What is dyspepsia and why does it occur? Symptoms and diagnostic methods. Methods of treatment with drugs and folk remedies, preventive measures.
The content of the article:- What is dyspepsia
- Reasons for development
- Symptoms and diagnosis
- Treatment methods
- Medicines
- Folk remedies
- Diet
Dyspepsia is a physiological condition that is accompanied by digestive disorders and manifests itself in the form of pain in the epigastrium, nausea, heaviness in the abdomen, heartburn, and rapid satiety with food. Dyspepsia can be organic and functional. Depending on the type of disorder, the gastroenterologist selects the appropriate treatment regimen.
What is dyspepsia?
Dyspepsia syndrome is a digestive disorder, the leading symptom with which patients turn to gastroenterologists. Middle-aged females are at risk.
Dyspepsia develops as a result of increased sensitivity of special receptors in the stomach and impaired intestinal motility, which provoke a disruption in the production of digestive juice. In this case, patients complain of heaviness in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, pain (especially on an empty stomach), overcrowding and a feeling of early satiety with food. Food masses move from the stomach to the intestines at a slow pace.
Gastric dyspepsia can be organic or functional. The development of the organic form of the disease is caused by the influence of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract: gastritis, peptic ulcers, inflammatory reactions in the stomach and pancreas. The development of functional dyspepsia is said to occur when there are no obvious physiological disorders that could provoke the syndrome.
Depending on the cause that provoked the disorder, the following types of dyspepsia are distinguished:
- Enzymatic. Develops due to insufficient amounts of digestive enzymes. In turn, it is divided into gastrogenic, pancreatogenic, enterogenic, and hepatogenic types.
- Nutritional pathological. This process is caused by insufficient nutrients in the diet.
- Infectious. This type of dyspepsia is caused by intestinal infections: dysentery, salmonellosis.
- Intoxicating. Caused by acute poisoning, extensive traumatic lesions, severe general infections.
- A disorder that is accompanied by malabsorption. Occurs as a result of impaired absorption of nutrients in the intestine.
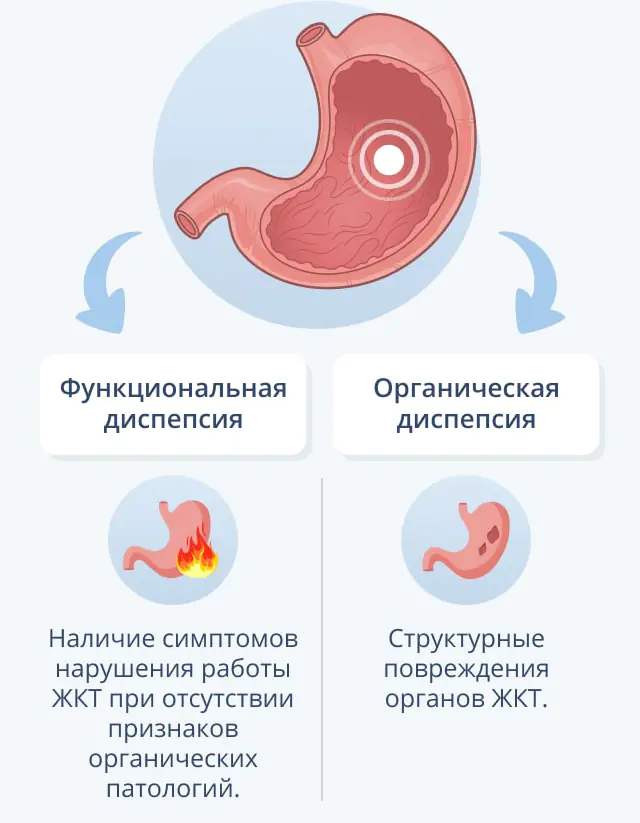
Functional gastric dyspepsia can be ulcer-like, dyskinetic, reflux-like, or vague.
Despite the fact that dyspeptic disorders can significantly impair the quality of life, the prognosis in most cases is favorable. Competent, timely treatment and elimination of the root cause that provoked the manifestations of dyspepsia can help you get rid of the feeling of discomfort, pain, and heartburn. It is necessary to remember the undulating course of the disease and the high probability of re-exacerbation if the diet and other recommendations of the attending physician are not followed.
Causes of dyspepsia
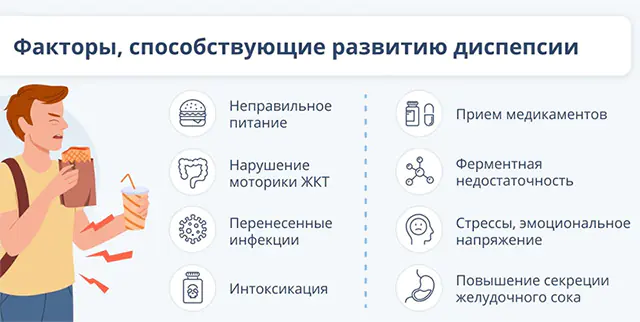
The causes of dyspepsia are associated with excess production of hydrochloric acid, nutritional disorders, use of medications, psycho-emotional disorders, infection of the mucous membranes with Helicobacter pylori, and gastric motility disorders.
Insufficient intake of vitamin C, as well as B vitamins, can also cause the development of the disorder. In children, dyspepsia often develops against the background of food toxic infections.
The described factors lead to an increase in the sensitivity of receptors located in the stomach, disturbances in motility and the production of digestive juice. Such disorders provoke heaviness in the stomach, nausea, vomiting, and sensations of a distended stomach.
Dyspeptic syndrome is often accompanied by the progression of cholelithiasis, allergies, GERD, gastric and duodenal ulcers, pancreatitis, tumors, cholecystitis, gastritis, and digestive tract infections.
Symptoms and diagnosis of dyspepsia
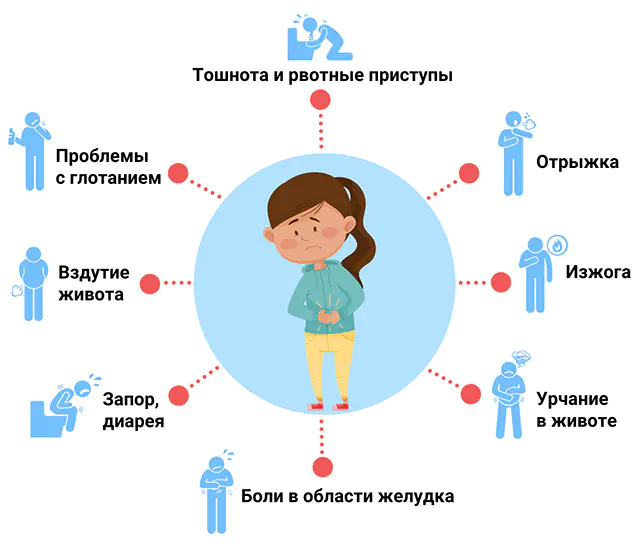
Symptoms of dyspepsia (pictured above) often manifest as complaints of discomfort and pain in the abdominal region, which affect the upper third of the abdomen, its midline. During endoscopic and ultrasound examinations, organic changes in the gastrointestinal tract are not detected. The patient notes that he feels better after bowel movement.
Functional dyspepsia occurs in several variants, depending on the form of the pathological process:
- Ulcer-like. It is accompanied by intense pain, which intensifies on an empty stomach and at night. Symptoms worsen after psycho-emotional stress. To reduce pain, it is enough to eat and take an antacid. During an attack, the patient feels fear.
- Dyskinetic. Complaints of a feeling of fullness in the stomach, heaviness, nausea, bloating. After vomiting, the patient feels relieved and quickly satiates with food.
- Reflux-like. Complaints of heartburn, burning pain behind the chest, sour belching.
- Uncertain. This form manifests itself in different variations; there is no specific clinical picture.
Functional dyspepsia tends to last a long time, without progressive symptoms. Feeling better can be easily alleviated with the help of medications and diet.
Diagnosis of dyspepsia begins with a face-to-face examination and oral questioning of the patient. Ultrasound diagnostics and blood tests (general analysis and biochemical parameters) are required. The coprogram allows you to determine whether there are blood impurities in the stool and evaluate the digestive activity of the gastrointestinal tract. Using esophagogastroduodenoscopy, the doctor examines and evaluates the condition of the inner surface of the esophagus.
The decision on how to treat dyspepsia is made by the gastroenterologist according to the results obtained. Dyspepsia must be differentiated from dysphagia, pathological weight loss, and the development of bleeding from various parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
To assess how relaxed the stomach walls are, antroduodenal manometry is used. If necessary, an additional x-ray of the stomach is prescribed.
As the pathological process progresses, diagnostics are prescribed to detect Helicobacter pylori infection: a breath test, as well as the presence of antibodies in the blood plasma. After carrying out the necessary studies, the patient again turns to the gastroenterologist. Comprehensive diagnostics allows you to exclude organic pathologies, confirm the diagnosis and select the appropriate treatment regimen.
Methods for treating dyspepsia
Treatment of the disease requires an integrated approach. The main goals of therapy are to reduce the severity of clinical manifestations and prevent the recurrence of the disorder. It is necessary to adjust the diet, normalize the psycho-emotional state, and give up bad habits. Daily moderate physical activity is indicated to normalize the general condition and restore intestinal motility. It is also necessary to refrain from the uncontrolled use of drugs that cause unwanted side effects from the gastrointestinal tract: acetylsalicylic acid, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. To normalize the psycho-emotional state, swimming, yoga, and working with a psychotherapist if necessary are recommended.
Medicines for dyspepsia
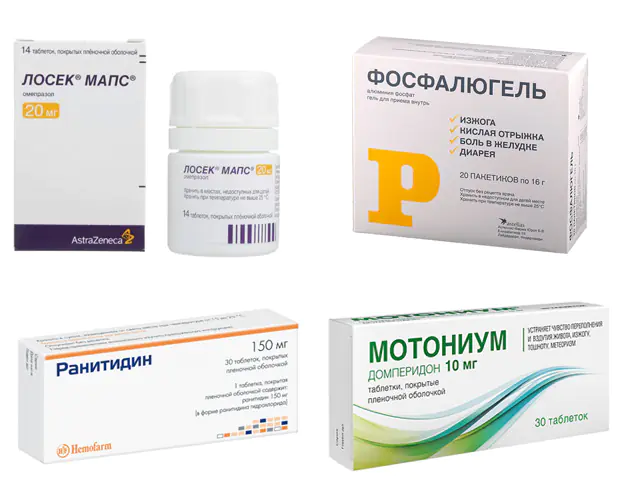
The doctor selects medications for dyspepsia, taking into account the type of disorder, age, individual characteristics of the patient’s body, and concomitant disorders of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Effective medications for the treatment of dyspepsia.
- Losek. Proton pump inhibitor based on Omeprazole with antiulcer activity. Inhibits the last stages of the formation of hydrochloric acid and is used in the complex treatment of ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum. Before use, exclude the presence of neoplasms. The cost of the drug is 250 rubles. (97 UAH). Analogs: Zerocide, Chrismel, Losek Maps, Cisagast.
- Zantin. H2-histamine receptor blocker based on Ranitidine with antiulcer effect. Maintains effectiveness for up to 12 hours. The tablets are taken twice a day, including before going to bed. In severe cases, a solution for intramuscular administration is used. The price of the drug is 300 rubles. (116 UAH). Analogue - Ranitidine.
- Phosphalugel. Antacid for the treatment of ulcer-like dyspepsia based on aluminum phosphate, agar-agar, pectin, potassium sorbate. Available in the form of a gel with a sweet taste. Does not alkalize gastric juice and maintains natural physiological acidity. Does not provoke secondary hypersecretion of hydrochloric acid. The gel is used in its pure form or pre-diluted in water. Take 1 sachet up to 3 times a day. If the patient is bothered by soreness between meals, more frequent use is possible. Cost - 490 rubles. (190 UAH). Analogue - Alfogel.
- Motonium. Prokinetic for the treatment of dyskinetic forms of dyspepsia, which normalizes the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Available in the form of tablets for internal use. Restores intestinal peristalsis and is quickly absorbed after internal administration. Take 1 tablet half an hour before meals. three times a day. If necessary, the product can be used before bedtime. Failure to comply with the dosage regimen is fraught with increased drowsiness and disorientation. As therapy, it is recommended to rinse the stomach and use sorbents. The price of the drug is 180 rubles. (70 UAH). Analogs: Motilak, Domperidone, Motonium, Passazhiks.
- Neobutin. A drug based on Trimebutin, which normalizes intestinal motility and eliminates pain. The tablets are taken before meals three times a day. Cost - 200 rubles. (77 UAH). Analogue - Trimedat.
- Novo-Passit. This complex medicine based on valerian, lemon balm, St. John's wort, hawthorn, and oldflower is designed to normalize the psycho-emotional state. Available in the form of syrup and tablets for oral administration. Has a sedative effect and eliminates neurotic reactions. Tablets are used three times a day before the main meal. If you experience nausea during therapy, the medicine can be used with meals. It is recommended to refrain from drinking alcohol while taking it. The price is 190 rubles. (73 UAH). The drug has no exact structural analogues.
In more than 20% of cases of dyspepsia treatment, anti-Helicobacter therapy is required. Antibiotics are prescribed only if a breath test and laboratory diagnostics confirm the active growth and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms.
Important! At the first signs of dyspepsia, it is recommended to refrain from self-medication and seek advice from a gastroenterologist. Dyspeptic disorders can be manifestations of other disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, so self-medication can blur the clinical picture and make it difficult to make an accurate diagnosis.Folk remedies for dyspepsia

Traditional treatment of the disease is used as a supplement to medications, diet, and moderate physical activity.
Effective folk remedies for treating dyspepsia:
- A tablespoon of dried black poplar (buds) is poured with boiling water, left for 20 minutes, and taken 1/4 cup three times a day. A tincture can also be prepared from the plant. To do this, the raw materials are poured with alcohol or vodka and left in a dark place for 2 weeks. After which it is poured into a dark glass container and subsequently stored on the refrigerator door. The resulting tincture is taken 10-15 drops, which are pre-diluted in a small amount of liquid. For severe signs of dyspepsia, the product can be used after each meal. After normalization of health - as a means of symptomatic therapy, only if necessary. In case of individual intolerance to the active substance (lacrimation, itching and redness of the skin), it is recommended to avoid using black poplar.
- Blackberry roots are washed and boiled in a large amount of liquid until the water is reduced by half. The resulting product is filtered and mixed with beetroot or pomegranate juice. When intestinal motility slows, take 1/2 glass three times a day.
- Blackberries can also be mixed with calendula in equal proportions, pour boiling water, take 1/2 cup up to 4 times a day. This remedy reduces the inflammatory process, pain, and bloating. The course of treatment is 2-3 weeks, after which a break of 7 days is taken. The course of treatment can be repeated periodically.
- To reduce dyspeptic symptoms, use celery roots. The plant is thoroughly crushed, steamed with hot water and left to act for 3 hours. Take 0.5 cups in small sips 2 times a day during or after meals.
- Fennel and black cumin seeds have a pronounced therapeutic effect. The dried raw materials are mixed in equal proportions, poured with boiling water, and left for 20 minutes. Take 100 ml after each meal. This drink combats increased gas formation, pain and a burning sensation in the epigastrium, accelerates the regeneration of damaged tissues and reduces inflammation. If well tolerated, this recipe can be used on an ongoing basis. Black cumin can be replaced with marjoram or basil.
- If the patient complains of prolonged hiccups, the use of dill seeds is indicated. The plant is brewed with boiling water, left for 10 minutes and consumed in 50 ml. Dill also reduces bloating, improves digestion, has a moderate diuretic effect, and can enhance lactation in nursing women.
- To restore metabolic processes, the use of a mixture of aloe juice and light natural honey is recommended. The components are mixed, 1 teaspoon is dissolved in 1/2 glass of water and consumed in the morning and evening. This allows you to improve digestion, cope with pain, belching, and discomfort in the abdomen.
Diet for dyspepsia

A diet for dyspepsia involves avoiding fried, spicy, overly spicy foods, carbonated drinks, and coffee. Portions are small, food must be chewed thoroughly. The diet should contain a sufficient amount of fiber (plant fiber), proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
In addition, for dyspepsia, it is necessary to exclude allergenic foods that cause hypersensitivity reactions, especially gluten, dairy products, and simple carbohydrates.
After eating, it is not recommended to immediately take a horizontal position: moderate physical activity is indicated.
Patients who are unable to independently monitor their diet and adherence to the basic principles of a healthy diet are advised to seek advice from a qualified nutritionist.
There is no specific prevention of dyspepsia. In order to prevent discomfort, it is recommended to maintain a healthy lifestyle, adherence to work and rest, and sleep hygiene. Normalization of the psycho-emotional state and elimination of situations that provoke stress are also indicated. To prevent dyspepsia, it is recommended to use a high pillow for sleeping and walk for 30-40 minutes after eating, and refrain from overeating.
Video about what dyspepsia is and how to treat it:



