Such injuries cause a person to develop a severe general condition due to changes in blood composition, disruption of the central nervous system and the functions of internal organs due to intoxication. Timely and correct assistance will help reduce the damage from the burn to a minimum.
Classification of burns
The severity of the damage depends on several factors, including the height of the temperature, the duration of exposure to the harmful factor on the skin/mucous membranes, and the location of the injury. Especially serious damage is caused by steam and flame under pressure. More often people experience burns to the limbs and eyes, less often to the head and torso. The larger the surface of the damaged tissue and the deeper the damage, the higher the danger for the victim. Thus, a burn of 30% of the body surface is often fatal.
To provide first aid, it is important to know what type of burn was received. The speed and degree of tissue restoration of the patient after injury largely depends on how correctly pre-medical measures were chosen. Incorrect actions that do not correspond to the type of burn can aggravate the situation, further harming a person’s health.
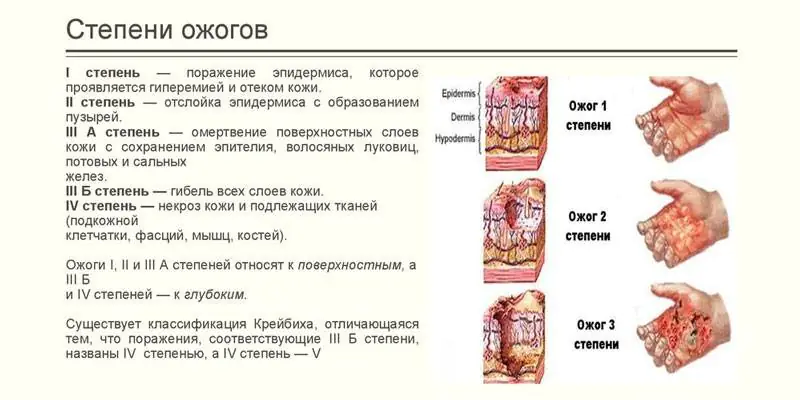
According to the depth of the lesion
Minor burned areas of the body can be treated at home without resorting to medical help.
There are the following degrees of injury from fire, electricity and chemicals:
- First. These are superficial tissue injuries in which swelling, redness of the skin, and burning pain are observed. Symptoms disappear within 3-6 days, after which the dermis begins to renew itself through exfoliation. Pigmentation remains at the site of injury.
- Second. Characterized by the appearance of blisters (blisters filled with liquid). In the damaged area, immediately or after some time, the surface layer of skin begins to peel off. The blisters burst, which is accompanied by intense pain. If tissue infection does not occur, healing occurs in approximately 2 weeks.
- Third. Necrosis (necrosis) of the deep layers of the dermis occurs. After such burns, scars are sure to remain.
- Fourth. This stage is characterized by necrosis and charring of deep-lying tissues. Damage may affect muscles, bones, subcutaneous fat, and tendons. Healing occurs very slowly.
By type of damaging factors
Providing first aid for a burn depends on the nature of the impact. There are several types of damaging factors by which burns are classified.
Type of burn injury
Contact with fire, boiling water, steam, hot objects.
As a rule, the hands, face, and respiratory tract are affected. When contacting boiling water, the damage is often deep. The steam can damage the respiratory tract; it does not leave deep damage on the skin. Hot objects (for example, hot metal) cause blisters and leave deep burns of 2-4 degrees of severity.
Contact with the skin of aggressive substances - acids, caustic alkalis, salts of heavy metals.
Acids cause shallow lesions, with a crust appearing on the injured areas, which prevents the acid from penetrating deep into the tissue. Alkalies can leave deep damage to the skin. Zinc chloride and silver nitrate can only cause superficial lesions.
Contact with conductive materials.
Electrical trauma causes very serious, dangerous consequences. The current quickly spreads through tissues (through the blood, brain, nerves), leaves deep burns and causes disruption of organs/systems.
Ultraviolet, infrared or ionizing radiation.
UV radiation is dangerous in the summer: injuries are shallow, but can be extensive, as a rule, they are grade 1-2. Infrared radiation provokes damage to the eyes and skin. The degree of damage depends on the duration and intensity of exposure to the body. Not only the dermis, but also nearby tissues and organs suffer from ionizing rays, although their damage is shallow.
First aid for burns
The first thing to do is to eliminate the damaging factor. After treating the affected areas of the body (the choice of method depends on the type of burn), an aseptic dressing should be applied to prevent infection of the body. First aid for burns also includes measures to prevent shock and transport the victim to a medical facility. It is extremely important to perform any actions carefully to avoid further tissue damage. First aid includes:
- extinguishing burning clothing;
- evacuation of a person from a dangerous zone;
- removing smoldering or heated clothing;
- careful removal of stuck things (they are cut off around the injury);
- applying an aseptic dressing (if necessary, even over the remaining piece of clothing).
In the absence of these products, it is permissible to use clean cotton fabric, ironed or treated with an antiseptic (alcohol, vodka, potassium permanganate, etc.).

Pre-medical measures
The rules for providing first aid for burns provide for pre-medical measures only for grade 1-2 injuries. If the affected area covers an area of more than 5 cm, multiple blisters are observed on the tissues, and the victim feels intense pain, you should immediately call an ambulance. For serious burn injuries of grade 2 or higher, or if more than 10% of the person’s body is damaged, urgently hospitalize. It is prohibited to do the following as part of first aid:
- move or carry the victim without first checking the pulse, breathing, presence of fractures, after loss of consciousness due to electric shock or other types of injuries;
- treat burned tissues with any available means (butter or sour cream), this will aggravate the situation, since fatty foods disrupt the heat transfer of the skin;
- clean the wound yourself in the absence of sterile bandages, cover the affected areas with fabrics with lint or cotton wool;
- apply a tourniquet without an open wound with serious blood loss (this measure will lead to tissue death and amputation of the limb);
- apply bandages without understanding how to do it correctly (if there is an urgent need, you can easily wrap the area of the burn injury with sterile material without pulling the burned area tightly);
- puncture blisters (this will cause infection);
- tear off clothes stuck to the wound (dry tissues should first be soaked, or better yet, wait for the doctors to arrive).
First aid for thermal burns
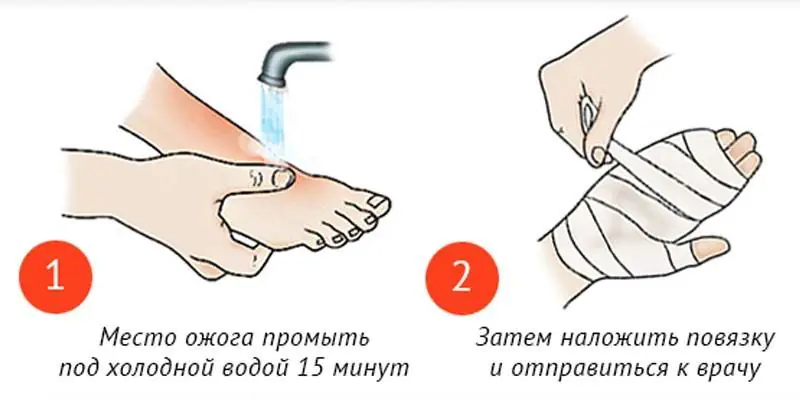
Mild injuries can often be successfully treated at home, but only if first aid was provided correctly. When receiving thermal injuries, after the cessation of exposure to the traumatic factor, you need to:
- Cool the injured area under running cold water (the procedure should last at least 10-20 minutes).
- Treat the skin with an antiseptic (but not iodine), then lubricate it with an anti-burn agent.
- Apply a sterile, loose bandage to the wound.
- In case of intense pain, give the victim an anesthetic - Nurofen, Aspirin, Nimesil or others.
- If necessary, transport the patient to a medical facility.
With chemical
First, it is imperative to determine what substance caused the damage to the skin/mucous membranes. First aid for chemical exposure includes the following measures:
- The injured area is thoroughly washed with water for at least 15 minutes. The exception is when the burn is caused by substances that react with water, for example, quicklime.
- If the tissues have been burned with a powdery substance, remove it with a dry cloth before washing.
- An antidote is used (for alkaline exposure, it is recommended to use a weak solution of citric acid or vinegar; for lime burns, the skin is treated with fat or lard, the acid is neutralized with a soda solution).
- If the victim has swallowed a chemical substance, be sure to perform gastric lavage.
With electric
First medical aid for burns consists of isolating the victim from the damaging factor, after which you should check the victim for breathing and pulse and call an ambulance. If there are no vital signs, you need to:
- Perform a closed cardiac massage.
- Breathe mouth-to-mouth or mouth-to-nose.
- Carry out resuscitation measures until the ambulance arrives.
- Superficial injuries caused by electric shock are treated in the same way as a thermal burn.

A burn is tissue damage caused by various factors: high temperatures, ionizing and ultraviolet radiation, acids, alkalis, electric current, incendiary mixtures.
Thus, thermal, electrical, solar, chemical and radiation burns are distinguished. Most often the skin, eyes and respiratory tract are burned.
Thermal skin burns
Thermal skin burns are the most common type of household burns.
Clinical manifestations
Based on the severity of skin damage and the depth of tissue damage, the following degrees of burns are distinguished:
I degree - persistent redness of the skin and severe pain are noted at the site of the lesion;
II degree - in the area exposed to high temperature, bubbles with transparent contents form, the affected area is very painful;
III degree - necrosis (necrosis) of all layers of the skin. Upon examination, a combination of deathly pale (dead) areas of skin, areas of redness and blisters is revealed; all types of sensitivity disappear in the burn area, there is no pain.
IV degree - not only the skin, but also the tissues located underneath it (fatty tissue, muscles, bones, internal organs) are subject to necrosis; upon examination, charring of the skin is revealed.
More often there is a combination of different degrees of burns. Their III and IV degrees refer to deep burns, are accompanied by aggravation of the general condition of the victim, require surgical intervention, and heal with the formation of deep scars. The severity of the victim’s condition depends on both the degree of the burn and the area affected. Second degree burns, covering more than 25% of the body surface, as well as third and fourth degree burns, covering more than 10% of the body surface, are extensive and are often complicated by the development of burn shock. The victim, who is in a state of burn shock, is restless, tries to escape, and is poorly oriented in what is happening; after some time, excitement is replaced by apathy, prostration, adynamia, and a drop in blood pressure. In children, people over 65 years of age, and weakened patients, burn shock can develop even with a smaller area of damage.
First aid for thermal skin burns
The very first action should be to stop the impact of the thermal factor on the victim: it is necessary to take the victim out of the fire, put it out and remove his burning (smoldering) clothes. The burned areas of the body are immersed in cold water for 10 minutes, the person (if he is conscious) is given any painkiller - metamizole sodium, tramadol; in severe cases, narcotic analgesics (promedol, morphine hydrochloride) are administered. If the burned person is conscious and the burn surface is quite extensive, it is recommended to give him a solution of table salt and baking soda to drink in order to prevent dehydration.
First degree burns are treated with ethyl (33%) alcohol or a 3-5% solution of potassium permanganate and left without a bandage. For burns of II, III, IV degrees, after treating the burn surface, apply a sterile bandage to it. After these activities, all victims must be taken to the hospital. Transportation is carried out on a stretcher. For burns of the face, head, upper half of the body, the burned person is transported in a sitting or half-sitting position; for lesions of the chest, abdomen, front surface of the legs - lying on your back; for burns of the back, buttocks, back of the legs - lying on your stomach. If hospitalization in the near future for any reason is impossible, provide assistance to the victim on the spot: in order to anesthetize the burn surfaces, they are sprayed with a 0.5% solution of novocaine for 5 minutes (until the pain stops), bandages are applied to the burns syntomycin emulsion or streptocid ointment. They continue to feed him a solution of soda and salt, and periodically give him painkillers.
Chemical burns of skin and mucous membranes
The difference between chemical burns and thermal burns is that with chemical burns the damaging effect of the chemical on body tissue continues for a long time - until it is completely removed from the surface of the body. Therefore, an initially superficial chemical burn, in the absence of proper assistance, can turn into a third or fourth degree burn within 20 minutes. The main chemicals that cause burns are acids and alkalis.
Clinical manifestations
As a result of an acid burn, a scab (crust) of dead tissue is formed. When exposed to alkalis, wet necrosis (necrosis) of tissue occurs and a scab does not form. It is necessary to pay attention to these signs, since measures aimed at helping a victim with burns from acids and alkalis differ. In addition, if the patient is conscious and adequately perceives reality, be sure to check with him what substance he was in contact with. With chemical burns, as with thermal burns, there are 4 degrees of severity of tissue damage.
First aid for chemical and mucous skin burns
The victim is removed from clothing soaked in a damaging agent (acid or alkali), and the skin is washed with running water. There is a known case when a girl who worked in a chemical laboratory died from an acid burn simply because the man who was nearby was embarrassed to undress her. For burns caused by exposure to acid, apply sterile wipes moistened with a 4% solution of sodium bicarbonate to the burned surfaces; in case of alkali burn - sterile wipes moistened with a weak solution of citric or acetic acid (in enterprises where there is contact with alkalis or acids, the first aid kit must have a supply of these substances). The patient is given any painkiller and is urgently hospitalized in the nearest hospital (preferably in a hospital with a burn department).
Eye burns
When the organ of vision is burned, isolated burns of the eyelids, conjunctiva or cornea, or a combination of these injuries, may occur. Eye burns, like skin burns, occur under the influence of various factors, the main of which are lesions associated with exposure to high temperatures, chemicals, and radiation. Eye burns are rarely isolated; as a rule, they are combined with burns of the skin of the face, head and torso.
Thermal burn of the eyes
The causes of thermal burns to the eyes are hot water, steam, oil, and open fire. As with skin burns, they are usually classified into 4 degrees of severity.
Clinical manifestations
With a first-degree eye burn, slight redness and slight swelling of the skin of the upper and lower eyelids and conjunctiva are noted. With a second degree burn to the eyes, blisters appear on the skin, and films consisting of dead cells appear on the conjunctiva and cornea of the eye. A third degree burn affects less than half the area of the eyelids, conjunctiva and cornea. The dead tissue looks like a white or gray scab, the conjunctiva is pale and swollen, and the cornea looks like frosted glass. With IV degree burns, more than half the area of the eye is affected; the entire thickness of the skin of the eyelids, conjunctiva, cornea, lens, muscles and cartilages of the eye are involved in the pathological process. The dead tissue forms a scab of gray-yellow color, the cornea is white, similar to porcelain.
First aid
The substance that caused the burn is removed from the victim's face. This is done using a stream of cold water and a cotton swab. Continue to wash the eye with cold water for some time to cool it down. The skin around the eye is treated with ethyl (33%) alcohol, albucid is instilled into the conjunctival sac, and a sterile bandage is applied to the eye. After first aid is provided, the victim is urgently hospitalized in an eye clinic.
Chemical burns to the eyes
The cause of chemical burns is contact with the eyes of acids, alkalis, medicinal substances (alcohol tincture of iodine, ammonia, concentrated solution of potassium permanganate, alcohol), household chemicals (adhesives, paints, washing powders, bleaches). Chemical substances entering the eye have a pronounced damaging effect, penetrating deeper into the tissue the longer the contact continues.
Clinical manifestations
Chemical burns to the eyes are divided into 4 degrees according to the severity of damage, as with thermal injury. Their clinical signs are similar to thermal burns of the eyes.
First aid
The affected eye is opened, the eyelids are turned out, after which the eyes are washed with a stream of cool water, and pieces of the damaging agent are carefully removed from the conjunctiva. Then albucid is instilled into the palpebral fissure, a sterile bandage is applied to the damaged eye, and the victim is urgently hospitalized in an eye clinic.
Burns of the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus
More often, chemical burns of these organs occur as a result of ingestion of acids and alkalis by mistake or due to a suicide attempt. The most common are burns caused by concentrated acetic acid. Less common thermal burns are the result of exposure to hot liquids (water, oil) or inhalation of hot steam.
Clinical manifestations
Burns of the oral cavity, pharynx and esophagus are accompanied by pain in the mouth, pharynx, and behind the sternum (along the esophagus). The pain intensifies when trying to speak or swallow; There is increased salivation, difficulty breathing (up to suffocation) and swallowing, and the inability to take any food (both solid and liquid). Repeated vomiting may occur, and there is an admixture of scarlet blood in the vomit. An increase in body temperature and an excited state of the victim may be observed. When examining him, one notices the burnt skin on and around the lips and the red, swollen oral mucosa. In case of a chemical burn caused by vinegar essence, a specific vinegar smell emanates from the patient.
First aid for burns of the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus
In case of chemical burns, the stomach is washed with a large amount of cool water (up to 5 l) through a tube. In case of a burn with hot water and oil (thermal), gastric lavage is not performed. If the victim is conscious, he is given to drink 10 ml of a 0.5% solution of novocaine (1 tablespoon), after which he is forced to swallow pieces of ice, vegetable oil in small portions and suck on an anesthetic tablet. The patient is urgently hospitalized in the hospital.
Burns – tissue damage, which can be caused by chemicals, high temperature, sunlight, electric current, x-rays, medications.
Any burns are dangerous not only for tissues, but also for the life of the person who received these burns; they can lead to many complications, including death.
Classification of burns
Human skin is one of the main components of our body, a necessary attribute for water and temperature balance. When damaged, its ability to regulate metabolism is sharply reduced, and the body’s ability to resist bacteria and viruses is also reduced.
A burn is an open lesion of the skin, its appendages, mucous membranes and what is hidden under the skin at the site of the burn.
Burns are divided into several areas:
Reason for receiving:
- Chemical: from various pesticides, cleaning products, etc.;
- Thermal: from hot steam, fire, boiling water, from touching hot household appliances, etc.;
- Electric, from current;
- Radiation, from the sun or other radiation;
- Combined.
By degree of damage:
- 1st degree burns manifest themselves through swelling, redness, and also burning pain, but after three days the redness and swelling disappear, the damaged layer of skin peels off and tissue healing soon occurs.
- 2nd degree burns manifest themselves through severe swelling and redness, the appearance of blisters that are filled with a yellowish but transparent liquid. When the epidermis is removed, a moist pink wound will open. The first three days there is severe pain, but by the end of the first week both pain and inflammation decrease, and after ten days healing begins, while redness and pigmentation remain, but no scars remain.
- 3rd degree burns appear through a brown or grayish scab, while pain at the burn site is not felt as such, but healing is extremely difficult with suppuration and takes a long time. Afterwards, “burnt out” areas remain, in place of which scars will appear in the future. 3rd degree class A, all skin layers are damaged except the germ layer, the deepest, manifested through tense and large blisters. 3rd degree class B, all skin layers are damaged, huge blisters filled with bloody fluid are formed.
- 4th degree burns - complete damage not only to the skin, but also to the fact that underneath it, the scab will be denser and thicker, with obvious signs of charring. Damaged tissue is rejected extremely slowly, healing is accompanied by purulent complications, and in the future scars, tightening and other deformations appear at the sites of such burns.
The location of the lesion is very important; if part of the face or neck is damaged, then the risk of the appearance and development of swelling and inflammation increases, which will lead to problems with breathing, vision, etc. Damage to the upper body leads to restriction of movement and pain when sighing.
The burn itself “lives” its own life, it can mature; after damage has occurred, a first-degree burn gradually turns into a second, or a second-degree burn eventually becomes a third-degree burn.
At first, the burn is sterile, since high temperature kills everything, but later, due to a decrease in protective barriers, inflammation, infection and other problems often arise.
First aid
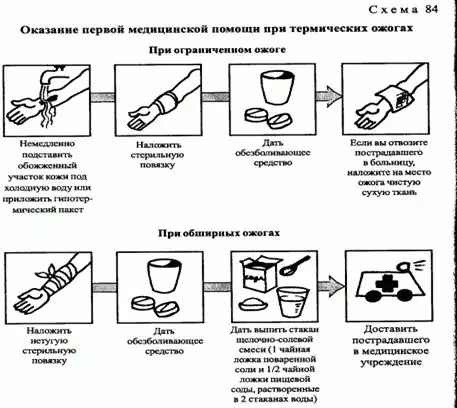
For thermal burns you must:
· Remove all remaining clothing; if there is an area with stuck clothing, do not touch it, but cut off the fabric around it.
· Cool the injured areas, immerse them in cold water, if the burns are not extensive, apply cold compresses.
· Wounds should be covered with sterile cloth.
· Give painkillers, insist on drinking and immobilize the victim.
· Take the victim to a medical facility as soon as possible.
For chemical burns you should:
· Thoroughly rinse areas of the body that have been exposed to chemicals as soon as possible and for 20 minutes. If you were able to rinse only after twenty minutes, then the washing process itself should take about forty minutes. The stream of water should be weak so that with its help the chemicals do not spread to other areas of the skin.
· Next, dissolve a spoonful of soda in a glass of water and wash the wound with the solution to neutralize the effect of the chemical.
· If possible, apply a compress with a neutralizing solution to the burn wound.
· Be sure to offer the victim something to drink and give pain relief.
· At the same time, an ambulance is called.
It is forbidden!
Cool the damaged areas with ice by directly applying it to the wound.
Apply ointments, creams and oils, and especially moisten with alcohol.
For extensive burns, before help arrives you should:
· Trim clothing, but do not remove remnants from damaged areas.
· Cool the areas with cold compresses, but do not immerse them in cold water, just cover the wounds with a damp bandage.
· If there is a need for resuscitation.
· Raise the burned areas of the body above the cardiac level.
Minor burns can be treated at home under the supervision of a doctor, but severe burns should be treated only in specialized centers under the supervision of appropriate doctors in order to avoid the death of the victim and his disability.
Single-post wooden support and methods for strengthening corner supports: Overhead line supports are structures designed to support wires at the required height above the ground and water.
Organization of surface water flow: The largest amount of moisture on the globe evaporates from the surface of the seas and oceans (88‰).

Papillary patterns of the fingers are a marker of athletic abilities: dermatoglyphic signs are formed at 3-5 months of pregnancy and do not change throughout life.



