- Definition of folliculitis and boil
- Clinical picture
- Causes
- Diagnostic features
- Treatment options
- Folliculitis
- Furuncle
- Preventive measures
- Complications
Pyoderma is one of the most common skin pathologies among people of all ages. It is characterized by the development of skin suppuration and has a lot of clinical manifestations. The most common are folliculitis and boils. This article contains expanded information about the differences between these ailments.
Definition of folliculitis and boil
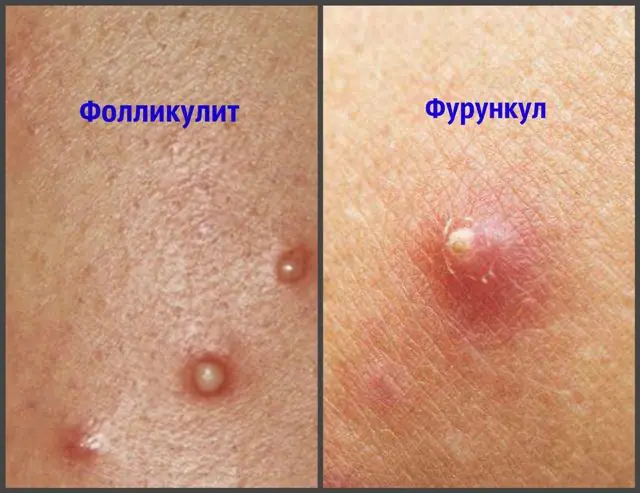
Folliculitis - a disease whose development is provoked by a bacterial infection. It affects the hair follicles, resulting in the formation of pustules (pastula) under the surface layer of the skin. The inflammatory process can appear only on the surface layer of the epidermis or go deeper into the tissue. Without timely treatment, advanced folliculitis often transforms into a furuncle (furunculosis).
Furuncle - This is a deep form of staphyloderma. It is an acute inflammation that affects not only the hair follicle, but also the tissues surrounding it. The entire affected area forms an inflammatory node. The cause of development is recognized as staphylococcus. The inflammatory process is accompanied by suppuration and the development of necrosis.
- Read also about the types of folliculitis
Clinical picture of folliculitis and boils
At first glance, it may seem that folliculitis and boils are very similar and can be confused. But despite this, in reality the diseases have different symptoms.
Symptoms of folliculitis
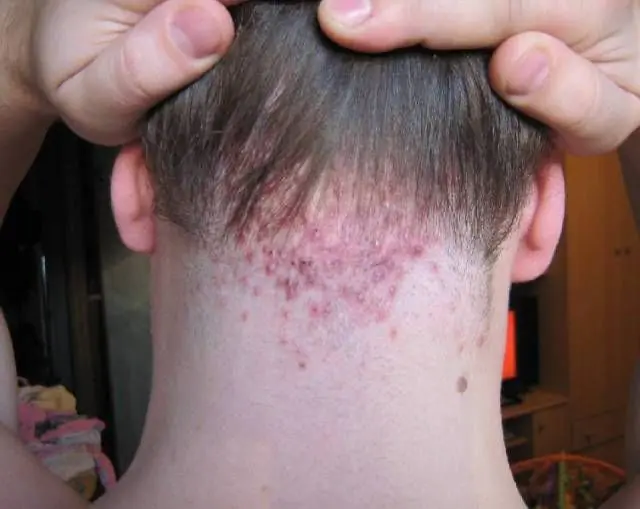
In the photo there is folliculitis on the head
At the initial stage, folliculitis is characterized by the formation of papules and hyperemia around them. Initially, the papules are pink-red in color, and their dimensions can vary in size from a pea to a hazelnut. Gradually, the inflammation increases, and these dense formations increase in size, and pus appears inside them. Thus, without proper treatment and with weak immunity, papules transform into pustules, from the middle of which a hair sticks out. His infection strikes a little later. The hair weakens, so it can be easily removed.
The localization is completely varied, but mainly areas with an abundance of vellus hair are susceptible to infection - on the skin of the legs, thighs, forearms, as well as on the back of the neck. Sometimes pastulas appear in places where the body rubs against clothing. Coarse and curly hair bends in different directions and can grow into the skin, which causes a symptom of folliculitis such as irritation, even without the spread of infection.
