Hemangiomas, better known as red moles, are benign growths that originate from blood vessels.
Red moles appear mainly in children of both sexes, less often in adults. It is impossible to prevent or predict their occurrence.
There is still debate as to which pathology a hemangioma is classified as - a vascular tumor or a congenital malformation. Recent data confirming the occurrence of tumors due to proliferation of vascular endothelium allow the neoplasms to be classified as vascular tumors.
What is a red mole?
Why are moles and dots red? Because it is actually vascular tissue filled with blood. If ordinary moles are skin growths, then red moles are several small (or single) overgrown blood vessels. In a pronounced process, the accumulation of blood vessels merges into a blue or burgundy spot.
Prevalence and localization
In most cases, vascular tumors are detected immediately after birth (87%), and 70% of the total mass are girls, who, accordingly, fall into the highest risk group. This pathology accounts for about 48% of all soft tissue and skin tumors in childhood. 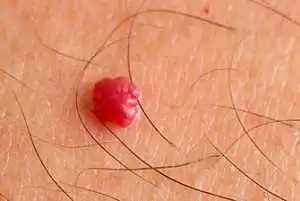
On the body, a red mole can be localized in any part; about 80% of tumors occur in the upper part of the body. Very rarely found in internal organs - liver, brain, lungs, bones.
- about 95% of all diagnosed vascular tumors are simple formations
- about 3% are cavernous
- and another 2% are mixed and combined variants of the disease.
Causes
No doctor can still give an exact answer as to why these formations appear. Why there are many red moles in the facial area is also difficult to explain. This is probably due to the abundant vascular network of facial tissues.
In children
It is generally accepted that a congenital tumor develops as a result of an intrauterine disorder in the formation of vascular tissue, which occurs against the background of incompetence and the processes of development and growth.
How does this happen? During the formation of organs and systems, vascular tissue penetrates all parts of the body without exception along a certain chain of pericytic cells. These cells, being a kind of conductors of information, react to the slightest lack of oxygen: if the fetal tissues experience hypoxia, the synthesis of special proteins that attract pericyte cells is immediately launched. These cells begin to pave new blood supply routes, thus eliminating hypoxia. In some cases, even after the cessation of hypoxia, the synthesis of specific proteins does not stop; the vascular system continues to develop, turning into voluminous tumor-like formations.
The second name for red moles is vascular hyperplasia. This means that the tumor arises as a result of disruption of the growth processes of vascular tissue, which lead to an increase in its quantity. How and in what way this process occurs is difficult to answer with 100% accuracy, since this requires monitoring the characteristics of intrauterine tissue development. The data presented are based on autopsy results of aborted and stillborn fetuses.
In adults
- Acquired pathology is associated with hormonal disorders, explaining the appearance of hemangiomas in adults (pregnancy, menopause, diseases of the endocrine system, as well as hormonal therapy or oral contraception).
- There are suggestions about the negative impact of ultraviolet and radiation exposure, viruses and chemicals that provoke tumor growth in adults.
- Microtraumas and skin cracks with permanent damage to the capillary network lead to such neoplasms.
- Long-term and uncompensated hypovitaminosis C, leading to thinning and fragility of capillaries, is also relevant among the causes.
- Red moles accompany the course of other diseases (for example, diseases of the liver, pancreas, cancer of internal organs). It is not uncommon for a cluster of red moles in a certain area of the body to indicate a predisposition to cancer in this area, a nearby organ.
Red moles in newborns
This is a common occurrence in babies, and if such a mole is noticeable in a newborn, then most often by the age of 3-5 the red mole may disappear. Since this is a benign tumor, it is not dangerous if:
- Does not bother the baby (skin itching, irritation, pain)
- Does not increase in size (in a month, for example, it doubled)
- Located in a non-hazardous place (if it is located under the eye, on the nose, genitals, on the face, then its removal is indicated)
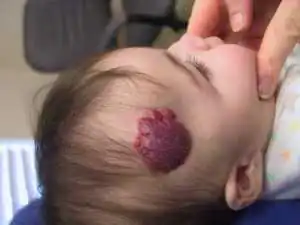
Red moles are characterized by rapid peripheral growth, especially intense in the first months of a child’s life. Therefore, 10-12% of hemangiomas in children are removed for medical reasons. During the growth process, the tumor destroys tissue and leads to a cosmetic and sometimes functional defect, especially when located near or on vital organs (eyes, ears, brain). Impaired function of organs and tissues occurs due to compression of them by the tumor.
Features in adults
Primary hemangiomas do not occur in adults, i.e. They arise from existing, undiagnosed tumors. As a rule, visible formations are treated even before school age, so in adulthood either untreated superficial moles or tumors on internal organs are discovered.
Of particular danger is a vascular tumor on the spine, which is localized in the vertebral body and weakens its structure, sometimes leading to fractures.
Classification
According to morphology
Capillary. The histological structure of the neoplasm is compact layers or concentric groups of capillary vessels, closely adjacent one to one. The wall of each vessel consists of a basement membrane and 1 or several layers of epithelial-like cells. The lumens of fused capillaries are filled with formed elements of blood. In some cases, groups of vessels form lobules separated by stroma.
Cavernous. It consists of multiple cavities of various shapes and sizes, which are lined with 1 layer of endothelial cells, similar in structure to the endothelium of blood vessels. In some cases, rupture of the septa occurs with the formation of papillae in the lumen of the caverns.
According to location, vascular hyperplasias are divided into:
- Simple, with a subcutaneous location throughout the body;
- Cavernous, localized under the skin;
- Combined, having a supra- and subcutaneous part;
- Mixed, including other tumors, for example, lymphangioma, originating from lymphoid tissue.
By origin:
- Congenital, appearing immediately after birth or in the first months of life;
- Acquired, occurring in adults. Acquired red moles can only be of a subcutaneous location, i.e. simple. Complex forms of the disease, discovered due to complications or by chance, are congenital and not diagnosed in childhood.
With the flow:
Simple, not presenting a risk of complications or dysfunction of organs;
Difficult:
- near large vessels or vascular nodes;
- on or near vital organs and structures (eye, brain, ear);
- in places that are difficult to access (vertebrae).
Features of red moles
Vascular tumors have a number of characteristic properties that differ from other neoplasms:
- Rapid tumor growth during the first three months after birth.
- Accelerated (2-3 times compared to full-term) growth of education in premature babies.
- The likelihood of spontaneous regression of simple tumors (mostly small) during the first years of life. This explains the cessation of hemangioma growth when exposed to a number of factors, such as heat, cold, and certain chemicals.
- The impossibility of spontaneous resolution of cavernous, combined and mixed variants of pathology.
- Unpredictability of further development even after growth and involution have stopped.
Clinical picture
Simple angioma
This is a spot of varying sizes, predominantly red, rising above the skin. With simultaneous finger pressure on the edge of the tumor and healthy tissue, the angioma becomes pale and shrinks, and after the compression stops, it returns to its previous shape and color. In babies up to 3-4 months, peripheral growth of the vascular tumor is clearly visible. This can be verified by making an initial paper stencil of the tumor and applying it to the hemangioma after 15-20 days.
Cavernous angioma
This is a formation in the subcutaneous tissue with unchanged skin above it. It can be diffuse without clear boundaries or encapsulated. A bluish-colored formation is detected under the skin; in some cases, feeding vessels are visually visible. When pressing on the skin above the tumor, the formation decreases, and when the compression stops, it returns to its previous size.
The skin over the tumor may be warmer than the rest of the skin. No pulsation is detected above the formation. In some cases, upon palpation, the lobulation of the formation is noticeable. Cavernous hemangiomas located on the head, neck and near the ears are characterized by rapid growth with active germination into surrounding structures.
Combined angioma
This is a formation with a cutaneous and subcutaneous part; the subcutaneous part, as a rule, is larger.
Mixed tumors
These are various variations of the combination of a vascular tumor with lipoma, lymphangioma, keratoma and other neoplasms.
Spontaneous resolution
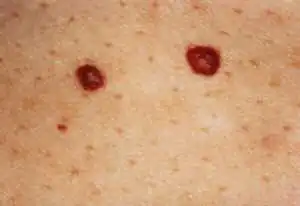
True regression of simple or superficial hemangiomas is observed in 10-15% of cases, especially when tumors are located in closed areas of the body. The brightness of the formation decreases, whitish areas appear, and peripheral growth completely stops. After 6-8 months. the hemangioma transforms into a smooth whitish-pink spot that does not rise above the surface of the skin. The skin over the spot undergoes atrophy, leaving only a small depigmented area by the age of 3-4 years.
Complications
Red dots are dangerous due to rapid growth and subsequent compression of nearby structures with disruption of their function, which is especially important when hemangiomas are localized in the brain, in the liver, or near the eye.
- Ulceration and inflammation during growth. Some types of red moles undergo reverse development after such complications.
- Bleeding due to injury, especially dangerous with extensive cavernous and combined hemangiomas, as well as tumors located on internal organs, since such bleeding is very difficult to stop.
- Infection (bleeding, ulcerated moles), i.e. the addition of a bacterial skin infection.
Diagnostics
With superficial hemangioma, the diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical and histological data. For extensive and deep processes, angiography is performed to determine the connection of the tumor with the vascular network, as well as radiography, which provides accurate data on the size and depth of the vascular tumor.
Treatment of red moles
Is it possible not to treat red moles? If the tumor does not interfere with organ function, is not dangerous for bleeding and does not grow, these marks of intrauterine life can be left without treatment, especially since these tumors do not carry the risk of malignancy. Moreover, it is not recommended to remove moles if they do not bother you, do not increase in size, or are located on closed parts of the body (they are not a cosmetic defect).
For extensive and deep processes, the doctor selects treatment - surgical or conservative; methods can be combined to increase efficiency. Therapy depends on the type of tumor, its location and size, growth rate, the presence of complications, and the age of the child.
Simple hemangiomas
Low-temperature destruction or cryodestruction is considered an effective method for treating small red moles. It can be performed in several ways: direct application of crystalline carbon dioxide to the surface of the tumor for 15-20 s or instrumental cryodestruction using liquid nitrogen. The effectiveness of treatment is up to 96%.
For simple angiomas of large size, hormonal treatment with prednisolone is advisable at the rate of 4-6 mg per 1 kg of weight, taking 1/3 of the dose at 6 a.m. and the remaining portion at 9 a.m. The duration of treatment is 28 days with the drug taken every other day. Gradual withdrawal of the drug is not required. During treatment, blood sugar and potassium are monitored.
Laser removal allows targeted action strictly on the tumor with minimal cosmetic defect. Modern laser systems with various types of pulses can coagulate both superficial and deep subcutaneous tumors without destruction of healthy tissue and complications.
Cavernous
When the process is located in a cosmetically unfavorable part of the face (cheek, nose, forehead, bridge of the nose), sclerosing therapy is used: special substances are introduced into the angioma, leading to aseptic necrosis and subsequent scarring of the tumor under the skin without scar formation and tissue deformation. Hydrocortisone, quinine-urethane, sodium chloride solution 10%, ethyl alcohol 70% are used as sclerosing agents. For complete sclerosis of the tumor, 10-15 injections are performed with breaks between each injection of 14-30 days, i.e. the process is quite lengthy.
When cavernous hemangioma is located on the thigh, shoulder, back and other closed parts of the body, surgical removal of the tumor is performed.
Combined
When the tumor is localized on closed parts of the body, radical surgical excision is advisable. Removing red moles rarely leads to any complications; the tumor is removed entirely with minimal cosmetic defect.
When localized on open parts of the body and face, microwave cryodestruction is recommended: irradiation of the hemangioma with an ultra-high-frequency electromagnetic field, followed by cryodestruction. This combination makes it possible to significantly enhance the destructive effect of freezing, while maintaining the ability of epithelial cells to regenerate.
Hormonal, sclerosing and radiation therapy with Buki rays, which have a middle range between X-ray and ultraviolet irradiation, is also used.
Deep and extensive hemangiomas with dangerous localization
Such tumors are located on the neck, near the ears, on the head and are characterized by constant peripheral growth. The tendency to bleeding and ulceration of these types of angiomas does not allow the use of the treatment methods described above.
In case of such a pathology, angiography is mandatory to determine the nature of the blood supply to the hemangioma and its anatomical relationship with nearby tissues and structures. One of the effective treatment methods is tumor embolization with hydrogel, which reduces the blood supply to the tumor and its size.
Then cryodestruction is carried out without removing the tumor itself: after the necrobiotic process, the tumor partially resolves, leaving behind areas of atrophic skin, i.e. a cosmetic defect that can be eliminated by skin grafting if the patient wishes.
In ancient times, people believed that birthmarks on a baby were signs of fate and predicted his future. Now scientists are considering more natural reasons for the appearance of such formations. Let's consider what factors influence the appearance of spots, and in what cases do they require removal? Why might a birthmark appear in a newborn?
Types of birthmarks
A child may have a wide variety of birthmarks on his body - smooth or covered with fluff, reddish or brown, convex or flat. The main types of birthmarks in newborns are nevi and angiomas.
What shade can nevi be?
Nevi are among the most common types of skin marks. They usually come in a variety of brownish shades, ranging from dark brown to pale. The basis of nevi are melantocytes. These epidermal cells contain melanin, a pigment that affects skin tone. It is necessary to protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation. Sometimes these cells are localized in one place, which leads to the appearance of a mole. Dark birthmarks indicate an abundance of melanin, while light ones indicate a lack of it.
A Mongolian spot in a newborn should also not be a cause for concern for parents. It is also a place of concentration of melanin and is a spot, or several spots of different sizes from 1 to 10 cm in diameter, blue, green or even black. The most common location is the baby’s lower back, mainly the tailbone or butt. Mongolian spots are safe, they do not cause any discomfort to the child and go away on their own before adolescence. This type of nevus is named so because of their frequent detection in Mongolian children (90%), Mongolian spots are also often found in Asians, representatives of the Mongoloid and Negroid races.
