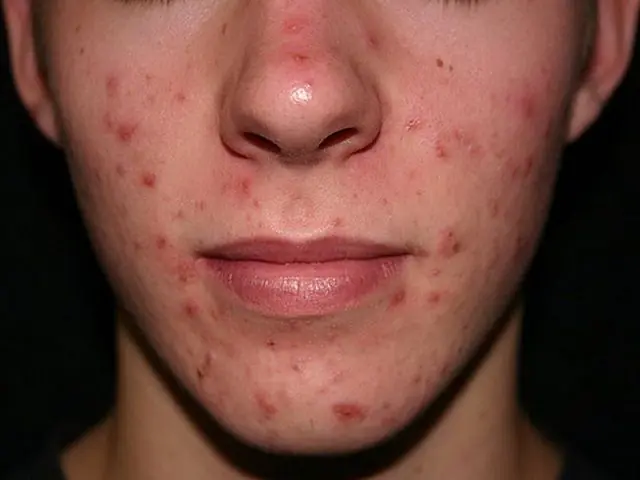
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
Syphilitic folliculitis is an acne-like syphilide that manifests itself with a syphilis relapse. The disease is accompanied by non-scarring baldness (alopecia). Partial or complete hair loss most often occurs in certain areas of the head: in the area of beard and mustache growth. In its advanced form, syphilitic acne is extremely difficult to cure. Therefore, it is important to make a timely diagnosis and prescribe the correct therapy.
Causes of syphilitic folliculitis
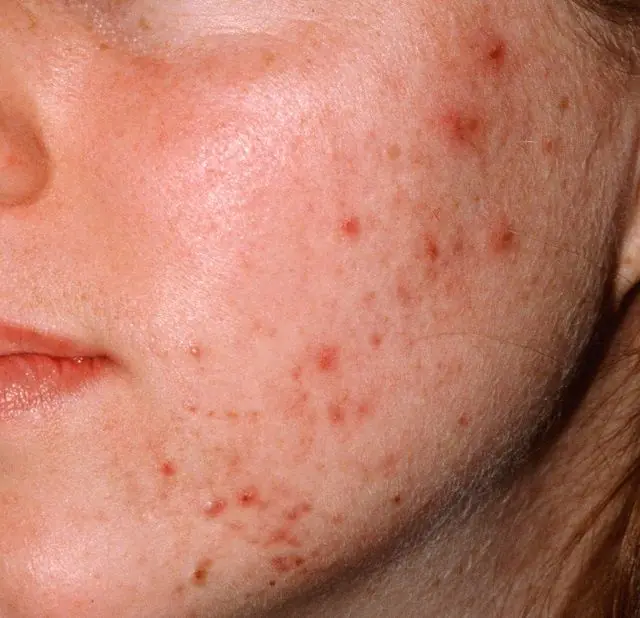
Infection of the follicle begins due to minor bruises of the dermis: abrasions, excoriation, scratches, separation of pus through small skin defects. The risk of damage is increased in persons with weak immunity and in those suffering from immunodeficiency. Reduced protection of the body's immune system makes it easier for the follicle to become infected and provoke the progression of the disease.
There are superficial and deep folliculitis. This depends on the depth of the lesion and inflammation of the bulb. Since syphilitic folliculitis occurs in people infected with syphilis, this type of disease is more characterized by a deep stage, which is accompanied by hair loss.
Syphilitic folliculitis symptoms
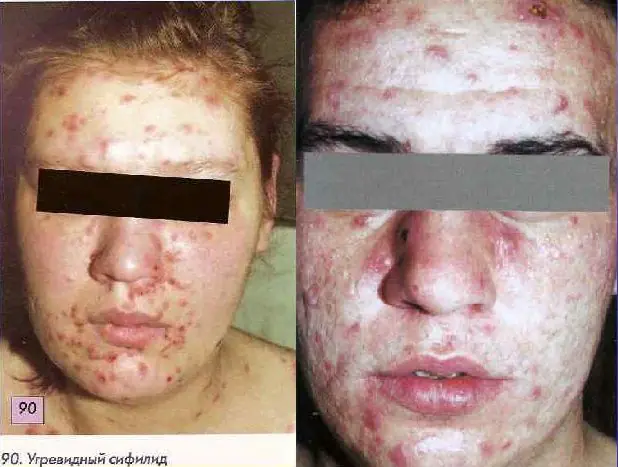
Pictured is syphilitic folliculitis
Syphilitic folliculitis is a serious disease that develops with secondary syphilis. The patient has damage to the skin (mainly in the scalp and face) and mucous membranes. Externally, the disease looks like a rash, in the form of ordinary acne, which leads to frequent errors when making a diagnosis. Therefore, the patient does not immediately turn to a specialist, which is the reason for the rapid development of the disease.
The hair follicle consists of the hair root and surrounding tissue. A blister of pus forms in it, which surrounds the hair shaft and the sebaceous gland. Feeling the damaged follicle is painful. In addition, dense contents are palpated. Hair falls out in the affected areas and non-scarring alopecia forms. The color of the papules is bright pink, but over time they fade. The rashes are characterized by heterogeneity; they do not merge or increase in size.
Purulent syphilitic folliculitis develops when the body is intoxicated and is especially manifested in cases of weakened immunity, vitamin deficiency and concomitant infections. The patient experiences a loss of strength. The lymphatic system is also affected. Regardless of the form of the disease, an enlarged liver and abnormal liver tests are observed. With an exacerbation of syphilide, the symptoms expand with the following signs:
- fever;
- malaise;
- weakness;
- arthralgia;
- soreness of the lymph nodes and an increase in their size;
- hyperpigmentation;
- chancre;
- asymmetrical arrangement of formations.
If you have symptoms of syphilitic folliculitis, you should consult a dermatovenerologist.
Diagnosis of syphilitic folliculitis
Diagnosis if syphilitic folliculitis is suspected:
- Analysis of the condition of the hair follicle.
- Analysis of the infectious agent.
- Exclusion of a special origin of the disease (syphilis, gonorrhoea).
At the appointment, a dermatologist examines the rash and performs dermoscopy to determine the depth of damage to the blisters. The secretion from the purulent follicles is collected for research, bacteriological culture, examination for fungus and spirochete pallidum (the causative agent of syphilis). To exclude gonorrhea and syphilis, PCR diagnostics and RPR testing are performed. If necessary, an immunogram and blood sugar test are prescribed.
In its advanced form, syphilide is difficult to treat, so timely diagnosis will allow for proper therapy and avoid complications. If treatment is ineffective, irreversible consequences may occur for internal organs and the nervous system. If treatment is not carried out in time, folliculitis will be complicated by a boil, abscess, carbuncle, hidradenitis and phlegmon.
With secondary syphilitic folliculitis, there are no symptoms of damage to internal organs. It is differentiated from dermatological diseases. Syphilitic lesions can be established through immunological tests and microscopic examination of the contents of the follicles.
Treatment of syphilitic folliculitis

Syphilitic folliculitis is a contagious infectious disease that requires complex treatment. Since the disease occurs in people infected with syphilis, it is impossible to get rid of ulcers without treating the underlying disease. Antifungal drugs and antibiotics are prescribed as maintenance therapy. The emphasis is on antibacterial therapy. The lesions are treated with antiseptic solutions. To prevent the spread of the disease, healthy areas of the skin are treated with salicylic or boric alcohol. Treatment of syphilitic folliculitis is carried out in a hospital.
At the same time, immunotherapy is prescribed, which increases the effectiveness of the main treatment. A set of therapeutic measures is selected by a dermatovenerologist. To strengthen immune defense use:
- Phagocytosis stimulants that promote the formation of antibodies.
- Interferon preparations that are effective in the early stages.
- Pyrogens that increase the body's resistance to infections.
- Enzyme therapy that improves blood circulation and restores tissue.
- Immunocorrectors of the T-cell level, which have a positive effect on lymphocytes, phagocytes and prevent the exacerbation of acne in the future.
- Preparations of vitamins B and C.
- Biogenic stimulants that increase protective functions.
With proper treatment, syphilide goes away, the rash disappears after 1.5–2 months. The disease may return 4 months after the initial manifestation. Relapse may last for 5 years or more.
During the treatment period, the patient must observe the rules of hygiene and proper nutrition. It is important to reduce fat content and increase the amount of protein foods. It is unacceptable to have sexual activity until the disease completely disappears.
- Related article: Treatment of folliculitis with folk remedies



