- Why do papillomas appear in newborns?
- Main types of papillomas
- What are papillomas confused with?
- Treatment methods for papillomas
- Conservative therapy
- Surgical removal
- Prevention of papillomas
Papilloma in a newborn baby is a benign neoplasm caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). The growth consists of epithelial tissue and affects the skin or mucous membranes of the child, it can be congenital or appears in the first weeks of the baby’s life. If it is detected, parents need to contact a pediatrician or dermatologist - the doctor will make a diagnosis and, if necessary, offer treatment options. Trying to cleanse children's skin on your own is not recommended. It is better not to use folk remedies for papillomas!
Why do papillomas appear in newborns?
The main cause of the formation of neoplasms is the papillomavirus, which penetrates the child’s body through mucous tissue or damage to the skin and penetrates the structure of human cells.
The incubation period ranges from 2 weeks to several years. The infection often has a hidden, asymptomatic course for a long time, but under certain conditions, HPV activation begins, its reproduction and clinical manifestations in the form of papillomas and warts.
The main reasons that provoke the formation of papillomas in a newborn are:
- Decreased immunity of the baby, including colds;
- Pathologies of the digestive system, including dysbacteriosis and helminthiasis;
- Allergies.
Infection of a newborn can occur in several ways:
- Vertical (generic). It involves infection of the child from the mother, which occurs during the passage of the baby through the birth canal infected with HPV. In this case, the virus can enter the infant’s respiratory tract, causing a rare form of infection - respiratory.
- Intrauterine. Another type of vertical transmission. The fact that HPV infection is possible even in the prenatal period is evidenced by the formation of papillomas in newborns and infants born as a result of cesarean section, when children did not come into contact with the birth canal of their mothers. The small size of the virus allows it to penetrate not only through the placental barrier, but even through the pores of condoms.
- Contact and household. After birth, HPV carriers, including medical personnel, with whose skin and mucous membranes the child comes into contact, can infect the baby. Infection can be transmitted through dirty tools, dishes, toys, personal hygiene items - towels, clothes.
- Autoinoculation (self-infection). The transfer of virus elements from one part of the body to another occurs when a child scratches existing papillomas or licks his fingers.
The main types of papillomas in newborns and infants
The photo shows papillomas in newborns and infants in different parts of the body
In newborns and infants, papillomas can affect the skin of any part of the head and body, including the eyelids, ears and fingers. Also, growths are localized on the mucous membranes of the nose, in the oral cavity and on the tonsils, found in bronchoalveolar lavage (washes from the bronchi and alveoli of the lungs), the anogenital area, on the cervix and in the vagina. They can be single or group, have a diameter from 1-2 mm to 2-5 cm, and are capable of growing.
The following types of papillomas are diagnosed in newborns and infants:
- Acrochords (filamentous). Most often they are congenital. They are located one at a time or in groups on the skin anywhere, but more often on the face and neck, in the armpits, and inguinal folds. Small formations standing on thin stalks often go unnoticed and come off when rubbed with laundry or during hygiene procedures, releasing droplets of blood.
- Vulgar (simple). Small round growths with a dense rough surface. The favorite location for simple papillomas in a newborn baby is the knees, buttocks, and the backs of the hands. See what vulgar papillomas look like.
- Flat. Dense flesh-colored formations, slightly raised above the skin, not forming a stalk. Their appearance in babies is accompanied by itching, leading to scratching of the skin and inflammation. Read about the symptoms of flat papillomas.
- Plantar. Typical for older children who can already walk. They are localized on the sole of the foot and look like yellowish lumps with dark dots inside, resembling a callus. They cause pain and discomfort when walking, and can merge, spreading over large areas. Read how to remove a plantar wart.
- Epithelial hyperplasia. With this form of papillomatosis, small papillary formations affect the oral mucosa - the walls of the cheeks, palate, tongue. During eating, papillomas in infants are often damaged and inflamed, causing pain.
- Juvenile laryngeal papillomatosis. A condition in which nodular and papillary growths affect the glottis area and the back wall of the larynx. The airways are constantly irritated and may become swollen, speech impaired, and suffocated. It is considered a rare, but serious, life-threatening disease characteristic of babies born from an infected mother. Detected before the age of 1 year.
- Warty dysplasia. It primarily affects children aged 3 years and older. Rough, red-brown spots may appear on the hands, feet, and fingers. Most often, the rashes are multiple and may merge. The disease is quite rare, but dangerous - 30% of such formations eventually become malignant tumors.
Usually, papilloma in a newborn baby does not cause pain or any discomfort. However, scratching and injury by clothing provokes the addition of a bacterial infection and inflammation, as well as the spread of rashes. If the tumor is located in the folds of the groin or in the anus, the baby's bowel movements can lead to irritation and ulceration of the growth. To avoid such complications, it is necessary to pay due attention to the hygiene of the child’s genital organs.
Important! You cannot tear off papillomas by force - this can cause the spread of the virus in the body and the appearance of even more formations on the body.What is papillomas confused with in newborns?
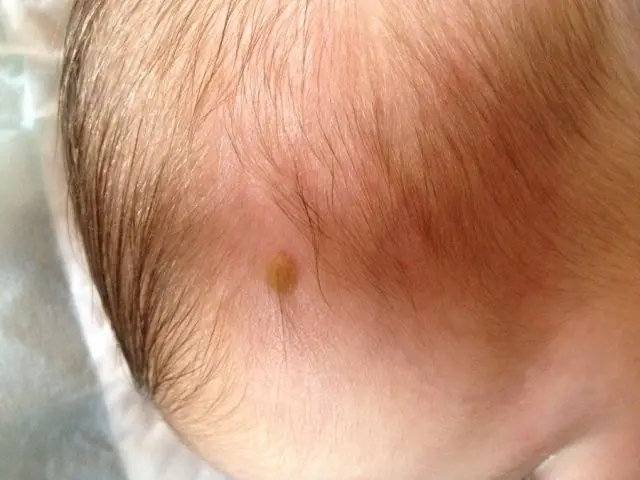
The photo shows a birthmark on a newborn
HPV cannot always be recognized at first glance. Papilloma-like formations in young children also occur in other diseases:
- Molluscum contagiosum. Children under 4 years of age are most susceptible to this viral infection. The symptoms can be very similar to papilloma in infants - the bumpy rashes are often elongated and have a stalk. Infection with molluscum occurs easily, it quickly spreads throughout the body, but does not pose a threat to the health of children and goes away on its own after a few months.
- Nevi (moles). They are tubercles or diffuse spots on the skin (less often on mucous membranes) from light brown to blue-black or red. About 60% of nevi are congenital.
- Melanoma. Malignant skin tumor. In newborns, it develops mainly from a congenital pigmented benign formation (mole).
- Congenital skin abnormalities. They are characterized by the proliferation of dermal papillae and the appearance of growths, but are not associated with HPV infection.
For a correct diagnosis, an examination by a specialist and a comprehensive examination, individual for each case, are necessary. A blood test and PCR test help determine the presence of HPV in a baby’s body; in case of damage to the larynx or bronchi, examination of these organs using an endoscope.
Methods for treating papillomas in newborns
Papilloma in an infant or newborn child does not always require urgent therapeutic measures. Most often, the doctor suggests simply observing the tumor for some time (1.5-2 years) without injuring it, and periodically performing repeated screenings. In childhood and adolescence, the likelihood of self-healing from HPV is high. If the growth does not disappear or, on the contrary, new elements appear, resort to the following treatment methods.
Conservative treatment of papillomas in newborns
It is used for single rashes and includes the following areas:
- Boosting immunity. The use of vitamin complexes is prescribed - solutions for oral administration Multi-tabs Baby (pictured above), Polivit Baby. For frequent exacerbations, immunomodulators in the form of nasal drops or injection solutions are indicated - Derinat, Roncoleukin. When the body’s resistance is high, HPV goes into a latent, “sleeping” form.
- Antiviral therapy. It involves the use of interferon-based products in the form of tablets and suppositories, which helps reduce the spread of infection. Anaferon and its analogs are prescribed - Viferon, Genferon Light.
- Local treatment. Includes the use of ointments and lotions based on acids and alkalis, which “burn out” the tumor. They use Solcoderm, Superchistotel (read the composition of Superchistotel) and their analogues - Feresol (read reviews of Feresol), Verrukacid, trichloroacetic acid (read reviews). If used improperly, it leads to burns and scars.
Surgical removal of papillomas in a newborn baby
Removal of growths is mandatory in the following cases:
- There is rapid growth of the papilloma or a change in its color - redness or darkening.
- In the area of the tumor, pain, swelling of the tissue occurs, or a spider vein appears.
- The growth has an irregular shape.
- The location of the papilloma contributes to its damage - for example, around the eyes and lips, in the oral cavity, anogenital area or skin folds.
- Laryngeal form of the disease, when the formation itself and the swelling it causes threaten to block the airways.
Methods for removing papillomas in newborns:
- Cryodestruction. It involves exposure to cold - liquid nitrogen - on the growth. It is considered a bloodless and least traumatic method of surgery, eliminating scars. The price of the procedure is 400-1800 rubles in Russia and 50-450 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Laser excision. With this method, blood loss is very small, the wound heals quickly, and postoperative complications are extremely rare. Depending on the complexity, the cost of laser removal of papillomas in a newborn varies greatly and ranges from 1200-8000 rubles in Russia and 300-2200 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Traditional scalpel cutting. Treatment of children in this way is carried out in rare cases - when it is necessary to take material for further study. The price of excision is 800-5000 rubles in Russia and 250-500 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Radiocoagulation. A single exposure of tumor tissue to high doses of ionizing rays. The method is rarely used for newborns, but radioknife is effective in cases of damage to the larynx. The cost of treatment is 1200-5000 rubles in Russia and 150-1500 hryvnia in Ukraine.
Surgeries in public clinics may be free, or parents will need to purchase anesthesia drugs and consumables.
Doctors consider the most effective complex method of influencing HPV, when the removal of papillomas in newborns is combined with antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy.
Note! Excision of tumors does not eliminate the presence of HPV in the baby’s body, but only removes the manifestation of the virus’s activity. Under favorable conditions, the infection can become more active and cause a new wave of rashes.- Read about the features of treatment of papillomas in children.
Prevention of papillomas in a newborn
To prevent HPV infection and the appearance of papillomas in newborns, there are several methods of protection. Since intrauterine infection of the fetus is possible, future parents should be tested for HPV when planning a pregnancy. In addition to a blood test, a woman should undergo an examination by a gynecologist and undergo vaginal smears. If papillomas are detected on the genitals (they are called genital warts), the neoplasms must be removed.
If condylomas are detected already during pregnancy, you need to consider whether they will interfere with the birth process. If the growths do not threaten the health of the mother and child, it is advisable to postpone therapy until the postpartum period.
At the planning stage, it is possible to vaccinate a woman against HPV strains that cause damage to the larynx in a newborn, the formation of condylomas and the occurrence of cervical cancer.
- Read about the dangers of warts during pregnancy
To avoid the virus from entering the body and the appearance of papillomas in a baby, you need to properly care for his skin, keep it clean, prevent dryness and cracking, and promptly treat scratches with antiseptics. If it is impossible to clean the baby’s skin with water, it should be wiped with wet wipes (can be antibacterial) and then dried.
It is equally important to prevent a decrease in the child’s immunity. The baby should regularly be in the fresh air, not experience stress, and receive all the beneficial substances from the diet - from mother’s milk or special formulas.
Watch a video about skin problems in children: