Pain in the elbow joint of the right or left hand is not considered a rare pathology and does not depend on age. Rather, the main factor provoking its development is injury or professional activity. This joint experiences motor loads (flexion-extension) every day and is influenced by various weights that a person carries.
The structure of the elbow joint
It is important to know! Doctors are shocked: “An effective and affordable remedy for joint pain exists.” Read more.
So, its anatomy is not that simple. The left or right elbow includes several joints: brachioradial, humeroulnar, proximal radioulnar. Together they create a complex mechanism.
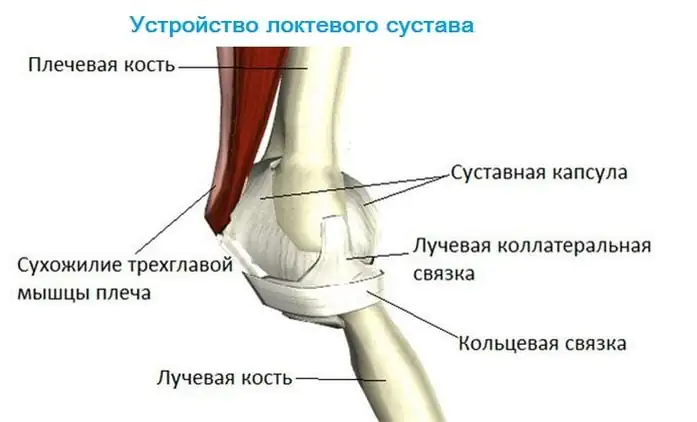
Flexion and extension of the elbow joint are provided by muscles. They are attached to the joint using tendons. There are 4 ligaments used to secure the articular capsule. This “mechanism” includes blood vessels that provide blood inflow and outflow, as well as lymph nodes. Also in the elbow there is a network of nerves through which it is innervated.
Pain in the elbow joint: causes
Both the left and right elbow can hurt. Moreover, the reasons are completely different. Naturally, in order to begin to treat this pathological condition, you need to consider them in more detail. The cause of pain in the elbow joint is:
- Impact, bruise, microtrauma due to improper bending or straightening of the arm, increased load (carrying heavy bags).
- Impaired local circulation. Here the cause of the pathology is compression of blood vessels, both small and large.
- Age-related degenerative changes in cartilage, as well as premature tissue wear, provoked by inflammatory processes in the synovial bursa.
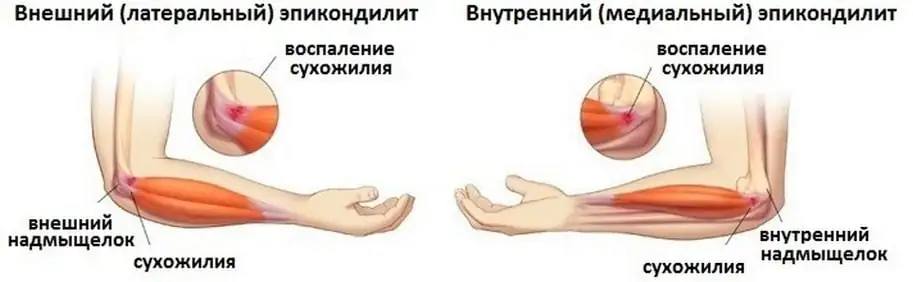
- Epicondylitis (it can be external and internal) is an inflammation of the ligaments of the elbow joint. This reason is the most common. This disease causes pain after performing physical exercises, carrying heavy objects, or prolonged similar rotations of the arm to the right or left side. The load leads to microtrauma of the ligaments. At rest, unpleasant sensations do not appear.
- Cervical osteochondrosis. The appearance of the elbow in this case remains virtually unchanged. In this case, not only the joint can hurt, the discomfort spreads to the entire right or left hand. Increased pain occurs due to hypothermia. In addition, the hand may become numb.
- Arthrosis. This disease is characterized not only by pain. When bending or straightening the elbow joint, a crunching sound is heard. If treatment has not been prescribed, the joint becomes deformed and changes in appearance.
- Arthritis. This pathology does not develop independently. Basically it is systemic in nature. In addition to the pain that the patient feels, he experiences redness on the outside or inside of the joint, and it becomes swollen.
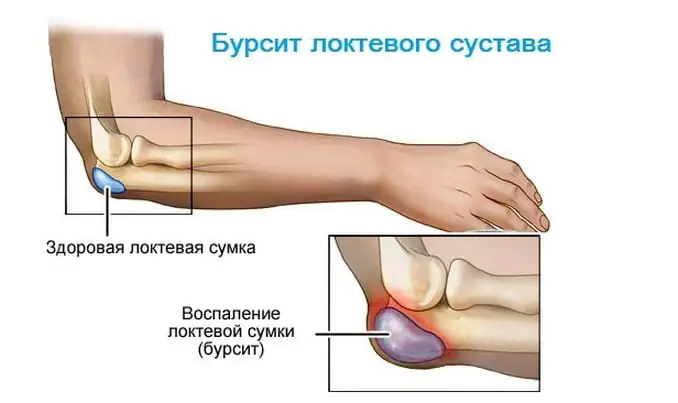
- Bursitis (disease of the synovial bursa).
Pain in the elbow joint is also provoked by certain cardiovascular or neurogenic pathologies:
- Inflammatory pathology of nerve roots. It occurs due to injury to the joint.
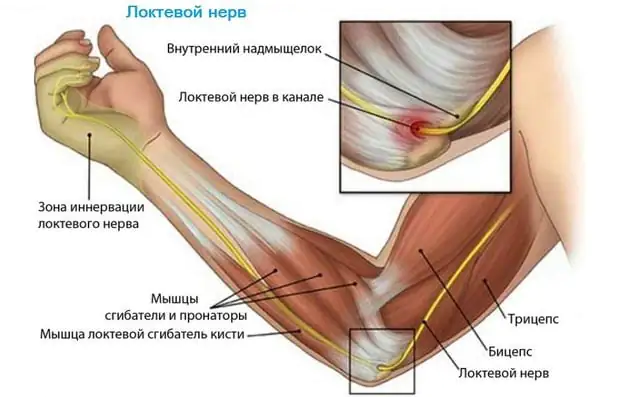
- Cubital tunnel syndrome. It is caused by a genetic predisposition or a congenital disorder of the anatomy of the elbow.
- Myocardial infarction. This pathological condition provokes pain in the joint and its numbness.
- Oncological and systemic pathologies.
Injuries can also provoke pain in this area: dislocations, fractures, bruises. Sometimes the elbow can hurt due to damage to internal organs, so you need to pay attention to the slightest disturbances in the functioning of the joint.
Rheumatologist and psychophysiologist, academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Pavel Valerievich Evdokimenko will tell you in more detail about the causes of the disease:
Classification of pain sensations and features of their manifestation
It can be done depending on the location of the discomfort and the time of its occurrence:
- When flexed, it appears due to deforming arthrosis, bursitis, arthritis, trauma or pathological neoplasm. This type of pain causes medial epicondylitis, a tendon rupture.
- When extending, the elbow hurts due to all the pathologies listed above, as well as osteoarthritis and lateral epicondylitis. In this case, the person is unable to hold the object at arm's length or clench the hand into a fist.
- On the inside, pain appears due again to medial epicondylitis, bruise or other traumatic injuries.
- Because of the training. Here, the cause of the development of unpleasant sensations is considered to be injury or severe muscle tension. Incorrect exercise also causes discomfort.
- The appearance of unpleasant sensations during a handshake may indicate a serious injury to the elbow joint.
- If the specified part of the arm begins to hurt after lifting weights, it means that the person is developing subacute epicondylitis.
- At rest, pathology can develop due to inflammatory or degenerative diseases of the joint.
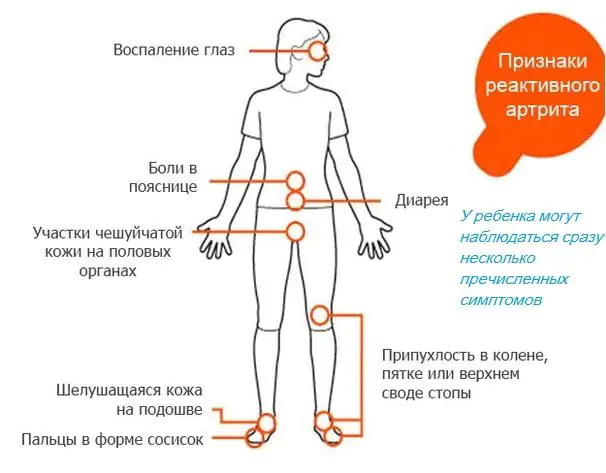
- If a child’s elbow hurts, then he most likely received an injury. In addition, such a symptom indicates the development of reactive arthritis provoked by viral or bacterial infections. If such a pathology occurs in a child, under no circumstances should it be neglected, as this can lead to significant health problems in the future.
You can also classify pain according to the nature of its manifestation:
- Reflected. They appear due to damage to internal organs or other parts of the body. There are no external changes to the elbow here.
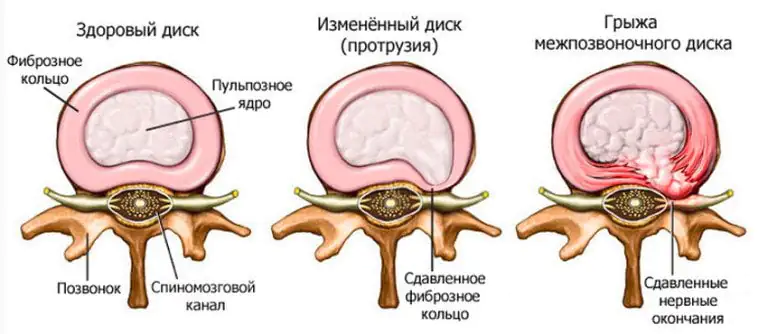
- Projected. They are thought to be caused by injury or compression of the spinal canal.
- Neuropathic. Here the pain can be severe, accompanied by burning and tingling.
- Spicy. They are characteristic of a serious injury to the elbow joint: fracture, sprain, rupture of ligaments. Acute pain also accompanies reactive and rheumatoid arthritis, bursitis.
- Burning. The cause of this condition is inflammation of the nerves, gout.
- Aching and dull. Arthrosis and even malignancy provoke such sensations.
- Sharp (provoked by trauma).
- Permanent. They appear due to the development of serious diseases of the support system.
As you can see, it is impossible to immediately determine what pathology caused the pain in the elbow joint. To do this, you should immediately consult a doctor (orthopedist, traumatologist, neurologist, therapist, rheumatologist) and undergo a thorough examination.
Features of pathology diagnosis
The patient examination involves the use of the following procedures:
- A conversation between a doctor and a patient, during which the location of pain, its nature, and the time when it manifests itself most strongly is determined. The specialist also tries to find out what caused the pain.
- External examination and palpation of the affected left or right elbow. During this procedure, the doctor can detect changes in the structure of the joint.
- X-rays (prescribed in case of injury or suspected development of a degenerative disease).
- Neurological tests.
- CT or MRI. Such procedures are more often recommended if a malignant tumor is suspected (a lump has appeared in the joint area), or osteochondrosis.
Which of the two diagnostic procedures is better to choose and what is their difference, says experienced neurologist Mikhail Moiseevich Shperling:
- A general blood test that can confirm or refute the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
- ECG. A cardiogram is prescribed if the patient has burning pain in the elbow.
- Ultrasound of the elbow.
- Specific tests.
- Rheumatic test.
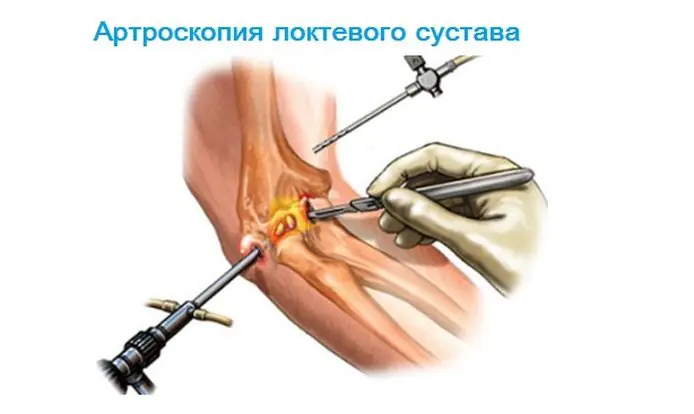
- Arthroscopy.
Such a comprehensive examination of the left or right elbow joint will make it possible to determine why it hurts, what kind of load is allowed on it, and what treatment will be most effective.
Even “advanced” joint problems can be cured at home! Just remember to apply this once a day.
Pain in the elbow joint: first aid
This pathology must be treated in consultation with a doctor. However, if you cannot urgently visit the clinic, you can provide first aid to the victim. If the patient has suffered an elbow injury, muscle or bone damage, the following actions must be taken:
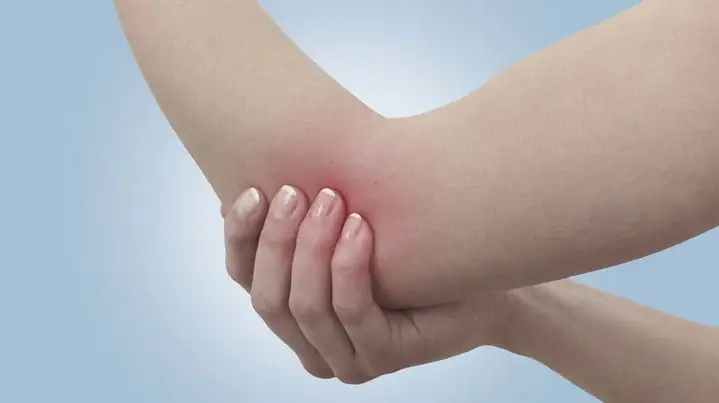
- Completely remove all load from the affected (left or right) arm and immobilize it. To relieve severe pain, you can apply a cold compress to the joint. If your elbow is too swollen, this procedure will help reduce the swelling.
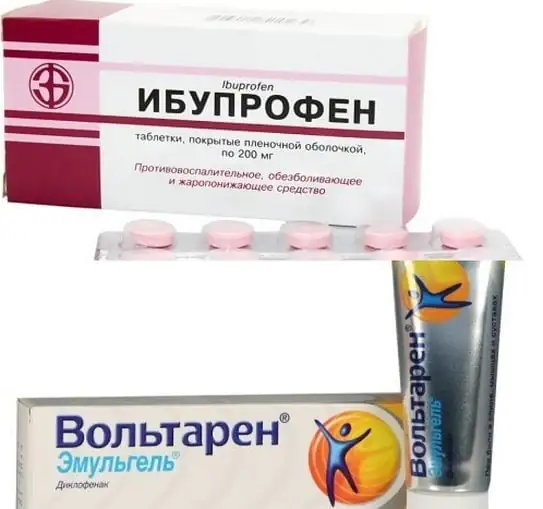
- Since the elbow joint hurts very much during an injury, the patient may need painkillers: Ibuprofen, Voltaren. The use of ointment with an anesthetic effect is allowed.
If you hear a crunching sound after a fall or blow to the elbow joint, this may indicate a bone fracture. It is impossible to cure such damage on your own, so you need to urgently contact a traumatologist.
Treatment
If the patient cannot clench his hand into a fist, his elbow begins to crack when moving, and a lump has appeared on the side (left or right) that hurts greatly, then he should not delay treatment.
Drug treatment
Depending on what pathology provoked the pathological condition, the person is prescribed the following medications:
- NSAIDs in tablet form or steroid injections: Colchicine. They can eliminate pain and reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process. If a patient’s elbow is very painful due to gout, he is additionally prescribed the diuretic Allopurinol.
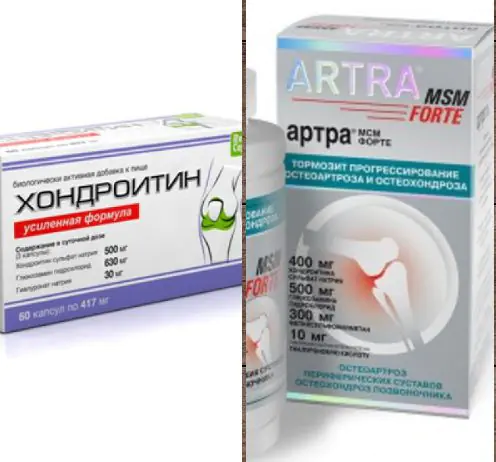
- Chondroprotectors: “Arthra”, “Chondroitin”. They are used to treat damage to the cartilage tissue of joints.
- B vitamins: Milgamma. They help fight neurological causes of pain.
- Local warming and pain-relieving ointments: Voltaren, Fastum-gel.
- Antibacterial drugs to eliminate signs of purulent arthritis and bursitis. They are prescribed to the patient in the form of injections.
- Vasodilator medications that help restore blood circulation in the joint.
- Muscle relaxants to eliminate muscle spasms.
Drug therapy is only part of a comprehensive treatment. It is complemented by other ways and methods of combating pathology.
Non-drug treatment of pain syndrome
If bending the arm and clenching a fist is difficult for the patient, the elbow begins to crunch, hurts a lot and even goes numb, the following methods can be used to restore the functionality of the joint:
- Reducing the load on the left or right elbow joint using orthopedic devices: orthoses, bandages.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures: UHF, electrophoresis with dimexide, laser and magnetic therapy, mud or paraffin applications, ozokerite.
- Aspiration of joint fluid, as well as drainage of the synovial bursa (if fluid accumulates inside it).
You can clearly see how the drainage procedure works in this video:
- Shock wave therapy.
- Professional massage using medicinal ointment.
- Physical therapy, manual therapy, and x-ray treatment.
- Simple therapeutic exercises.
In the most extreme cases, elbow pain can be treated with surgery. It involves replacing bone damaged by injury and eliminating its fragments. If the elbow hurts severely, the patient will be advised to go to bed. The joint may be encased in plaster at that time. Despite the fact that some dystrophic diseases cannot be completely cured, the fight against them must be continued.
Elbow pain: treatment with folk remedies
Despite the fact that the pain is localized in the inner part of the joint, on the side or on top, it must be treated in any case. To do this, in combination with other methods of therapy, you can use folk remedies. If clenching a fist or bending your arm is difficult, the following recipes will be useful:
- Fresh cabbage or burdock leaves will help eliminate swelling. They need to be beaten a little with a hammer and tied to the affected elbow overnight. The sore elbow should be treated in this way until the discomfort subsides.
- The skin around the affected joint can be smeared and rubbed with alcoholic tinctures of mustard, honey or turpentine. In some cases, the patient may have a burning sensation. If it is strongly expressed, then it is better to refuse to use such means.
- Application with clay will help eliminate pain and numbness in the elbow. The raw material must be heated to 45 degrees, treat the joint with vodka, and then apply gauze and a layer of clay (1 cm) on it. To improve the effect, the compress should be wrapped in a woolen cloth. It lasts only an hour, however, several such procedures will help improve fist clenching and get rid of pain. Perhaps your hand will stop going numb.
- Compress with warm sea salt. Its temperature should be 65 degrees.
- Laurel oil has a warming effect. You need to smear it on the skin directly above the affected joint.
- If your elbow hurts, a folk remedy such as fresh celery juice, which can be rubbed into the joint or taken orally, will help overcome the discomfort. Treatment is carried out over 14 days.
Folk remedies, as well as drugs, cannot completely cure systemic or degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system. However, they help to significantly improve the patient’s life.
Elena Malysheva gives excellent advice on what to do for bruises in the area of interest to us:
Preventive measures
In order for the compression of the fingers to occur normally, the training to not cause discomfort, and for the elbow to not go numb when bending, it is necessary to promptly eliminate all those factors that can provoke the pathological condition. Prevention plays a huge role here. It provides for the implementation of the following rules:
- Athletes or people performing complex work are required to perform daily therapeutic exercises to flex and extend the joint.
- You should not lean on your elbow for a long time while working at the computer or reading books. This provokes cubital tunnel syndrome.
- It's important to eat right.
- It is advisable to prevent any injury to the elbow joint.
- You should avoid hypothermia and visit saunas or steam baths.
- Provide quick and effective treatment of all inflammatory and infectious processes in the body.
- If you feel numbness in your hand, you should urgently consult a neurologist.
Be that as it may, if an elbow hurts, a person cannot fully work or rest. It is advisable to avoid all those factors that can provoke such a pathological condition. An active and healthy lifestyle is the main method of preventing the disease.
Pavel Valerievich Evdokimenko, a rheumatologist and psychophysiologist, academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, provides useful information about performing gymnastics:
How to forget about joint pain?
- Joint pain limits your movements and full life...
- You are worried about discomfort, crunching and systematic pain...
- You may have tried a bunch of medications, creams and ointments...
- But judging by the fact that you are reading these lines, they did not help you much...
But orthopedist Valentin Dikul claims that a truly effective remedy for joint pain exists! Read more >>>
Pain in the elbow joint causes a lot of discomfort when moving and at rest. The cause is injury or pathology of joint tissue. After clarifying the diagnosis, treatment is prescribed, consisting of medications, physiotherapy, massage and folk remedies. Soreness of a different nature can bother a person once or cause inconvenience with its constant presence. The response appears after mechanical damage or the development of an illness due to the specifics of professional or sports activity. Comprehensive treatment, selected taking into account the cause of the pathological condition, will relieve the unpleasant symptom.
Why does pain occur in the elbow joint?
The elbow joint connects three bones: the humerus, ulna and radius. In the joint capsule they form three simple joints, making the structure of the elbow joint complex. Four ligaments are involved in the variety of movements that can be made with the arm using the elbow. Innervation is provided by large nerve trunks passing through the mobile joint.
Any deviation that changes the structure or physiology of the elbow is reflected by painful sensations, the increase in strength of which directly depends on progressive processes. In addition to pain, inflammatory tissue or inner lining is accompanied by characteristic signs: swelling, redness, and local increase in body temperature.
Elbow injuries occur quite often. Even a small blow with a bent arm causes an unpleasant sharp pain in the elbow joint. This is explained by the closely located ulnar nerve. Serious injuries render the arm incapacitated and require long-term treatment.
Description of diseases
A pain symptom is present in every pathology associated with the elbow joint. With the help of the emerging syndrome, the body signals a developing disease:
- Arthrosis. Processes that destroy cartilage tissue develop after injury or due to age. The lack of chemical compounds that ensure the maintenance of cells in optimal condition leads to irreversible changes and deformation of the elbow joint. The elbow begins to hurt after the cartilage pad becomes thinner, ceasing to function as a shock absorber. The top layer of bone changes to a more dense structure, forming osteophytes. They are an additional source of pain when moving. The pathology most often affects older people or after receiving damage during an injury.
- Arthritis. Inflammatory phenomena in the joint are manifested by acute aching pain. The causative agents are infectious diseases, microdamages after bruises, and malfunctions of the immune system. The pathology is accompanied by swelling of the elbow joint and redness over the inflamed area. On palpation, the skin is hot, movements in the joint are sharply limited.
- Epicondylitis. The connective tissue of the ligaments becomes inflamed, which causes sharp pain when trying to move the joint. The main reason is physical activity, heavy lifting, and similar movements during work or sports.
- Reactive arthritis. Develops as a complication after infections or viral pathologies. In addition to inflammation and pain in the elbow joint, there is decreased vision, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, dry skin with peeling on the feet, and severe swelling of the toes.
- Osteochondrosis. Significant degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs and segments of the cervical spine are manifested by pain that radiates to the upper limb. At the same time, the elbows hurt at rest, even without making passive movements.
- Bursitis. A painful reaction to inflammation in the synovial bursa near the elbow joint is accompanied by hyperemia and the formation of an oblong compaction on the bend of the arm.
- Tendinitis. Development of dystrophic and inflammatory processes in tendons. The disease is provoked by injuries, infectious and degenerative processes, metabolic and immune processes.
- Shulman's disease. Or diffuse eosinophilic fasciitis. A rare disease involving the fascia, muscle fibers, subcutaneous tissue in the pathological process, pain in the elbow joint and immobility.
- Chondromatosis. Pathology of unknown etiology, develops in large joints. Pathogenesis consists of the formation of cartilaginous elements on the surface of the synovial membrane
- Chondrocalcinosis. Deposits of calcium salts in the cartilaginous part of the elbow joint. The main symptoms of the disease: pain in the elbow, swelling, impaired motor function.
- Gout is a pathology with higher than normal levels of uric acid. The urinary system cannot cope with a large amount, and the acid turns into crystals, settling in the joint capsule.
- Cubital tunnel syndrome. Ulnar neuropathy occurs when the cubital tunnel becomes narrowed. The cause is injuries and congenital structural features.
- Ulnar nerve neuritis. If there is aching pain in the elbow joint, fingers become numb, movements are limited, fine motor skills of the fingers of the affected limb are absent, all signs indicate inflammation of the ulnar nerve.
- Hemophilia. Bleeding disorders are transmitted genetically to males. The joint capsule fills with blood, causing inflammation, inability to perform normal movements, infection with the formation of an abscess.
- Myocardial infarction. An acute form of cardiovascular pathology causes pain behind the sternum and in the left arm.
- Oncological neoplasms.
Causes
- dislocation - displacement of the head of a bone in a joint with preservation of integrity or damage to the joint capsule;
- subluxation - happens in childhood with a sudden upward movement of the arm;
- bruise - mechanical damage due to a blow without damage to the skin;
- sprain – complete or partial rupture of a ligament during a sudden movement;
- fracture - damage to the bone simultaneously with the nervous and circulatory system;
- Volkmann's ischemic contracture is a complication after pathological conditions associated with acute circulatory disorders in the elbow, severe pain appears, the arm cannot be straightened due to the formation of adhesions on the connective tissue.
Frequently performing movements along one trajectory with a load that exceeds daily stress in strength.
Lifting weights to chest level and above causes severe tension, which leads to pain.
Symptoms
Pain in the elbow joint varies in nature and occurrence:
- the appearance of a symptom when bending the arm indicates destruction of the joint due to cartilage dystrophy, injuries to ligaments and tendons, inflammatory diseases;
- extension movement brings pain with arthrosis, arthritis, bursitis, tendevitis, as well as osteochondrosis with the formation of intervertebral hernias and protrusions, epicondylitis;
- from the side of the junction of the radius and humerus - for injuries and medial epicondylitis;
- it hurts to clench your hand into a fist - the person has a serious injury or neurological problems;
- when lifting a small load, your elbows hurt - you can suspect elbow inflammation;
- constant aching pain in the elbow joint due to diseases of the internal organs, severe stages of arthrosis, osteochondrosis.
Pain in the elbow joint may intensify due to the following symptoms:
- accumulation of physiological fluid in the tissues around the elbow joint;
- change in skin color: from bright red to purple-bluish with hematoma;
- local increase in temperature of the affected area;
- general intoxication with fever and intestinal upset.
Diagnosis of pain in the elbow joint
To eliminate pain in the elbow joint, you need to accurately determine the cause.
Only a medical specialist can conduct a full examination:
- Taking an anamnesis: the doctor finds out complaints, heredity, previous diseases, and whether there have been previous injuries to the elbow.
- Specialized tests to determine the degree of joint mobility and pain.
- Laboratory blood test for the presence of inflammation and rheumatoid factor.
- X-ray if there is a suspicion of trauma or tissue degeneration.
- Computed tomography to clarify the diagnosis of cancer or osteochondrosis.
- Arthroscopy of the joint to get a complete picture of the pathology.
- Taking synovial fluid for bacteriological analysis to identify the pathogen for prescribing effective treatment.
- Electrocardiogram to evaluate the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
- Ultrasound examination of the joint or internal organs;
- Consultation with a neurologist, rheumatologist.
Treatment measures
It is possible to achieve a lasting therapeutic effect by making the correct diagnosis and following treatment recommendations exactly. For each pathology, pain treatment will be different. Non-narcotic analgesics can be considered an “ambulance” drug. Baralgin Pentalgin, Tempalgin will eliminate pain for a short period, after a while the symptoms will appear again, consult a specialist before taking medications.
Medication methods
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs will relieve inflammation and pain for any elbow disease. Ketaprofen, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen are also prescribed for feverish conditions to reduce body temperature. When taking the drug regularly, you should not exceed the dosage so as not to irritate the gastric mucosa. For protection, it is recommended to take Ameprozole and Pantoprazole at the same time.
- Glucocorticosteroids are used for severe inflammation. Steroid hormones (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone) are injected into the joint, acting directly on the site of inflammation.
- Chondroprotectors for stopping degenerative processes and self-healing of cartilage tissue. Dona, Artra, Structum contain glucosamine and chondroitin - the “building material” of joint cells. Medicines are intended for long-term use. Treatment can be carried out by intra-articular injection.
- Diuretics to remove excess fluid. Furosemide, Lasix, Diuver - will eliminate local and general swelling and alleviate the condition of heart and kidney pathologies.
- Colchicine is a narrowly targeted herbal remedy used to relieve an attack of gout. To enhance the therapeutic effect, Allopurinol is prescribed, which negatively affects the synthesis of uric acid.
- Muscle relaxants (Mydocalm, Sirdalud) will eliminate muscle spasms that affect pain. For a lasting result, it is necessary to simultaneously inject B vitamins (Milgamma, Combilipen).
- For purulent lesions - antibiotic therapy. Amoxiclav, Azithromycin, Cephalexin have an antibacterial effect, destroying the pathogen. While taking the antibiotic, a probiotic (Linex, Normobakt, Bifidumbacterin) is prescribed to maintain good gastric microflora.
- Vasodilators (Papaverine, No-shpa) increase the lumen of blood vessels, improving blood circulation.
- Sedatives (Novopassit, Tenoten, Persen) for mental disorders during illness.
- Local anesthesia with ointments and gels for external use: Voltaren, Dolobene, Nise. Direct exposure to the diseased area helps to administer anesthesia faster than tablet forms.
First aid for injury
In case of mechanical damage to the elbow due to an impact or fall, it is necessary to carry out a series of manipulations in a timely manner before the victim gets to the trauma center. The correctness of actions often determines how long it will take for the patient to recover his sore arm.
The most important rule is to ensure that the hand remains motionless so that the injured limb is at rest. This can be achieved using a homemade tire made from scrap materials. If there is an unnatural position of the arm, it should not be forcibly straightened. The hand should be left in the same position.
In the first minutes after the injury, apply ice or a cold object to the elbow. You can hold it for no more than 15 minutes, after wrapping it in a thin cloth so as not to overcool the damaged joint. To relieve pain - Ketorol, Naproxen, Nimesil. It is convenient to use Frost cooling spray, which is sprayed onto the elbow and instantly numbs it.
In the future, you must be examined by a traumatologist to ensure there is no fracture or damage to the internal organ.
Physiotherapeutic procedures for pain in the elbow joint
Auxiliary methods will help restore the full range of motion and speed up recovery. To unload the joint during illness, orthopedic bandages are prescribed to fix the joint of varying degrees of rigidity, depending on the severity of the pathology.
Electrophoresis, combined with Dimexide, delivers the medicine into the deep layers directly to the affected tissues. Magnetotherapy uses pulsed electromagnetic current to not only heal, but also restore the elbow joint. The cumulative effect after sessions lasts for several months.
It is useful to use mud baths or paraffin wraps. The diseased area is saturated with chemical elements, absorbing them through the skin. Shockwave therapy uses acoustic waves directly on the joint.
If fluid or blood accumulates in the joint or synovial bursa, a puncture of the joint is performed to pump out the contents. After which a medicine is injected into the cavity to relieve the inflammatory process - glucocorticoids (Hydrocortisone, Diprospan).
Therapeutic massage courses are carried out at a stage when there are no symptoms of an acute condition. After the session, blood supply and tissue nutrition improves, metabolic reactions are stimulated, and motor function improves. For preventive purposes, massage is carried out twice a year, at least ten sessions.
Physiotherapy
In order for rehabilitation exercises to bring the desired effect, when performing the complex you must follow some rules:
- Before performing the main part, do a warm-up to increase blood flow and warm up the muscles.
- Exercises are performed on an empty stomach, therefore, there should be at least 1.5 hours between meals and exercise.
- Drink clean water at least 2 liters per day.
- At the end of the session, the hand is washed with cool water and rubbed with a towel.
Strict adherence to the recommendations and techniques for performing physical therapy exercises will help to significantly increase the range of motion even after severe conditions. Classes must be regular; isolated cases of implementation will not live up to expectations.
Exercises for pain in the elbow joint:
- Slowly and smoothly perform flexion and extension at the elbow joint, with the hand pointing upward.
- For the next exercise you will need a massage ball measuring 7 cm in diameter. Roll the ball clockwise on the table with your hand.
- Place your hand on the table with the inner surface. Bend your hand, moving it along the table.
- Bring your arms together in front of you and bend them, pulling them toward your chest.
- Take a stick of small diameter and roll it on the table with both hands. The movement is reminiscent of rolling out dough.
- In a standing position, raise your straightened arms up and bend them, placing them behind your head.
Each exercise is performed 8-10 times with each hand without jerking or sudden movements. If pain occurs, immediately stop the session and inform your doctor.
Folk remedies
- Propolis ointment will relieve inflammation and have an antibacterial effect. To prepare, you need to take 70 g of propolis and the same amount of sunflower oil. Combine in a bowl and heat in a water bath until dissolved, then cool and rub into the sore elbow 2 times a day.
- Honey has an analgesic and anti-edematous effect. Apply liberally to the elbow and rub in with light massage movements for 10 minutes. If necessary, you can put a film on top and wrap it in a blanket and leave it overnight.
- A compress using blue clay will provide the necessary chemical elements to the sore joint. The powder is placed in a bowl and diluted with cool water to the consistency of a thick dough. Apply the resulting mass to gauze and wrap the joint. Leave the compress for 2 hours.
- Grind the eggshells in a coffee grinder until powdered. Mix the curdled milk with the shell until the consistency of sour cream. Use as a compress, treatment time – 4 hours.
- Wash the cabbage leaf and lightly beat it with a rolling pin to release the juice. Wrap the elbow, secure with cling film, cover with a warm blanket and leave for 10 hours.
- Grate raw potatoes, distribute over joints and wrap in cellophane. The anti-pain compress can be left overnight.
- Combine camphor alcohol with beaten egg whites, then add dry mustard powder to the consistency of an ointment. Spread the healing mixture on the joint, cover with film and a warm scarf.
- A warm bath with sea salt has a beneficial effect on eliminating pain in the elbow joint. The procedure lasts 15 minutes, after which the hand must be washed and lubricated with moisturizer.
Prevention of elbow joint
The health of the joints of the hands is indispensable for normal life. Everyday self-care manipulations require the normal functioning of not only the fingers, but also the elbow joint. To ensure free movement in the joint, it is necessary to follow the prevention recommendations:
- proper nutrition with a limit on fatty, salty and smoked foods, the inclusion of vegetables and fruits, lean meat and dairy products in the diet is encouraged;
- wear orthoses to prevent injuries and diseases with increased load on the joint;
- It is contraindicated to lean on the elbow for a long time;
- do gymnastics to strengthen muscles and ligaments after injuries and during heavy physical work;
- avoid prolonged exposure to cold air;
- If you experience discomfort when moving, loss of sensation and the ability to move your arm, consult a medical specialist.
Elbow joint formed by the articulation of the humerus, radius and ulna. The articular surfaces of the bones are covered with hyaline cartilage, which promotes soft and smooth movements in the joint. The elbow joint is a complex part of the body, since three smaller joints can be distinguished in its cavity: radioulnar, humeroulnar and brachioradialis.
Diagnosis of various diseases of the elbow joint usually does not cause difficulties for specialists. This is due to the fact that the elbow joint is well accessible for examination and various diagnostic procedures.
Elbow pain can occur for many reasons. A thorough clinical examination to confirm the diagnosis can be supplemented by a variety of functional tests. Particular attention should be paid to the position of the elbow. With joint effusion, thickening of the synovium and degenerative joint diseases, the arm will be slightly bent at the elbow.
Diseases and causes that cause pain in the elbow joint:
1. Osteochondrosis, inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and gout, chondrocalcinosis, tumors, tendinitis and osteoarthritis are the most common causes of pain in the elbow joint. However, compression syndromes such as cubital tunnel syndrome can also occur in the elbow joint due to osteophytes narrowing the ulnar nerve groove.
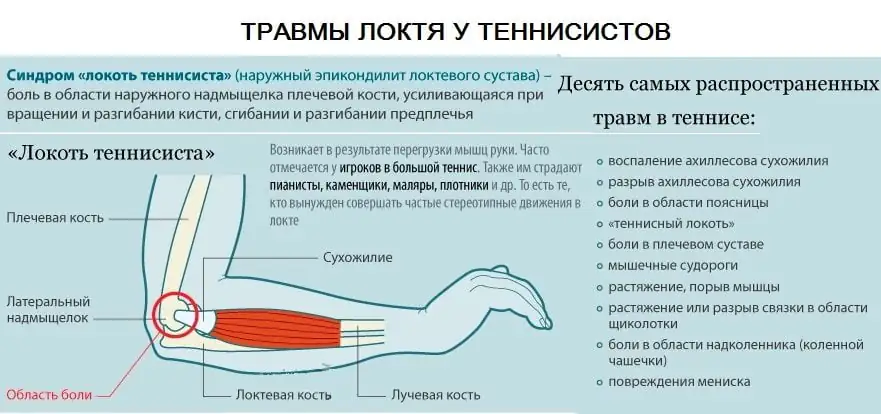
2. One of the most common causes of elbow pain is lateral epicondylitis or "tennis elbow". Less common is medial epicondylitis, also called golfer's elbow.
In addition to local pain upon palpation, typical signs include the occurrence of pain in the corresponding area of the elbow during passive movements: extension - “tennis elbow”, or when bending the hand - “golfer’s elbow”, as well as pain from muscle tension.
Specific tests help distinguish symptoms of epicondyle pathology from symptoms associated with other diseases.
3. External epicondylitis (“tennis elbow”)
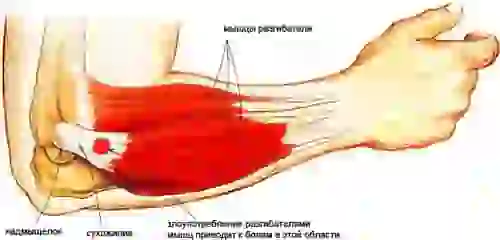
Attached to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus are the muscles involved in wrist extension—the extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis (the clenched fist muscles) and the brachioradialis muscle. Inflammation of the tendons of these muscles where they attach to the bone is called lateral epicondylitis. The muscles are weak flexors of the forearm, so if they are damaged, the function of the elbow joint is practically not affected.
This pathology usually affects people over 35 years of age. The appearance of pain in the elbow joint is preceded by an unusual load - working in the garden, playing sports after a long break, etc. The patient accurately indicates the place of greatest pain, corresponding to the external epicondyle of the humerus. Pain may radiate down the outer surface of the forearm to the hand. The pain is easily reproduced by resistance to active extension of the wrist joint.
4. Internal epicondylitis (“golfer’s elbow”)
The tendons of the muscles attached to the medial epicondyle are affected - the pronator teres, the ulnar and radial flexors of the hand, and the long palmaris muscle. Medial epicondylitis is less common than external epicondylitis. Palpation pain is detected at the site of muscle attachment. Pain may radiate along the ulnar surface of the forearm to the hand.
5. Olecranon bursitis
The superficial bursa of the olecranon process is located above the eminence of the olecranon process, and does not communicate with the cavity of the elbow joint. Inflammation of the bursa occurs in isolation as a consequence of chronic injury to the posterior-inferior surface of the elbow (in car drivers resting their elbow on the door), or in combination with arthritis due to gout and RA. In the area of the olecranon, a low-painful round formation the size of a chicken egg with a soft consistency appears. It becomes clearly visible when the arm is extended at the elbow joint. With isolated bursitis, the function of the elbow joint is not noticeably affected.
Other causes of elbow pain:
1. Lesions of one elbow joint are often observed with hemophilia and Charcot neurotrophic arthropathy. Monoarthritis of the elbow joint, as well as deforming arthrosis, are rare.
2. The cause of “joint blockades” may be osteochondritis dissecans of the humeral epiphysis or synovial chondromatosis. In these diseases, “articular mice” are often found in the cavity of the elbow joint.
3. Limited mobility of the elbow joint, in the absence of visible changes, can be caused by diffuse fasciitis. With this pathology, the skin on the inner surface of the forearms and shoulders becomes like an orange peel, it cannot be folded, and an absolutely painless lump can be felt underneath it.
4. Pain in the elbow joint can also be referred. Its cause may be pinched nerve roots for osteochondrosis of the spine or intervertebral hernias localized in the C5 - C6 and ThI - ThII segments. With this pathology, there is a violation of flexion in the elbow joint, disorders of skin sensitivity on the surface of the forearm, and the possible development of atrophy of the biceps muscle.
5. Elbow injuries. Most often, posterior dislocations of the elbow joint are observed, less often - anterior and lateral ones. Dislocations can be combined with fractures of the bones that make up the elbow joint, as well as with tendon separation. Mechanism of injury: fall on the hand, sports, industrial, automobile injuries.
With a posterior dislocation, the elbow joint is deformed, the forearm is shortened, the protruding olecranon process is visible. I am worried about severe pain, movements in the joint are severely limited. When attempting to extend the joint, spring resistance is detected.
With anterior dislocation the forearm is elongated compared to the healthy limb, and retraction is detected in the area of the olecranon. With lateral dislocations, the forearm is displaced inward or outward. With anterior and lateral dislocations, there is often damage to the ulnar or median nerve with loss of sensation in the hand.
When a tendon ruptures, the biceps brachii muscle most often suffers; sometimes the tendons of several muscles can be torn off. In this case, the function of active movements of the upper limb is impaired, the strength of flexion in the elbow joint is reduced, asymmetry in the shape of the muscles occurs compared to the uninjured limb, and swelling and pain are noted.
HOW TIBETAN MEDICINE ELIMINATES ELBOW JOINT PAIN
Tibetan medicine has truly vast experience in treating diseases of the musculoskeletal system, which dates back thousands of years. Tibetan doctors consider lifestyle and nutrition correction to be one of the main principles of treatment. That is, a person should avoid hypothermia, wear clothes appropriate for the season, keep the body (hand) warm, and not carry out hardening procedures (dousing with water). Food should be warm (hot); cold food and drink should be excluded from the diet. Doctors of Tibetan medicine also pay attention to the psycho-emotional state of a patient with a similar illness. Violation of the functions of the nervous system ("wind"), affecting the entire body, "hits" the most vulnerable and weak points of a person. Therefore, such warming procedures as moxotherapy (warming with wormwood cigars), the Mongolian method of oil-herbal massage “Khorme” have a sedative effect on the nervous system, coupled with conversations with the doctor and his recommendations.
What do doctors at the Naran Tibetan Medicine Clinic do first:
- Diagnosis is carried out by questioning, examination, pulse diagnostics, palpation
- Based on the combined data of eastern diagnostic techniques, it is established the exact cause of the pain
- Relieve pain in one or two sessions using proven acupuncture
- They begin treatment by combining several methods, taking into account the characteristics of the disease that caused a similar symptom.
RESULTS OF TREATMENT AT THE NARAN CLINIC
- Pain relief
- Restoring mobility of the elbow joint
- Improving blood and lymph circulation and nutrition in cartilage tissue
- Improving the conduction of nerve impulses
- Elimination of general and local stagnation of energy flows
- Boosting immunity
- Normalization of metabolism
- Elimination of muscle spasms
The Naran Clinic celebrates its 30th anniversary in 2019, which, of course, is modest in comparison with “eternity,” but is impressive on the scale of Russia. Be the first to open a clinic of Tibetan medicine in Moscow, and then branches in the largest cities of St. Petersburg, Kazan, Yekaterinburg, Vienna (Austria), maintain a high bar for thirty long years, be in demand by discerning Muscovites, cure thousands of people, earn their recognition, Of course, this speaks of high-class doctors, professionals in their field.
Unfortunately, many patients do not pay attention to such “little things” as unpleasant pain in the joints. Find time and contact specialists who have been treating such diseases for a long time. Come at the first signs of ill health, this will avoid much suffering in the future. If you think that joint diseases are the lot of “old people” and you are far from this, do not flatter yourself too much. If you are 40 now, then at 60-70 you will want to be as mobile and active as you are today. Moreover, now age limits have expanded and people remain strong and attractive for a long time.



