Even a single boil in a child, in the absence or inadequate self-treatment, can pose a danger to his health. If the disease develops into another common form, then we are talking about furunculosis in a child.
The presented photos clearly show the difference between a single boil in a child and multiple furunculosis. Sometimes the problem torments the child and parents for years. Is it possible to completely get rid of it, how to treat a boil in a child under one year of age or older?
Causes of furunculosis in children
The direct causative agent of purulent skin disease, such as furunculosis in children, as well as in adults, is Staphylococcus aureus. It is a saprophyte that lives on the skin and mucous membranes of all people without harm to them, but under some circumstances it acquires pathogenic properties.
The reasons that allow staphylococcus to become pathogenic are divided into external and internal.
External causes boil down to disruption of the integrity of the skin:
- injuries, even minimal ones, cuts, abrasions;
- scratching after an insect bite or other skin diseases or allergies;
- scuffs from uncomfortable shoes or clothes.
Note that microtraumas occur in almost all children; staphylococcus also surrounds the child literally everywhere - at home, in kindergarten, in the sandbox, in the air. Parents and family members can be carriers of staphylococcus. But furunculosis, which requires treatment, does not occur in all children for external reasons.
The process of development of the disease is influenced by internal factors that are individual for each child.
Internal reasons:
- weakened immunity due to diseases or the presence of helminthic infestations or protozoan infestations (giardiasis);
- dysbiosis and gastrointestinal problems;
- metabolic disorders;
- diseases of the endocrine system (type 1 diabetes);
- diseases of the nervous system;
- vitamin deficiency;
- anemia;
- physical exhaustion due to poor nutrition (hypotrophy or anorexia)
- overfatigue due to excessive stress, including sports;
- increased sweating.
If the hygiene requirements accompanying these reasons are violated, the risk of disease increases.
Symptoms of furunculosis in children
It is impossible to hear complaints from children about the appearance of discomfort, pain, itching and swelling in the area of development of trouble. The mother or person caring for the baby should notice and begin timely treatment when a boil appears on the child’s skin.
This usually occurs during air baths before daily bathing. Inspection of the skin should be daily and systematic. Particular attention should be paid to the inguinal folds, armpits, intergluteal folds, nasal passages, ear canals and cervical folds. Familiarize yourself with boils in children using the photo presented.
The baby has his own language to tell his mother about unpleasant sensations. Perhaps the first manifestation will be anxiety, sleep disturbance, refusal to eat, and crying. In children, unlike adults, hyperthermia and symptoms of intoxication appear much earlier and more often. High temperature can cause cramps, regurgitation, nausea and vomiting, and stool disorders.
Teenagers may complain of pain and the appearance of an abscess on the body. With pre- and puberty-age children, there is another danger. This age period is characterized by rashes of pustules and the appearance of boils on the child’s face due to hormonal changes. Increased attention to their appearance, fear of ridicule from peers forces them to squeeze out ulcers.
Parents should know that if they find a boil in their child in the area of the face, ear, neck, or scalp, they should immediately contact a surgeon. In close proximity are the most important blood vessels leading to the cranial cavity. Direction of lymphatic drainage increases the risk of fatal complications.
You should pay attention to boils in children located in the joint area. These areas are often injured and there is a danger of pus breaking into the joint cavity.
Types of boils in children
Furunculosis in children has a code according to ICD 10 (International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision) L02.
The following types of boils fall under this code:
- single boils, regardless of their location;
- cystic acne on the face in adolescents, affecting the deeper layers of the dermis;
- pilonidal sinus - boils in the intergluteal fold when wearing tight underwear, sweating and insufficient hygiene after defecation;
- Hidradenitis suppurativa is a purulent inflammation of a large number of sweat glands located in places of increased sweating (groin, armpit), recurrent.
Treatment of boils in children
Since June 8, 2007, there has been Order No. 408 of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation, which determines the standard of treatment for boils and other purulent skin diseases in children and adults. It concerns the provision of specialized medical care for any location, form and stage of diseases under code L20, regardless of the presence of complications in a hospital setting.