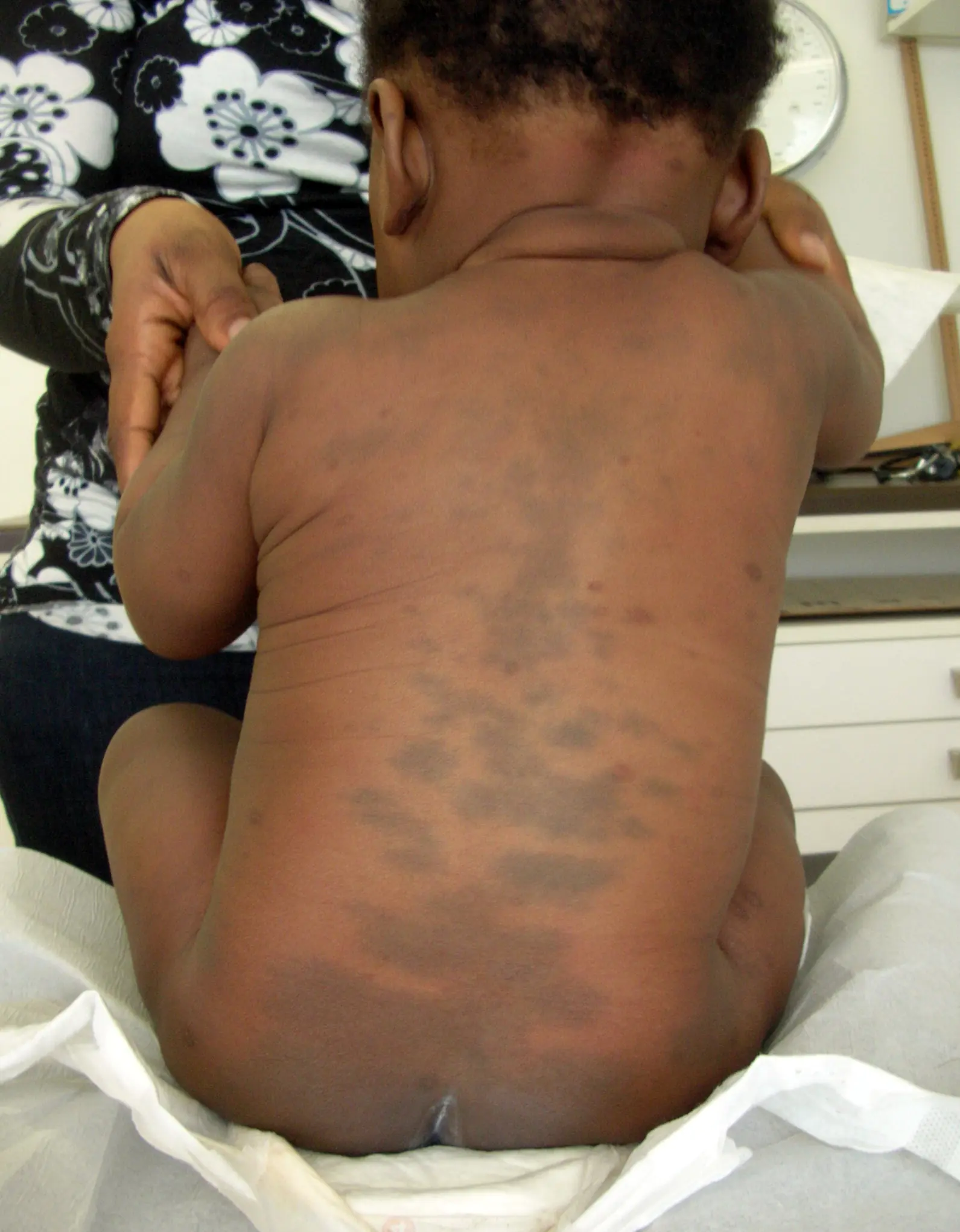
There are also white formations. These include anemic nevi that arise due to underdeveloped blood vessels.
They need to be distinguished from millet grasses - milia. The latter look like convex dots filled with whitish content. They are a type of skin rash. Anemic nevi are a congenital phenomenon, and they are easy to identify: you need to rub the spot. The surrounding skin will turn red, but the formation will remain white.
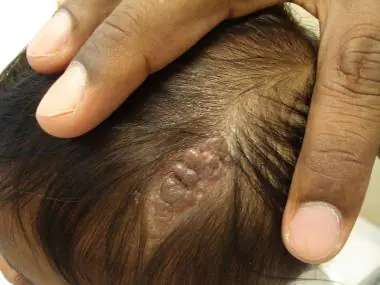
Light brown Jadassohn nevi indicate a congenital defect of the sebaceous glands. They are usually found on the baby's head, under the hairs. This occurs in 3 out of 1000 babies. It is recommended to remove it before adolescence, since in 10-15% of cases, they can subsequently develop into a cancerous tumor.
What if it’s a matter of blood vessels?
Another type of birthmarks is angiomas. They are of vascular nature. Congenital formations of small vessels on the skin are called hemangiomas. If such accumulations form in the lymphatic system, then they are classified as lymphangiomas. Even congenital, they appear externally only by the age of three.
In a newborn, only vascular hemangiomas can be detected. They are distinguished by a whole range of shades of red. Such formations are divided into several subtypes:
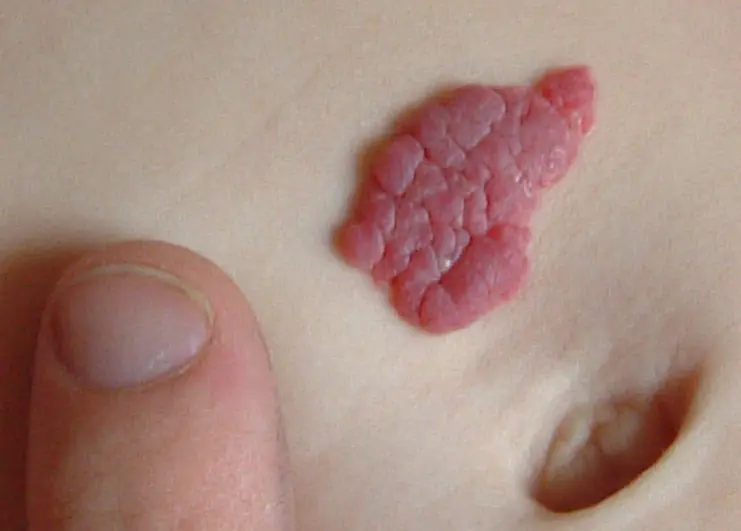
Strawberry (strawberry) hemangioma
These formations are convex, similar to red “berries”. They appear immediately after birth, usually on the face. The sizes can be different - from a millimeter to several in width. Strawberry hemangioma can increase in size, which is why it is dangerous, as it can affect the healthy tissues of the child.
Often this type of hemangioma stops growing, gradually brightens, shrinks and disappears completely by the age of 10.
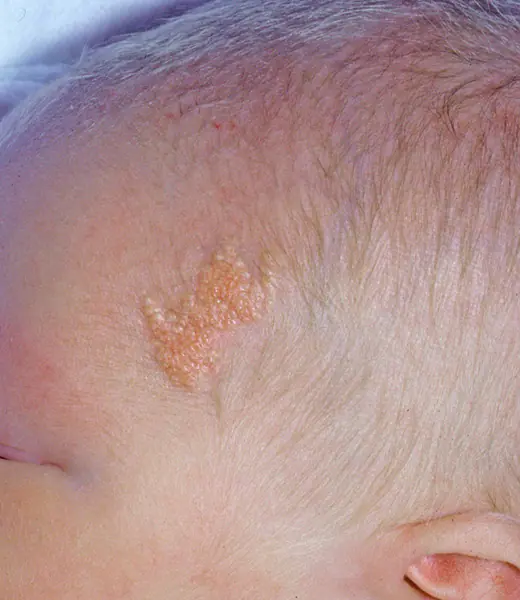
Stellate (spider) angioma
It looks like a star with a bright base and “rays” extending from it. Most often it occurs on the child's neck. Disappears on its own in the first years of life.
Cavernous hemangioma
Loose, purple hemangioma, deeply embedded in the skin. It feels warmer to the touch than the surrounding epidermis. If you press, the baby will cry due to unpleasant sensations. This type of neoplasm requires treatment.
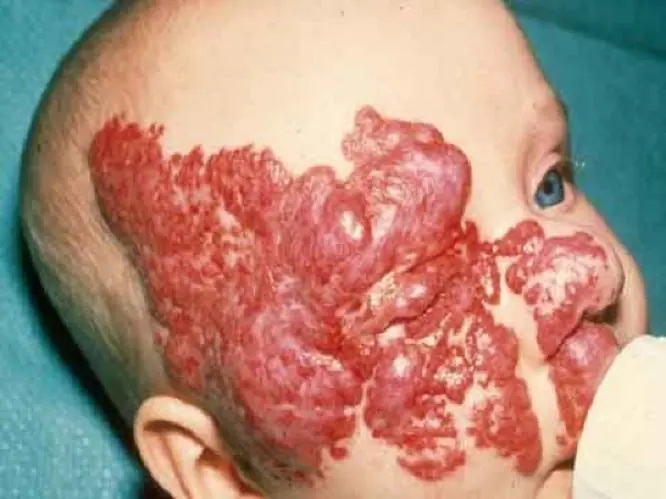
Flaming (fiery) nevus
Looks like a red or purple stain from spilled wine. It can appear anywhere on the baby’s body. Such formations do not go away on their own. If they are not removed, they will remain for life. If the “wine stain” is in a visible place or continues to grow, it is better to take the trouble to correct the defect.
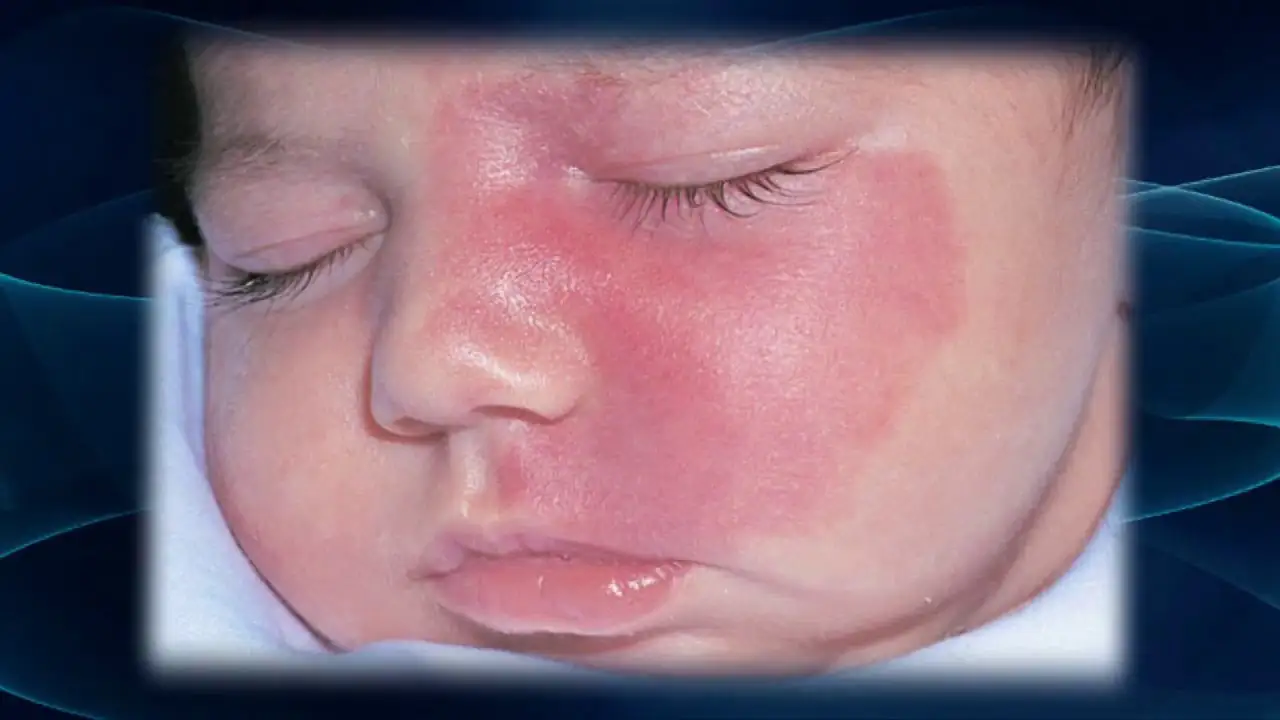
“Stork marks” (capillary hemangioma)
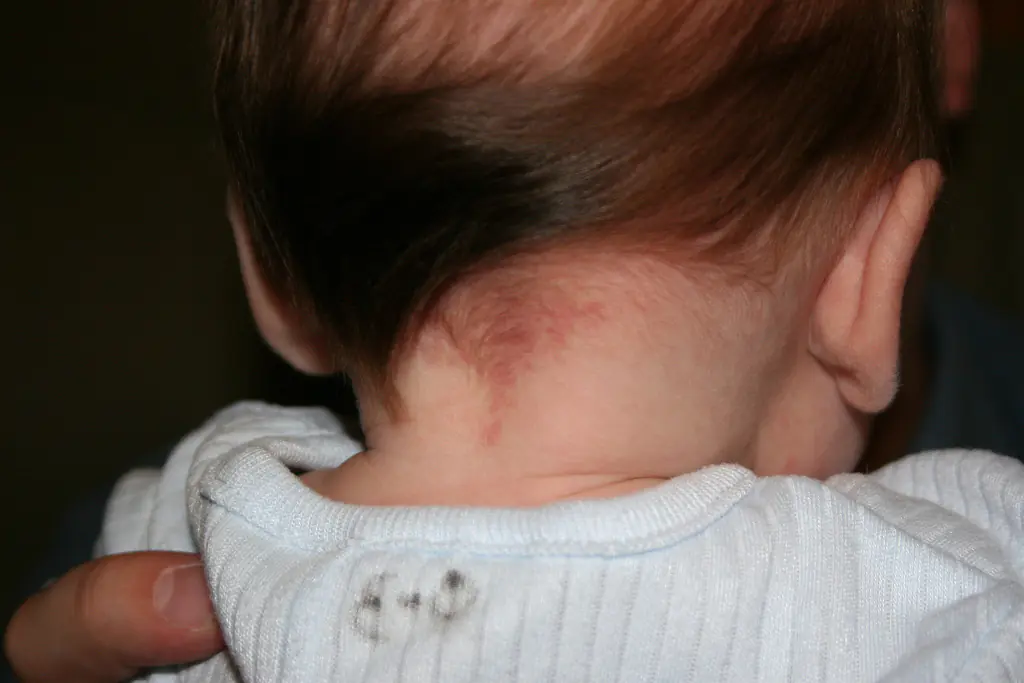
Such marks are also called “stork bites.” And if there is a mark on the baby’s forehead - “an angel’s kiss.” The formation is usually pink or red, but can also be orange, and resembles the mark of a bird's beak, which is how it gets its name. The formation is flat and does not rise above the skin. It is often found on the back of the baby’s head, in the neck area. When stressed, for example, when a baby cries, it acquires a brighter color. By the age of two, “stork marks” in most cases go away on their own.
In addition to the above, there are other types of birthmarks. But they are much less common.
If you notice that a child’s hemangioma is increasing in size, immediately contact a specialist (surgeon). He will be able to assess the danger of the condition and prescribe appropriate treatment or removal of the tumor.
Causes of skin formations

The reasons for a birthmark in a newborn, of course, are not that his mother loved to pet dogs and cats, as the ancients believed. However, scientists cannot say exactly why such marks may appear. Only risk factors for their occurrence have been identified.
Why do birthmarks appear in newborns? This is affected by:
- Hereditary factor;
- Hormonal surges in the expectant mother;
- Exposure to toxic substances on the body of a pregnant woman;
- Bad ecology;
- Climate change;
- Infections of the genitourinary system.
But it happens that a birthmark appears in a newborn even without exposure to risk factors.
Birthmark on a baby: what to do?
Is your baby's birthmark small, smooth, does not grow and does not cause concern to the baby? Everything is fine, nothing to worry about. But you need to take the new growth seriously. Observe the nevus and notice whether the mark grows or hurts. If changes occur, you should visit a pediatrician or pediatric dermatologist.
If a newborn has a birthmark on his body, several rules should be followed:
- Keep this area away from direct sunlight.
- Make sure that the baby does not scratch the area with the mark.
- Try to ensure that the nevus is never exposed to caustic substances, such as household chemicals.
In rare cases, marks on the skin can be fatal. Where can it appear? Under the influence of negative factors, a simple mole degenerates into a malignant formation - melanoma. Therefore, if the spot increases in size, you should urgently contact a specialist. If the formation is removed in time, there will be no health consequences.
Should moles be removed from babies?
It is recommended to eliminate formations in infants only if there is a danger to life. In babies, the immune system is not yet very developed, and any intervention can lead to serious consequences.
In what cases do doctors recommend surgery at an early age:
- The birthmark is very large;
- The formation rapidly increases in size;
- There are more than five marks, and they are concentrated in one place;
- The mole is located in a traumatic place (under the armpits, on the belt, on the skin of the eyelid, in the anus);
- Nevus interferes with the normal functioning of organs (on the hand, in the nose, in the eyes).
Particular importance should be given to those cases if a mole transforms - changes color or shape, grows, hairs fall out of it, it begins to bleed or itch.
How to get rid of formations?

The doctor may recommend one of the methods for removing nevi, depending on the size and condition of the formation, as well as the health of the baby:
Use of pharmaceuticals
Special medications are injected into the mole tissue to promote the death of overgrown cells. No anesthesia is required, but is not suitable in case of allergy to the active substances of the drug.
Using a laser
Excision of pathological tissues with a laser beam. It is quick and painless, but the procedure is not always possible for hard-to-reach areas.
Cryotherapy
Exposure of the mole to low temperatures. Suitable for eliminating small nevi.
Surgery
Removal of the formation using surgical instruments. It is used in cases where other methods cannot be used.
Carrying out the intervention under the supervision of a doctor, with preliminary examination of the birthmark tissue, reduces the likelihood of complications to zero. After removal of large formations, scars may remain. If they are located in a visible place, when the baby grows up, you can remove the scar using cosmetic procedures.
If you believe in fate, try telling your baby's destiny using moles. But pay attention only to happy signs:
- A mark on the baby’s cheek means love;
- A spot under the hair means high intelligence;
- Moles on the hands - to talents and good luck;
- Nevi on the back - to a life without worries;
- Mark on the leg - to hard work, calmness, confidence;
- A “sign” on the butt means success with the opposite sex.
As you can see, a mole is not a reason to panic at all. With the right approach, it will not be the cause of illness, but a happy sign that emphasizes the individuality of your son or daughter.
Remember that only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis; do not self-medicate without consultation and diagnosis by a qualified doctor.
By nature, birthmarks in children are not capable of harming a small organism. The appearance of pigment formation occurs after birth or after 10–15 weeks. Moles in newborns do not indicate the presence of a disease or pathology of the body. Nevus in infants is most often located on the back of the head, on the forehead, on the stomach.
Causes of birthmarks in newborns
The reasons for the appearance of birthmarks in a newborn should be considered:
- Hereditary factor. If a man or woman has a birthmark on the face or foot, there is a high probability that the child will be born with a similar location of the pigmented formation.
- Stress during childbearing. With nervous excitement, a drop in blood pressure occurs, as a result of which the blood vessels narrow and placental blood exchange is disrupted. Bursted blood vessels transform into a red birthmark in a newborn.
- Prolonged exposure to the sun. In babies born in the summer, the number of moles may increase or the existing formations will become darker in color.
- Changes in the hormonal background of a child are one of the reasons for the appearance of a mole in a newborn.
Medical statistics indicate that girls, premature and fair-skinned children are susceptible to the appearance of brown nevi after birth.
Types of nevi
A birthmark appears in a newborn at birth or within two months after birth. There are the following types of moles:
- Vascular formation - a large number of vessels, which are presented in the form of a convex or flat nevus. The color of the vascular spot is bright red or light pink. It is recommended to remove benign formations of this type, because after a while they increase in size and cause discomfort. The child is embarrassed about his appearance if the vascular nevus is located on the face.
- A simple mole has a smooth surface and is light brown or black in color. Appear after birth or in the first twelve months of life. The appearance of a simple nevus should not worry the parents of the baby, provided that the mole does not change shape, structure and color. If the nevus is located in a place that is subject to constant injury, doctors recommend removing it.
Vascular formations are divided into the following types:
- A flaming mole or port-wine stain appears on the baby's scalp or face. The shape of such a spot is flat, the color is red. As the child grows, the size of the nevus also increases. It is not recommended to resort to removal of the formation, as it can be treated, which is based on the effect of a laser beam or infrared radiation.
- Hemangioma. It is not immediately detected on the baby’s body. After three to four months it will begin to manifest itself. Hemangiomas appear in various parts of the body and increase sharply. Medical statistics say that upon reaching the age of ten, the hemangioma will disappear, so there is no need to remove it when detected.
- The stork's bite is located on the back of the head, eyelid, and bridge of the nose. This type of nevus is pink in color. There are situations when many spots accumulate in one place.
Among the simple formations there are:
- A red nevus appears at birth or within three years and can be located in any area. Red nevi do not need treatment or removal unless there is a rapid increase in size.
- The hanging formation is benign. Because a hanging nevus involves epithelial cells, the appearance is similar to a growth. The color varies from flesh to dark brown. There are hanging moles in the armpits and groin. The presence of growths is dangerous for a child, so it is necessary to regularly visit a dermatologist for examination and examination, during which the absence or presence of cancer cells will be determined.
- The anemic spot is small in size and forms on the back or face. Vascular underdevelopment can provoke the appearance of an anemic spot. It is necessary to remove the formation using a surgical method.
- The flat blue nevus is large in size. Divided into simple and cellular. The color of the simple varies from blue to dark blue, the diameter does not exceed one centimeter, and has a smooth surface. Cellular nevus is malignant, exceeds three centimeters in diameter, and the surface is covered with nodules. Localization – buttocks, feet, hands. Removing blue spots is dangerous to health.
- The brown spot has a flat structure and can disappear on its own after five to six years. They do not pose a danger to the child's body.
- The Mongolian spot, which is located on the buttocks and thighs, is characteristic of a child with Asian roots. It is not dangerous and disappears two years after birth.
- Red spots appear on the baby's head. After the child turns one year old, the red spot will disappear without surgery or therapy.
- Strawberry hemangioma. Occurrence is rare. It has a soft structure and bright color. If the formation appeared at birth, after two years it will disappear on its own or change color to light.
When moles are dangerous
When moles appear in a newborn, it is necessary to pay attention and regularly visit a dermatologist. The doctor will use a dermatoscope to examine the formation, determine its nature and the presence of cancer cells. When bathing or changing your baby, you should carefully examine new spots or changes in existing ones. Birthmarks in a baby are not dangerous if there are no alarming symptoms. These signs include: intense increase in size and change in color, localized on the face, clear boundaries have disappeared, blood or clear liquid is released. It is necessary to visit the office of a pediatric dermatologist if the nevus in the area that is swollen and irritated is covered with hair. A cause for concern is the appearance of a bumpy surface or compaction that begins to peel off.
After the examination, the dermatologist will determine the period during which parents need to monitor the spot. If the situation worsens, the doctor will prescribe surgery to remove the nevus to avoid degeneration into a malignant formation. It is allowed to remove the growth after two years if there is no need to get rid of the stain.
When is treatment required?
If a brown nevus appears in a newborn, there is no need to worry and conduct a comprehensive medical examination. It is necessary to monitor the size, shape, and surface of the birthmark. In the absence of intense enlargement, redness or darkening, or bleeding, it is not advisable to remove the spot. If there have been cases of melanoma along the family line, parents must observe:
- Avoid mechanical damage to the nevus.
- Regularly visit a pediatrician, who will examine the formation independently or refer you to an appointment with a pediatric dermatologist.
- Minimize the baby's exposure to direct sunlight. When visiting the beach, apply protective creams to the child’s skin and put a hat on the head.
If a newborn's birthmark rubs, rubs, or the child accidentally tears it off with his hand, the formation must be removed. Without surgical intervention, the risk of the spot transforming into a malignant tumor increases. Hanging moles, which become inflamed more often than others, must be removed. When scheduling removal, parents follow the dermatologist's instructions.
Medicine offers several safe ways to remove growths on a child’s skin:
- Laser removal. The procedure is performed under general or local anesthesia. The choice of anesthesia depends on the size of the spot.
- The cryodestruction method is indicated for older children, as the procedure is painful.
- Removal with a scalpel. A surgical method for excision of large formations, hemangiomas. The operation requires general anesthesia.
The development of melanoma in infants is a rare occurrence, but visiting a doctor should not be neglected. This helps control the development of nevus and detect malignant cells.



