The human eye is a unique organ, thanks to which we see everything that is around us. But when the eye is affected by various negative factors, for example, extremely high or low temperatures, hot sparks, chemicals, then we can not only lose visual acuity, but even completely lose such a divine gift as the ability to see. Today we will learn how to help a person who has suffered an eye burn under the influence of various factors. After all, correctly provided first aid will not only alleviate the patient’s condition, but will also keep him clear-eyed.
What is an eye burn?
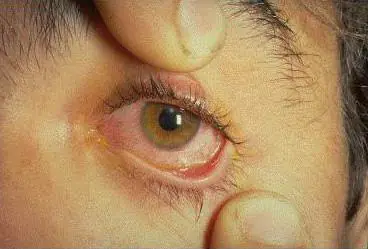
This is an injury to the anterior organ of vision resulting from excessive chemical, temperature or radiation exposure. The most common thermal burns to the eye are caused by burning particles, welding or chemical elements. With such an injury, the conjunctiva and skin of the eyelids are primarily affected, then the cornea, lacrimal ducts and deeper structures of the organ of vision, down to its posterior parts.
Degree of damage
Eye burns can be divided into 4 categories:
- The first stage is damage to only the superficial part of the eye.
- Second degree – slight darkening and redness of the cornea of the eye occurs.
- The third stage – there is a very strong clouding of the cornea. The eye is covered with a thick film.
- Fourth degree – injury to both the cornea and retina.
Retinal burn: causes
- Exposure to bright light after prolonged exposure to darkness.
- The influence of ultraviolet radiation. Although this does not threaten a person with loss of vision, there are cases when sunlight, which is reflected from the snow, sharply enters a person’s eyes and can harm him (the so-called snow blindness, which is often found in the north of Russia, for example in the city of Vorkuta). In addition, a burn to the retina can occur due to the fact that a person watches a solar eclipse without glasses.
- Exposure to light from a spotlight and laser beams.

Corneal burn: causes
- Working with chemicals such as acid, cosmetics, perfumes, medicines, paints, etc.
- Thermal damage to the organ of vision is a burn to the cornea of the eye caused by exposure to a hot liquid, such as boiling water, steam, or hot oil.
- Working with a welding machine.
- Combined burn of the cornea of the eye - damage caused by the use of flammable objects or mixtures.
Symptoms of the lesion
The following indicators can be considered signs of injury:
- frequent headaches;
- burning in the eyes;
- redness of the white membrane of the organ of vision;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- aversion to light penetration;
- tearfulness;
- blurred vision;
- feeling of something foreign in the eye.

First aid for eye burns caused by welding
- The victim should be offered painkillers “Analgin”, “Diclofenac”, as well as antihistamines “Suprastin”, “Tavegil”.
- The person should be taken to a darkened room where the sun's rays will not reach. If it is not possible to place him in such a room, then at least you need to put dark glasses on his eyes.
- Call emergency medical assistance.
Treatment of eye burns resulting from working with a welding machine
- Upon arrival, the doctor first helps a patient who has received an eye burn from welding, like this: he dilutes several crystals of potassium permanganate in boiled water, then he always rinses the eyes with this solution and takes the patient to the hospital.
- Already in the medical institution itself, the doctor removes the foreign body by injecting medication with soluble calcium.
- After the eye is cleaned, an antiseptic ointment is applied under the eyelids. The patient is then admitted to a hospital (if necessary), where the doctor prescribes further treatment. Or the specialist may let the patient go home, but on the condition that he comes to the clinic to check the affected eye.
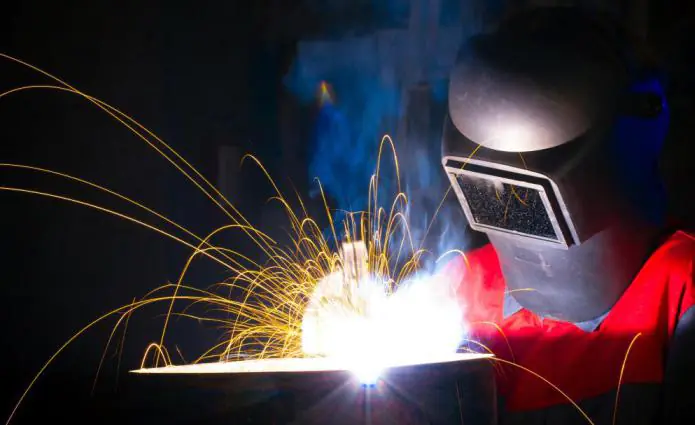

Prohibited techniques
If a person has received an eye burn from welding, then the following methods of so-called “treatment” will not lead to anything good:
- Rubbing. Of course, the patient at this moment feels as if sand was poured under his eyelids. However, this sensation is caused by an inflammatory process, and not by the presence of any particles in the eyes. Therefore, friction can only complicate the situation.
- Rinsing eyes with tap water. The fact is that in this case you can easily get infected, but such cleansing will not give the desired effect. Only boiled water can be used for such manipulations.
- Grandmothers' advice: putting honey, aloe juice, tea leaves into the eyes. These methods should absolutely not be used, since their effect can be exactly the opposite.
Chemical burn of the eye: what is it?
This is the entry into the organ of vision of ammonia, acids, alkalis and other chemical components at work or at home. A chemical burn to the eye is the most dangerous, since it is the one that leads to the fact that a person can simply remain blind. The severity of such damage is determined by temperature, chemical composition, concentration, as well as the amount of the substance that provoked the occurrence of such a dangerous situation. With this burn, the patient may experience the following symptoms:
- lacrimation;
- cutting pain in the eyes;
- fear of light;
- loss of vision (in severe cases).
In addition to damage to the organ of vision, the skin around it also suffers. It is very important to provide first aid to a person in a timely manner. And how to do this correctly, read below.
First aid for chemical eye burns
- First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the irritating substance from the conjunctival sac. This should be done by abundant rinsing. To do this, use saline solution. If it is not found at the scene of the incident, then, as a last resort, ordinary clean water in large quantities will do.
- After this, it is recommended to apply a sterile bandage to the affected area.
- Call an ambulance immediately.
Treatment of chemical burns
After the victim is brought to a medical facility, doctors begin to carry out the following manipulations:
- Rinse the eye with medicinal liquid.
- If the burn is alkaline, then the ophthalmologist prescribes ascorbic or citric acid to the patient. For mild to moderate damage, vitamin C is prescribed 2 g for 1 month. For severe burns, a 10% solution in artificial tears is instilled 14 times a day immediately after the injury for 2 weeks.
- In case of damage to the organ of vision of the II and III degrees, 25-100 thousand units of penicillin diluted in a solution of novocaine are injected daily under the conjunctiva of the eyeball.
- Glucose injections in combination with subcutaneous administration of 8-10 units of insulin have a good effect.
- To prevent secondary infection, a specialist may prescribe oral sulfonamide drugs and intramuscular antibiotics.
- If the chemical burn to the eye is severe, then plastic surgery is indicated. During the healing period, cortisone and fibrin film from donor blood are used locally.
What is thermal damage to the organ of vision?
This is damage to the tissue of the cornea and eyeball resulting from interaction with agents such as fire, hot steam, heated liquids or molten substances. Thermal burns of the eye are common both at work and at home. It often occurs in combination with the same lesion of the face, legs, arms and the whole body.
First aid for heat injury
How to help a person at first?
- The person who has volunteered to support the victim needs to wrap her fingers with a sterile bandage and open the patient’s eyelids as much as possible.
- Then you should cool the affected person’s organ of vision under water for 20 minutes. The liquid temperature should be no more than 12-18 degrees. For cooling, you need to use any suitable containers that can create a flow of water. For example, it could be a syringe without a needle, a rubber balloon or a plastic bottle. Another way to cool the eye is to lower your face into a suitable container of cool water and blink periodically.
- Antiseptic “Levomycetin” or “Albucid” should be instilled into the affected organ. After this, cover the eye with a sterile napkin and give the victim a tablet of any analgesic.
- Be sure to call an ambulance.
Treatment of thermal burns of the eye
The treatment of this lesion is quite specific and complex, so it should be dealt with by specialized specialists in the ophthalmology department of the hospital. Before treating a thermal burn of the eye, the doctor must assess the area of tissue damage and the severity of the damage.
As a rule, with this type of injury, anti-inflammatory and restorative therapy is prescribed, which promotes the restoration of affected tissues. Surgical intervention is indicated if it is necessary to eliminate the dead layers of the organ of vision and in case of its restoration.
An eye burn, which must be treated promptly, is an injury that occurs when the body is exposed to certain factors (chemicals, high or low temperature, radiation exposure). It is very important at the moment of organ damage to correctly provide first aid to a person, so as, firstly, not to harm him even more, and secondly, to help cope with the pain before the ambulance arrives.
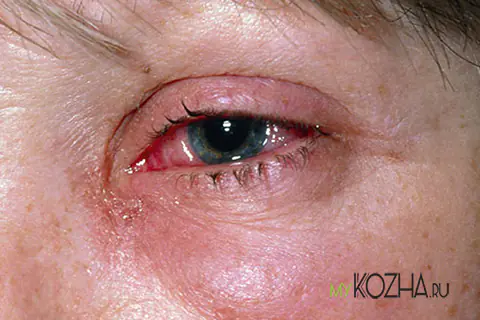
A thermal burn of the eye is damage to the tissues of the cornea and eyeball resulting from interaction with high-temperature damaging agents: flame, hot steam, heated liquids or spread substances. Such injuries often occur both at home and at work, and are often combined with burns of the face, limbs or the whole body. They
are difficult to treat and in some cases can lead to a very negative consequence - loss of vision. Due to the reflex closure of the palpebral fissure, which occurs in the event of danger, the eyeball itself, as a rule, suffers much less frequently than the eyelid.
Clinical manifestations and severity
Clinical manifestations of thermal burns are quite varied and depend on factors such as quantity, concentration, temperature, localization, properties and duration of exposure to the damaging substance. But in most cases, damage to the tissue of the eyeball and corneal epithelium causes severe pain, clouding of the cornea, the sensation of a foreign body, as well as swelling, photophobia, lacrimation and decreased vision.
There are 4 degrees of severity of thermal eye burns:
- Mild lesions of the first degree. With such injuries, swelling of the eyelids, superficial erosions of the cornea, and conjunctival hyperemia are observed;
- Burns of moderate or second severity. The skin of the eyelids becomes blistered, and superficial damage to the corneal stroma is observed;
- Severe third degree burns. Such lesions are characterized by necrosis of the epidermis, conjunctiva and cornea. The affected tissues become covered with a dark crust, and lens cataracts develop;
- Particularly severe fourth degree burns. They are characterized by deep necrosis of eye tissue with possible perforation of the cornea. Secondary glaucoma develops, severe damage to the vascular tract and loss of vision are observed.
If the size of the burn occupies less than half the area of the eyelid, conjunctiva, cornea and sclera, the injury is assigned a 3rd degree of severity. If the burn occupies more than half the surface of the above tissues - 4th degree of severity. It should be noted that in the first hours and sometimes even days after receiving an injury, it is very difficult to diagnose the extent of the injury. Thermal injury may look mild, but after a few days it can become more severe, accompanied by irreversible changes, even death of the eye.
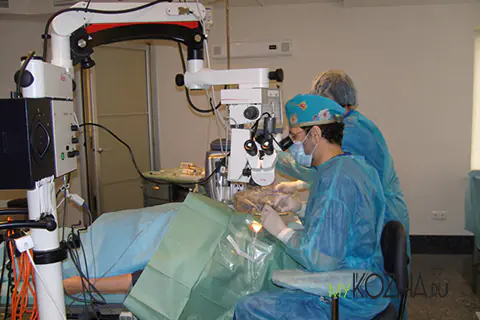
First aid
First aid consists of eliminating the damaging factor and cooling the affected organ. And if the first point usually does not raise questions, then the second requires a little clarification. So, how to properly cool your eye if it’s burned?
- Wrap your fingers in a sterile bandage and open the eyelids of the injured person as much as possible;
- Carry out the cooling process under running water (12-18° C) for 20 minutes;
- For cooling, you can use any suitable container that can create a flow of water, for example, a syringe without a needle, a rubber balloon or a plastic bottle. You can cool the affected organ by placing your face in a suitable container with cool water and blinking periodically, or by running a piece of cotton wool soaked in water along the eyelid from the temple to the nose.
After this, it is recommended to drip an antiseptic solution (albucid, chloramphenicol) into the damaged eye, cover it with a sterile napkin, give the victim a tablet of any analgesic and call an ambulance. You should definitely contact a specialist if for more than a day:
- Pain persists or worsens;
- The feeling of a foreign body remains;
- Signs of an eye infection include swelling, redness, or mucus discharge;
- Visual acuity decreases.
Treatment
The process of treating thermal burns of the eyes is quite specific and complex, so it should be dealt with by specialized specialists in the eye department of the hospital. Before treating a burn, the doctor must assess the area of tissue damage and diagnose the severity of the burn.
As a rule, in case of thermal injuries, anti-inflammatory and restorative therapy is used to promote the restoration of damaged tissues. Surgery is indicated if it is necessary to remove dead tissue and in case of restoration of vision.
You can speed up the healing process using traditional medicine methods that have proven effective for eye burns. You can restore eyeball tissue and improve vision by eating raw carrots and fish oil daily. To relieve inflammation of the affected area, you can use decoctions of medicinal herbs.
Thermal burns of the eyes are serious injuries that have extremely varied consequences, one of which may be complete or partial loss of vision. Therefore, a victim who has received an eye burn should immediately receive first aid and contact a specialized specialist. The health of the visual organs depends on how timely treatment is started.
An eye burn is an injury or acute damage to a separate area of the visual apparatus (mucous or choroid, eyeball, conjunctiva, lens, retina, skin of the eyelids) by aggressive substances.
A person receives up to 90% of external information through vision. Injuries (physical, chemical, thermal) lead to a decrease in the sharpness of the device, the development of complications up to the onset of complete blindness. According to statistics, eye burns account for 10% of all known injuries. Chemical injuries are in the lead (75-80%), household and thermal injuries account for 40%.
In everyday life, seemingly harmless household items can cause eye injury: hydrogen peroxide, vinegar, alcohol, cigarettes, lime, hot pepper if used carelessly or incorrectly. If safety measures are not followed, people often get burned at work by hot steam, splashes of metal, or hot sparks from welding.
Symptoms of a burn completely depend on the degree of damage and the time interval from the moment of injury. However, a feature of burn damage is immediate redness, swelling of the eyelids and skin. The mucous membrane gradually swells, the cornea becomes cloudy, intraocular pressure rises or falls, and the field of vision decreases. If the first (mild) degree of injury in patients does not require pre-medical care and special treatment, and minor hyperemia and swelling of the cornea go away on their own. At the 3rd degree burn stage, the sclera of the eyes, cartilage and eyelids begin to necrotic, the skin becomes covered with blisters. At grade 4, with deep damage, the cornea becomes similar to a porcelain plate. If you do not act and do not start treatment urgently, then complications (uveitis, cataracts, secondary glaucoma) are inevitable.
Reference! It is not always possible to determine the extent of the burn immediately after injury. Most often, in the first minutes, patients experience shock and do not feel pain. Meanwhile, the burn quickly spreads and affects large areas of the eye, especially if caused by chemical elements. In case of damage to the choroid or retina by laser, infrared rays, symptoms at the initial stage may be completely absent. Regardless of the type and complexity of the injury, the patient must be urgently taken to the emergency room. Forecasts depend not only on the degree of the burn, but also on the volume and speed of timely medical care provided.
In the international classification of diseases ICD-10 eye burn has codes:
T26.0 Thermal burn of the eyelid and periorbital area
T26.1 Thermal burn of the cornea and conjunctival sac
T26.2 Thermal burn leading to rupture and destruction of the eyeball
T26.3 Thermal burn of other parts of the eye and its adnexa
T26.4 Thermal burn of the eye and its adnexa, unspecified localization
T26.5 Chemical burn of the eyelid and periorbital area
T26.6 Chemical burn of the cornea and conjunctival sac
T26.7 Chemical burn leading to rupture and destruction of the eyeball
T26.8 Chemical burn to other parts of the eye and its adnexa
T26.9 Chemical burn of the eye and its adnexa, unspecified localization
Classification of eye burns
Taking into account the etiology, ophthalmologists divide burn injuries into:
- thermal (boiling water, flame, steam);
- chemical (lime, acids, alkalis);
- radiation (ultraviolet, ionizing radiation, infrared rays);
- combined, caused by several harmful factors at once.
Depending on the location, the following may be affected:
- cornea;
- conjunctival sac;
- eyelids;
- periorbital region;
- eyeball;
- adnexal apparatus.
Taking into account pathomorphological changes, the injury is divided into 4 stages:
1 acute stage with a duration of 1.5-2 days, during which hydration and tissue necrobiosis rapidly develop, the cornea swells, and the protein-polysaccharide complex begins to disintegrate and dissociate.
Stage 2 within 2-18 days from the moment of burn injury it causes trophic disorders of the eye and swelling of the cornea.
Stage 3 with a process duration of 2-3 months, it leads to tissue hypoxia, neovascularization of the cornea, and disruption of eye trophism.
Stage 4 (the most severe) with a duration of one to several years can enhance the synthesis of collagen proteins by corneal cells and trigger the scarring process.
Depending on the depth of tissue damage, there are 4 burn degrees:
First degree – minor in the form of conjunctival hyperemia, superficial corneal erosion. It goes away without a trace after a few days.
Second degree (moderate), causing damage to the superficial layers of the skin of the eyelids and the stroma of the cornea, covering the skin of the eyelids with burn blisters, and slight clouding of the cornea.
Third degree with the acquisition of a grayish-white scab and a matte surface of the conjunctiva (cornea) of the eye, damage to the tissues of the cartilage and sclera of the eyelids. Possible development of cataracts and iridocyclitis. Although the burn damage to the surface of the eyeball does not exceed 50%.
Fourth degree accompanied by charring, necrosis of the sclera and conjunctiva of the eyes. The cornea is damaged to the deep layers, the surface resembles a porcelain-white opaque plate. In the absence of emergency treatment, corneal perforation, the development of cataracts, secondary glaucoma, and uveitis may occur.
Chemical burn to the eye
Chemical eye burn is a type in which chemical reagents (alkali, alcohol, acid) get into the eyes. The defeat is serious. The degree is determined based on the consistency and concentration of the reagent that gets onto the conjunctiva and cornea of the eye.
Chemical damage to the eye is an ophthalmological emergency. Alkalis and acids cause severe corrosion, eye irritation, up to a decrease in visual acuity and disability in humans. The severity level is determined taking into account the type, volume, and temperature of the ingested chemical. Children and the elderly experience such burns most severely. The prognosis will depend entirely on timely treatment.
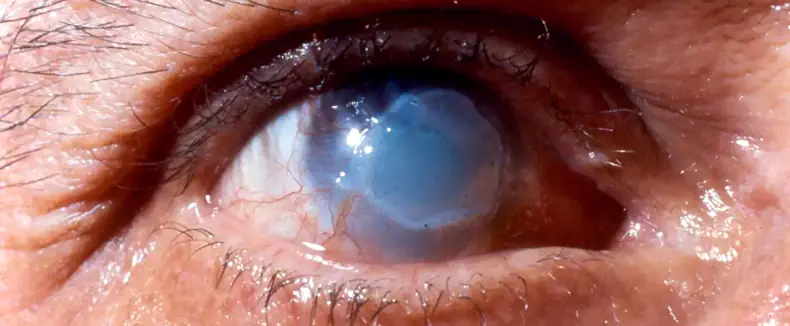
Chemical acid is a toxic substance. A chemical burn to the eye provokes coagulation and coagulation of the white of the eyeball, followed by coating with a kind of crust to prevent deeper penetration into the tissues of the organ.
An acid burn to the eye is not considered a particularly dangerous injury, although it leads to necrosis and profuse lacrimation in the damaged area. If highly concentrated acids (sulfuric, nitric, hydrofluoric) get into the eyes, they easily penetrate into the deep layers of tissue, causing more severe consequences.
Alkalis completely dissolve protein when it comes into contact with the eyes, without forming a crust that can retain the substance and prevent deep penetration.
Alkali burn is a dangerous type that leads to:
- damage to the external and internal elements of the eyeball, nerve endings;
- destruction of mucosal cells;
- formation of wet necrosis;
- clouding of the cornea;
- increased intraocular pressure.
Usually in the first minutes the victim does not feel pain and does not fully understand the seriousness of the situation. The countdown for a chemical burn with alkali can last for minutes, leading to irreversible consequences. If the solution penetrates into deep tissues, it will be almost impossible to remove. The toxic substance spreads quickly. If immediate action is not taken, it can cause loss of vision and blindness.
Eye burn from welding
Welding eye burn is radiation damage to the retina from infrared and ultraviolet rays. The risk group includes electric welders who mishandle equipment and do not follow safety precautions.
The peculiarity of an eye burn from welding is a delayed harmful effect only after a few days, when vision begins to sharply decline, photophobia, pain in the eyes and lacrimation begin to appear. A retinal burn can also be caused by exposure to an ultraviolet lamp or bright sun.
Radiation damage to the eye requires immediate first aid. If the victim cannot do it on his own, then you need to help administer medications and place them in the conjunctival sac:
- corticosteroids (hydrocortisone ointment, Dexamethasone);
- antibacterial drugs (Floxal, Levomycetin, Okomistin);
- anesthetic drops (Inocaine).
Next, assist in sending it to the nearest medical facility. clinic.
Corneal burn
The cornea is an important structural part of the front part of the eye, necessary for regulating visual function. A burn to the cornea of the eye leads to partial or complete loss of vision in 45% of cases. Most often, the cornea suffers due to exposure to high temperatures (flame, boiling water, steam, ionizing radiation), or aggressive elements (lime, acid, alkali, caustic soda, caustic potassium, ethyl alcohol, ammonia, slaked lime).
Burns of the cornea of the eyes caused by chemicals are the most severe, quickly spreading beyond the contact area with the aggressive agent, affecting large areas. The degrees can be established only after 2-3 days from the moment of injury. However, tissues are instantly subject to enzymatic destruction, and liquefaction necrosis develops.
Less commonly, eye damage can be caused by acid (citric, hydrochloric, nitric, boric, acetic, sulfuric), provoking the formation of a scab and disintegration into molecules. Alkaline burns are dangerous because they quickly penetrate into the deep structures of the eye, destroying them to the ground.
Worth knowing! Household chemicals, insecticides, poisonous plants, paint varnishes, herbicides, ear drops, and alcohol tinctures when instilled into the eyes can cause a chemical burn. Thermal damage from flame, boiling water, and incendiary mixtures even at T +45 degrees leads to the formation of a scab on the damaged area and becomes dangerous for the cornea.
Radiation burns from infrared and ultraviolet rays and ionizing radiation can occur during contact with laser devices. They cause damage to the anterior part of the eyeball or retina with subsequent dystrophic changes.
The main symptoms of a corneal burn:
- photophobia;
- involuntary contraction of the circular muscles;
- lacrimation;
- pain, pain, presence of a foreign body in the eye;
- swelling;
- redness of the eyelids;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- blurred vision;
- reduction in severity.
The note! Symptoms do not always appear immediately. So, when burned by the sun, an ultraviolet lamp begins to appear only after 10-12 hours.
Stages of corneal burn:
First degree with the manifestation of corneal swelling, protein breakdown, tissue necrosis.
Second degree with a duration of 2-18 days, leading to trophic disorders, swelling of the cornea.
Third degree with growth of the lesion into the blood vessels and stroma of the cornea, hypoxia of the eye tissues.
Fourth degree with a duration of 6 months to several years - to the formation of scars, adhesions, and degenerative changes.
First aid for a corneal burn:
- rinse the conjunctival cavity with saline solution, clean water, so up to 0.6 hours in a row, for a chemical burn - 10-15 minutes;
- drink a pain reliever;
- apply a dry bandage, consult an ophthalmologist.
First aid for thermal burns of the eye:
- transfer the victim to a dark room;
- instill drops with anesthetic;
- apply a compress for 10-15 minutes, apply an aseptic bandage for welding burns.
The main thing is to provide first aid no later than 5 minutes from the moment of injury.
What you should absolutely not do:
- rub your face and eyes with your hands or a rough cloth;
- apply hot compresses to the affected areas;
- rinse your eyes with untreated tap water or river water;
- instill irritating agents (Albucid) onto the mucous membrane.
A burn to the cornea of the eye is considered a dangerous injury, fraught with complications: perforation, erosion, glaucoma, cataracts, conjunctivitis, scarring of the skin on the eyelids. The prognosis directly depends on the depth of tissue damage, the speed and correctness of the initial actions taken. Even after treatment, patients remain under observation by an ophthalmologist for up to 1 year.
Thermal burn of the eye
Thermal burn of the eye - damage (cornea, mucous membrane, skin of the eyelids) by an object of low or high temperature (fire, liquefied gas, ice, steam, hot liquid). Most often, the anterior parts of the eyes are affected.
There are 4 degrees of thermal burns to the eyes. 1-2 are characterized by the formation of bubbles on the mucous membrane of the eye, redness of the skin of the eyelids.
The prognosis is favorable if:
- promptly rinse your eyes with a stream of water;
- remove particles of the traumatic substance;
- apply an aseptic bandage.
At grade 3, the cornea begins to become cloudy, acquiring the shade of matte porcelain, and the deep tissues of the skin of the eyelids necrotize. At grade 4, the tissues are already charred and patients cannot avoid spending a long time in the hospital. The consequences are sad. If scar changes begin to form in the tissues, glaucoma, cataracts, and dry eye syndrome may begin to develop.
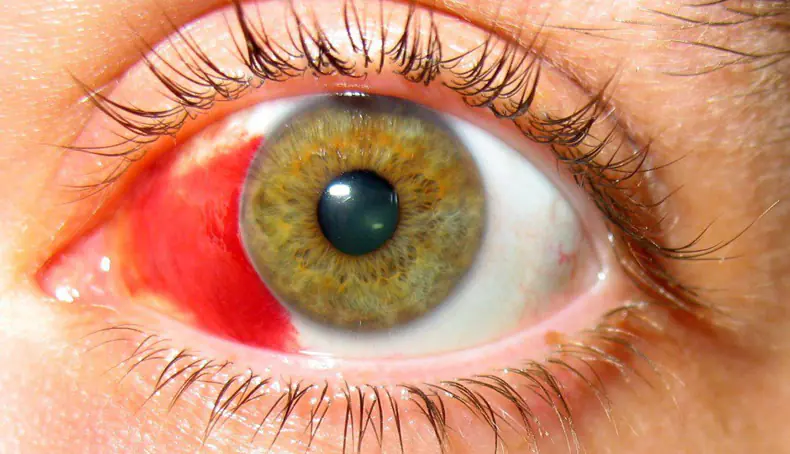
Treatment of eye burns
Treatment of eye burns of any type should be carried out only under the supervision of a qualified ophthalmologist, who should be contacted in case of injury to the visual organ, regardless of whether emergency first aid was previously provided or not. The doctor will conduct diagnostic procedures and then prescribe drops for eye burns or other treatment methods.
Main groups of drugs:
- anti-inflammatory drops (Dexapos, Dexamethasone);
- ointments and drops with an antibacterial effect (Levomycetin, Tetracycline);
- glucocorticosteroids (Betamethasone, Maxitrol);
- regenerating dialysate (Dexpanthenol);
- antihypertensive drugs (Dorzolamide);
- tear fluid substitutes;
- NSAID drugs;
- parabulbar injections (Methylethylpyridinol).
Treatment is carried out exclusively in inpatient settings. In addition to medications, it is possible to instill drugs (Scopolamine, Atropine) to relieve pain and prevent the formation of adhesions.
Additionally, patients with burns are prescribed eyelid massage and physiotherapy. In severe cases, surgery is performed. If the anterior chamber of the eye is affected by chemical reagents, then after removing the penetrated components, doctors perform corneal paracentesis. In the event of a threat of loss of the eye - vitrectomy, keratoplasty, necrectomy of the cornea and conjunctiva, plastic surgery of the conjunctival cavity.
In case of delayed burns and scar formation on the cornea, penetrating keratoplasty is possible, and in case of development of secondary glaucoma, antiglaucomatous surgery is possible.
For chemical and thermal burns, a doctor is involved in developing special treatment. You cannot solve the problem yourself at home and treat an eye burn with folk remedies in order to avoid worsening the situation. It is acceptable to apply a lotion of chamomile decoction or strong tea leaves as first aid to relieve unpleasant symptoms in case of damage caused by welding or a bactericidal lamp. However, in any case, you need to consult an ophthalmologist for advice.
Doctors believe that 90% of eye burns can be avoided if you follow industrial safety precautions and use safety glasses when working with flammable chemical components and light filters. If a burn injury could not be avoided, the consequences will depend entirely on the depth, severity of tissue damage, and stage of pathology.
If at 1-2 degrees burns disappear without a trace after a certain period of time, then at 3-4 degrees there is a high probability of the formation of scar changes in the tissues, a decrease in the transparency of the cornea, the occurrence of cataracts, glaucoma, and dry eye syndrome. The most dangerous are radiation and chemical burns, leading to irreversible consequences: damage to retinal cells, blindness, atrophy of the eyeball, formation of a cataract, fusion of the conjunctival cavity.
First aid for eye burns
Regardless of the cause of the eye burn, the victim is advised to urgently go to the emergency room to provide quality care.
If it is not possible to call an ambulance or visit an ophthalmologist, then the main thing is to eliminate the damaging factor (radiation, high temperature, chemical substance), to prevent the development of complications and the addition of a secondary infection to the burn.
First steps for a thermal burn:
- pull back the lower eyelid, apply ointment (Floxan) or drip drops with an antibacterial effect (Albucid, Sulfacyl sodium, Levomycetin);
- apply a sterile bandage to the eyes;
- deliver the victim to a medical facility.
In case of injury from a chemical substance:
- rinse the eye with saline solution, clean water or potassium permanganate, soda solution (if acid damage occurs);
- rinse with boric, vinegar solution in case of exposure to alkali on the cornea;
- carefully remove the foreign body from the cornea, conjunctiva in case of mechanical injury;
- apply a sterile bandage;
- call an ambulance to be sent to the hospital.