- See also symptoms of oil folliculitis
Symptoms of a boil
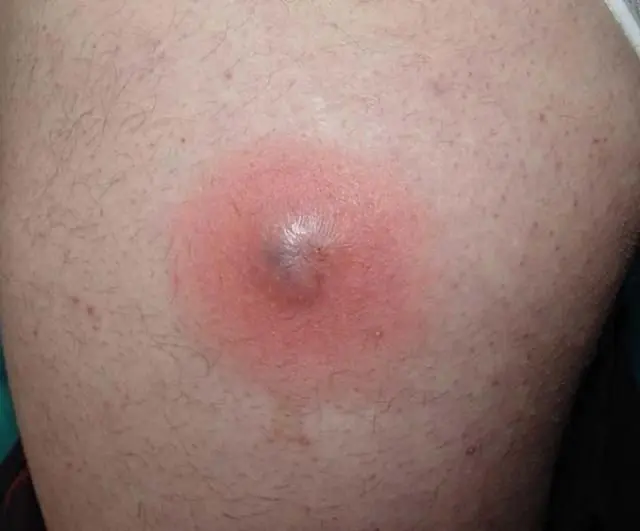
Photo of a boil on the leg
At the initial stage of the disease, when the inflammatory process is just beginning, the boil can be small in size, not exceeding the size of a pea. This resembles the manifestation of folliculitis. However, the process quickly gains momentum, and the infiltrate noticeably increases in size, over time it becomes up to 3 cm in diameter.
Its compaction is observed. The source of inflammation goes deep into the skin and involves the surrounding connective tissue and sebaceous gland. Thus, a congestive-hyperemic node is formed, cone-shaped, noticeably rising above the surface of the skin.
Papules have a purulent center, from which a white, slightly blood-stained substance often oozes. The color of the inflamed areas becomes dark red over time.
After 4-5 days, an involuntary opening of the abscess occurs. Purulent masses flow out of it, and rejection of the necrotic core is observed. Under the influence of drugs and the internal forces of the body, the affected area is cleansed. Usually during this period the patient experiences general symptoms of intoxication, which include malaise, headache, increased weakness, and loss of appetite.
Quite often, a boil is accompanied by more alarming symptoms. Many people note a deterioration in their overall health with a sharp rise in temperature. Soreness and aches appear in the body. In some cases, throbbing pain occurs. It is noteworthy that if single boils occur, then debilitating manifestations of the disease may not be observed.
All symptoms disappear after the pus is completely removed from the tissues and the swelling subsides. From this moment, the process of healing and restoration of tissue structure begins. A scar most often forms on the affected area. It has a red-blue color for some time, but over time it fades and becomes almost invisible.
The localization of the boil is varied. It can form over the entire surface of the skin where there are hair follicles. But, as a rule, such suppurations occur on the back of the neck, on the forearms, and often appear on the face, in the lumbar region, on the buttocks, thighs, and mammary glands.
The exception is suppuration around the ears, nose and fingers. They are considered especially painful. Moreover, if a person has a weak immune system, then this pathology can strike many times. The disease may persist for several years in a row with short breaks, or it may appear once in a lifetime.
Causes of folliculitis and boils
The reason for the development of both diseases is the same numerous external and internal factors to which a person is exposed. This includes ecology, lifestyle, individual characteristics of the body, and much more. But it is worth noting that the causative agents of the diseases are different - this is the important difference between folliculitis and boils.
Causes of folliculitis
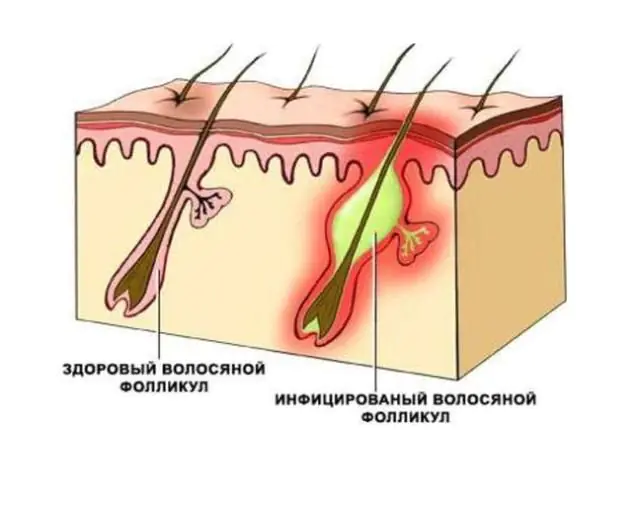
The causative agents of folliculitis are microorganisms of various kinds. Various viruses, fungal microorganisms, bacteria, etc. can provoke the inflammatory process. It is worth understanding that just getting the pathogen on the skin is not enough for infection to occur. Numerous factors allow the pathogenic microbe to become active, which can be divided into two groups: external (exogenous) and internal (endogenous).
Exogenous factors include:
- Ignoring personal hygiene rules;
- Injury to the skin and lack of proper antiseptic treatment, lack of fixing bandages to protect from contact with the external environment;
- Wearing tight, tight synthetic clothing;
- Hypothermia of the body;
- Climatic and environmental conditions, for example, high temperature combined with high environmental humidity, water and air pollution, etc.;
- Abuse of cosmetics or use of low-quality cosmetics;
- Stressful situations.
Endogenous factors include:
- Reduced immunity;
- Features of the skin, for example, hyperhidrosis, a tendency to clogged pores, excessive activity of the sebaceous glands;
- Diabetes mellitus and any other metabolic disorders;
- Liver and gastrointestinal diseases;
- Exhaustion of the body due to non-compliance with the work and rest regime or due to a lack of vitamins and minerals;
- Bad habits - drinking alcohol, any drugs, smoking tobacco;
- Lack of adequate nutrition;
- Anemia;
- Long-term therapy with steroid drugs, antibiotics, etc.
- See also causes of chronic folliculitis
Causes of boils
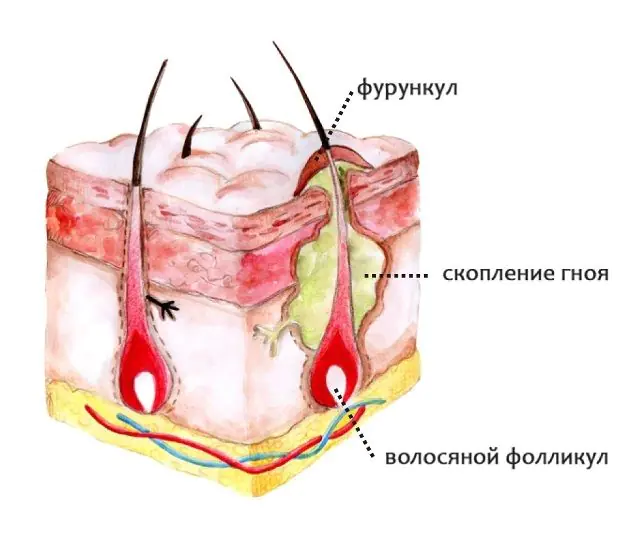
Some bacteria can cause purulent inflammation on the skin in the form of a boil. The most common causative agent of furunculosis is Staphylococcus aureus. It can be present in the human body without affecting his health in any way. This microorganism can live on the skin and/or mucous membranes, without causing harm, but waiting for a special “convenient” moment. When the integrity of the epidermis is compromised, the bacterium penetrates through the injury and provokes the development of a purulent-inflammatory process in the hair follicle and sebaceous gland.
Predisposing circumstances to the appearance of symptoms of a boil are the presence of diabetes mellitus, hematological diseases, hormonal imbalances, HIV infection, etc. They significantly reduce the protective functions of the human body. If they are present, the course of the disease is complicated and may be more protracted and more difficult to treat.
Susceptibility to the disease increases if the following factors are present:
- Carrying out immunosuppressive (suppressing immunity) therapy;
- undergoing chemotherapy;
- Contact sports, use of shared equipment, premises, swimming pools;
- Presence of varying degrees of obesity;
- Skin diseases;
- Poor nutrition;
- Living in conditions of close contact with other people without observing sanitary and hygienic standards, for example, in military barracks, prisons, homeless shelters.
Features of diagnosing folliculitis and boils
The appearance of the first signs of skin damage, the initial stage of tissue inflammation, is a reason to visit a dermatologist. The diagnosis is made after a detailed examination, identification of clinical signs of the disease, as well as after a diagnostic procedure such as dermatoscopy. The collection of material from the affected areas is carried out in laboratory conditions.
In addition, to determine the origin of the disease, identify the causative agent and determine a set of medicinal and instrumental measures for the treatment of folliculitis and boils, laboratory tests are carried out to culture the discharge. For this analysis, a scraping is taken from the inflamed area of the skin and the type of microorganism is then determined.
When the boil has already begun to open, a smear from the separated substrate is sent for bacteriological examination to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics.
Recurrent diseases are a serious indication for a full general examination, including:
- Blood test for sugar level;
- Clinical blood test;
- Bacteriological culture of urine;
- Test for HIV infection;
- Immunological research;
- Consultation with an endocrinologist.
It is worth understanding that in order to determine the correct and effective set of treatment measures, it is necessary not only to know the differences between a boil and folliculitis, but also to distinguish these pathologies from other skin diseases.
Methods for treating folliculitis and boils
Both diseases - folliculitis and boils - require general treatment methods, starting from the first days after the onset of symptoms. The resulting pustules should be treated with a solution of brilliant green. You can also use camphor or salicylic alcohol, fucorcin or methylene blue as external treatment agents. It is not forbidden to use lotions, gels and creams containing salicylic acid without harm to health. Among the topical products, ointments with an antibacterial effect are applicable, for example, Lincomycin, Erythromycin, Dalacin-T, Epiderm, Zinerit. Regardless of what kind of disease develops, furunculosis or folliculitis, at the stage of maturation of ulcers, ichthyol bandages can be applied to the affected area, dry heat, and UHF therapy can be applied.
How to treat folliculitis?
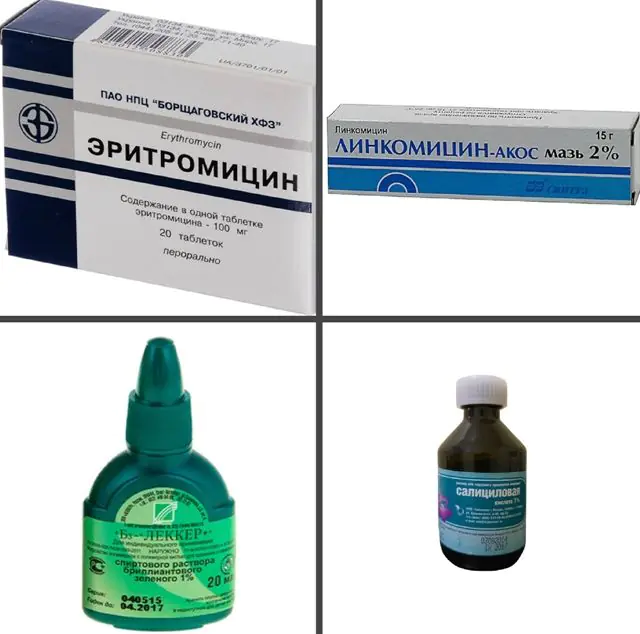
The photo shows drugs for the treatment of folliculitis
If the course of folliculitis is complicated by additional symptoms of intoxication and weakening of the body, then the ulcers are forcibly opened, the pus is removed, after which the wound is treated with antiseptic drugs. Sometimes the application of fixing bandages is indicated to prevent injury and penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. In particularly difficult cases, compresses are applied using ichthyol ointment, which helps remove purulent contents.
The chronic course of this disease requires the prescription of antibiotics belonging to the sulfonamide group. For internal use, antibacterial drugs are prescribed (Doxycycline, Erythromycin, Cephalosporin). Immunostimulating drugs may be used.
- Read also about the treatment of superficial folliculitis
Treatment of a boil
Photos of drugs for the treatment of boils
Several years ago, autohemotherapy was used to treat furunculosis, but it could not take root as an effective method. It is a procedure for injecting the patient with his own venous blood. The results of treatment were unsatisfactory. The method of immunization with staphylococcal toxoid also failed. In recent years, it has also not been used to treat furunculosis.
At the present time, antibacterial therapy is considered the most popular. Antibiotics work best against staphylococci, including aureus. The range of such drugs is quite wide. Augmentin, kefzol, methicillin, oxacillin, rifampin, chloramphenicol, cephalexin, zeporin, lincomycin, erythromycin, oleandomycin, metacycline - any of them can defeat furunculosis, but it is important that the medication is prescribed by an experienced doctor.
In addition to antibiotic therapy, external treatment is also carried out. To draw out the pus, the areas affected by the bacterial infection are covered with bandages moistened in a hypertonic solution. Over time they dry out. After complete removal of the purulent contents, an antibacterial cream is applied to the ulcer and secured with a bandage. Hypertonic solutions of sodium chloride, turunda, ointments with a high content of chloramphenicol and methyluracil can also be used for treatment. In cases where removal of the necrotic core is difficult, trypsin or chymorepsin is used. These are proteolytic enzymes that stimulate cellular metabolism and accelerate skin cleansing.
If over time the boil does not open spontaneously, then you should seek help from a surgeon. Before the procedure, local anesthesia is administered. Using sterile instruments, the doctor makes a puncture or miniature incision to be able to quickly remove the pus. This procedure should not be carried out at home to avoid complications of the disease. During squeezing or self-puncture of the infected area, infection may spread to nearby healthy tissues and through the lymphatic system, which usually leads to the development of lymphangitis.
At the stage of healing and recovery, drugs with antibacterial effects and healing properties are used.
If a boil develops on the face - in the area of the upper lip, nose and cheeks, the doctor will urgently prescribe antibiotics in the form of injections. Such drugs as methicillin, oxacillin, erythromycin, etc. have proven themselves well. Such localization of ulcers carries a great danger, because The infection can, under certain conditions, quickly spread to the brain.
It is noteworthy that with frequently recurring furunculosis, the course of treatment with antibacterial drugs can last several months or even years - it all depends on the clinical picture.Preventive measures against folliculitis and boils

It is impossible to completely insure against boils and folliculitis, but there are a number of measures that will reduce the risk.
Preventive measures include a set of measures:
- Using individual towels and personal hygiene items to avoid spreading the infection to other family members.
- Refusal of uncomfortable tight clothing made from synthetic fabrics to avoid skin irritation.
- Daily change of bed and underwear.
- Washing towels, bed linen and underwear in hot water to kill pathogenic microbes, mandatory ironing after drying.
- The use of dressing materials is for one-time use only. Dispose of used dressings using paper bags.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Regular body hygiene using mild antibacterial soap will help prevent the development of boils and folliculitis.
- Timely treatment of cuts, abrasions and other even the smallest wounds.
- Eating healthy foods that support a healthy nutrient balance and immune system.
- Avoid shaving and other cosmetic procedures on the affected areas.
- Refusal to swim in open reservoirs, swimming pools, visit public baths, locker rooms in sports sections, etc.
See also methods for preventing candidal folliculitis.
Complications with folliculitis and boils

In the photo, lymphadenitis as a complication of a boil
Any incompletely cured infectious disease provokes a relapse in a more acute form or the development of complications. For example, if folliculitis is not treated, pathogens can penetrate deep into the tissues and provoke the formation of boils, abscesses, and carbuncles, which are more difficult to treat and pose a great danger. It is also possible that other infections may occur, such as fungal or viral. Possible consequences are papillomatosis, dermatophytosis, etc. The most dangerous thing is the entry of pathogens into the human bloodstream; diseases caused by this fact can threaten the patient’s life.
The most common complications of furunculosis are lymphangitis and lymphadenitis. The development of a disease localized on the face, in the area of the nasolabial triangle, or on the mucous membrane of the vestibule of the nose is considered especially dangerous in terms of worsening the state of health. In such cases, in the absence of appropriate treatment, the infection can easily penetrate inside the skull, causing inflammation of the sinuses of the dura mater, for example, sinus thrombosis, purulent meningitis, and brain abscess. Because of this, such diseases cannot be ignored, because the worst thing that can follow is death.
Complications can be caused by independent attempts to fight boils or careless actions with the affected area - improper external treatment, attempts to independently squeeze out the boil, unintentional injury, etc.- Related article: Syphilitic folliculitis: symptoms and treatment



