
Good day, dear readers!
Today we will look at such a skin disease as furunculosis, and everything connected with it.
What is furunculosis?
Furunculosis - multiple purulent-necrotic lesions of hair follicles, as well as their sebaceous glands and surrounding connective tissue.
Furuncle - purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle and surrounding connective tissues.
The main differences between the concepts “furuncle” and “furunculosis” are the widespread nature of the latter. Boils with furunculosis do not appear only once. Constant relapses and chronic course of this skin disease are the main feature of furunculosis.
The main symptoms of furunculosis – the formation of a painful pustule on the skin against the background of redness of the skin, in the center of which a purulent-necrotic core forms. After the rod is rejected, the tissue scars and heals.
The main cause of furunculosis – a bacterial infection, mainly staphylococci, which affects the skin against the background of decreased immune reactivity or other diseases.
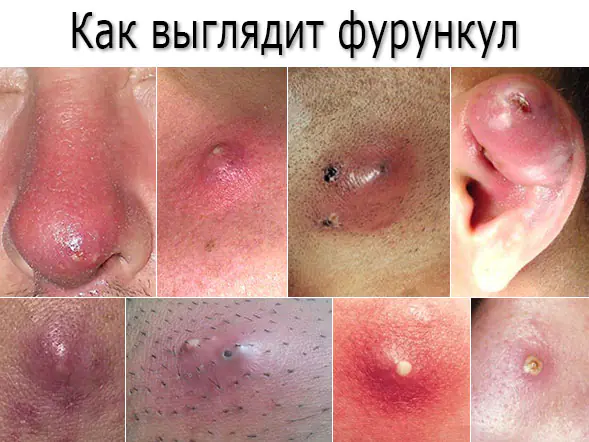
The most common formation of boils is on the forearms, back of the head, lower back, buttocks, abdomen and legs, but furunculosis on the face is also not uncommon, and boils on the nose, ears and other parts of the face are the most painful.
The prognosis for furunculosis is positive, but if you do not pay enough attention to this disease and do not prescribe adequate treatment, complications may appear - thrombosis, lymphadenitis, and even sepsis.
The appearance of boils can be associated with seasonality - autumn and spring.
The appearance and development of furunculosis can be primary or secondary.
The initial appearance of boils usually occurs on healthy skin. One of the most popular pictures looks something like this: on the skin of almost any person there is a certain microflora (especially staphylococci), which, when the skin is mechanically damaged (cuts, abrasions), penetrate into the epidermis layer. If the wound is not disinfected, bacterial and possibly other types of infection create an inflammatory focus at the site of sedimentation and begin to actively multiply. The immune system sends protective cells to the site of inflammation, which “contain” pathogenic microorganisms and their metabolic products in one place. That is why the boil has a purulent core in one place at the peak of its formation, which, together with the elevation, resembles a “microvolcano”.
The secondary appearance of boils is usually widespread, and here it is more fair to talk about furunculosis, since their appearance and development usually occurs against the background of other diseases, for example, staphyloderma (staphylococcal pyoderma). The reason for this phenomenon is no longer one factor - the penetration of infection. Here it is fair to talk about a combination of 2 or more factors. The main ones are “skin trauma or large pores – introduction of bacteria under the skin – reduced reactivity of the immune system.”
After infection enters the skin, the development of a boil occurs in 3 stages, the duration of each of which, in the absence of complications, is up to 10 days:
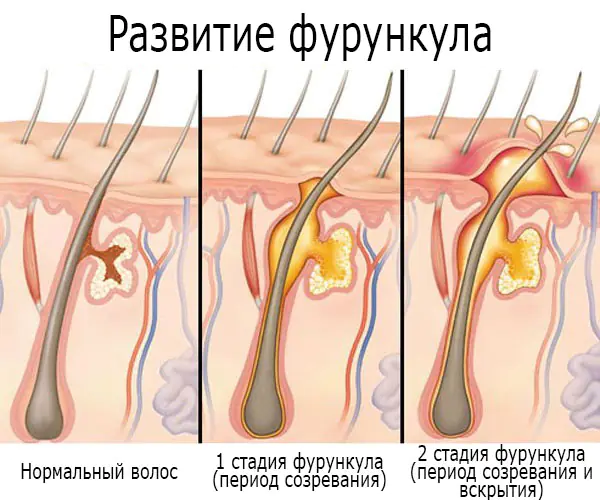
Furuncle stage 1 (beginning) – accompanied by an inflammatory process at the site of sedimentation and active reproduction of the infection. The site of inflammation turns red, but the red spot does not have clear boundaries. A hard infiltrate, a compaction, forms in the center of the redness, and when pressed, the patient feels some pain and tingling. The surrounding tissues gradually swell, and the compaction, as the boil develops, increases in size.
Furuncle stage 2 (3-4 days) – is accompanied by an increase in the boil up to 3 cm in diameter, as well as the formation of a purulent-necrotic core in the middle of it with a pustule on the surface. The pathological process involves the nearby sweat gland and connective tissue. The surrounding blood vessels dilate and collagen swelling occurs. The skin over the boil becomes smooth and more painful. Inside the towering cone-shaped “mountain”, elastic and collagen fibers are destroyed, and a dense protective ring is formed from them, preventing infection and purulent contents from leaving the boil, which prevents toxic substances from spreading throughout the body. By the way, this is precisely the reason why it is not allowed to squeeze out a boil without understanding the rules for opening it, otherwise there is a great risk of breaking the “barrier” between the body and the boil.
Furunculosis (a large number of boils) can cause symptoms of intoxication of the body - general malaise and weakness, nausea, lack of appetite, fever, headaches.
At the end of the development of the 2nd stage of the boil, the pustule is opened spontaneously or artificially, and a necrotic core with yellow-green pus, which may also contain an admixture of blood, comes out
Furuncle stage 3 – is accompanied by the appearance of a “crater” at the site of the opened pustule, which is first filled with granulations, and after a couple of days scars.
After a while, the location of the boil is almost invisible. However, massive skin lesions, especially with deep, large boils, and if they were treated incorrectly or not treated at all, often result in the appearance of scars and skin irregularities, which not all specialists can remove. By the way, one of the methods for smoothing the skin after furunculosis is peeling, which, depending on the depth of the scars, unevenness and skin type, can be superficial, medium and deep. In fact, peeling is the removal of the top layer of damaged skin, in its place a new, healthy layer appears.
It should also be noted that with furunculosis, not all boils can develop according to the scheme provided above. Some boils may be limited to only the formation of an infiltrate and not have a core, while some, on the contrary, are accompanied by abscesses and phlegmons.
Once again we would like to remind you that the appearance of a boil is possible only around the hair follicle.
ICD-10: L02;
ICD-9: 680.9.
Symptoms of furunculosis
The main symptom of furunculosis – multiple rashes of boils (boils). A boil is a dense formation in the area of the inflamed follicle, the skin over which turns red, up to 3 cm in diameter. As it matures, the boil becomes painful, in appearance - a cone-shaped mountain with a purulent-necrotic core in the middle. The tissue around the boil swells. After the eruption of the rod and purulent contents, the swelling with pain subsides, and a scar forms at the healing site. Some boils may be limited only to the formation of a reddened infiltrate.
- General malaise, weakness;
- Loss of appetite, nausea;
- Headache;
- Increased body temperature - up to 38 ° C.
Complications of furunculosis
- Abscesses;
- Cellulitis;
- Thrombosis;
- Lymphangitis;
- Lymphadenitis;
- Arachnoiditis;
- Pyelonephritis;
- Meningitis;
- Phlebitis;
- Sepsis.
Causes of furunculosis

The causative agent of furunculosis – bacteria, mainly Staphylococcus aureus, less often white.
It is important to note that staphylococci are found on the surface of the skin of almost any person, however, the integrity of the skin and good health do not allow infection to cause harm to health.
The development of furunculosis is usually caused by a combination of 2 or more factors, which can be endogenous (internal) and exogenous (external) in nature.
- Skin contamination;
- Violation of the integrity of the skin - injury, microcracks, cuts (especially when shaving), scratching with nails, rubbing with uncomfortable shoes or clothing;
- Poor quality nutrition, strict diets;
- Hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- Frequent stress.
- Decreased immune system reactivity;
- Metabolism (metabolism) disorders;
- Increased sweating and sebum secretion;
- Alcohol abuse, smoking;
- The presence of some diseases, mainly of an infectious nature and of the skin - dermatoses (eczema, xeroderma, staphyloderma, etc.), obesity, diabetes mellitus, anemia, hypovitaminosis, acute respiratory infections, caries, HIV infection, meningitis, sinusitis.
Types of furunculosis
Acute furunculosis – characterized by an acute course, responds well to treatment, after which the appearance of new boils does not occur.
Chronic furunculosis – characterized by the constant recurrent appearance of more and more new boils, often less pronounced and in erased forms of the course. Difficult to treat.
Diagnosis of furunculosis
Diagnosis of furunculosis includes:
- History, visual examination;
- Dermatoscopy;
- Bacteriological examination of the contents of the boil (bacteriological culture).
Additional diagnostic methods:

Treatment of furunculosis

How to treat furunculosis? Treatment of furunculosis includes several stages:
1. Bringing boils to maturity;
2. Relief of infection;
3. Opening the abscess.
All treatment of furunculosis includes constant skin hygiene, however, water procedures must be limited, and in the case of taking a bath, warm water with the addition of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) is allowed, which will help disinfect the skin.
In the article we have already mentioned that the appearance and development of boils has 3 stages, which are accompanied by various processes. A very important point is the body’s protective mechanism - the formation of a “ring” around the inflammatory process, beyond which the infection and purulent contents cannot enter the body and spread throughout it. But the infection and pathological exudate must be removed somehow before they come out. How to get it if you can’t squeeze boils?
Thus, the first stage of treatment for furunculosis is to provoke rapid maturation of the boil so that its contents come out, or release it out.
Ultraviolet irradiation is used to artificially ripen the boil.
To accelerate the rejection of the rod and the unauthorized opening of the abscess, crystalline salicylic sodium is applied to the center of the boil, fixing it with a dry bandage
After a fluctuation zone has been identified, crystalline salicylic sodium is applied to the center of the furunculosis elements and fixed with a dry bandage. Such applications have a keratolytic effect and promote accelerated rejection of the rod.
At this and other stages of therapy, the skin around the boils is treated with antiseptics.
The use of Elon ointment will help to significantly speed up the process of ripening and opening of the boil. Thanks to the turpentine group substances and essential oils included in the composition, the ointment not only increases blood flow to the site of inflammation, but also has antimicrobial, disinfectant and anti-inflammatory properties, which significantly simplifies the second and third stages of boil treatment. The use of the ointment is simple - just apply Elon to the affected area of the skin and cover with a sterile bandage or plaster. The bandage needs to be changed once or twice a day; the duration of the course of using the ointment is three days. The light green color and herbaceous aroma allow you to use Elon on any part of the body, and the completely natural composition of the ointment makes it safe for the complex treatment of furunculosis. You can find this ointment in pharmacies in your city.
Another very useful for the maturation of boils, as well as pain relief, disinfection and reduction of inflammation is “Ichthyol ointment”. To use, it must be applied to loosened cotton wool and applied to the boil. When cotton wool dries, it turns into i.e. "Ichthyol cake". “Ichthyol cakes” need to be changed 1-2 times a day. They cannot be applied to an open boil.
During infiltration, “Yoddicerin” and “Bactroban” are also used.
To stop the infection, an antibiotic is selected based on diagnosis and its resistance (resistance) to the infection.
After selecting an antibiotic, they make “blockades” - they inject the boil around the perimeter with an antibacterial drug with novocaine.
Blockades do not allow the purulent process to spread beyond the boil to healthy tissue. Novocaine, in turn, relieves pain.
If the blockade is ineffective - if the inflammatory process with pain intensifies, the blockade is repeated, every other day or daily, until the boil opens and its contents (purulent-necrotic core) come out.
After the blockade, a bandage with a 1% solution of silver nitrate is usually applied to the inflamed area, which is changed daily.
Antibiotics for furunculosis: Dicloxacillin, Erythromycin, Oxacillin, Amoxicillin, Methicillin, Cephalexin, sulfonamides.
To avoid an allergic reaction to antibacterial drugs, some doctors prescribe antihistamines: Diphenhydramine, Pipolfen, Suprastin.
To prevent complications of furunculosis in the form of the formation of abscesses and cellulitis, electrophoresis with antimicrobial drugs is used.
The continuous appearance of new pustular formations may indicate the presence of systemic damage to the body by infection, then treatment is aimed at treating the underlying disease.
After self- or artificial opening of the abscess, the wound and surrounding skin are carefully treated with 3% hydrogen peroxide. The surrounding fabric can also be treated with alcohol, methylene blue or brilliant green.
The opening of the abscess is performed by a surgeon. Surgical treatment methods are also used for abscesses, advanced carbuncles, and phlegmon. After opening, stitches may be needed.
Bandages with antibacterial ointments are applied to the treated wound - erythromycin, syntomycin, and proteolytic drugs are added to them, which have local immunostimulating properties, which is why the wound heals faster. Bandages need to be changed every other day.
For even better healing of the skin, when the wound is covered with granulation tissue, bandages are applied to it:
- Ointments - ichthyol, “Liniment Vishnevsky”, “Liniment synthomycin”, “Liniment streptotsid”, “Levomekol”, indifferent fatty dressings (fish oil, sterile vaseline oil, synthomycin emulsion), “Miramistin”, “Streptotsid”, 5-10% dermatol or xeroform;
- Powders — “Dermatol”, “Xeroform”;
- Aerosols - Polcortolone, Oxycort.
Treatment of furunculosis does not stop until the infiltrate (compaction) is completely reabsorbed, otherwise various complications may appear.
Important! During treatment of furunculosis, constantly change clothes and towels!
- methods of physiotherapy - infrared irradiation (sollux), UHF;
- diet - includes limiting spicy and fatty foods, spices, alcoholic beverages, fast foods and other unhealthy foods;
- additional fortification of the body - taking vitamins (A, B1, B2, B3 (PP), B6, C) and microelements (iron, phosphorus), which will help strengthen the immune system, normalize metabolic processes, accelerate recovery and regeneration of the skin;
- the use of immunostimulants, immunomodulators, biostimulants - “Timalin”, “T-activin”, “Timogen”, “Levamisole”;
- the use of antistaphylococcal gammaglobulin and transfusion of antistaphylococcal plasma;
- An effective remedy for furunculosis is autohemotherapy.
- Massage the site of the inflammatory process;
- Squeeze out the boil, especially during its maturation;
- Use warm compresses, poultices and other wet procedures.
Treatment of furunculosis with folk remedies

Important! Before using traditional methods of treating furunculosis, be sure to consult your doctor!
Calendula. Mix dried crushed calendula leaves and butter together in a ratio of 1:5. Apply the ointment to the boil and bandage it overnight.
Wax, spruce sulfur and onion. Melt 50 g of beeswax in an enamel pan, then add to it 1 teaspoon of spruce sulfur, 10 “butts” of onions and 250 ml of olive oil. Place the pan over low heat and simmer the product for an hour, periodically skimming off the resulting foam. Afterwards, set the product aside to cool slightly, strain and pour it into a glass jar for storage. When the product has cooled, use it as an ointment, wrapping it with a bandage.
Aloe. Tear off a leaf from an adult aloe plant and place it on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator for a couple of days, wrapped in a damp cloth. Afterwards, rinse, cut off the peel and wrap it around the boil with a bandage overnight. Aloe helps to “pull” the contents of the boil out.
Bulb. Bake a medium-sized onion in the oven until soft, cut it in half and apply to the boil. Change the compress every 4-5 hours until the boil matures.
Elder. Pour 2 tbsp. spoons of black elderberry berries 400 ml of boiling water, cover the container and leave the product to infuse for 4 hours, strain and take 50 ml 4 times a day. Efficiency increases when chamomile is added to the decoction.
Nettle. Pour 2 tbsp. spoons of dried nettle 500 ml of boiling water, cover the container and leave the product to infuse for 1 hour, strain and take 1/3 cup 3 times a day for 10 days.
Prevention of furunculosis
Prevention of furunculosis includes:
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- If the surface of the skin is injured, be sure to treat the wound and the surrounding skin;
- Timely consultation with a doctor for various health problems;
- Eating mainly foods enriched with vitamins and minerals;
- Avoiding hypothermia;
- Avoiding stress;
- Strengthening and hardening the body;
- If you have contact dermatitis, avoid contact with the pathogen.
Which doctor should I contact for furunculosis?
Video about boil
Pustular skin diseases are a large group of pathologies. Patients with a variety of manifestations come to see a dermatologist. Furunculosis in adults is quite common, especially in men. It causes a lot of trouble and, if not treated correctly, can lead to serious complications.
The pathology is treated by a dermatologist, but if symptoms are severe or complications develop, the help of a surgeon may be required.
Causes of furunculosis
Causes of furunculosis in adults on the face photo
The cause of the disease is pyogenic bacteria. Most often, furunculosis is caused by Staphylococcus aureus, less often by Staphylococcus epidermidis and mycobacteria (Mycobacterium fortuitium). But since the first two bacteria are representatives of opportunistic microflora and are present in the body of many people, special conditions are required for their active development. Provoking factors may be:
- increased sebum production and excessive sweating;
- suffered stress;
- poor nutrition and diets, even starvation;
- long-term use of corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, as well as treatment with cytostatics;
- poor skin care;
- hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- bad habits - smoking and alcohol abuse.
Furunculosis often occurs against the background of other pathologies:
- endocrine disorders (obesity, diabetes, thyroid problems);
- anemia and vitamin deficiencies;
- any pathologies accompanied by severe skin itching, which leads to the appearance of scratching - an “entry gate” for infection;
- diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, cholecystitis, intestinal dysbiosis);
- foci of chronic infection (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, periodontal disease, gingivitis, caries);
- diseases of the urinary system;
- tendency to an allergic reaction;
- chronic intoxication of the body;
- metabolic failure.
And yet, the leading provoking factors are a decrease in general and local immunity, as well as the presence of microtraumas (cracks, scratches, scratches, abrasions) - a kind of “entry gate” for infection.
Some believe that psychosomatics is the basis of all diseases. The cause of furunculosis can be negative emotions, mainly irritation and anger. Experts suggest that this condition provokes the constant production of stress hormones. This quickly depletes the adrenal glands, which in turn leads to a decrease in immunity and exacerbation of chronic processes, including the development of furunculosis.
Classification
What does furunculosis look like photo
According to the course of the pathological process, acute and chronic furunculosis are distinguished. There is also a recurrent form, in which a new one quickly forms in place of a healed abscess. The course of such furunculosis is long and difficult to treat with antibiotics. Most often, this form develops in adolescents, allergy sufferers, alcoholics and people with diabetes.
According to its etiology, the disease can be primary or secondary, that is, it develops as a concomitant pathology against the background of another disease.
The clinical picture can be classic, when the body is gradually covered with numerous abscesses, or erased, in which the formation of a necrotic core does not occur.
According to their prevalence, they distinguish between localized furunculosis - damage to a separate area, and disseminated furunculosis - ulcers appear throughout the body.
Stages of development and symptoms of furunculosis
Furuncle development stage photo
The pathological process goes through 3 stages and lasts for about 10 days.
At the first stage, a painful infiltrate occurs. Inflamed tissues become denser and swell. At the center of each is a hair follicle.
From about 3-4 days of illness, the process moves to the next stage. The formation of the rod begins. On the surface of the skin, at the site of infiltrates, ulcers of a yellowish or whitish hue, 3-4 cm in size, form. They look like cones. Above them there is only a thin membrane that can break through. Then the rod and contents are rejected. When this happens, the pain decreases sharply, swelling and redness gradually disappear. The general condition of the person improves. At the site of the abscess, a deep ulcer forms with residual pus.
After the boil has broken through and the wound has cleared, the healing stage begins. Tissue regeneration begins. A scar may remain at the site of the abscess. Its size directly depends on the depth of the abscess.
When ulcers form on the face and neck, facial expressions are disrupted. If the process is generalized, the patient’s general condition may suffer - body temperature rises, headache and myalgia appear.
Furunculosis in children
The etiology, pathogenesis and clinical picture of furunculosis in children are no different from a similar pathological process in adults. However, due to the fact that the child’s body is more delicate, the disease can be more severe and with complications.
There are also some differences in the treatment of furunculosis in children. In particular, doctors are more carefully selecting antibiotics and their dosage.
Diagnostics
There are usually no difficulties in making a diagnosis. The doctor carefully collects anamnesis and examines the skin. The main clinical signs are the presence of a fluctuation zone and the formation of a necrotic core. After this, the specialist makes a preliminary conclusion. To clarify the diagnosis and select adequate therapy, bacteriological culture may be prescribed to determine the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics. The material for the collection is the contents of the abscesses.
Additionally, the patient undergoes a clinical blood test, which shows the severity of the pathological process. The main changes in it are an increase in the number of leukocytes, an increase in ESR and a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left. And the more pronounced they are, the more severe the pathological process.
In the chronic and often recurrent form, the patient is additionally examined to assess his immunological status. For this purpose, he donates blood for an immunogram and HIV infection, as well as bacteriological blood culture for sterility.
Complications and consequences
The main and rather unpleasant consequence of furunculosis is cosmetic defects on the skin. In patients prone to the formation of keloid scars, traces of the pathological process are very pronounced.
Furunculosis photo on the face
In people with weakened immune systems, abscesses and cellulitis may form, affecting not only the skin, but also subcutaneous fat.
The infection can spread to the brain and cause basal meningitis or meningoencephalitis.
Ulcers on the neck and shoulders are accompanied by regional lymphadenitis - inflammation of nearby lymph nodes.
The most common causes of complications are squeezing or puncturing boils, as well as their improper treatment. With mechanical action, the pus may not come out, but, on the contrary, under pressure it may enter deeper tissues, lymph and blood. With their current, staphylococcus penetrates into the internal organs, where new purulent-necrotic foci are formed. In addition, acute thrombophlebitis and thrombosis may develop.
The circulation of the pathogen in the blood - sepsis - is a serious complication in which the general condition of a person is greatly affected. This is an increase in temperature to 40 0 C, muscle and headaches, confusion.
Treatment of furunculosis
A dermatologist treats furunculosis. But if an abscess or phlegmon has formed, they must be opened. In such cases, the patient is sent to a surgeon. If complications develop, the patient is hospitalized.
In severe cases, detoxification measures, massive antibiotic therapy, blood transfusions (blood transfusion according to a stepwise or classical scheme) and UFOB - ultraviolet irradiation of blood are carried out.
All rules are aimed at preserving the shell of immature abscesses.
- Limit the duration of showers and baths, and the water should be warm, but in no case hot;
- refuse scrubs, peelings, rubbing the body with a washcloth and other cosmetics and procedures that can damage the skin, and with it the integrity of the boil shell;
- It is strictly forbidden to squeeze out boils, apply warm compresses, lotions, or massage the skin around them.
Failure to comply with these rules can accelerate the maturation of boils or further aggravate the pathological process. And if the integrity of the membrane is violated, it can provoke the entry of purulent contents into the surrounding tissues, and from there into the blood and lymph.
The skin around the pustules can be wiped with antiseptic agents. This will prevent further spread of the infection.
Diet plays an important role in furunculosis. Sweets and fatty foods should be excluded from the menu. You should avoid spices and reduce your salt intake. Food should contain as much protein as possible, including animal protein, as well as plant fiber.
If patients are weakened, their diet should consist of the following foods:
- porridge with butter;
- chicken bouillon;
- steamed minced fish cutlets;
- boiled or baked meat;
- dairy products;
- berries, vegetables and fruits, both fresh and baked.
Products that can cause allergies and containing fast carbohydrates should be completely excluded from the menu.
In case of furunculosis, antibacterial therapy is mandatory. Drugs are selected individually, and the sensitivity of the microorganism is always taken into account. In most cases, antibiotics are prescribed in tablets; less often, in severe cases of the pathological process, they are administered parenterally (intramuscular or intravenous). Usually the choice is made on broad-spectrum drugs:
- from the penicillin series - Amosklav or Flemoxin;
- from cephalosporins - Ceftriaxone or Cephalexin;
- from macrolides – Clarithromycin or Sumamed;
- from lincosamides – Lincomycin.
Antibiotics are taken for about 5-7 days, sometimes the course of treatment is extended for 10 days. It directly depends on the severity of the pathological process.
Since furunculosis occurs against a background of reduced immunity, along with antibiotics, the doctor usually prescribes drugs that help strengthen it:
- vitamin and mineral complexes, which include zinc, magnesium, cobalt and selenium;
- products with vitamins A and C;
- complexes containing B vitamins (for example, brewer's yeast);
- autohemotherapy according to a special scheme (intramuscular injection of the patient’s own blood);
- staphylococcal vaccine;
- gamma globulin;
- immunomodulators and immunostimulants (Polyoxidonium, Lykopid, etc.).
In case of allergies or in cases of severe detoxification, antihistamines are prescribed.
In the presence of numerous abscesses, treating the skin with topical medications is difficult. In particular, the patient cannot always easily reach them. However, all lesions should be lubricated with a disinfectant, such as salicylic alcohol or calendula tincture. After which an antibiotic ointment is applied - gentamicin, tetracycline, Levomekol. After opening the abscesses on your own, use ichthyol ointment or Vishnevsky balm. They will clean the wound and speed up healing.
For therapeutic and preventive purposes, the patient is prescribed sessions of UHF and UV irradiation - ultraviolet irradiation, which has a detrimental effect on pathogenic microorganisms.
The help of a surgeon is needed in case of abscessing furunculosis, when the surrounding tissue is involved in the pathological process. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. The abscess is opened, removing the rod and necrotic tissue, after which a sterile bandage is applied. It is changed daily, treating the wound with antiseptics, followed by lubrication with syntomycin or erythromycin ointment. Healing can take up to a month, depending on the size of the abscess and the state of the immune system. As soon as the granulation stage begins, the ointments are replaced with Vishnevsky's liniment.
If there is a large accumulation of pus, the wound is drained, leaving it open for the outflow of exudate. This measure prevents further progression of inflammation and its transition to a chronic form.
Nowadays, lasers are increasingly being used. The procedure for removing an abscess is practically painless and very effective. And most importantly, there are practically no traces left at the site of the inflammatory process.
Folk remedies cope well with single boils. With furunculosis, of course, you can try to treat areas of skin with ulcers, but if the lesion is too extensive, this will be problematic. What can help with furunculosis:
- a paste of aloe leaves is applied to the ulcers;
- 4 times a day, make applications from a mixture of grated laundry soap and water;
- Place cakes made from a mixture of egg yolk, honey, flour and water on the boils;
- Lubricate the fires with decoctions of oak bark or horsetail.
Any traditional medicine recipes are used only as additional treatment at home. Without antibiotics and concomitant therapy for furunculosis, they will be ineffective.
Prevention
To avoid the appearance of furunculosis, you should not only strengthen your immune system, but also adhere to the banal rules of prevention, which involve eliminating all provoking factors:
- maintain personal hygiene and keep your skin clean;
- treat any microtraumas and damage to the skin with antiseptics;
- do not squeeze pimples;
- adhere to a balanced diet and do not overindulge in sweets;
- engage in sports or vigorous physical activity;
- wear comfortable clothes that will not chafe your skin;
- Avoid overheating and hypothermia.
In addition, in case of chronic pathologies, especially diabetes mellitus, one should keep the disease under control and try to prevent possible relapses of the pathology.
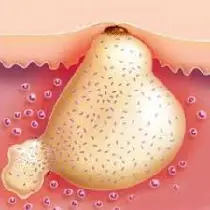
Furunculosis is a dermatological disease accompanied by the formation of ulcers on the skin.
The disease affects the deep layers of the skin and is caused mainly by staphylococcal infection. The fact that the focus of the pathological process is located quite deep gives grounds to say that after suffering from furunculosis, scars may appear at the site of localization of pustular formations.
Furunculosis can cause multiple skin inflammations. It is prone to frequent relapses and can last for several years. The disease is not only unpleasant - it is very dangerous, therefore its causes, main features of manifestation and methods of treatment should be known to everyone.
Reasons for the development of furunculosis
The causative agent of furunculosis and the only reason for its development is the presence of strains of Staphylococcus aureus on human skin. In healthy people, these microorganisms are also present, but they constitute only part of the opportunistic microflora. This means that under the influence of certain factors, staphylococci are capable of launching a massive attack, causing the development of various diseases. One of these is furunculosis.
In order to give rise to the disease, it is necessary to create favorable conditions for staphylococcus. These are often mechanical damage to the skin: abrasions, scratches, cracks, cuts, etc. But we cannot exclude the influence of other factors that contribute to the development of furunculosis:
- poisoning;
- abrasions on the surface of the epidermis;
- hypothermia;
- chronic pathologies;
- neglect of hygiene rules;
- obesity;
- diabetes mellitus;
- severe intoxication of the body;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- use of certain groups of medications.
Frequent reasons for the development of furunculosis are severe stress, psycho-emotional disorders, weak immunity, unable to resist the attack of pathogenic microorganisms.
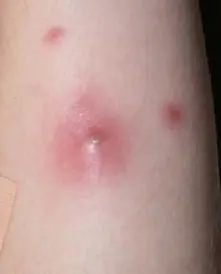
Stages of development and forms of manifestation
The development of furunculosis occurs in 3 stages:
- The first stage is characterized by the formation of an infiltrate. The skin around the source of inflammation turns red, thickens and becomes swollen. When touched, it is painful. A hair follicle is visible in the center of the neoplasm.
- 3-4 days after the formation of the infiltrate, the necrosis stage begins. A shaft begins to form around the hair, inside which there is pus and dead tissue. A round abscess of white or yellowish color appears on the surface of the skin. On top of it there is a thin membrane that is prone to spontaneous opening. As a result, a boil occurs. At the same time, there is a decrease in pain and pressure in the part of the body affected by the boil. Hyperemia gradually disappears, swelling decreases significantly. In this case, they talk about a “boil breakthrough.”
- Healing phase. At this stage, tissue regeneration occurs in the area of the damaged area of the body. If the boil was of impressive size, it is quite possible that after opening it the person will be left with scars or scars.
On average, the disease goes through all 3 phases within 10 days.
Most often, boils can be located in the area:
- face (nose, cheeks, forehead, behind-the-ear area);
- neck (back and sides);
- forearms;
- elbows;
- hips;
- buttocks;
- less often - knees and shins.
The face is the most common location for ulcers. Boils localized above the upper lip, in the area of the nose and ear canal are quite painful.
Clinical picture
In the area where the infection has occurred, a small abscess appears surrounding the hair follicle. After a few days, the pathological process completely engulfs the entire follicle. In appearance, the boil has a cone-shaped shape, inside of which there is purulent contents. The neoplasm reaches 3-4 cm in diameter, but if left untreated it can increase.
An inflamed (edematous and hyperemic) area of skin appears around the abscess. When you touch it, a sensation of pain arises, the source of which, as felt, is located inside the pustular capsule. The boil breaks out 7-10 days after its formation, accompanied by the leakage of pus and the release of the rod. The skin on the damaged surface gradually scars.
If the location of the boil is the face or neck, the above symptoms are accompanied by increased body temperature and signs of intoxication of the body. Muscle pain and a feeling of chills may occur. In severe cases of furunculosis, facial expressions are impaired, and the patient suffers from severe headaches.
Furunculosis on the face - photo
What furunculosis looks like on the face at the initial and late stages of development can be seen in the photos below:
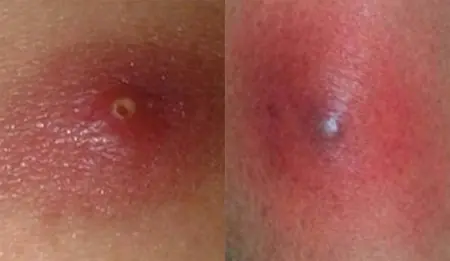
Diagnostics
Furunculosis is not particularly difficult to diagnose. To begin with, a thorough history taking and visual examination of the areas of skin affected by ulcers are carried out. Based on the data obtained, the doctor makes an initial conclusion about the nature of the disease.
If doubts arise about the correctness of the diagnosis, the patient may be prescribed an additional procedure - bacterial culture to determine the causative agent of the pathology. During the procedure, a small amount of the contents of the pustules is collected for further laboratory testing.
A blood test and immunological tests are required. If these measures do not provide a complete picture of the disease, a detailed instrumental examination of the patient is carried out. But doctors rarely resort to such diagnostic methods.
Complications
The main complication of furunculosis is the occurrence of cosmetic defects caused by scarring. The formation of abscesses is especially dangerous in people with general exhaustion of the body. In such patients, the disease is often complicated by the formation of an abscess (abscess) or phlegmon (purulent melting) of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
The formation of boils in the upper lip area is of great danger. From here, the infection can spread to the brain through the lymph and venous bloodstream. This can also lead to the development of sepsis.
Infection of the veins causes thrombophlebitis. From the blood vessels, staphylococcus penetrates the sinuses of the dura mater, leading to a serious illness - basal meningitis. It is characterized by the formation of edema on the face. On palpation, thickening of the veins is noted; the patient may complain of their soreness.
The patient's temperature may rise to 40 °C or higher, and muscle stiffness may occur. The patient complains of headaches and blurred vision, and may experience confusion.
If ulcers have formed on the neck or shoulder, lymphadenitis may develop - purulent inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes. When Staphylococcus aureus penetrates the blood, ulcers can appear on internal organs - liver, kidneys, etc.
Complications of furunculosis can occur against the background of:
- attempts to squeeze or puncture the boil;
- injuries received while shaving;
- improper treatment using only local medications (ointments, gels, compresses).
Ulcers localized on the nose or in the area of the nasolabial triangle lead to various complications of furunculosis.
How to treat furunculosis?
To undergo an examination with further development of a treatment regimen, you must consult a dermatologist. If the abscess needs to be opened, the patient is given a referral to a surgeon.
During treatment, it is necessary to limit hygiene procedures and manipulations that could damage the membrane of an immature abscess. You can take warm baths (but not hot ones, as they can speed up the pathological process), or lightly rub the affected areas of the skin with antibacterial agents. In this case, it is necessary to carefully treat the epidermis around the abscess to prevent the spread of infection.
- squeezing out the abscess;
- the use of wet warming compresses and lotions;
- massaging the skin in the area of purulent lesion.
Such measures will lead to aggravation of the situation and damage to other tissues.
Diet
With furunculosis, you need a diet enriched with proteins, including those of animal origin. Plant fiber is also of great importance. It is better to exclude sweets and fats from the menu.
For exhausted patients, a different menu is being developed, which necessarily includes:
- porridge with added butter;
- chicken broths;
- steamed fish cakes;
- baked fruits and vegetables, meat;
- fermented milk products.
You need to eat as many berries, vegetables and fruits as possible. At the same time, you should reduce the amount of allergenic foods, salt and spices consumed.
Local therapy
If there is only one boil, then without the risk of relapse it can be treated only with local drugs. Therapy is carried out at home, following a few simple rules.
- Trim the hair around the boil, trying not to touch it, but under no circumstances shave the abscess!
- Treat the surface of the new growth with potassium permanganate, then with ichthyol. The latter remedy is used as a compress, which is wrapped on top with a bandage or gauze. Ichthyol is used morning and evening. Before reapplying the ointment, the remnants of the previous product must be removed using a cotton swab dipped in warm water. After this, the infiltrate is treated with an alcohol solution of salicylic or boric acid.
- If an abscess has just begun to form, then to prevent its further development, you can use iodine or a solution of brilliant green.
- To prevent further formation of a purulent core, the boil can be treated with salicylic acid.
- After opening the abscess, treat its location with a hypertonic solution of furatsilin. It is also useful to wash the cavity of the resulting wound with the antiseptic drug Chlorhexidine. Manipulations are carried out 2 times a day.
- After complete cleansing of the ulcer from pus, applications or dressings with Vishnevsky ointment, Levomekol, Sintomycin liniment, Erythromycin, etc. are used. Dressings should be done once every 2 days, while the use of circular dressings is not recommended. The edges of the medicated napkin are carefully attached to healthy skin using adhesive tape.
When there are boils on the face, the patient needs to remain in bed and try to talk as little as possible so as not to strain the muscles. Sometimes it may be necessary to hospitalize the patient in a hospital.
Antibiotics for furunculosis
Treatment of multiple boils is carried out using antibiotics. The drugs are selected by the doctor individually for each patient, taking into account the data obtained from the antibiogram on the sensitivity of staphylococcus to specific pharmaceuticals. Often they resort to the use of systemic (tablet) medications, less often - injections (intramuscular or intravenous).
Basically, broad-spectrum drugs are used:
- Flemoxin or Amoxiclav, belonging to the penicillin series.
- Cephalexin or Ceftriaxone - from cephalosporins.
- Sumamed or Clarithromycin are from the group of macrolides.
- Lincomycin - from lincosamides, etc.
The course of therapy usually lasts 10 days, but can be shortened or prolonged (rarely) exclusively by the attending physician.
Immunotherapy and vitamin use
The maximum effect of antibiotic therapy can only be achieved with parallel immunotherapy and the use of vitamins. To stimulate the immune system, it is advisable to use:
- multivitamin complexes containing minerals (zinc, selenium);
- preparations based on vitamins C and A;
- vitamin complexes based on B vitamins (especially in case of depletion of the body and constant physical or emotional stress);
- autohemotherapy (blood transfusion);
- staphylococcal vaccine.
To improve the functioning of the immune system, it is important to properly organize your diet, give the body proper rest and avoid gastrointestinal pathologies. If necessary, your doctor can prescribe medications that normalize and support intestinal microflora. This is especially important when taking antibiotics.
Folk remedies
For a single boil, treatment can also be carried out using folk remedies. Many of them can be used in parallel with medications prescribed by a doctor. Below are the most effective alternative medicine recipes to combat furunculosis.
- Mix beeswax in a proportion of 100 g with spruce sulfur, lower parts of onions and vegetable oil. The last ingredient must first be boiled, and only then add wax and sulfur. After half an hour, put the onion into the boiling mixture, then boil it for another hour, regularly skimming off the foam that forms on the surface of the mixture with a spoon. The cooled medicine is poured into jars, and when it thickens, it is applied to the affected areas of the skin several times a day.
- Cut an aloe leaf and apply the pulp to the boils. You can use a paste made from this plant.
- Wipe with laundry soap and mix with a small amount of water. Soak sterile gauze or bandage in the mixture and apply to sore areas. Applications need to be changed 4 times a day.
- Mix the egg yolk with 15 ml of honey and a small amount of flour. Add a little water and make a cake, which you then apply to the boils.
- Lubricate the affected areas with decoctions of horsetail or oak bark.
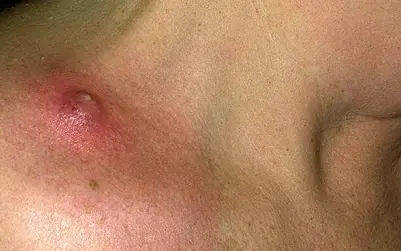
Surgical assistance
If the boil enlarges and damages healthy tissue, it is surgically opened. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. During the manipulation, the abscess is opened, its contents are removed along with the shaft and hair follicle.
After the procedure, a sterile bandage is applied to the treated area. It must be changed daily, lubricating the area of skin affected by the intervention with antiseptic solutions or ointments.
The wound healing period lasts from 1 to 4 weeks. It all depends on the size of the abscess.
Sometimes, when opening an abscess, it is necessary to insert a drainage tube, with the help of which the pus will be drained. This procedure helps prevent re-suppuration.
Recently, treatment of furunculosis has been carried out using a laser. This therapy is painless and highly effective, and after it there are practically no scars left at the treatment site.
Prevention
You can prevent the development of furunculosis by following these simple rules:
- keep your body clean and use only individual towels and hygiene products;
- treat damaged skin areas with antiseptic agents;
- Avoid squeezing pimples and other formations on the skin;
- carefully monitor your diet, consume flour, sweets, and fried foods to a minimum;
- provide adequate physical activity to stimulate the body's defenses.
A strong immune system can cope with infectious processes and prevent their progression. But if boils do appear, you must immediately consult a doctor for diagnosis.