The standard includes diagnostic and therapeutic measures based on a hospital stay of 14 days. Standard examination includes:
- history taking, visual examination, auscultation, palpation and percussion within the general therapeutic framework;
- measurement of blood pressure, respiratory rate, pulse and temperature;
- general blood test with leukocyte count;
- chest x-ray, ECG;
- culture from the source of inflammation, in some cases puncture of the abscess.
Treatment and diagnostic standard measures in the hospital:
- expansion of blood test parameters (counting red blood cells, platelets, determination of hematocrit);
- biochemical blood test (total protein, albumin, creatinine, alanine and aspartame transaminases);
- Analysis of urine;
- examination for syphilis, HIV, carriage of hepatitis B and C viruses;
- determination of blood group and Rh status;
- examination by an anesthesiologist.
Pharmacological groups according to the standard allow their use in 30-100% of cases.
- Analgesics and NSAIDs, narcotic (Trimeperidine, Fentanyl) and non-narcotic (Tramadol, Ketorolac).
- Means for treating and preventing infection are antibiotics and antifungals.
- Antiseptics and disinfectants (Povidone-iodine, Chlorhexidine).
- Solutions for infusion therapy.
- Anesthetics and muscle relaxants for anesthesia and local anesthetics (Lidocaine, Ropivacaine topically).
- Drugs affecting the central nervous system (Diazepam, Droperidol).
Treatment at home is allowed for typical boils in “non-dangerous” localizations in children over 1 year of age.
Carbohydrates should be excluded from the diet of a sick child, including cereals, pasta, potatoes, soda and sweets.
Treatment of boils in children with folk remedies
Treatment of a boil in a child with folk remedies is permissible only with the permission of the surgeon. They recommend oil compresses with fir, camphor and sea buckthorn oils, treatment with herbal decoctions of string, chamomile, eucalyptus. Rabbit cabbage juice and ficus leaf puree are unlikely to fall into the category of treatment methods recommended by a doctor.
Wherever the child’s boil is located, a doctor should treat it. No self-medication, no proven folk methods can be used without permission!
Treatment of furunculosis in children with medications
The advisability of prescribing antibiotics for single boils is determined by the following condition.
For children under one year of age, intramuscular antibiotics are recommended for any location of boils, especially with widespread furunculosis.
Boils in children over 1 year of age are treated with antibiotics only if the ulcers are located on the face and neck, if we are talking about single ulcers. There are no reasons for refusing antibiotics in the treatment of furunculosis in children.
Which ones are preferable?
Amoxiclav, Doxycycline, Clindamycin, Clarithromycin, Cefuroxime, Ciprofloxacin are the drugs of choice.
Local treatment of boils is carried out using solutions of antiseptics and disinfectants and ointments (Ichthyol, Syntomycin, Tetracycline, Zinc). If surgical opening of the abscess and removal of the rod was performed, as well as after its spontaneous removal, dressings are recommended to be done daily until the skin defect is completely healed.
To speed up repair, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapy.
You can get rid of furunculosis only with an integrated approach to the problem:
- sanitation of foci of chronic infection;
- immune system support;
- vitamins, iron supplements;
- vaccine therapy according to indications.
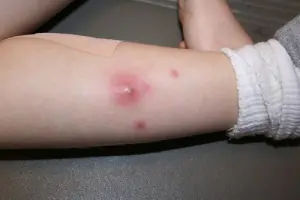
The skin of a child is characterized by increased sensitivity to the effects of various types of unfavorable factors, both external and internal. That is why the appearance on children's skin all kinds of irritations, acne and other formations are quite common.
In most cases, this situation does not cause concern, but if the baby develops large purulent boil – this is a reason to see a doctor as soon as possible.
If boils in a child are multiple in nature, we are talking about a serious disease - furunculosis. This condition is very dangerous and can cause significant harm to the health of the baby.
Therefore, the baby requires qualified medical care. And before starting treatment, it is necessary to establish the cause that provoked the occurrence of this problem and eliminate it. Only in this case will the therapy be correct and complete.
What to do if a child has flux? Find out the answer right now.
General information
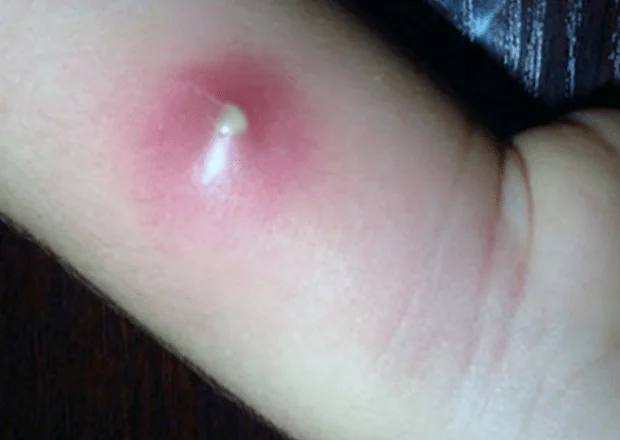
A boil is large pustular formation. A boil forms around the hair follicle, damaging not only it, but also the surrounding tissues (sebaceous glands and connective tissue).
The causative agent of the disease is most often Staphylococcus aureus, however, other pyogenic bacteria can also lead to the development of furunculosis.
In the event that a bacterial infection of the body is of a large-scale nature, numerous purulent formations – boils – appear on the child’s skin. In this case we are talking about a dangerous disease - furunculosis.
This pathology is considered not only as a cosmetic defect, although large boils, especially if they are located on open areas of the body, do cause a lot of aesthetic inconvenience.
Furunculosis, first of all, is a dangerous disease that causes pain to the child, but can provoke the development of more serious complications, since with furunculosis the integrity of the skin, a natural protective barrier that blocks the path of pathogenic microflora, is disrupted.
Reasons for the development of furunculosis
Numerous unfavorable factors (external or internal) can lead to the occurrence and development of furunculosis in a child.
External
Domestic
- Long-term negative effects on the skin (for example, wearing clothes that are too tight, which regularly rub the baby’s delicate skin).
- Neglect of personal hygiene rules, improper skin care of a small child (for example, lack of daily bathing, prolonged exposure of the baby to a dirty diaper or clothes).
- Mechanical damage to the skin (scratches, scratching) followed by infection of the wound.
- Improper nutrition, leading to depletion of the body (reducing the volume of portions, long breaks between feedings, fasting, consumption of low-quality food, poor in nutrients).
- Endocrine pathologies (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism).
- Immunodeficiency conditions in which the child’s immune system is not able to cope with bacterial infection.
- Disruption of the digestive process.
- Metabolic disorder.
- Anemia.
- Regular physical fatigue, chronic fatigue.
Read about the symptoms and treatment of neurodermatitis in a child here.
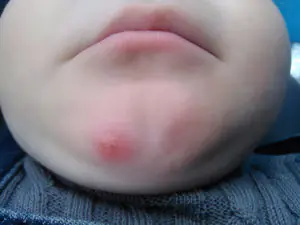
Due to a wide variety of factors and individual characteristics of the child’s body, a wide variety of pustular formations can appear on the baby’s skin.
Therefore, in dermatology it is customary to classify them as follows:
- Furuncle – a single formation that affects only 1 hair follicle.
- Carbuncle – a larger abscess affecting several hair follicles. It is an abscess formed as a result of the merger of several single boils.
- Cystic acne formations. With this form of furunculosis, the deep layers of the epidermis are affected, resulting in a large number of small rashes that can appear on the face and other parts of the body. Most often, teenagers face this problem during puberty.
- Pilonidal sinus - a very large and painful purulent formation that occurs in the area between the buttocks. Most often, this problem is encountered by children who are overweight and lead an inactive lifestyle.
- Hidradenitis suppurativa - a disease that affects the sweat glands. In the damaged areas, multiple large abscesses appear (most often in the armpits, groin area), in which there is no necrotic core.
Damage to the sweat glands is also associated with bacterial infection, however, antibiotic therapy alone is not enough and the child will require surgery to remove the affected sweat gland.
Symptoms and signs
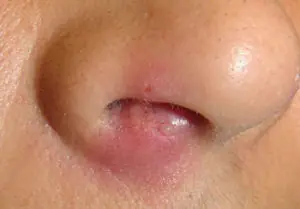
Recognize a boil possible based on certain characteristics, such as:
- The appearance on the skin of a single pustular formation, which has a dense center rising above the surface of healthy skin. The core of the boil gradually forms in this center. The skin around it swells, hyperemia is observed.
- A white head appears in the center of the formation, filled with purulent contents and covered with a thin film.
- The child experiences discomfort, itching, and pain in the affected area.
- A boil can form on almost any part of the body, with the exception of those areas where there are no hair follicles (for example, the skin of the feet and the inner surface of the palms).
- The inflammatory process leads to an increase in the nearby lymph nodes.
- Hyperthermia often appears (up to 39 degrees).
- The child's general well-being is affected.
Purulent formations go through 3 stages of development:
- Infiltration – thickening and redness of the skin affected by a bacterial infection.
- Suppuration – as a result of the destructive activity of pathogenic microflora, intoxication of surrounding tissues occurs and suppuration occurs. At this stage, the core of the boil is formed.
- Healing – a scar forms on the affected area, swelling and redness gradually disappear.
The process of development and healing of a boil takes an average of 10-12 days, although it all depends on the state of the child’s immune system and the treatment prescribed to him.
Complications and consequences
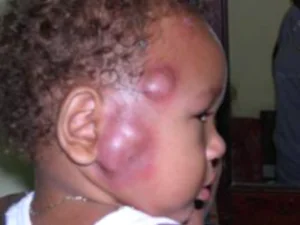
The most dangerous complication that occurs as a result of improper treatment of furunculosis or lack of therapy is extensive intoxication of the body, which can lead to blood poisoning and, as a result, the death of the child.
In medical practice, there are cases where an unsuccessful attempt to independently squeeze out a boil later led to the development of sepsis and death (one such example is the famous composer A. N. Scriabin, who unsuccessfully squeezed out a boil and subsequently died from blood poisoning).
Others dangerous consequences furunculosis are:
- purulent damage to the brain and other internal organs;
- the formation of blood clots that interfere with the normal outflow of lymph;
- other diseases of the lymphatic system.
Recommendations for the treatment of pityriasis rosea in children can be found on our website.
Diagnostics
To detect furunculosis and differentiation it from other diseases with similar symptoms, it is necessary to conduct a number of diagnostic studies:
- examination of the affected area of skin;
- blood and urine tests;
- dermatoscopy;
- bacteriological examination of the affected area;
- instrumental studies (ultrasound, CT, MRI) of internal organs.
Treatment options

The main method of treating furunculosis is to use prescribed by a doctor medicines, such as:
- Antiseptics for topical use (hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green) are necessary for tissue disinfection.
- Compresses using a sorbent drug that draws purulent contents from the wound.
- Bandages using antibacterial ointments (Ichthyol, Vishnevsky ointment).
These measures must be carried out in strict sequence, otherwise the treatment will not only have no effect, but may also aggravate the situation.
Folk
Time-tested methods such as:
- Grated potato compress. A small potato should be grated on a fine grater, placed in a gauze bandage and applied to the affected area of the skin until dry.
- Aloe compress. A freshly picked leaf of the plant is crushed, this mass is applied to the boil, and wrapped in a gauze bandage, which must be changed 3 times a day.
to contents ↑
Are antibiotics needed?
Since the cause of furunculosis development is bacterial infection, taking antibiotics is a prerequisite for successful treatment.
Moreover, the child is most often prescribed broad-spectrum drugs that have a detrimental effect on most types of pathogenic microflora.
Other methods
Today, methods are actively used to treat furunculosis. physiotherapy, for example, exposure to a high frequency magnetic field. One of the most effective ways to combat the disease is laser removal of boils.
What not to do?
If a boil occurs, you should not self-medicate and try to open and clean the wound yourself.
This can lead to even more boils and the appearance of more serious consequences (for example, sepsis). In addition, the inflamed area should not be heated, as the inflammatory process in this case will only intensify.
Do I need to open it?
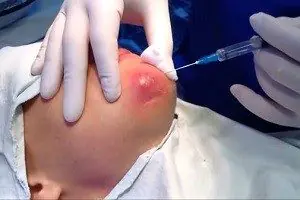
In some cases, it is necessary to open the boil (for example, if we are talking about a very large formation), but this must be done only an experienced specialist.
For smaller boils, an autopsy is not necessary; you just need to wait and follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Having noticed a purulent formation on the child’s skin, many parents try to remove it on one's own. And this does not always work out successfully.
In many cases, after such treatment, the problem arises again and on an even larger scale.
In addition, removing the boil is not all, it is necessary find out why it appeared, and eliminate this cause. And only a doctor can do this. Only in this case will the treatment be complete.
Prevention
Reduce the risk of developing furunculosis is possible if:
- provide the child with proper hygienic care;
- dress the baby in comfortable clothes that do not chafe the skin;
- protect the child from injuries, and if they occur, immediately treat the wound with an antiseptic;
- ensure proper and nutritious nutrition, an active lifestyle;
- identify and treat various diseases in a timely manner.

Furunculosis – unpleasant and dangerous diseaseaccompanied by damage to the skin.
A furuncle is a purulent formation that affects the hair follicle and the tissues closest to it.
The pathology causes a lot of suffering to the child and can cause the development of dangerous conditions, life-threatening. Therefore, when the first signs of pathology are detected, it is necessary to begin treatment.
How to treat boils in children at home? Find out from the video:
We kindly ask you not to self-medicate. Make an appointment with a doctor!
Small pustules - pimples - often appear on the skin of children, especially teenagers. This is unpleasant, but completely treatable and, in essence, harmless. Much more dangerous is the appearance of a large abscess in the thickness of the skin - a boil. It forms around the hair follicle, spreading to the surrounding tissue.
If the boils become multiple, appearing one after another, this phenomenon is already called furunculosis. This pustular disease brings significant suffering to the child, and if left untreated, it can have serious consequences for the health and even the life of the baby.
What is the reason for the development of furunculosis?
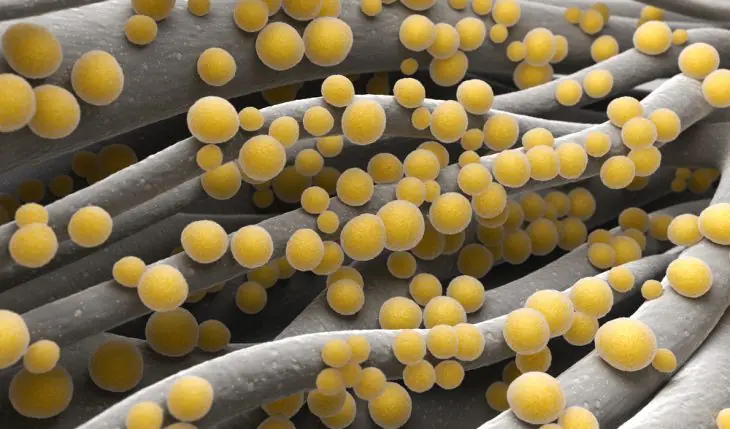
The causes of furunculosis are multiple.
Suppuration, in essence, is caused by Staphylococcus aureus, which is normally found on the mucous membrane of the nose and intestines, without causing any painful phenomena. If it gets on the skin, this microorganism can penetrate deep into it (if there is an entrance gate: scratches, abrasions and other microtraumas) and cause an inflammatory process.
But many children have skin microtraumas and, however, they do not develop any boils! Consequently, the mechanism of formation of this disease is not so simple.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of furunculosis are divided into local and general. According to researchers, only a combination of factors from the first and second groups can lead to the development of furunculosis.
Local risk factors:
- abrasions, scratches, abrasions, scratching of the skin, that is, a violation of the integrity of the skin;
- skin contamination, non-compliance with hygiene standards;
- blockage of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland;
- allergic skin diseases.
General risk factors:
- decreased immunity;
- chronic diseases of the digestive tract, including dysbiosis;
- metabolic disorders;
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, etc.);
- diseases of the nervous system;
- anemia (anemia);
- hypovitaminosis;
- physical exhaustion due to poor nutrition (hypotrophy in young children and anorexia in adolescents);
- regular physical fatigue (for example, among schoolchildren who are overly active in sports);
- frequent overheating or, conversely, hypothermia;
- condition after suffering serious illnesses.
Recently, in addition, varieties of Staphylococcus aureus have been identified that successfully resist the protective effect of the immune system. Researchers believe that furunculosis occurs in children who are carriers of these particular strains of staphylococcus.
Symptoms of furunculosis
Usually, a single boil first appears on a child’s skin, going through 3 stages in its development:
Infiltration manifested by the appearance on the skin in one place or another (often in places of microtrauma) of a dense, painful tubercle of intense red color. The tubercle gradually increases in size, swelling of the surrounding tissues appears, and pain increases. The child's body temperature rises.
Suppuration characterized by the growth of a boil up to 1-3-5 cm in diameter; the tubercle takes on a cone-shaped shape, and its apex becomes a pustule: a vesicle with purulent contents. Under it, in the center of the boil, invisible from the outside, there is a “plug” of tissue that has undergone purulent-necrotic decay.
The child’s general condition deteriorates sharply, the temperature rises to 38° and above. General weakness and headaches are added: these are symptoms of intoxication. The pain in the area of the boil becomes sharp, the child does not allow him to touch the sore spot. Regional lymph nodes enlarge.
Relief occurs with the breakthrough of pus to the outside when the pustule is opened. After pus, necrotic yellow-green tissues, often having the shape of a rod, are released from the boil. From this moment on, the pain goes away and the child’s well-being improves.
Healing : the depression remaining at the site of the opened boil becomes scarred, acquiring a red-blue color. Then the scar becomes lighter and almost matches the color of healthy skin.
All three stages of boil development, provided treatment is started in a timely manner, last from 10 to 12 days.
In the case of furunculosis development, ulcers appear in different places of the skin one after another (before one boil has time to heal, another is already brewing), or even simultaneously. The condition and well-being of the child suffer greatly. Young children with furunculosis are treated in a hospital, as are older children, if the boils are located in particularly dangerous places (see below).
Complications of furunculosis
The degree of danger and the possibility of developing complications depend on where the boil occurs.
The most common areas of localization of ulcers are the lower extremities, buttocks, lumbar region, abdomen, forearms, and back of the head. Almost a boil can occur on any part of the body, except the palms and soles (there are no hair follicles there).
But the most dangerous boils are on the face (especially in the area of the nasolabial triangle), on the neck, in the groin, in the intergluteal folds, in the armpits, and also in the depths of the ear canal. In these cases, the ulcers are located in close proximity to the blood and lymphatic vessels and can provoke the development of complications such as:
- sepsis (“blood poisoning”);
- purulent meningitis;
- thrombophlebitis;
- thrombosis of the lymphatic tract;
- lymphangitis;
- lymphadenitis;
- purulent metastases to various internal organs (liver, kidneys, etc.).
Treatment of furunculosis

Treatment methods for furunculosis are divided into local, general and surgical.
Target local treatment – accelerate the maturation and “breakthrough” of the boil, reduce pain and inflammation, prevent the spread of the suppurative process.
For this purpose, both official medicine is used (antibacterial and anti-inflammatory ointments, compresses with Dimexide and other drugs, rubbing with alcohol tinctures of medicinal herbs), and folk recipes (applying onions boiled in milk; compresses from grated raw potatoes, from cabbage leaves, greased honey, etc.).
The following antibacterial ointments are used locally: Baktroban, Levomekol, Azelik, Fucidin, gentamicin, heliomycin, etc. To speed up the opening of the boil, ichthyol ointment, Vinilin, and Vishnevsky ointment are used.
General treatment prescribed for chronic furunculosis, when boils are localized in dangerous places (listed above). It consists of the use of antibiotics, vitamins, immunostimulants, as well as the treatment of concomitant chronic diseases.
- Antibiotics are prescribed both locally and orally, and in some cases intravenously. Sometimes they resort to complex prescription of antibacterial agents. Only a doctor prescribes antibiotics, taking into account the sensitivity analysis of the pathogen. Azithromycin, Unidox Solutab, Josamycin, Clarithromycin, Augmentin, Kefzol, etc. are used most often. The course of antibiotic therapy for furunculosis is at least 5 days.
- Vitamins necessary in the treatment of furunculosis: retinol acetate (vitamin A), ascorbic acid (vitamin C), thiamine (vitamin B1), riboflavin (vitamin B2), nicotinic acid (vitamin PP). Most often they are prescribed to the child orally, but sometimes they are also used by injection. Vitamin B complex is found in brewer's yeast, which can be purchased at the pharmacy.
- Drugs that stimulate the immune system are used strictly as prescribed by a doctor. Drugs such as interferons, Derinat, Lykopid, Polyoxidonium, Intraglobin, Myelopid, Gabriglobin, Octagam, Seramil, etc. can be used.
Several decades ago, anti-staphylococcal immunoglobulin and staphylococcal toxoid were used to strengthen the body's defenses, but the use of these drugs did not give the desired result. Currently, they are not used for furunculosis, as is autohemotherapy (intramuscular injection of a small amount of his own blood taken from a vein to the patient). For children, this procedure was, of course, additional traumatization.
Surgery used when there is a clear risk of complications, as well as in cases where boils do not respond to conservative therapy.
Surgical intervention consists of creating a cross-shaped incision in the skin at the apex of the boil and removing pus and necrotic core through this incision. This procedure in children is performed under local anesthesia. At the end of the operation, the wound is treated with a disinfectant solution and a sterile bandage is applied to it. Sometimes, if the wound cannot be completely cleared of pus, drainage is left in it - a rubber strip that facilitates the drainage of purulent discharge. After the operation, the child undergoes daily dressings.
The advantages of surgical treatment of a boil are the rapid improvement of the patient’s condition, but the child has to overcome an additional negative emotional burden: all children, of course, are afraid of operations.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention for this disease.
Prevention of furunculosis, as well as all pustular skin diseases, consists of following the following recommendations:
- Teaching children from an early age to keep their skin clean and wash their hands regularly. It should be noted that bactericidal soaps are not suitable for constant use: they also destroy the beneficial, protective microflora of the skin. Both the hands and the entire body of the child should be washed with regular baby soap, and bactericidal soap is very appropriate for washing those areas of the skin that were exposed to pus when the boil opened.
- Any abrasions, cuts, or scratches on a child’s skin should be treated immediately after their detection with antiseptic solutions (diamond green, methylene blue, fucorcin, etc.).
- When cleaning the ear canals in children (as well as in adults), sharp objects should not be used to avoid causing injuries that provoke the development of furunculosis.
- Children's clothing must correspond to weather conditions so that during a walk the child does not overheat, but also does not freeze. In addition, you should avoid purchasing clothes for children made from hard synthetic fabrics that can chafe the skin.
- Children with any pustular skin diseases should be isolated from the children's group, because in close contact, these diseases can be contagious.
- Treatment of all chronic diseases the child has is mandatory.
- A child with a boil should not be bathed in a bath, since the abscess can spontaneously open at any time, and then all skin integuments will be exposed to the danger of Staphylococcus aureus. The area where the boil is located cannot be washed at all; it is only permissible to wash the child and give him hygienic wipes. If there are several boils, and they are located in different parts of the body, water procedures are strictly prohibited.
- If a child has a boil, you should not try to open it and squeeze out the pus yourself: this can even lead to such a serious complication as sepsis. Opening a boil is a medical procedure.
Summary for parents
Be attentive to your children, not only babies, but also teenagers. Do not leave any microtraumas on your child’s skin untreated. And do not try to treat furunculosis in children on your own; consult a doctor immediately.
Which doctor should I contact?
If a child develops a boil, it is best to consult a dermatologist. After examination, a small patient may be referred for treatment to a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, hematologist, infectious disease specialist, or immunologist. A cosmetologist will help eliminate the consequences of furunculosis. A nutritionist will tell you about the nutritional characteristics of this disease. In some cases, the help of a surgeon is required.



