All people have moles. Some of them perceive “flies” as decoration. Others worry that the appearance of these tumors is a health threat. It is especially unpleasant when it is in an inconvenient place; involuntarily, it is often touched by clothes and looks unaesthetic. Is it possible to remove the formation? If it bothers you in any way, you should definitely consult a dermatologist. It is not recommended to resort to traditional methods of getting rid of moles, warts, and birthmarks without knowing the degree of their danger.
Content:
- Features of nevi
- Where can moles be located?
- Reasons for the formation of moles
- What is the difference between nevi of varying degrees of danger?
- Indications for removal of nevi
- Methods for removing nevi
- Surgery
- Laser therapy
- Cryodestruction
- Electrocoagulation
- Radio wave removal
- Folk remedies

Features of nevi
Moles (nevi) are benign growths on the skin that are brown or red in color. There are 2 types of moles:
- Pigmented - formed from cells (melanocytes) with a high content of melanin pigment. They can be convex or flat, light brown or almost black.
- Vascular, which are clusters of small blood and lymphatic vessels. They come in pink or red.
There are so-called warty nevi, which are a group of tiny growths. Unlike ordinary warts, they are not viral in origin.
Moles are not completely harmless new growths. The peculiarity is that they can degenerate into skin cancer under the influence of unfavorable factors. However, only a dermatologist can tell you whether these moles can be removed.
Experts distinguish several types of skin tumors, taking into account the degree of their danger to human health:
- nevi (benign);
- melanomas are malignant growths of pigment cells;
- Basaliomas are cancerous skin tumors formed from epithelial cells.
Nevi can be of either congenital or acquired origin.
Note: As a rule, moles have a diameter of 1-5 mm. But there are also unusual congenital neoplasms. These include, for example, a “giant pigmented nevus” (a benign birthmark with a bumpy surface that can cover a large area of skin).
Some moles appear in people already in adulthood (dysplastic nevi).
Where can moles be located?
They can be found on the back, chest, buttocks, limbs and other parts of the body, including the genitals. Often nevi of various types (flat, convex, hanging, having different diameters and shades) are found in the groin, under the arms and even in the eyes or on the head under the hair.
Moles on the body most often exist in humans from birth. In a baby they may not be visible immediately, but over time they acquire normal sizes and become noticeable. At first, their number is usually about 10. During life, it can increase (some people have up to 50-100 nevi on their body).
Moles on the neck They are dangerous because they are easily injured, since this part of the body is constantly rubbed by a collar or scarf. In the summer, such a mole is exposed to sunlight, which can trigger the development of cancer. Hemangiomas (hanging nevi formed from intertwined capillaries) or moles on a long stalk formed from epithelial skin cells often form on the neck. They are especially easily damaged (during shaving, changing clothes), sometimes they are even accidentally torn off.
Note: If accidental damage to the growth occurs, it must be immediately lubricated with brilliant green or treated with alcohol or hydrogen peroxide to prevent inflammation.
Moles on the face. They may appear on the cheek, above the upper or under the lower lip. Often they are “family” - they appear in the same place among several relatives. As they age, they enlarge and become more convex.
Particular attention should be paid to a gradual significant increase in the number of nevi, as well as changes in their appearance and pain. This may be a sign of cancer development.
Reasons for the formation of moles
An important role is played by a person’s hereditary predisposition to the formation of moles of various types. It is believed that the reason for their appearance is the individual characteristics of the structure of genes that affect the formation of epidermal cells.
Skin type matters. Fair-skinned people who freckle easily after exposure to sunlight have low levels of melanin in their skin. This dye protects her from sun exposure. For such people, the tan does not “accumulate.” In the sun they turn red, the skin dries out and is easily damaged. People with fair skin need to cover their moles in sunny weather and try to stay in the shade more. It is harmful for them to visit a solarium, where the skin is artificially exposed to ultraviolet rays.
Hormonal changes occurring in the body also affect the formation of moles and the occurrence of pathological processes in them. This may explain the fact that nevi appear more often in women than in men. Their number and size increase during pregnancy, after childbirth, and during menopause, when hormonal levels change dramatically. Sometimes moles appear in large numbers in adolescents during puberty. Nevi may appear after treatment with hormonal drugs.
Radiation exposure to the skin, as well as exposure to ultraviolet light, contributes to the formation of flat dark spots on the skin (lentigines), as well as small red moles.
The cause of nevi can be skin trauma and even frequent massage.
Video: When a mole is dangerous
What is the difference between nevi of varying degrees of danger?
Conventionally, moles can be divided into “calm”, “suspicious” and “potentially dangerous”.
Quiet nevi do not change their appearance for many years and do not degenerate into cancer. Their characteristics are a smooth surface, a rounded shape, clear boundaries, uniform coloring of the entire surface (the color can be brown or red). The diameter of the growth is no more than 5 mm. If hairs grow on a mole, this is a sure sign that it is benign.
Suspicious nevi differ in that they appear in humans already in adulthood. Over time, the following changes may occur:
- the growth increases, uneven edges form, the diameter exceeds 10 mm;
- the surface of the spot is smooth, shiny, and has a different structure from the surrounding skin;
- the neoplasm itches, the skin on it cracks, and weeping crusts form;
- graininess appears in the structure, the color of the nodules is not uniform;
- The nevus develops a dark or red rim.
Dangerous nevi are large pigment spots with a non-uniform surface. They are removed surgically at the first opportunity, as melanoma can develop from them.
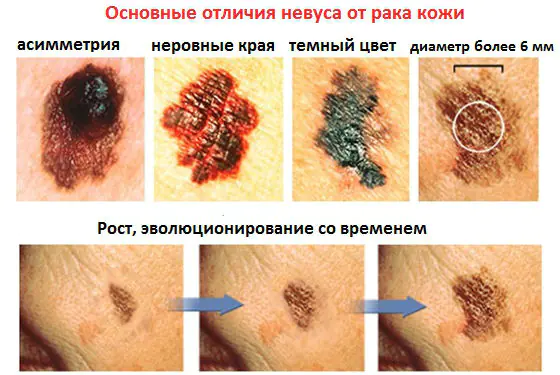
Find signs of danger by regularly inspecting moles yourself. At the same time, oncodermatologists advise following the ACORD method, that is, paying attention to such signs of oncology as asymmetry of the tumor, uneven edges, uneven coloring, changed size and dynamics of development.
You should consult a doctor urgently if the mole becomes inflamed and painful, bleeds, or ulcerates. Alarm should be caused by a change in the proportions of the spot and the structure of the surface (the appearance of red dots on it), the occurrence of pulsation in the nevus, as well as itching and burning.
In the early stages, melanoma is curable, in the later stages it is not.
Video: When moles need to be removed. How is removal done?
Indications for removal of nevi
It is necessary to remove nevi if they are “suspicious” or “dangerous”. In each case, the issue is resolved individually, but it is necessary to remember the harm that self-medication causes.
It is recommended to get rid of moles on the scalp, neck, above the chest, in the folds of the skin, under the arms, on the feet or palms, in the pubic area and perineum - that is, in those places where the likelihood of damage is very high. The risk of damage is especially high in “hanging” neoplasms, since the pedicle may twist and necrosis may occur. They also usually try to remove any large moles located on the face, as they look unaesthetic.
Is it always possible to remove moles? If there are no obvious signs of a health threat, then doctors do not advise removing them “just in case,” since this can, on the contrary, provoke malignant degeneration of cells and their spread throughout the body.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women are advised to remove moles on any part of the body only if absolutely necessary. Surgery is stressful for the body. In addition, after childbirth or cessation of lactation, the neoplasm often decreases and alarming signs disappear. If this does not happen, the tumor is eliminated later.
It is recommended to remove moles from children only in cases of obvious danger. At the same time, doctors try to prescribe non-surgical treatments (plasters, ointments). For the surgical removal of nevi, the same methods are used as for eliminating them in adults.
Methods for removing nevi
If there is no urgent need, surgical removal of moles is carried out in the cool season. Local or general anesthesia is used.
Surgery
The nevus is excised along with nearby healthy tissue. It is necessary to remove the tumor in this way if it is deeply embedded in the skin or there are signs of degeneration into melanoma.
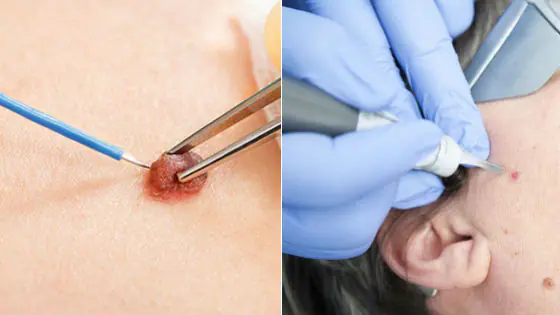
Contraindications are the presence of a person with low blood clotting, as well as an infectious skin lesion in the area of the mole. Since operations are performed under anesthesia, the state of the cardiovascular system is taken into account, as well as the possibility of an allergic reaction to the drugs used.
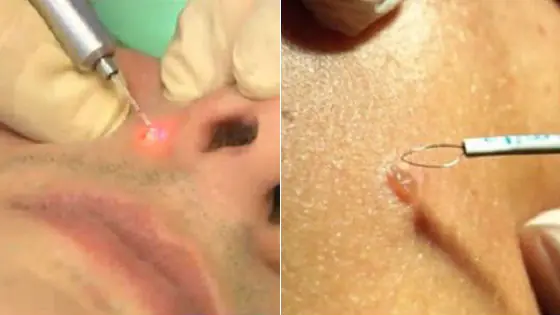
Laser therapy
The tumor is burned out with a laser beam. The advantage of the method is that there is no bleeding, since the blood vessels are immediately sealed.
Cryodestruction
The mole is frozen using liquid nitrogen. The disadvantage is the inability to control the depth of impact. After removal of a large nevus, a scar often remains on the skin.
Electrocoagulation
Moles are burned using a thin platinum electrode through which a high-frequency electric current is passed. The wound heals quickly. There is practically no trace left.
Radio wave removal
To remove small superficial nevi, a radio knife is used - an electrode that emits radio waves. The mole is removed by heating and vaporizing the tissue. There is no scar left since the effect is non-contact.
Folk remedies
In folk medicine, popular methods for removing moles and warts are applying celandine leaves to them, treating them with a suspension of crushed chalk and sunflower oil. It is recommended to use an ointment made from 3 cloves of garlic, 1 tbsp. l. butter and 50 g honey. The mixture is applied to the mole for 4 hours every day until the mole disappears (about 1 month).
Under no circumstances should you resort to similar methods of eliminating moles that have a stalk and change in appearance. Only a doctor can determine the degree of danger of such a neoplasm and its tendency to malignant degeneration.
Measures to prevent the development of skin cancer include constant self-monitoring of the condition of nevi. They should not be injured, exposed to harmful radiation, chemicals, hormonal ointments and medications not prescribed by a doctor.
Possible complications after removal
As with any other operation, after removing a nevus, a scar or light spot may remain on the skin. If the wound is not properly cared for, it becomes inflamed.
A mole often reappears at the site of removal. In this case, it is necessary to check it for the presence of cancer cells (do a biopsy). If a mole is removed due to malignant degeneration, metastases may remain.
The accumulation of melanocytes leads to visible pigmented formations - moles. Their location on the body has no patterns. The presence of such formations does not cause discomfort to a person, but can serve as an aesthetic defect. There are also situations when the nevus is located on the body in traumatic places. Patients, having discovered such a tumor, begin to worry and think about getting rid of it. Whether moles can be removed or not is decided by the doctor individually in each case. He discusses the method of removal with the patient. There are dangerous and safe formations. Not every one of them is recommended to get rid of.
Signs of dangerous moles
Pigmented formations that can develop into a malignant form are considered dangerous. A thorough examination is required before their removal. But already at the first examination, the doctor can assume the presence of cancer based on external signs.
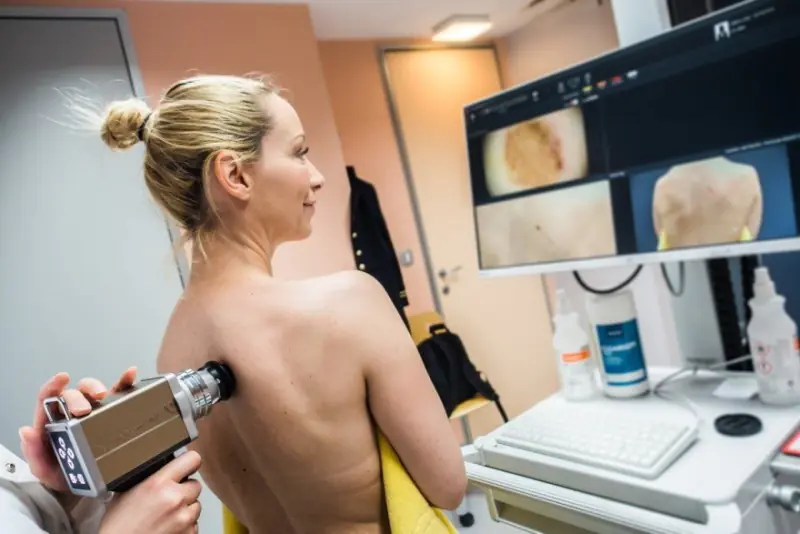
The distinctive features of a dangerous nevus are:
- its sudden occurrence in adults;
- active growth;
- change in shape and thickening of the spot;
- glossy shine or flaking;
- emerging asymmetry;
- the occurrence of itching, burning sensation;
- loss of hair in the pigmentation zone;
- multi-colored area;
- bleeding;
- swelling and redness in the affected area;
- the appearance of nodules on the spot;
- exudative discharge from the formation.
If one or more signs of pathology are detected, it is strictly prohibited to remove pigment formations in beauty salons. This type of mole requires only professional examination in specialized clinics. Oncologists or surgeons prescribe tests. This is necessary to prevent infection, as well as for accurate diagnosis of moles.
Pros and cons of mole removal
All doctors are inclined to believe that any pigmented tumors that cause concern should be removed. Previously, it was assumed that a complication occurred at the site of the removed mole. But later it was found that compliance with all postoperative measures completely eliminates the risk of adverse consequences.
Hygiene rules after removal of a nevus:
- disinfect the wound at least once a day;
- abstain from water procedures for at least five days;
- do not tear off the formed crust from the wound;
- avoid ultraviolet radiation.
In rare cases, removal is considered preventive. It is indicated when there is a high probability of injury to the nevus.
If the cause of the nevus is a hereditary factor and similar formations are located in the same places in other relatives, then removal is contraindicated. Statistics show that most often such moles appear again in the same place.
Is it possible to remove moles for pregnant and lactating women?
Pregnancy and breastfeeding are a special time for a woman. Her body is being rebuilt, hormonal levels are changing, and the work of all systems and organs is intensifying. Therefore, nevus removal is not recommended.
Doctors can only authorize the procedure if there is a threat to the mother’s life. In this case, the doctor will insist on terminating the pregnancy. If treatment can be postponed to a later date, then the operation is postponed until postpartum.
Women carrying a child should not resort to home methods of getting rid of pigmented formations. This in most cases ends in complications, which is very dangerous for the mother and child.
Moles that appear on the mammary glands can interfere with the baby’s feeding process. In such a situation, you should trust a dermatologist, who will determine the degree of risk of injury.
What moles can be removed
Doctors recommend removing nevi if they:
- are located on the scalp, since there is a high probability of injury when combing;
- appeared on the face, lips and spoil the patient’s appearance;
- located in the armpits and intimate area, as they are susceptible to injury during shaving;
- are located in the neck, décolleté and are injured by jewelry;
- sharply begin to change, grow and become asymmetrical.
Removal of tumors should be carried out in specialized medical institutions. After removal, the mole is submitted for histological examination. Getting rid of a nevus on your own can trigger the development of melanoma.
Which nevi cannot be removed
Not all birthmarks can be removed. It is forbidden to get rid of large formations, as this is fraught with the development of inflammation. Before performing such an operation, the doctor conducts an extensive examination to ensure that the risks of complications are minimal.
If a dermatologist has even the slightest suspicion of melanoma or papilloma, then you need to show the nevus to an oncologist. Removal is carried out in an oncology clinic, where the patient remains after the operation for subsequent therapeutic treatment.
Any intervention without examination often leads to the degeneration of pigmented formations into a malignant form.
What are the dangers of mole removal?
The big risk during surgery is the transformation of the mole into cancer. With any incorrect action regarding a tumor, the risks of degeneration into oncology increase sharply. In this case, atypical cells spread throughout the body through the bloodstream and enter any organ and tissue.
Regular preventive examinations allow you to determine the malignancy of tumors at an early stage. This helps to avoid sudden complications.
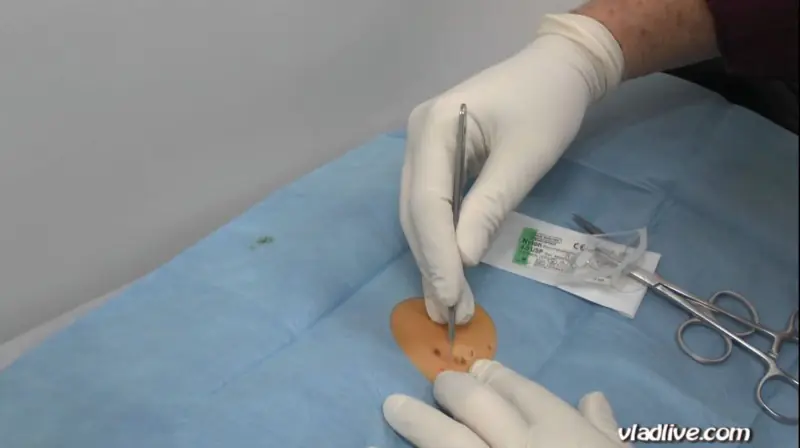
Mole removal methods
If the examination shows that removal of the nevus is possible, then the doctor and the patient choose the method of excision. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages.
The main methods for removing pigment formations are:
- Laser. It is performed under local anesthesia. A laser beam is used for burning. The operation is practically bloodless, since the coagulation of blood vessels occurs during the process. Very short recovery period. The formation is removed in one go. The disadvantage of the method is that the tumor is excised layer by layer, and this excludes the possibility of postoperative histological examination. It is impossible to determine the nature of the mole.
- Cryodestructive. Exposure to liquid nitrogen at low temperatures is used. Anesthesia is carried out locally. This method can remove hemangioma. It is difficult to control the depth of cauterization and it is impossible to select material for histology. Removal of large tumors results in noticeable scars.
- Electrocoagulative. Low frequency currents are used. It is used less and less due to the high risk of injury. There is a plus - you can take a nevus for examination.
- Radio wave. Small superficial nevi are removed. During the operation, a high-frequency radio knife is used. Does not injure the skin and does not leave noticeable marks.
- Surgical. Best suited for excision of large pigmented formations, as well as nevi with deep penetration into the skin. During the operation, a scalpel is used. The nevus and part of the skin are excised. The material for further research is taken in full. Long rehabilitation period. After removal, scars and scars often remain.
At any age, it is necessary to be attentive to skin tumors. Parents are required to carefully monitor moles on their children's skin. Timely contacting a dermatologist eliminates the adverse effects of nevi on the body.
Content:
Is it possible to remove a nevus?
Patients often turn to different doctors with the question: is it possible to remove this or that nevus? And sometimes they hear opposite recommendations on this matter. There is a point of view that if you remove a nevus, then something will certainly break in the human body, a certain balance will shift. It is followed by a small number of doctors and a significant number of people. Neighbors and friends instill fear by telling various scary stories in which, somewhere after the nevus was removed, someone certainly died or became very ill. This point of view is due to the similarities between nevus and melanoma. According to Soviet (some doctors still live there) medical ethics, many people are not told that melanoma was found and removed. They go and tell their relatives and friends that they had a nevus removed. Over time, a person may die from melanoma metastases, despite timely and complete treatment. Most of the acquaintances and relatives will continue to believe (and tell everyone around) that the person died because he decided to remove the nevus. Adding to the chaos and confusion of melanoma with nevi is the habit of some health care workers to call all dark formations melanoma. And the true belief that melanoma can be benign (it is not). The third reason for the appearance of rumors and speculation is medical error. No doctor is immune from it. And a small number of melanomas cannot be diagnosed from the very beginning. They decide to remove the nevus, for example, with a laser. But it turns out to be melanoma and begins to relapse and metastasize. Not all melanomas are dark in color. In fact, almost any nevus can be removed. However, this should be done correctly, to the right depth. Complications such as scars or abscesses occur very rarely. It should be noted that in the compulsory medical insurance system everything is supposed to be done free of charge for the patient. However, it is possible to remove a nevus according to compulsory medical insurance only if it is highly likely to develop into melanoma or is very similar to melanoma. Cosmetic indications are not considered; the compulsory medical insurance fund does not have enough money for them. Therefore, when you contact a doctor at a clinic with this question, keep in mind this feature of compulsory medical insurance. Very large congenital nevi can be removed only after multiple operations with the movement of skin flaps by stretching the skin with special expanders.
Is it possible to remove a nevus at home?
It is unlikely that you will be able to remove a nevus on your own at home, and it is a harmful activity. The products offered in pharmacies for self-removal of warts and papillomas are not designed for a deep and dosed effect. Therefore, you will experience a relapse and a deep scar. In addition, after an unsuccessful attempt to remove the nevus at home, it becomes damaged, becomes less stable, and more easily degenerates into melanoma.
Is it necessary to remove the nevus?
The nevus must be removed in several cases:
- There is a suspicion of melanoma or other malignant tumors, which cannot be excluded without removal. Some nevi will need to be completely removed surgically for detailed examination under a microscope (histology). Otherwise, based on external signs, it will be impossible to exclude melanoma. If the nevus is large, and only one focus is suspicious, you can take only this piece with a scalpel or radio wave apparatus. Laser and electric knife are not suitable for these purposes. In addition to melanocytic nevi, there are sebaceous, warty and others. They will also need to be removed if skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma or skin sarcoma is suspected.
- High risk of nevus developing into melanoma. The doctor assesses the risk of each specific neoplasm turning into melanoma and, based on the degree of risk, decides whether the nevus needs to be removed. The doctor is helped in making a decision by deviations in external signs: violation of uniformity of color, clarity of boundaries, increase in size, symmetry. Damage and trauma to the nevus in the past, sunburn, and family predisposition are important. It should be noted that any melanocytic nevus has a small percentage of chance of developing into melanoma. So, if the nevus is completely removed, this risk will be significantly reduced. Sebaceous nevus has an increased likelihood of transformation into basal cell carcinoma; for prevention purposes, it also needs to be removed.
- The external repulsive appearance of a nevus causes psychological problems in humans. If a nevus causes psychological problems or interferes with a person’s daily work and personal relationships, it must be removed. It is not only important here how a person perceives himself. Some people will still avoid communication, subconsciously considering such formations to be contagious.



