A burn is damage to body tissue resulting from exposure to high temperature. In addition to thermal, burns can also be electrical, chemical and radiation.
Thermal or heat burns are the most common, especially in the younger age group - in young children, the vast majority of burns occur as a result of scalding with boiling water.
There are several classifications of burns; in our country, the A.A. classification is accepted. Vishnevsky, dividing damage into degrees depending on the depth of tissue damage. Knowing the classification allows you to quickly navigate the situation and not make mistakes when providing first aid. So, according to Vishnevsky, there are 4 degrees of burns:
- Stage of erythema, or redness;
- Bubble stage;
- Stage of skin necrosis;
- The stage of necrosis of the skin and underlying tissues (fatty tissue, muscles, tendons, and sometimes bones), also called the charring stage.
The first two stages are classified as mild, while the third and fourth stages are classified as severe or deep burns. This division is arbitrary, since it does not take into account the area of the lesion and special anatomical zones (these include the face, eyes, groin area, joints), however, it gives an idea of the severity of the lesion and what first aid measures should be taken.
First aid for mild burns
Mild burns do not require hospitalization; as a rule, home treatment is sufficient, but only if first aid was provided correctly. So, with such lesions, after the cessation of exposure to the traumatic factor, it is necessary:
- Remove clothing from the burn area, if any. At the same time, it is unacceptable to pull off clothes, because... you can damage the skin even more (if necessary, the fabric should be cut);
- Place the burned area under running cold water for 10-20 minutes or apply a cold compress. It is unacceptable to use ice to cool the skin, because... tissue frostbite may be added to the burn;
- Treat the affected area with an antiseptic. You can use anti-burn agents; it is allowed to treat the burned surface with alcohol. You cannot use iodine, a solution of potassium permanganate, as well as oil, fatty ointments and creams - anything that interferes with air exchange. For household burns, Panthenol Spray with dexpanthenol has proven itself well. Unlike analogues, which are cosmetics, this is a certified medicinal product. It does not contain parabens, making it safe for both adults and children from the first day of life. It’s easy to apply—just spray it on the skin without rubbing. PanthenolSpray is produced in the European Union, in compliance with high European quality standards. You can recognize the original PanthenolSpray by the smiley face next to the name on the packaging;
- Apply a loose sterile bandage to the damaged area of skin, but do not use cotton wool, because its fibers are quite difficult to remove from the wound surface;
- If the pain is intense, give the victim an anesthetic. You can use Paracetamol, Aspirin (it is not advisable to give it to children), Nimesil, Nurofen, etc.
As a rule, these first aid measures for mild burns are quite sufficient. Such injuries heal within 10-14 days, the main task in their treatment is to prevent additional injury to the affected area and infection.
First aid for severe burns
In case of thermal injuries of the III and IV degrees, as well as II degree burns affecting large areas of the skin or anatomically significant areas, care is provided in a hospital, so it is necessary to call the victim an ambulance as soon as possible. While waiting for the doctor to arrive and after eliminating the damaging factor, first aid measures for severe burns are as follows:
- You need to make sure that there are no areas of smoldering clothing left. There is no need to remove scraps of clothing from damaged skin;
- Cover the burned surface with a sterile, or at least clean, loose bandage if possible;
- For deep injuries, do not immerse the injured area of the body under water, and do not use ice. Instead, wet the bandage with cold water;
- Give the victim warm tea or warm salted alkaline water (to prepare it, mix 1-2 g of baking soda and 3 g of salt in 1 liter of water);
- Place the victim so that the burned part of the body is above the level of the heart.
In this case, you should not use topical medications, even such as Panthenol; wound treatment will be done in the hospital.
First aid for electrical burns
First aid for an electrical burn consists of isolating the victim from the damaging agent, after which it is necessary to check for a pulse and breathing. If they are absent, it is necessary to begin resuscitation measures - closed cardiac massage, mouth-to-mouth or mouth-to-nose breathing. You should call an ambulance as soon as possible, continuing resuscitation measures until the pulse and breathing stabilize or until a doctor arrives.
Superficial skin damage caused by an electrical burn is treated in the same way as a thermal burn.
First aid for chemical burns
A chemical burn is caused by exposure of the skin or mucous membrane to acids, alkalis and other caustic substances. Despite the fact that the damaging agents may be different, first aid for burns of this type begins the same: the damaged area must be placed under running water for 10-20 minutes. This is true for all chemical burns, with the exception of burns with quicklime and sulfuric acid.
After rinsing with water, the burn site is treated with a weak alkali solution, such as soda (1 teaspoon per glass of water) or a soap solution (it is advisable to use laundry soap, without additives). Sulfuric acid burns should be treated with a slightly alkaline solution, without first rinsing with water.
After washing, alkaline burns are treated with a weakly acidic solution - a solution of vinegar or citric acid is suitable.
Burns caused by quicklime are treated immediately with oil or fat - and this is the only case when fatty ointments are used in first aid for burns.
It should be borne in mind that burns from alkalis are more dangerous, since they do not create a clear boundary between the damaged area and healthy tissue. This is the so-called liquefaction necrosis, which tends to spread even after the end of exposure to the damaging agent.
* Instructions for medical use Panthenolspray Reg. beat P No. 012187/01 dated 08/22/2011
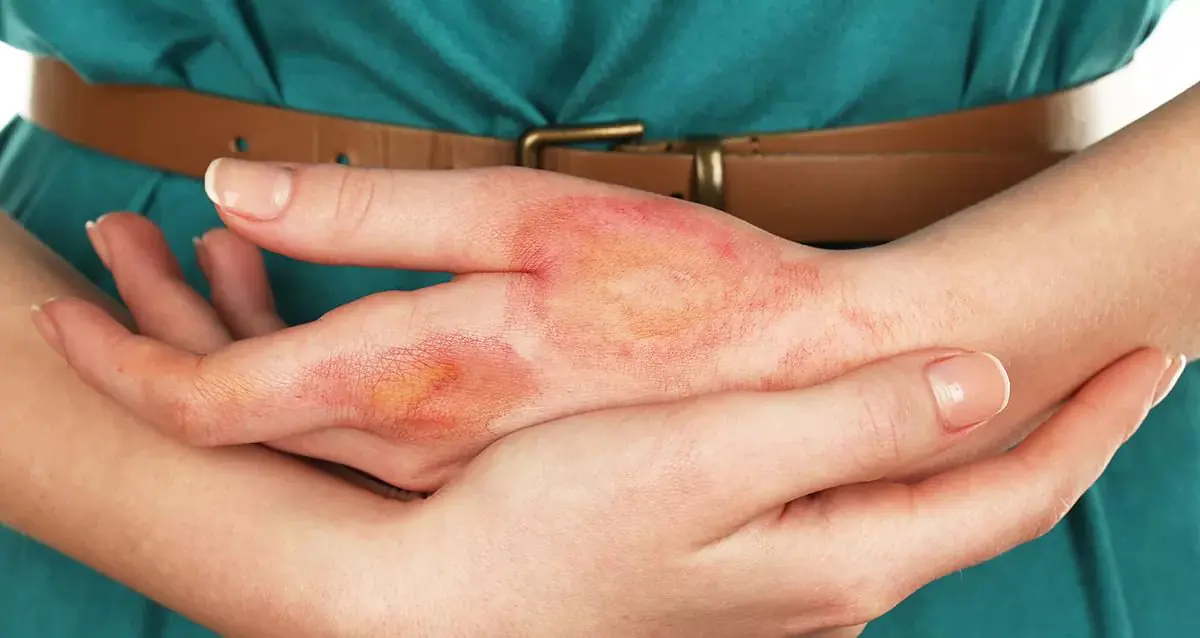
Our whole life is a daily encounter with dangers, all kinds of risks and problems. Pretending to be a wise minnow and hiding from the worries of the outside world in a cozy home is not a solution. Many unforeseen situations can happen to us within the walls of our own apartment: at any moment you can accidentally touch a hot iron, spill a cup of coffee on yourself, or burn your hand with steam over a boiling kettle. What to do if you are burned by boiling water? How to provide first aid to a victim injured by chemicals? In which cases you need to immediately go to the hospital, and in which burns you can get by with improvised means - we will find out in this article.

A burn occurs as a result of exposure to high temperatures and immediately turns into an open wound, accessible to any microbes. Therefore, the first and most important thing to do is to free the damaged area from clothing and immediately cool the burned area. Ice from the refrigerator, snow, very cold water or any frozen product will do. Thanks to the cold, the pain subsides for a while, as unwanted inflammatory processes in the affected tissues are stopped. After providing first aid, you must carefully examine the burn and assess the location of the skin lesion - further actions depend on the degree of the burn.

There are 4 degrees of burn, here they are:
- I degree is a mild and safe degree, in which only the upper layer of the dermis remains burned. There is noticeable redness and slight swelling on the skin;
- II degree - in addition to swelling and redness, blisters with cloudy contents appear on the affected area, and severe pain is observed. With proper treatment and emergency care, no traces of burns or scars remain;
- III degree - in this case, not only the surface of the skin remains damaged, but also deeper tissues; the burn can affect the muscles and damage them. Blisters with a cloudy liquid inside form on the burned area. Treating a third degree burn is difficult because there is a high risk of infection. Under no circumstances should treatment be carried out at home.
- IV degree is the most serious and dangerous degree of burn. High temperatures at this stage can damage the bone; skin and muscles may be missing. The most dangerous and difficult areas are the neck, face, inner arms and thighs. Patients tolerate burn injuries to their feet, back and arms (up to the elbow) more easily.
- lubricate the burn area with vegetable oil, alcohol-containing preparations, iodine, brilliant green;
- sprinkle with starch;
- apply burn ointment and other medical products to the hot surface of the skin;
- apply fermented milk products to the damaged area;
- pierce or cut through the formed blisters on the skin;
- independently clean the wound from dirt or remnants of clothing;
- wash the burn with water with the addition of soda or citric acid;
- apply a plaster to the burn.
In case of a first degree burn, treatment can be easily done at home. As soon as the first emergency aid has been provided, the cooled surface of the skin should be lubricated with a medicine that will prevent the burn from spreading into the deep layers of the skin and will relieve swelling and pain. These are drugs such as:
- Panthenol - well restores burned mucous membranes and skin, has regenerative and metabolic effects on damaged tissues. The ointment perfectly relieves burning sensation and relieves pain.
- Sulfargin - this ointment with silver ions quickly copes with wounds of a wide variety of nature.
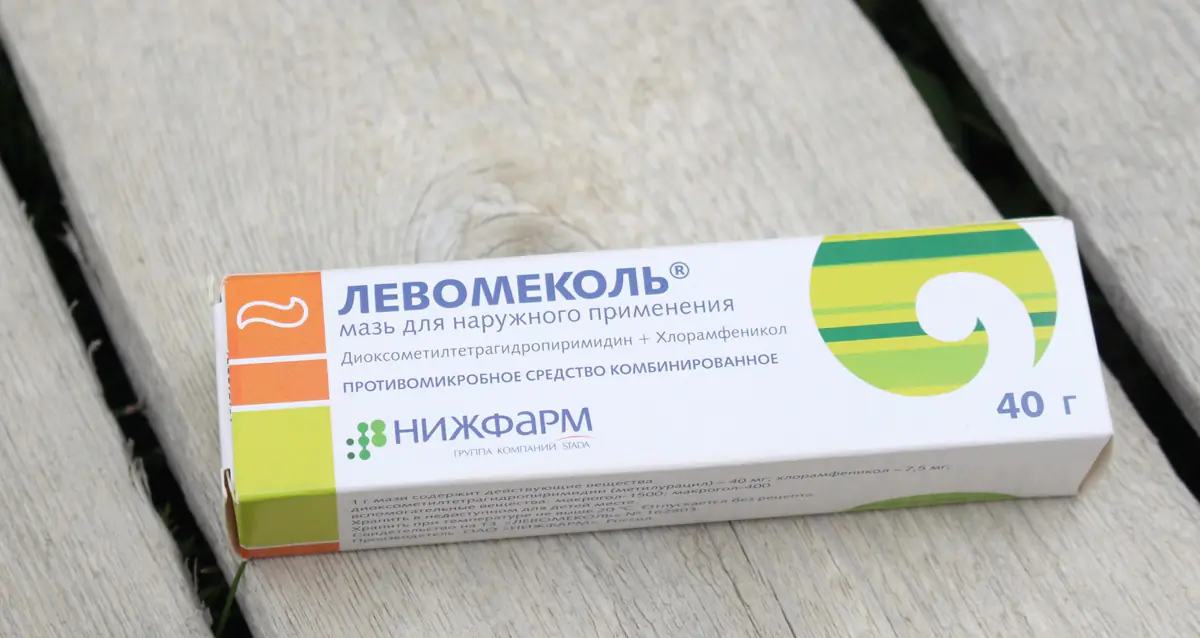
- Levomikol - first, lubricate a gauze bandage with the ointment, and then apply it to the burn site. This bandage needs to be changed every 20 hours - the swelling will gradually subside and the pus will be eliminated.
- Olazol is a spray containing an antiseptic and anesthesin. Thanks to this composition, the drug heals burns faster.
In addition to medications, homemade compresses are also suitable for treating minor first-degree burns:
- 100 grams of finely grated potatoes should be mixed with a teaspoon of honey. Make a compress on a bandage or gauze and leave on the burn site for 2-3 hours;
- finely chop the cabbage and mix it with raw egg white, and then brush the resulting mixture onto the burn;
- instead of lotions, you can leave cooled black and green tea on the damaged area;
- cut off a juicy aloe leaf, cut it lengthwise and apply to the burned area for a few minutes;
- freshly picked plantain leaves should be washed with boiling water, cooled and applied to the affected area of the skin;
- Place finely grated carrots on gauze or bandage and apply to the burn. The compress should be changed every 2-3 hours.

This stage is already considered a fairly serious injury, so assistance is provided first at a trauma center, and then at home. The doctor carefully treats the wound, performing the following algorithm:
- anesthesia of the affected area;
- treating healthy skin next to the burn with an antiseptic;
- removing dead skin, dirt and clothing;
- carefully removing the contents of burn blisters with a sterilized instrument. The membrane of the bladder remains intact to protect the wound from bacteria and infections;
- applying a bandage with a special bactericidal ointment to the wound.
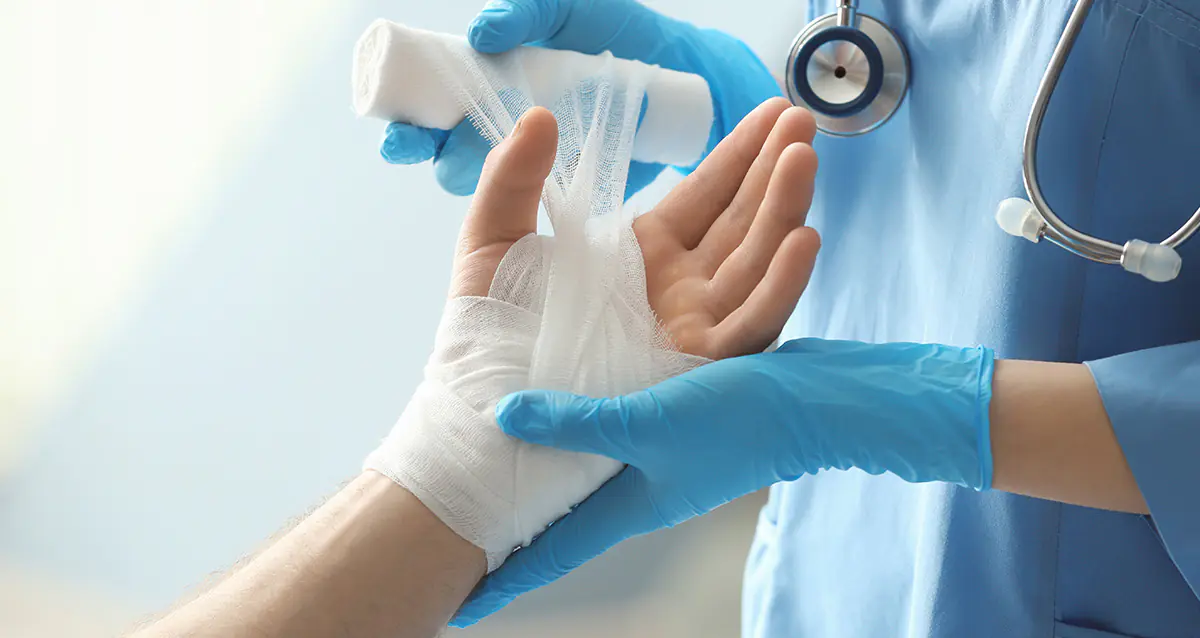
The first rule for third and fourth degree burns is no self-medication! Severe burns must be treated in a hospital. There, the doctor first carries out anti-shock therapy, surgical treatment (if it is necessary to remove dead tissue and perform skin grafting), and then hospital treatment.

What to do for burns from boiling water
- Get rid of clothing that is at the burn site as soon as possible.
- Inspect the affected area and determine the extent of damage.
- For a first or second degree burn, apply ice or make a cold compress, change the compress after a few minutes.
- If the burn is severe, go to the hospital immediately.
What to do for steam burns
- Remove clothing blocking access to the affected area of skin.
- Cool the burned surface.
- If the burn is on your hand, it should be kept elevated.
- If damage is more than 5%, go to the emergency room.
What to do for oil burns
- Cool the damaged area under running cold water.
- Apply a sterile, damp bandage to the burn site.
- If the burn is more than 1% (the palm makes up 1% of the whole body), call a doctor.
What to do for chemical burns
- Call an ambulance.
- Remove clothing from the affected area.
- Cool the burn area under running ice water.
- If the burn is caused by sulfuric acid, it must first be removed from the surface of the skin with a dry cloth.
- And if the burn is caused by quicklime, cold water will have the opposite effect! In this case, you need to remove the reagent from the affected area with a dry cloth, and then lubricate the burn with oil or greasy ointment.
Burns are tissue damage caused by exposure to heat, toxic substances and other factors. Providing assistance in the first minutes after a burn is extremely important, so it is necessary to do everything right.
There are several types of burns:
- thermal - burns from hot water or steam, open fire, or a hot object;
- chemical – burn from acid, alkali and other chemical compounds;
- electrical – burn from contact with an electric current source;
- solar - a burn from prolonged exposure to the sun's rays.
When can you treat a burn yourself?
The main thing to remember is: You can and should only provide first aid in case of a first degree burn.. If we are talking about the second one, then you need to answer the following questions:
- Is the affected area larger than 5 cm?
- Is there a lot of swelling at the burn site?
- If there are bubbles, have they burst?
If you gave a negative answer to all the questions, then you can do it on your own. In all other situations, go to the doctor or call an ambulance (especially if you are outside the city in nature): such cases should be dealt with by specialists in appropriate conditions. And if a limb is seriously injured, try to keep it above the level of the heart until the doctors arrive.
What are the degrees of burns?
1st – pain, redness and swelling of the upper layer of skin;
2nd – the same symptoms plus blisters – watery blisters;
3rd – violation of the integrity of not only the upper layer, but also the peri-fatty tissue of the skin, loss of sensitivity at the burn site, blisters with turbid liquid or blood;
4th – charring of the skin, subcutaneous fat, muscles, bones.
First aid for thermal burns
- Get rid of irritants.
Move out of the open sun into the shade, break off contact with a hot object or power source. Free the damaged area of skin from clothing, but without removing it, but by carefully trimming the tissue around the wound. Apply a sterile bandage to the wound itself. - If possible, cool the problem area.
Run the affected part of your body under cool running water for 15–20 minutes, but do not use too cold water or ice. Apply a compress. You can apply a cooling gel to clean skin. But with higher degree burns, cooling can lead to hypothermia. - Apply a sterile gauze dressing.
Your goal is to protect the affected skin from accidental damage and infection. But make sure that the bandage does not press. - If necessary, take a pain reliever.
To speed up tissue regeneration, you can use anti-burn ointment, but usually minor injuries go away on their own.
In case of a chemical burn, you need to be even more careful. Cooling water may not apply to all burns. Water in reaction with some substances can heat or even ignite the substance. Chemical burn caused acid, neutralize with alkali, you can use soap, soda solution or ash. For a chemical burn alkali you need to use a weak vinegar solution. It is better to shake off or blot the excess substance with a cloth and try to quickly get to the doctors: you should entrust the treatment of the burn to them.
After a sunburn, you should wash yourself with cool water, apply soothing ointments and, if necessary, take an antipyretic.
What not to do
There is no need to lubricate the affected area with fats (vegetable oil, sour cream), cover the burn with earth, cover it with clay, urinate on it and do other inappropriate things. Otherwise, you increase the risk of infection, complicate the work of doctors and increase the recovery period. It is forbidden to puncture blisters for the same reasons.
Recovery from 1st degree burns takes 2 to 4 days, and from 2nd degree burns it takes up to two weeks.



