- Causes of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
- Symptoms of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
- Diagnosis of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
- Treatment of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
- Prognosis and prevention of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
- Complications of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis (abscessing) is a rare dermatological disease with a purulent nature. The disease affects the hair follicles and scalp, but can also appear on other hairy parts of the body. Today, the main cause of Hoffmann's folliculitis is considered to be bacterial infection of the skin near the hairline. The disease mainly affects men aged 17-40 years. Racial predisposition to Hoffmann's folliculitis has also been proven - the disease is less common in European men than in African Americans. Undermining folliculitis most often develops slowly. It is characterized by a sluggish, chronic and long-term course, which sometimes takes several years. Only correct and timely treatment can speed up the recovery process and prevent relapse.
- Read what folliculitis is
Causes of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
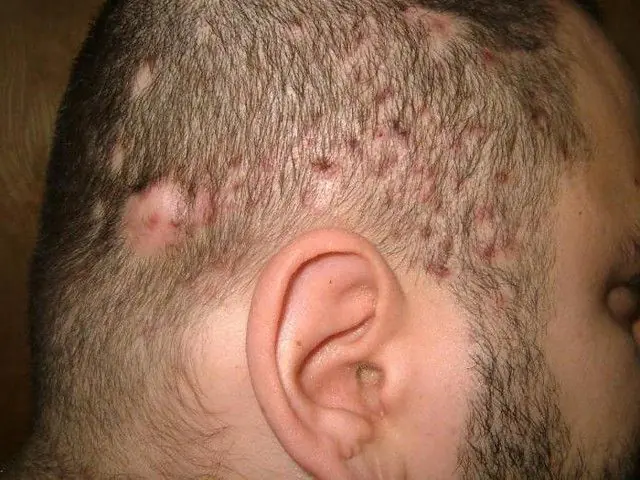
The photo shows an advanced form of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Since E. Hoffman's study of abscess folliculitis, pathogenic staphylococcal flora was considered the only cause of the disease. It has now become clear that the disease develops not only due to infection by microorganisms, but also due to the physiological characteristics of the skin. Bacteria colonize around the hair roots, which provokes the development of the disease.
In almost all patients, the secretion of the sebaceous glands changes, and after a while they become clogged. Similar symptoms of Hoffmann folliculitis indicate many other dermatological diseases (acne, comedones). However, for the development of perifolliculitis, an additional pathological reaction of the skin to the components of the breakdown of clogged sebaceous glands, in particular keratin, is necessary. Studies have shown that in patients with this pathology, granulomatous inflammation is formed due to the breakdown products of keratin. This aggravates infection with staphylococcal flora. Such processes and disturbances of microcirculation in the dermis lead to the occurrence of Hoffmann's folliculitis.
In addition, Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis can be hereditary and occur due to other factors:
- Disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Diabetes.
- Hypothermia.
- Oncological diseases.
- Disturbance of the hormonal system.
- Chemotherapy.
- Liver diseases.
- Long-term use of glucocorticosteroids.
- Antibiotic therapy.
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards.
Symptoms of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
With abscess folliculitis, the hair follicles become inflamed. At the initial stages of the disease, a burning sensation, itching appears and small seals measuring 0.5 cm are formed. With the progression of undermining folliculitis, the seals soften and increase to 2 cm, oblong or hemispherical nodes are formed, which are surrounded by places of hair loss. There may be several affected areas, they become hyperemic. The general condition of the patient also changes: regional lymph nodes enlarge and body temperature rises. When complicated, Hoffmann's folliculitis often causes the formation of fistulas in the lesions. After the pus comes out, a wound forms, which heals, but a scar forms in its place. The disease is prone to relapses, can last several years and is always accompanied by:
- redness of the skin over the formation;
- hair loss;
- discharge of pus with blood when pressing on the affected areas;
- abscess formation.
Diagnosis of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
The photo shows a medical examination of the head of a patient with Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Hoffmann's folliculitis is treated by a dermatologist and an infectious disease specialist. Specialists examine the patient and carry out a number of activities as part of the study:
- Dermatological examination.
- Histological study of affected tissues.
- Microbiological examination of abscess discharge.
- The sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics is determined in order to select the optimal treatment.
- A general blood test is prescribed to determine the nonspecific features of purulent inflammation.
- The presence of similar problems in relatives and chronic diseases is clarified.
Treatment of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
To treat Hoffmann's folliculitis, drug therapy is prescribed: antibacterial drugs internally (Clindamycin, Tetracycline, Rifampicin) and externally (Clindamycin). For local use use: Levosin, Levomekol, Ichthyol, Fulevil, antibacterial ointments.
According to some doctors, the effect of antibacterial drugs is short-term; it is more effective to simultaneously combine antibiotics with injections of corticosteroids in the affected areas. Of the antibiotics, broad-spectrum penicillin drugs of semi-synthetic origin are considered justified: Augmentin, Clavulin, Unazin, Amoxiclav, Claventin. Sometimes the cephalosporin series is used: Kefzol, Cefobid, Cefuroxime, Claforan. If antibiotic therapy is not possible, then sulfonamides are prescribed: Biseptol, Septrin, Groseptol, Bactrim.
High effectiveness is observed when drug treatment is combined with physiotherapeutic methods. UV therapy is effective because ultraviolet rays penetrate the tissue, providing a general strengthening and anti-inflammatory effect. Good results are observed when using: magnetic therapy, low-intensity UHF therapy, dry heat and carbon dioxide laser.
In case of complications and in advanced cases of Hoffmann's folliculitis, surgical intervention is resorted to. Surgical treatment is carried out against the background of antibacterial therapy with resection of the affected tissues of the head and subsequent reconstruction of the skin.
In addition to the above therapy It is necessary to strengthen the body’s immune system and monitor the diet. The menu should contain vitamins, vegetables, fruits and protein-rich foods. It is necessary to limit the consumption of sweets, baked goods, spicy and salty foods. It is important to maintain a drinking regime, because pathogenic microorganisms leave the body with liquid. During an exacerbation, it is recommended to drink 2 liters of water.
- Read about treating folliculitis with folk remedies at home
Prognosis and prevention of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
With proper treatment, the prognosis for abscessing undermining folliculitis is favorable. However, treatment is long and relapses are possible, since the disease is mainly caused by certain physiological characteristics of the skin. After the ulcers heal, noticeable scars remain, which are an aesthetic defect. This can be corrected with plastic surgery. Conservative and cosmetic treatment does not restore hair growth. For prevention purposes, you should avoid getting your hair dirty and maintain personal hygiene.
Complications of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis is not life-threatening. The disease must be treated because it causes aesthetic discomfort and sometimes pain to the patient. If you neglect the disease and do not adhere to hygiene standards, folliculitis will spread to other parts of the skin with hair. Abscess folliculitis can lead to the following complications:
- Scarring of the affected skin.
- Carbuncles.
- Boils.
- Abscesses.
In advanced and severe cases, the patient’s life is at risk, since with reduced immunity, pneumonia, meningitis and other disorders develop.
- Read - how to treat oil folliculitis