial injuries of the 1st degree is carried out on an outpatient basis. But your doctor should tell you how to treat a burnt throat at home. After all, only a specialist can accurately assess the location, depth and nature of the damage. Most often, for mild damage to the mucous membrane, it is recommended:
- gargle with medicinal herbal decoctions and infusions (you can use chamomile, oak bark, sage, calendula, thyme and infusions of these plants);
- apply cool compresses to the neck area;
- lubricate the throat mucosa with sea buckthorn and rosehip oils.
Treatment of a chemical burn of the throat and thermal injury of 2-3 degrees is no different, it is carried out only in a hospital, and includes the following:
- local anesthetic solutions (Lidocaine, Novocaine) - relieve pain;
- antiseptic rinsing solutions (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, Tantum Verde) - have a disinfectant effect;
- local regenerating compositions for lubricating or irrigating the throat (Aevit, Aekol, Karotolin) - accelerate tissue healing;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Dexalgin, Ketanov, Ketorol) – relieve inflammation and swelling;
- narcotic analgesics (Promedol) - relieve severe pain in severe injury;
- antihistamines (Suprastin, Tavegil) - reduce swelling and hyperemia;
- glucocorticosteroids (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone) – suppress inflammatory processes, reduce pain and swelling, and are used to relieve burn shock;
- antibacterial drugs (Amoxiclav, Ceftriaxone, Azithromycin) - prevent or treat existing infectious complications;
- sedatives (Relanium, Afobazol) - normalize the state of the nervous system after injury;
- detoxification agents (solutions of Glucose, Ringer, Hemodez) - administered intravenously to eliminate symptoms of intoxication and normalize electrolyte balance in case of deep injuries, treatment of burn disease.
During treatment of the larynx and throat, it is important to eliminate stress on the vocal cords and minimize the impact of irritating factors on damaged tissues:
- do not talk a lot, speak in a whisper if necessary;
- eat only pureed food at room temperature;
- do not smoke, give up alcohol, spicy and salty foods, hot dishes and drinks.
If the burn is severe and healing proceeds with the formation of large scars that cause functional impairment of the organ, surgical intervention may be required.
Superficial isolated burns of the throat do not pose a particular threat - tissues quickly recover even without special drug treatment. However, most often the damage covers deeper structures, extending to the larynx, trachea, esophagus, and lower respiratory tract. Severe burns are accompanied by serious functional impairments, are difficult to treat, and lead to disability. If you have a thermal or chemical injury to your throat, do not hesitate to consult a doctor. Only a specialist will be able to accurately determine the extent and extent of damage and advise how to treat a throat burn in a particular case.