Description and causes of ulcerative gastritis. Symptoms and diagnosis of the disease. Methods of treatment.
The content of the article:- What is ulcerative gastritis
- Reasons for development
- Symptoms and diagnosis
- Treatment options
- Medicines
- Folk remedies
- Diet
- Prevention
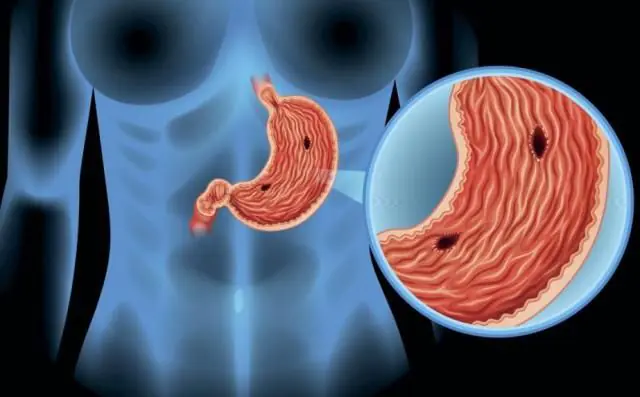
Ulcerative gastritis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process that is accompanied by the formation of ulcerative lesions on the surface of the gastric mucosa. The manifestations are varied, but most often there are complaints of pain, the presence of blood impurities in the stool. During therapy, medications, diet, and folk remedies are used.
What is ulcerative gastritis?
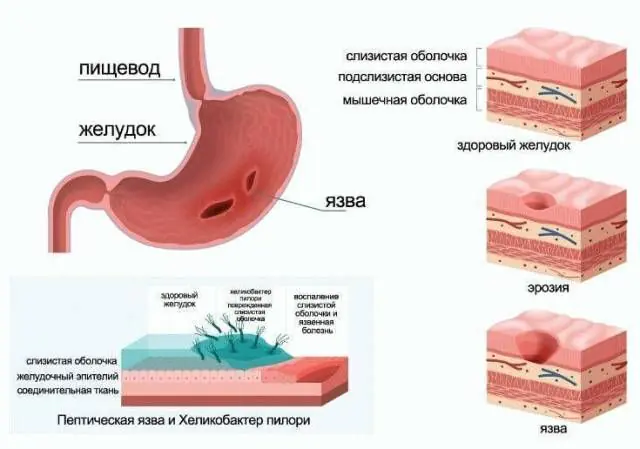
Ulcerative gastritis is a disease of the gastrointestinal tract that occurs as a result of the negative effects of digestive acids, which are synthesized by the cells of the gastric mucosa. When the protective layer disappears from the surface of the epithelium, gastric juice begins to corrode the body's own cells.
People with weakened smooth muscles of the stomach and damaged mucous membrane are at risk. The disease is more common among males.
When the pathology worsens, a person feels intense pain, which bothers him immediately after eating. The development of bleeding is observed in more than half of patients with ulcerative gastritis.
In some cases, the formed erosive changes do not affect the patient’s well-being, and the disease goes undetected for a long time. The lack of timely therapy leads to the development of chronic ulcerative gastritis, as well as complications such as the regular development of gastric bleeding, anemia, the formation of ulcerative lesions, and Helicobacter infection.
With timely detection and treatment of ulcerative gastritis of the stomach and compliance with all the doctor’s instructions regarding diet and use of medications, the prognosis is predominantly favorable.
Causes of development of ulcerative gastritis
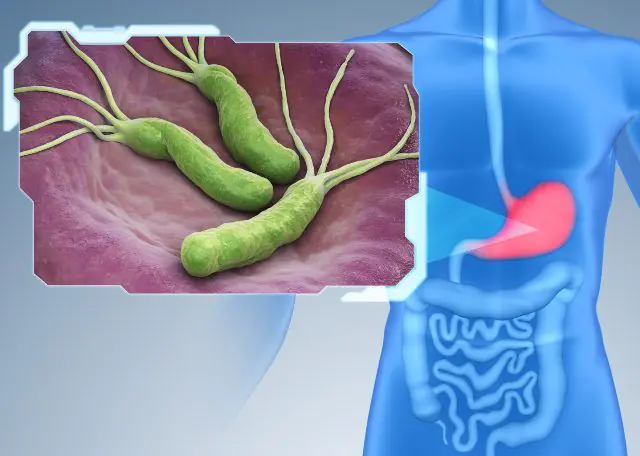
Helicobacter pylori as a cause of ulcerative gastritis
The causes of ulcerative gastritis are associated with the use of medications, the development of postoperative complications, exposure to infectious processes, alcohol consumption, and dysfunction of the urinary system.
The main causes of ulcerative gastritis:
- Infectious lesion. The most common pathogenic microorganism that provokes the development of the disease is Helicobacter pylori. An excess amount of bacteria and their metabolic products, active growth and reproduction of infection leads to weakening of smooth muscles and damage to the gastric mucosa.
- Uncontrolled consumption of alcoholic beverages. Alcohol abuse negatively affects the functional state of the gastrointestinal tract. Ethanol irritates and damages the mucous membrane.
- Smoking. The risk of negative effects on the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, as well as on the gastrointestinal tract, increases. There is a risk of developing gastric and duodenal ulcers, as well as erosive gastritis.
- Use of certain groups of medications. These include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetylsalicylic acid, steroid drugs, anticoagulants, analgesics. Regular uncontrolled use of NSAIDs leads to thinning of the mucous membrane and the development of ulcerative lesions.
- Violation of the integrity of the gastric mucosa. As a rule, it is observed in patients with a history of Crohn's disease, food allergies, intolerance to certain foods (gluten, lactose, sugar), increased acidity, infectious diseases of bacterial or viral origin.
- Traumatic lesions. As a result of blows, cuts, as well as surgical intervention, the mucous membranes of the stomach are injured, the blood supply is disrupted, causing deficiency conditions and thinning of the mucous membrane. The combination of several triggers at once leads to the formation of erosions.
- Regular psycho-emotional stress. It can also provoke the development of ulcerative gastritis. Normalizing your mental state and standard of living, as well as reducing stress, is the best prevention for the recurrence of the disease.
Symptoms and diagnosis of ulcerative gastritis
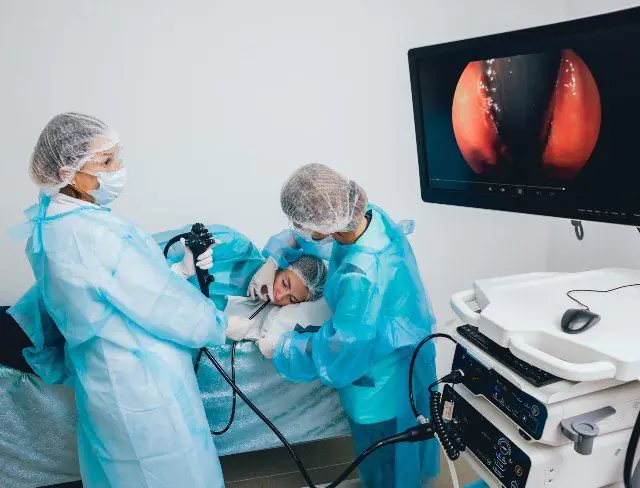
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy for the diagnosis of ulcerative gastritis
Early symptoms of ulcerative gastritis are similar to toxic infection or exacerbation of gastrointestinal tract disease and manifest themselves in the form of heartburn, nausea, abdominal pain, flatulence, and stool disorders.
As the disease progresses, symptoms appear in the form of nausea and vomiting, which are often aggravated by stress and psycho-emotional stress. In some cases, blood may be present in the vomit. The stool changes color and may also contain streaks of blood. Associated symptoms occur in the form of appetite and weight disturbances and general weakness.
A feeling of discomfort occurs after eating, accompanied by heartburn. The pain worsens even after drinking plain water. An accurate diagnosis can be made during exacerbation of ulcerative gastritis, when the stool is dark in color due to the presence of digested blood in it.
In the process of diagnosing ulcerative gastritis, an in-person examination and a thorough history taking are required. The gastroenterologist asks the patient about how long and often the bleeding has been observed, and whether there are accompanying symptoms (nausea, vomiting). Pay attention to how quickly body weight is reduced, what groups of medications were used previously, and whether there are any bad habits.
Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are carried out: indicators of a general blood count are analyzed to identify anemia and hidden blood loss. To diagnose Helicobacter, breath tests and PCR studies are performed.
Instrumental diagnostic methods include esophagogastroduodenoscopy, and at the same time a biopsy is performed. This research method helps to identify erosions. In case of massive blood loss, the procedure is carried out in the first few hours from the moment of admission to the hospital. If the patient’s health is stable, endoscopy is postponed for 1-2 days. During the examination, the doctor determines the type of erosion: hemorrhagic, flat, hyperplastic, single or multiple.
X-rays are indicated if EGD is contraindicated for the patient. Conventional gastrography is performed, as well as with the additional use of contrast agents. Ulcerative gastritis will be indicated by thickening, swelling, nodular formations inside the stomach, and enlarged gastric fields. The most informative technique is the use of double contrast radiography. The decision on how to treat ulcerative gastritis is made by the doctor according to the results obtained.
Ulcerative gastritis must be differentiated from the following pathologies: gastric ulcer, polyps, varicose veins of the esophagus, traumatic lesions, burns, radiation damage.
Methods for treating ulcerative gastritis
Treatment of the disease is carried out comprehensively, taking into account the causes of its development and accompanying manifestations. The patient is prescribed a diet, symptomatic treatment of ulcerative gastritis, and if Helicobacter is detected, combined antibiotic therapy. In severe cases of the disease and ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, surgical intervention is indicated. The doctor removes the affected areas of the mucous membrane to prevent further spread of the infection. If gastric bleeding occurs for the first time or there is a suspicion that the origin of gastritis is infectious, the patient is taken to the surgical department.
Medicines for ulcerative gastritis
Misoprostol for the treatment of ulcerative gastritis
The general scheme of drug treatment for gastric ulcerative gastritis involves the use of the following drugs:
- Maalox. Antacid drug in the form of chewable tablets and suspension for internal use. The use of drugs in this group allows you to neutralize the increased acidity of gastric juice and reduce the severity of pain. Use 1-2 tablets after a meal. Long-term, uncontrolled use of Maalox is fraught with allergies, negative effects on mineral metabolism, destruction of bone tissue, and stool disorders. Cost - 150 rubles. (60 UAH). Analogues: Almagel, Gastal, Alumag, Relzer, Trivin.
- Lansoprazole. Refers to proton pump inhibitors, which slow down the secretion of acids and accelerate the regeneration of affected tissues. Blocks the final stages of hydrochloric acid formation. Long-term use of this group of drugs is contraindicated, as it can cause fractures of bone tissue (hip, wrist, spine). Lansoprazole is available in the form of capsules for internal administration, which are used 30 mg 1 time per day before the main meal. According to indications, the doctor may decide to increase the dose. Price — 115 rub. (45 UAH). Analogues: Clatinol, Lanpro, Lansoprol.
- Misoprostol. A drug that accelerates the regeneration of damaged areas of the gastrointestinal tract. Available in the form of tablets for internal use. Prevents thinning of the intestinal mucosa in patients who are recommended to use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Shows antisecretory properties, heals peptic ulcers, increases the resistance of the gastric mucosa to adverse factors. Used during treatment, as well as for the prevention of ulcers. The medicine is contraindicated in pregnant and lactating women. Tablets are taken 1 pc. up to 4 times a day. An overdose is fraught with drowsiness, lethargy, bradycardia, tremor and diarrhea. The cost is 3330 rubles. (1300 UAH). Analogue - Mirolut.
- Kvamatel. A drug from the group of H2-histamine receptor blockers, under the influence of which the production of hydrochloric acid and the feeling of pain are reduced, and the regeneration of damaged tissue is accelerated. Take 1-2 tablets. twice a day. The duration of the course is up to 2 months. Courses of therapy can be repeated periodically. To prevent recurrent ulcers, take 20 mg tablets once a day. In case of overdose, it is necessary to rinse the stomach and consult a doctor for the selection of symptomatic therapy. The price is 360 rubles. (140 UAH). Analogs: Famosan, Famotidine, Famogard, Pepsidin, Topcid.
- Metoclopramide. A drug for the treatment of ulcerative gastritis, which reduces nausea and vomiting, is used in short courses in the minimum effective dosage. The drug also copes with hypotension and intestinal atony, and can accelerate intestinal motility. Cost - 100 rubles. (40 UAH). Analogue - Cerucal.
When a Helicobacter infection is detected, antibacterial drugs are used. If the causative agent of the disease is insensitive to the action of the active component of the antibiotic, combination therapy is prescribed: for example, Amoxicillin (Amoxil) is combined with Metronidazole. The duration of therapy is at least 10 days.
During the treatment of ulcerative gastritis with drugs, it is important to maintain a drinking regime. You can calculate the required amount of water according to the following scheme: 30 ml of liquid multiplied by body weight. Water not only accelerates the elimination of pathogenic microorganisms, but also normalizes metabolic processes and helps normalize food digestion.
Folk remedies for ulcerative gastritis
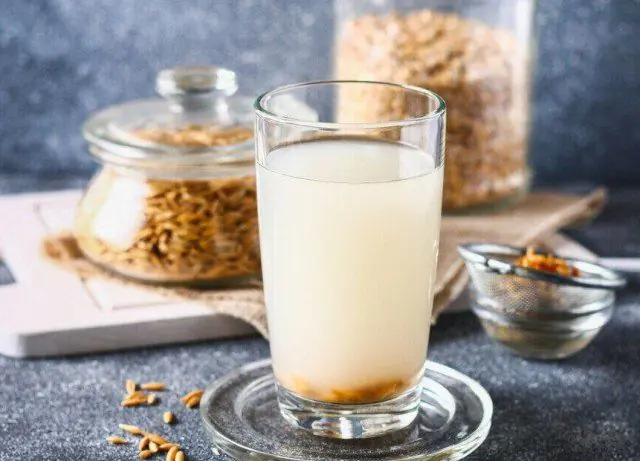

Oat infusion for ulcerative gastritis
Treatment of ulcerative gastritis with folk remedies is practiced as a complement to the use of medications and diet therapy. Before starting home treatment for the disease, it is recommended to consult a gastroenterologist.
Effective folk remedies for treating ulcerative gastritis:
- To reduce spasms of smooth muscles, flax seeds are used. The plant exhibits a calming, relaxing effect. Creates a protective membrane on the inner surface of the gastrointestinal tract.
- The use of a complex of medicinal herbs is indicated to reduce the inflammatory process, spasms, and normalize the acidity of gastric juice. Chaga is mixed with licorice roots and mint in equal proportions, poured with boiling water, and left for 1 hour. Take 1/3 cup in the morning before meals and throughout the day. The duration of therapy is 10 days, after which a break is taken. The course of treatment can be repeated regularly with prior agreement with your doctor.
- 3 tablespoons of olive oil are combined with a similar amount of sea buckthorn oil, consume 1 tablespoon on an empty stomach on a regular basis. This product creates a protective coating on the inner surface of the stomach and helps eliminate constipation.
- Mix equal parts of chamomile, calendula, dried cucumber, pour boiling water and simmer in a water bath for 10-15 minutes. Remove from heat, cool, take 1/3 cup twice a day during meals.
- 5 g of mumiyo are dissolved in a glass of warm water, liquid honey is added. Take twice a day after meals. The duration of therapy is 14 days. After 5-7 days the course can be repeated.
- To prepare an anti-inflammatory and enveloping oat infusion, whole oats (instant oatmeal is not suitable) are thoroughly washed and soaked overnight. The resulting liquid is boiled over low heat until jelly is obtained. Use 2-3 times a day to create a protective film and speed up the restoration of damaged tissues.
- An auxiliary treatment for ulcerative gastritis is freshly squeezed pineapple juice, which is consumed twice a day, 50 ml.
Diet for ulcerative gastritis

A diet for ulcerative gastritis is mandatory. Nutrition should be gentle and balanced: it should contain a sufficient amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, plant fiber, and water.
Portions are small, meals for ulcerative gastritis are fractional. If the patient has insulin resistance or diabetes mellitus, then the frequency of meals should not exceed 3 times a day. The last meal is 2 hours before going to bed. Food must be chewed thoroughly and refrain from swallowing large whole pieces.
It is allowed to eat potatoes, carrots, beets, cauliflower, broccoli, green peas, nectarines, bananas, peaches, apples, strawberries, raspberries, watermelons, melons, pine nuts, buckwheat, semolina, white rice, melted butter and unrefined vegetable oils. If well tolerated, high-quality dairy products with a low fat content, lean meat, and chicken eggs are acceptable.
It is recommended to refrain from eating foods that stimulate appetite and promote the secretion of excess gastric juice: broths, spices, smoked meats, pickles, fatty, fried, heavy foods. All sour fruits and berries, radishes, onions, sorrel, and spinach are also prohibited. From the menu for ulcerative gastritis, it is necessary to exclude the consumption of almonds, corn, pearl barley, barley, millet, whole grain pasta, cakes, pastries, sweets, fresh bread, canned food, and packaged juices.
Important! During meals, it is recommended to refrain from watching TV and using gadgets. This avoids overeating and has a beneficial effect on the digestion process.Prevention of ulcerative gastritis
At the first manifestations of disorders, it is recommended to contact an experienced, qualified gastroenterologist.
To prevent ulcerative gastritis, you must follow simple recommendations:
- Minimize the consumption of food that negatively affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract: smoked meats, canned food, semi-finished products, spicy, fatty, fried foods;
- Monitor the quality and quantity of food: a balanced diet, eating seasonal vegetables and fruits, avoid overeating;
- Avoid snacking and eating fast food;
- Do not drink alcohol, do not smoke;
- Treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in a timely manner, pay attention to early warning signs of ulcerative gastritis: anemia with a traditional diet, constipation, nausea, spotting;
- Eliminate potential sources of chronic infection - carious teeth, tonsils;
- Carry out sanitation to strengthen the immune system and prevent active reproduction of Helicobacter.
- Follow a work and rest schedule, go to bed and eat food at approximately the same time of day;
- Minimize physical inactivity to normalize digestion: at least 10,000 steps daily, swimming, yoga, Pilates, brisk walks in the fresh air, running;
- Observe the rules of personal hygiene: wash your hands before preparing and eating food, after visiting the street, public places, or the restroom;
- Avoid self-medication with medications, especially those with analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties.
To prevent re-exacerbation of ulcerative gastritis, use antacids, pepsin, Kvamatel, Misoprostol. The general treatment regimen is selected by the doctor. It is necessary to be under constant supervision of a gastroenterologist and undergo preventive laboratory and instrumental diagnostics 1-2 times a year.
How to treat ulcerative gastritis - watch the video:



