Urticaria can hardly be called an independent disease; it is more of a separate symptom that signals the development of a more serious illness, therefore, if a rash and blisters appear on the skin, it is recommended to contact an immunologist-allergist for research. According to statistics, urticaria symptoms occur in 10-35% of the population. The danger is represented by chronic urticaria, which lasts for 1.5 - 2 months.
The article provides information about what urticaria is, how and why the pathology manifests itself, and what its symptoms are. You can also find out what types of urticaria exist, as well as what methods are most effective in combating the disease.
What is urticaria?
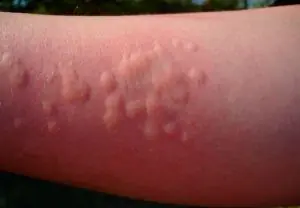
The disease received its name due to the external similarity of its symptoms to burns that appear on the skin after contact with nettles. As a rule, urticaria combines a number of ailments that are similar in clinical manifestations and have a similar nature of origin.
A rash, predominantly of an allergic nature, usually appears on the skin as a concomitant symptom with the development of various types of dermatitis and dermatoses. In addition, urticaria quite often appears against the background of bronchial asthma, allergic shock, as well as other pathologies of an autoimmune nature.
Additional Information! Most often, women aged 20 to 40 years are affected, although cases of the development of pathology in men also occur.
Etiology of the disease
The causes that contribute to the appearance of urticaria are divided into endogenous and exogenous. Based on the fact that the disease affects women twice as often as men, scientists have concluded that the main cause of the disease is hormonal imbalances inherent in the female body.
Conditions characterized by hormonal disorders:
- period of menopause and menstruation;
- state of pregnancy.
Consequences in the form of changes in the balance of hormones can occur as a result of taking oral contraceptives.
Factors contributing to the manifestation of pathology:
- past infectious disease;
- reduced immunity. The result is the manifestation of autoimmune urticaria;
- poor diet (allergic urticaria);
- influence of external stimuli.
Additional Information! Patients suffering from diabetes mellitus, diseases of the blood and gastrointestinal tract, inflammatory diseases of viral origin, as well as pathologies associated with the functioning of the endocrine system automatically fall into the risk zone.
External irritants, the impact of which can cause the development of pathology:
- water;
- Sun rays;
- low temperatures of water or air;
- vibration vibrations;
- allergens such as pollen and animal dander;
- sudden change in temperature;
- tight and uncomfortable clothing that causes discomfort when worn.
How does urticaria manifest itself in children and adults, symptoms of pathology?
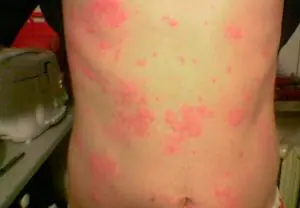
Urticaria is characterized by the appearance of a red rash on the skin, the appearance of which is accompanied by a continuous burning sensation. The area of the lesion and the number of nodules depend on the form of the disease. The severe form is characterized by the formation of multiple spots and blisters, which are constantly itchy and cause discomfort.
According to the nature of the pathology, they are distinguished:
The duration of the first type of disease, as a rule, does not exceed 4-6 weeks, which cannot be said about the second. Symptoms of chronic urticaria can haunt the patient for several months, or even years. A distinctive feature of the chronic form of the disease is its recurrent nature, that is, the rash either disappears or appears again.
In acute urticaria, the appearance of a rash is accompanied by an increase in body temperature and general malaise.
Urticaria in children often occurs if the child’s body is predisposed to allergic reactions. According to medical statistics, atopic dermatitis is a predisposing factor to the development of the disease.
Distinctive signs of urticaria rashes include:
- sudden appearance and disappearance of the rash;
- the absence of any marks reminiscent of the presence of blisters and burns on the skin;
- migratory nature of the rash. Nodules often change location, almost every 2-3 hours;
- scratching the affected areas leads to the fusion of rash elements and the formation of continuous blisters;
- the contours of the blisters are clearly marked.
What complications can develop with urticaria?
In advanced cases, urticaria in adults can lead to the development of the following complications:
- the appearance of Quincke's edema. The danger of this reaction of the body lies in the occurrence of obstacles to the respiratory process, which can even result in death;
- development of bacterial infection. In places where the pathology is localized, in the absence of timely treatment, purulent boils and other infectious formations may appear, the occurrence of which is accompanied by pain;
- depressive states. Almost 15% of patients affected by urticaria suffer from depression. Moreover, poor health and constant itching prevent the patient from getting a good night's sleep and rest.
Urticaria in children, symptoms of the disease
The main symptom of childhood urticaria is the appearance of blisters on the skin. The allergen, penetrating inside the body, provokes increased production of histamine, as a result of which fluid accumulates in the subcutaneous layer of the epidermis, and swelling, rashes and blisters appear on the surface.
The localization of pathology in children is most often the surface of the skin between the folds and areas of the epidermis, often in contact with clothing. In addition, rashes can occur on the buttocks.
Complications, as a rule, are expressed by the main symptoms, which are accompanied by disorders of the respiratory, digestive and other systems of the body.
Species classification of pathology
Along with the acute and chronic forms of the disease, there are other types of urticaria.
Types of urticaria in adults and children
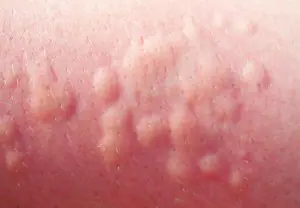
- sunny. The cause of solar urticaria is exposure to direct sunlight, so you should be careful not to get it on the skin, especially during lunch hours;
- food. The development of pathology is a peculiar reaction of the body to a food allergen, so parents should be extremely careful when introducing new foods into the child’s diet, especially for infants;
- cold The disease manifests itself due to a sharp change in temperature. Middle-aged women are at risk. Also, the occurrence of a rash can be triggered by eating cold food or drinks;
- aquagenic. Aquagenic urticaria is essentially a negative reaction of the body to contact with an aquatic environment. The danger of this type of pathology lies in its progressive nature, that is, as the disease develops, the symptoms become more pronounced, the rash appears more often;
- dermographic. This type of disease occurs due to mechanical effects on the skin. It can be classified as the simplest form of the disease, the percentage of self-healing in which is the highest;
- cholinergic. Reasons for the development of pathology: sudden changes in body temperature, increased sweating, excessive physical or emotional stress;
- stressful. Stress or so-called psychogenic urticaria occurs as a result of nervous stress. Patients susceptible to this type of pathology are characterized by such traits as increased anxiety, excessive irritability, short temper, and emotionality.
Traditional and folk treatment of urticaria
Treatment of acute urticaria begins with the identification and further exclusion of the allergen that provoked the development of the pathology.
To prescribe a course of therapy for chronic urticaria, you will need to take additional tests, in particular a general analysis of blood, urine and stool.
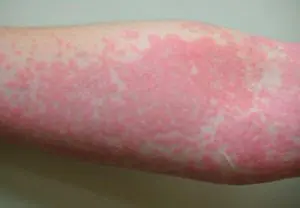
Drug treatment involves the use of the following drugs:
- laxatives;
- antihistamines;
- corticosteroids and adrenaline;
- external agents that have an antipruritic effect.
Before you begin treating urticaria at home, you should consult your doctor. The following folk remedies have a beneficial effect:
- tincture of cocklebur herb;
- infusion based on fragrant celery;
- dry mixture for oral administration based on nettle.
Treatment of urticaria during pregnancy
If urticaria makes itself felt during pregnancy, it is better to avoid using potent drugs. As a rule, in such cases, external non-hormonal agents are prescribed to prevent itching.
In addition, pregnant and lactating women are prescribed:
- vitamins to strengthen the immune system;
- liver support medications;
- sorbents that help remove toxins from the body;
- means that normalize digestion.
When fighting the manifestations of pathology, special attention should be paid to the rules of a healthy diet. Doctors recommend avoiding fatty and fried foods, alcohol, and citrus fruits. It is necessary to include vegetables and herbs, cereals, lean meats, and fermented milk products into your daily diet.
Video about hives
Small pink blisters on the body and limbs that itch incessantly cause a lot of discomfort for adults and children, especially if they appear with high frequency and the nature of their occurrence is unknown. Often this is a symptom of urticaria - a very unpleasant illness that can even endanger life if proper treatment is not carried out in a timely manner. Why does it occur and how to deal with it?
What is urticaria
This common skin condition has several alternative names: nettle fever, urticaria, or urticarial rash. Urticaria is a type of dermatitis, mainly of allergic origin. Sometimes this is only a symptom and not an independent disease, since urticaria in adults and children can accompany:
- bronchial asthma;
- allergic shock;
- autoimmune diseases.
The name of the disease is telling, since the rash in the form of small pink blisters visually resembles a nettle burn. According to official statistics, every third inhabitant of the globe encountered this problem, and for 15% of people it appeared twice. Mostly urticaria is diagnosed in people aged 20-40 years, women suffer from it more often than men, so the role of hormonal levels in its development cannot be ruled out. Another name for the disease - polyetiological dermatosis - well reflects the wide range of factors that can provoke its occurrence.
What does an allergic rash look like?
The main symptom of urticaria is flat, pink blisters, which can be small in size or form large plaques. In appearance (especially in photographs of patients), they are almost identical to the blisters that occur with a nettle burn, but the affected area is larger, and the rash is characterized by migration and sudden disappearance. The surrounding skin is dark red in color; when pressed, the bubbles become lighter. The appearance of an allergic rash is accompanied by severe itching.
Stages of pathology
Doctors call the leading mechanism for the development of urticaria the formation of reagins (special antibodies) in response to an allergen entering the body, which creates a state of sensitization: increased sensitivity to an irritant. When it re-enters, it combines with reagins, which leads to the release of mast cells, their degranulation (the process of destruction of granules) and the release of histamine. A classic allergic reaction of immediate type has the following stages of development:
- Immunological – the stage of sensitization, observed at the moment of direct contact with the allergen, characterized by the initiation of a response. The more the irritant is carried through the bloodstream, the more actively sensitized leukocytes (antibodies) are synthesized and accumulated. There are no clinical manifestations at this stage, but it is possible to notice changes in the activity of some enzymes and the concentration of immunoglobulins.
- Pathochemical – cellular and serum proteolytic and lipolytic enzymes are activated, allergy mediators are released: histamine, heparin, prostaglandins. They are then activated, interacting with the stimulus, which leads to changes in the tissues and fluids of the body.
- Pathophysiological - due to the activity of allergy mediators, vascular permeability increases, and a damaging effect on cellular tissue elements is observed. At this stage, local and general symptoms of urticaria appear, including irritation of nerve receptors (itching, burning), the development of edema, blisters, spasms of the bronchioles and intestines.
Causes of urticaria in adults
According to the etiology (nature of origin), the disease can be pseudo-allergic in nature (infections, chronic diseases, parasitic infestations) or allergic - occurs from direct contact with an irritant. If the exact factor that triggered its development remains unclear, it is reflected in the diagnosis as idiopathic urticaria. Common causes of urticaria rash:
- Infectious diseases (15% of cases) – bacterial and viral etiology (origin), especially chronic ones. The role of caries, adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages), tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils), and herpes is especially important.
- Diseases of the liver, stomach, intestines - gastritis, hepatitis, cholecystitis, and ulcers are especially closely associated with urticaria.
- Disorders in the immune system (20% of cases) are characterized by the development of autoimmune reactions, in which the body perceives its own cells as “strangers” and attacks them. This form can be severe, and the use of antihistamines does not produce results.
- Food (food allergies, up to 10% of cases) – plays a less significant role in adults than in children. It may be based on enzyme deficiency or chronic inflammatory processes.
- Neuroendocrine disorders (mainly in women) - problems with hormonal levels, diabetes, stressful situations, thyroiditis (lack of thyroid hormones).
- Factors of natural origin - sun, cold, heat.
- Leukemia (and other blood diseases) - leads to increased bleeding of blood vessels, provokes an urticarial rash with a tendency to allergies.



Provoking factors (triggers)
A large number of physical factors can act as irritants, each of which causes a different type of urticaria. They differ not only in the stimulus, but also in the nature of the flow. The general classification mentions the following varieties:
- Cold – the body reacts to cold air or water, and in some people, to food at low temperatures (ice cream, some desserts). In the reflex form, the reaction occurs when touching the allergen. Blisters form around areas that come into contact with it.
- Solar - a reaction to ultraviolet radiation occurs on uncovered areas of the skin and develops within a few minutes after contact with the allergen. Allergies occur mainly in summer, during times of increased solar activity.
- Thermal – is formed in people who react acutely to staying in a sauna, steam bath, bath, or to an increase in body temperature during physical activity. As a result of overheating, a large rash appears in the form of plaques fused together.
- Contact - an allergic reaction develops as a result of interaction with household chemicals and cosmetics (decorative and caring). The rash is mild and disappears almost immediately after contact with the irritant is eliminated.
- Allergic – observed upon contact with plant pollen, animal hair, dust. Symptoms disappear immediately after the irritant is eliminated; the severity of the condition is always individual: anaphylactic shock is possible.
- Medicinal – occurs when there is intolerance to gamma globulins, antibiotics and other medicinal substances; skin symptoms do not always appear immediately (up to 2 weeks), which makes it difficult to determine the cause of the allergic reaction.
- Dermographic - appears as a result of mechanical irritation: from tight clothing (or unpleasant fabric), a tightly tightened belt, sharp fittings. First, severe itching appears, followed by a rash in the form of thin small stripes. Characteristic for people with sensitive skin. Symptoms persist for several days, but there is no deterioration in general health.
- Aquagenic - the rash with such urticaria may be completely absent or invisible, but the itching will always be there. The reaction occurs when a substance produced by the skin reacts chemically with water.
- Idiopathic - this diagnosis is made when the exact allergen has not been identified, so the clinical picture is always different.
Symptoms and features of the course
Urticaria in adults begins with the sudden appearance of pink blisters on the skin and mucous membranes, most of them will appear within an hour: during this period the maximum concentration of histamine is observed. Afterwards, small blisters may appear, and after a few hours a second wave of urticaria occurs, but the rash may also disappear. External signs are often accompanied by a general deterioration in well-being:
- headache;
- temperature;
- weakness, weakness;
- decreased performance.
Acute
An abrupt onset, with the appearance of a large number of blisters on the skin within an hour after contact with the irritant, is the main symptom of the acute form. Its duration ranges from a day to 2 weeks. In addition to local manifestations, there are also signs of general malaise, including:
- nervous system disorders;
- headache;
- fever (up to 38 degrees), lethargy.
Often, if the rash does not disappear from the dermis within a few hours, local swelling of the subcutaneous tissue, muscles, fascia, and mucous membranes may develop, which leads to Quincke's edema. It mainly occurs on the face and is characterized by a rapid appearance (within 2-5 minutes) and painful itching. The exact symptoms depend on the area affected. If the larynx is affected, the person experiences asphyxia (suffocation) and faces speech impairment. A patient with such symptoms should be immediately hospitalized.
Urticaria is an allergic disease that manifests itself on the skin and mucous membranes in the form of blisters. Statistics show that women are more susceptible to this disease than men. The disease is common, a person faces this problem at least once in his life.
Causes of urticaria
According to doctors, the fact that urticaria is diagnosed in women twice as often as in men is explained by hormonal disorders that occur in the female body with age. The following factors can affect hormone levels:
- Pregnancy;
- Taking oral contraceptives;
- Menopause;
- Menstruation.
In most cases, doctors are unable to accurately determine the cause of a chronic allergic reaction. Therefore, you have to undergo a full examination and take a lot of tests. Chronic urticaria may appear for the following reasons:
- Infection entering the body;
- Decreased immunity;
- Allergy to specific foods;
- Physical effects on the skin;
- Presence of dermatitis;
- Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus of any group;
- Gastritis;
- Hepatitis;
- Leukemia;
- Herpes.
According to medical statistics, 15% of cases of urticaria occur precisely due to infection. Both viral and bacterial infections can cause rashes and skin irritation. It is important to immediately eliminate foci of inflammation, be it gastritis or caries. When immunity decreases, the body stops recognizing its cells and attacks them, which leads to autoimmune urticaria.
Physical factors provoking the disease
Doctors distinguish several types of physical urticaria, depending on the factors that provoked it:
- Sunlight. After exposure to sunlight on the skin of the patient (mostly women), a rash, redness and itching begins to appear. It is noteworthy that the rash is recorded only on those areas of the skin that are not covered by clothing.
- Cold. Unheated air or too cold water can also cause hives. In rare cases, symptoms of the disease are recorded when a person eats food that is too cold. Blisters appear around an area of skin that has been exposed to hypothermia.
- Water. Doctors call this type of urticaria aquagenic because it appears after a person comes into contact with water. It is noteworthy that there is usually no redness or blistering; the patient suffers from extremely severe itching.
- Strong vibrations. This type of urticaria is an occupational disease, as it occurs in people who, due to their occupation, are exposed to strong vibrations, for example, working with a jackhammer.
- Allergens. Hives can be caused by standard allergens: pollen during flowering, dust, animal hair. Symptoms completely disappear after a person protects himself from the allergen.
- A sharp increase in body temperature. Doctors call this type of urticaria cholinergic. It appears during a sharp increase in a person’s body temperature. This can happen not only due to illness, physical training, eating spicy or hot food, a surge of emotions - all this can cause a sharp rise in temperature. The blisters are small and pale, concentrated in the upper part of the patient's torso.
- Friction and compression. Hives may appear due to a too-tight belt, tight dress or shoes. It is noteworthy that physical pressure must continue for a long time for hives to appear. At the same time, the blisters here are oblong and do not appear on the skin at the same time as itching.
What does urticaria look like on the body?
The rash caused by urticaria is very similar to the rash caused by a nettle “burn.” Hence the name. Please note that inflammation and blisters may disappear and reappear. This course is called recurrent.
The rash is one of the main diagnostic symptoms of the described disease. Elements of the rash (blisters) can be round or oblong, small in size, slightly raised above the skin. Mostly pale pink in color. The skin around them is dark purple. The patient suffers from severe itching in the inflamed area.
The main feature of urticaria in adults is that it manifests itself quickly and then can also suddenly disappear. Itchy skin occurs due to irritated nerve endings. Much more of the neurotransmitter histamine enters the bloodstream than before. The level of itching (from tolerable to painful) varies precisely because of the amount of incoming substance.
Signs and symptoms
Essentially, urticaria is an allergic reaction exhibited by the body after contact with an allergen. Classic symptoms include:
- Redness of one or more areas of the skin;
- Blistering;
- Severe burning and itching in the area of inflammation;
- Temperature increase;
- Headache.
Depending on the course of the disease, urticaria can be acute or chronic. The acute form is recorded much more often than the chronic form.
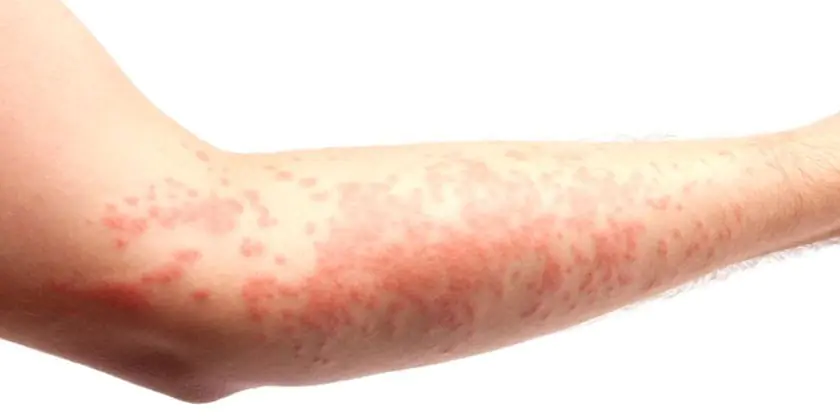
Figure No. 1. Acute urticaria in a child.
It can be diagnosed in young children and adolescents and can be a consequence of Quincke's edema. The diameter of the blisters in the acute form can reach one centimeter, and the rashes are concentrated not on individual areas of the skin, but throughout the body. The acute form of the disease can be cured in up to six weeks, but medical practice shows that this requires no more than a couple of days.
Chronic urticaria can be treated for longer than one and a half months; only adults from 20 to 40 years old are susceptible to this type. During treatment, periods of improvement and deterioration of the patient's condition may be observed. The rashes are light pink in color and change during exacerbations.
Course of the disease by period
The development of urticaria in the body occurs through immune and non-immune mechanisms. The first includes four more scenarios, based on four types of allergic reactions. According to the immune type, urticaria can appear on the skin and mucous membranes literally within a few minutes from the moment the allergen enters the patient’s body.
There are several mechanisms for the development of allergies, and they are all quite complex. It is important to know that swelling (rash) with urticaria occurs because the permeability of the capillaries increases and fluid accumulates around them. A substance such as histamine triggers the allergy mechanism. It is formed and accumulates in special cells - mast or mast cells. And the rupture of such a cell, and the release of histamine, leads to changes in the microcirculation and all the signs of allergies.
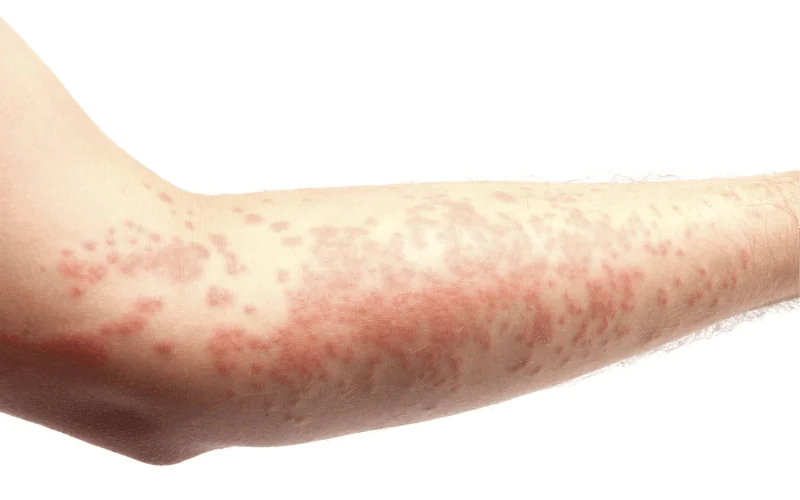
Figure No. 2. What does hives look like?
The patient feels itching, swelling on the skin, inflammation and blisters appear. All this is a consequence of the fact that the blood vessels have dilated, and the allergen has reached a critical point in the body. The non-immune course of the disease develops without major immune reactions. When an allergen enters the body, histamine and other biologically active substances are released. This form of urticaria is called chronic or idiopathic.
Establishing diagnosis
If you suspect urticaria, you need to make an appointment with a dermatologist or allergist. The specialist makes a diagnosis based on a patient interview and the manifestation of clinical signs of the disease. The doctor is able to determine what exactly the allergen is. For this, an in-depth examination is carried out. The patient will need to take allergy tests to identify the exact type of allergen. And a blood test for immunoglobulins (their level is increased with allergies).
Treatment
The most effective way to treat urticaria is to identify and eliminate the allergen that triggered the rash. If this was not possible, or when the disease is episodic, the doctor may prescribe antihistamines that will relieve the main symptoms. Moreover, during treatment you need to switch to a hypoallergenic diet and give up perfumes and cosmetics (in addition to hypoallergenic ones). Everything together will help prevent the appearance of new rashes and worsening the patient’s condition.
If classical treatment does not help, then the doctor may prescribe hormone-based medications. An equally effective addition to drug treatment would be immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive therapy.
Is hives contagious?
Many people worry about whether it is possible to catch hives from another person. The disease does not belong to the category of infectious, so the patient is not able to infect a healthy person, even if he is in very close contact with him. But you should be vigilant, because urticaria can become a symptom of infectious processes occurring in the body. Then infection from the infectious agent is possible.
Bathing for hives
Another popular question is whether it is possible to swim if you have hives. Taking a shower when you have hives is simply necessary, because it is important to maintain body hygiene. Without this, the disease may begin to progress and affect a larger area of skin. In order not to harm yourself, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- The water should be warm, but not hot or cold. The ideal option would be 35 degrees. Hot or cold water can irritate the skin and trigger hives.
- Avoid using hard sponges, as well as shower gels and scrubs with abrasive particles. Personal hygiene products should not irritate the skin or damage it mechanically.
- Give preference to hypoallergenic personal care products, without fragrances or dyes; they are safer for the skin and will not cause allergies.
- You should not take a shower for longer than 15 minutes, and in case of an acute form of the disease, you should be in contact with water for no more than 5 minutes.
- After taking a shower, pat your skin dry with a natural fabric towel and apply medications or creams to the dermis.
If there are pustules on the skin, you need to shower very carefully. Contact with the affected area should be kept to a minimum, as should the time of the water procedure.
Who is most susceptible to the disease?
Today it is believed that women are more susceptible to urticaria than men. However, the manifestation of the disease in the latter is recorded quite often. So, men suffer from it between the ages of 30 and 50 years. The occurrence of rashes in old age is considered a very rare occurrence.
Artificial urticaria is recorded in people aged 20 to 30 years. It is called artificial because the rash and inflammation occurs as a result of physical friction against the skin, squeezing or scratching. Cholinergic urticaria, caused by heavy exercise, taking too hot a bath, or eating spicy foods, occurs in both men and women.
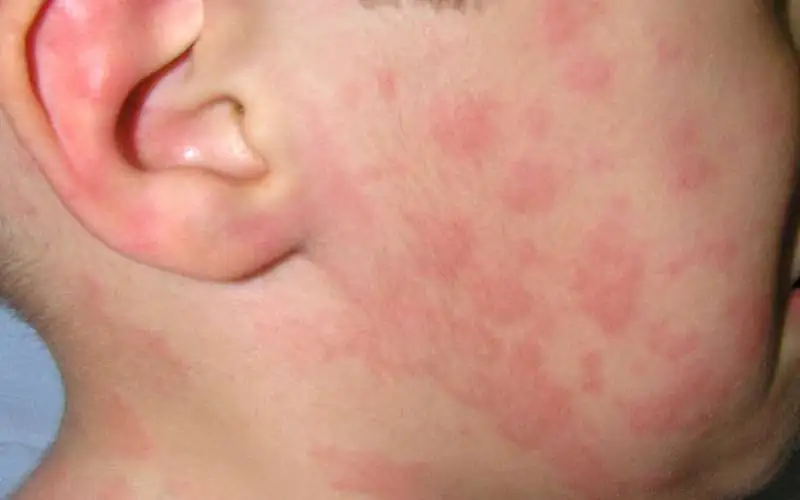
Figure No. 3. Cholinergic urticaria
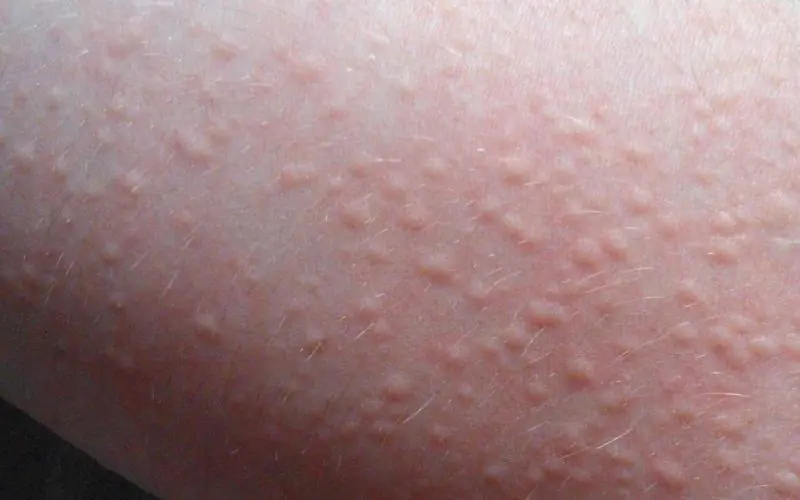
Moreover, the average age of patients is from 15 to 25 years.
Disease prevention
If the allergen that caused the rash has not been identified, then it is recommended to use the following preventive measures:
- Stop taking medications that could cause allergies;
- Minimize stress;
- Stop using tobacco and alcohol;
- Do not go to baths or saunas, which can cause overheating;
- Stop intense physical training;
- Adhere to a hypoallergenic diet, without seasonings and dyes;
- It is necessary to remove all animals from the apartment or house where the patient lives;
- Completely stop using feather pillows/blankets, completely switch to hypoallergenic cosmetics and hygiene products;
- Cure chronic diseases.
If the allergen has been identified, the patient must be completely isolated from it. The substance should not be contained in powders, household and hygiene products.
Consequences of the disease and complications
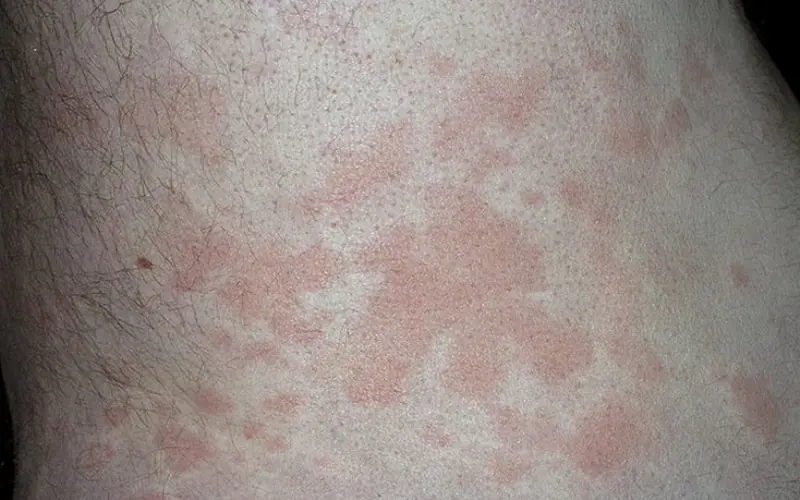
Many people who are faced with the problem of urticaria, even after undergoing tests, cannot determine the allergen that caused the rash. In such cases, idiopathic urticaria is diagnosed.
Figure No. 3. Idiopathic urticaria
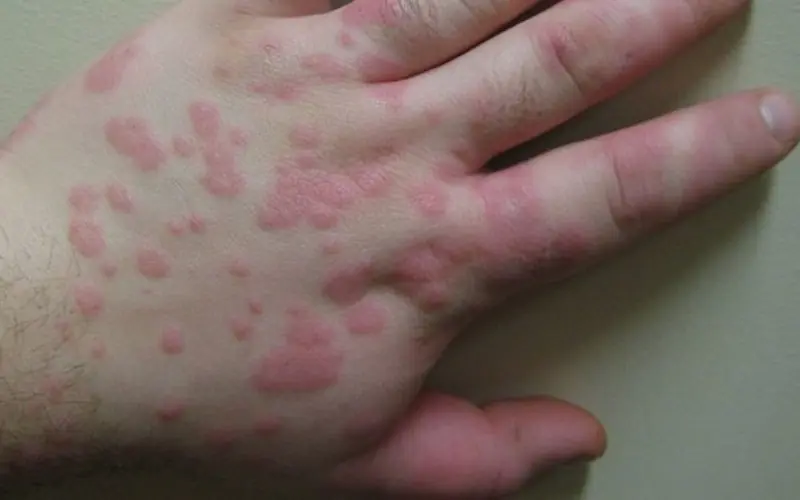
In such cases, the disease can become chronic and unpleasant to remind of itself. A significant proportion of cases end in angioedema (Quincke's edema), that is, swelling of the subcutaneous tissue, asphyxia (if the edema affects the larynx) and suffocation. When an allergen is detected in specific products or medications, the patient has to completely stop using them, which causes inconvenience.
This approach may complicate the treatment of other diseases. For example, people often have allergies to drugs used for anesthesia in dentistry, then the doctor has to select other drugs that do not harm the patient’s health.



