Dry skin causes a lot of problems for its owners. As a rule, the matter does not end with dryness; in parallel, other symptoms are present: dullness, irritation, itching, peeling, tightening. Dry skin is more susceptible to natural and household factors, ages more quickly and becomes more inflamed.
The objective sensations of those with dry skin are also far from pleasant. Clothes in contact with the skin and touch also cause irritation, and the very appearance of the skin, reminiscent of desert soil, depresses the mood.
The problem should not be ignored, since it is not only aesthetically unsightly, but is often a sign of certain diseases.
Why does the skin need water?
Moisture ensures elasticity and firmness of the skin, as well as cell nutrition. The degree of hydration is determined by the condition of the stratum corneum of the skin and the amount of sebum, which are responsible for moisture exchange between the dermis and the environment. The moderate stratum corneum and fat create a lipid film on the skin, which prevents moisture from leaving the skin and aggressive environmental factors from penetrating into the skin.
The unformed protective lipid film, caused by external or internal factors, leads to excessive evaporation of moisture, which means dry skin. At the same time, microcirculation of blood and trophism deteriorates, and collagen fibers suffer. The skin becomes not only dry, but also flabby.
Causes of dry skin
Dry skin occurs due to a decrease in sebum production in the presence of provoking factors. Sometimes ineffective sebum secretion is a hereditary feature of the body.
- If the problem occurs in young people, it is most likely genetic.
- In mature people, this condition occurs against the background of certain external and internal reasons. Hormonal changes lead to a decrease in the activity of the sebaceous glands, which immediately affects the condition of the skin. Lack of proper care makes the problem worse.
It should be understood that in cases where dry skin is caused by internal causes (diseases or conditions of the body), no external influences - creams, baths and other procedures aimed at moisturizing and nourishing the skin do not lead to the desired effect. And only treatment of the underlying disease can improve the condition of the skin.
Internal reasons
External reasons
- Skin diseases: keratosis, dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, allergies, fungal infection
- Hormonal imbalances (hypothyroidism, diabetes, menopause, pregnancy)
- Dehydration, which is a consequence of insufficient drinking, indigestion, hyperthermia, diarrhea, vomiting, etc.
- Metabolic disease
- Chronic renal failure
- Diseases of the central nervous system
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
- Autoimmune diseases
- Iron-deficiency anemia
- Natural skin aging
- Hypovitaminosis, especially A and E
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics and some other drugs
- Lack of nutritional intake, exhausting diets
- Passion for coffee and strong tea
- Bad habits (smoking, alcohol)
- Frequent stress
- Dry climate
- Prolonged sun exposure
- Dry air
- Freezing
- Hot or cold water
- Exposure to household or industrial chemicals
- Improper care: frequent use of alkaline soap, alcohol lotions, household chemicals, aggressive cosmetics, frequent peelings.
- Working on the ground, etc. without protective gloves
- Work in conditions of elevated temperatures (hot workshops)
Dry skin can be general or affect certain areas of the body (face, arms, legs, etc.). The localization of dryness can directly or indirectly indicate the reasons for its occurrence.
Manifestations of dry skin
There is a simple home test to help determine if you have dry skin: press your fingers on the skin until marks remain - if they do not disappear for a long time, there is a problem with dryness.
- Tightness. When such skin is accidentally or intentionally pulled, visible cracks appear in the stratum corneum;
- Itching. Dryness and itching of the skin accompany each other, with one phenomenon aggravating the other;
- Invisible, erased pores, as if lightly powdered;
- Irritation, redness;
- Peeling of the skin up to significant, when the skin is literally covered with scales. It becomes most noticeable after washing the skin and then drying it out.
- When complicated by an infection that has penetrated through microcracks: areas of inflammation with swelling.
Treatment of dry skin and flaking
It should be understood that a qualified specialist - a dermatologist - must find out the cause and then prescribe treatment. If harmless dry skin can be dealt with without medical help, then in case of illness, creams and other products will simply be useless.
If dry skin occurs with complications in the form of irritation and microcracks, basic therapy should include ointments with dexpanthenol. Only after the irritation has been relieved can you switch to cosmetics and creams. Alcohol-containing cosmetics, aggressive peelings, and film masks should be excluded. Do not actively dry your skin with a towel after washing.
Dry hand skin
In most cases, the cause of this phenomenon is external factors. If, in addition to dryness, there are also cracks on the fingers, this may indicate hypovitaminosis, allergic contact dermatitis, fungal infections, etc. (see causes of cracks on the hands). If you have weeping cracks between your fingers, you should consult a doctor - most likely it is eczema.
General recommendations
- Protect your hands with rubber or cotton gloves when working with aggressive compounds or on the ground, washing dishes.
- Protect your hands with warm gloves or mittens in winter.
- Use pH-neutral hand and body washes.
- Use sunscreen when tanning in the sun.
- Normalize your diet, be sure to include vegetable and animal oils in the menu.
Traditional medicine recipes
- Potato mask. Peel and mash boiled potatoes in their jackets, add a spoonful of warm milk. While warm, apply the mask to the skin of your hands 2-3 times a day for 4-5 days in a row. Leave until cool.
- Olive oil and lemon juice mask. Take hand cream (1 tsp) as a base, add 1 tsp. butter and half tsp. lemon juice. Apply before bed and put on fabric gloves over it. Repeat weekly.
- Honey-glycerin compress. Mix 1 tsp. glycerin, liquid honey, flour and water and apply the mixture to your hands, wearing cloth gloves on top. It is recommended to do it a couple of times a day, every day, for 20 minutes.
- Sour cream compress. About 200 ml of sour cream with a fat content of 20% is mixed with egg yolk and lemon juice. Clean gauze is soaked in this mixture and applied to the hands, covered with cling film and a towel. After 20 minutes, wash off the residue and put cloth gloves on your hands. It is better to do it before bed for several days in a row.
- Oil bath. Heat any vegetable oil until warm and immerse the brushes in it for 20 minutes. Carry out twice a week.
Wound healing, nourishing and softening creams:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
healing cream based on D-panthenol, vinylin, allatoin, vitamin E and yarrow and calendula extracts. Quickly restores the protective functions of the skin, heals cracks and regenerates the skin. Price about 85 rub.
- Aloe healer
Healing and eliminating dryness cream. Aloe extract restores skin, accelerates regeneration, prevents cracks and softens the skin. 110 rub.
- Velvet handles For very dry skin
Eliminates irritation, dryness and flaking. Ingredients: cocoa butter, D-panthenol, allatoin, glycerin and olive oil. 75 rub.
- Hand restoration cream Belita
Soothes, restores and softens the skin thanks to linden blossom and sea buckthorn extracts, sea buckthorn and wheat germ oil, glycerin, vitamin E. Price about 85 rubles.
- Oil cream from Vitex
Eliminates dryness and flaking. Ingredients: extracts of calendula, chamomile, burdock, apricot kernel oil and Shea butter. 90 rub.
Treatment of cracks
- Ointment made from honey and resin. In a metal saucepan, mix 10 g of oleoresin and honey, add 30 ml of vodka and 15 g of beeswax. Put on fire, stirring constantly until the mixture becomes homogeneous. Cool and refrigerate. The ointment is applied directly to the crack and sealed with a bactericidal plaster for 7-8 hours.
- Calendula ointment. Grind about 100 ml of dried plant flowers into powder and mix with 200 ml of melted pork fat. Bring until smooth in a water bath, cool. It is applied in the same way.
- Plantain ointment. Grind the dry herb into powder and add 9 parts of Vaseline and 3 drops of vegetable oil. It is applied in the same way.
Read more about the treatment of cracked hands in our article.
Dry elbows
Often occurs as a result of mechanical stress (working position with emphasis on the elbows) or infatuation with baths. Dry elbows may be a symptom of:
- hypothyroidism
- iron deficiency anemia
- diabetes mellitus
- autoimmune diseases
- skin diseases.
Traditional medicine recipes:
- Honey-coffee scrub. Add honey to the coffee grounds from a freshly brewed drink, mix and gently massage the resulting scrub onto the steamed skin of your elbows. Rinse with water and lubricate generously with vegetable oil.
- Compress of sunflower oil and sour cream - mix the ingredients in equal parts, soak clean gauze in the mixture, place it on the elbow, wrap it in a warm cloth for 20 minutes.
- Milk bath. Heat fresh milk and dip both elbows in it for 20 minutes.
Wound healing, nourishing and softening creams:

- SOS cream concentrate for very dry skin of hands and elbows from Evelyn - has an intensive effect on rough, dry skin, helps retain moisture in the skin thanks to the active complex: goat milk proteins, wheat germ oil, vitamins A, F, E, H, proelastin . Price about 70 rubles.
- Ointment Radevit – eliminates peeling,

nourishes and softens the skin, actively restores the skin. Contains vitamins D2, A, E, glycerin, petroleum jelly and other components. Price about 370 rub.
Dry facial skin
Very often this feature of facial skin is inherited. Due to the fact that the face is an open part of the body, external factors such as wind, sun, etc., provoke dry skin. Age-related skin changes and improper functioning of the sebaceous glands also aggravate the situation.
A number of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, central nervous system and endocrine system have dry facial skin among their symptoms. Hypovitaminosis E and A negatively affects the skin of the face.
General recommendations
- Minimize the harmful effects of environmental factors: wearing wide-brimmed hats in summer, warm wide scarves in winter.
- Use sunscreen from March to September. In winter, use creams from special “winter” series that protect the skin from wind and frost: ZIMA from Faberlic, Winter care from Biocon, Winter from Floresan.
- Wash only with neutral products, avoid bar soap.
- Regularly nourish the skin with creams designed for dry skin.
Traditional medicine recipes
- Fruit and berry mask. Crushed melon, plum and jojoba oil are mixed in equal quantities and applied to the face for a quarter of an hour. Wash off with warm water. Repeat as necessary.
- Egg-oil mask. Mix the beaten yolk of 1 egg with 1 tsp. oil (any vegetable) and carefully add 1 tsp into the mixture. pharmaceutical chamomile extract. Apply the mixture for 15 minutes, then rinse.
- Oatmeal mask. 3 tbsp. Mix oatmeal boiled in milk with 3 tbsp. olive oil, apply a thick layer to the face for 15 minutes. First wash with warm, then cool water.
Nourishing and softening creams
 |
 |
 |
|
– provides long-term hydration and nutrition thanks to coenzyme, sesame seed oil, apricot and wheat germ oil, nanosomes and lanolin; restores skin elasticity. Price about 170 rubles.
- LOCOBASE lipocream for dry and very dry skin
cosmetic product with a very high lipid content. Forms a fatty layer on the skin and protects it from drying out, without clogging pores and without the effect of a visible oily sheen. The active composition contains liquid paraffin, macrogol and cetostearyl ether. Price about 650 rub.
- Night cream Clean Line Intense nourishing
contains wheat germ and aloe oil and has an intense softening and nourishing effect. Thanks to aloe, it eliminates irritation and smoothes wrinkles. Price about 65 rubles.
Dry body skin
Severe dryness of the skin of the body is rarely caused by external factors, and is more often a consequence of any disease. Seasonal dryness of body skin is often associated with excessive sun tanning. People who regularly visit baths and saunas are also at risk of dry skin.
General recommendations
- Establish a drinking regime.
- Enrich your diet with dairy products, vegetable oils, fish, and nuts.
- Nourish and moisturize the skin with special creams after taking water procedures.
- Use sunscreen while tanning.
Traditional medicine recipes
- Peeling of sea salt, honey and olive oil – 4 tbsp. take 1 tbsp of honey. remaining ingredients. Lightly massage cleansed skin with the mixture, then take a shower.
- Chamomile and flax seed bath. Boil 5 tsp in 1 liter of water. flaxseed, separately boil 2 tbsp in 1 liter of water. dry chamomile - boil over low heat for 10 minutes. Strain both decoctions and add to the bath, which must be taken for 15 minutes.
- Milk and honey bath. Dissolve 200 grams of honey and 1 tsp in 1 liter of warm milk. oil (olive, almond) - add the mixture to the bath, which is taken for 15 minutes.
- Olive mask. While showering, thoroughly massage your body with heated olive oil, then rinse off the residue with warm water.
Nourishing and softening creams
 |
 |
 |
|
Provides intense skin hydration thanks to a complex of oils and a special Cream-Oil formula. Price about 250 rubles.
- Johnson's baby oil
Helps retain moisture in the skin, creating a special protective layer on the skin. Hypoallergenic. Price about 130 rubles.
- Nivea SOS-intensive body cream
Regenerating cream with panthenol, grapefruit, lime, camellia, almond oils. Eliminates dryness and tightness while maintaining the effect for 48 hours. Price about 270 rubles.
Dry heels and feet
The problem can be caused by wearing uncomfortable shoes, frequently walking barefoot, or lack of hygienic foot care. Hypovitaminosis, diseases of the endocrine system, fungal infections lead to dry feet. Dry skin on the feet if left untreated leads to the formation of areas of hardening and cracks, which can be complicated by bacterial infection (see treatment of cracked heels).
Skin is one of the most important organs. It shapes our appearance, provides sensation of touch, controls temperature and protects against infections. However, rough, thickened, flaky, itchy or painfully dry skin loses its ability to function properly - receptors become less sensitive, the risks of premature aging and sun damage increase, and the threat of infection increases. Effective solutions are usually very affordable and based on a daily skin care routine that is specific to dry skin.
Signs of excessive dry skin
Dry skin is the main cause of skin diseases; more than 40% of visits to dermatologists are related to dry skin. Dryness can occur anywhere on the body, but it most often occurs on the arms, legs, knees and elbows, and face because these areas are the most vulnerable. Dry facial skin can be a factor in premature aging.

Dry skin is unable to regulate its hydration. 
Internal and external factors can impair the skin's ability to hydrate and lead to excessively dry skin
When skin becomes over-dried, it can become very hard, flaky, flaky, very itchy and painful, even very rough and cracked. However, it is not always obvious that dryness is the cause of these skin problems, depending on the degree of dryness and the area of the body affected.
- Moderately dry skin
At first, dryness can be noticed in the form of slight compaction or slight roughness. - Dry skin
If the skin continues to lose moisture, it becomes rougher and may take on a cracked or rough appearance, possibly itching. - Excessively dry skin
If such dryness remains untreated or left untreated, or is ineffective, the skin can become extremely tight, rough and cracked. At this stage, the itching can also become severe and painful.
Areas of the body affected by dry skin
Dryness often appears on the skin of the legs and thighs. Dry skin on the feet is especially common, and often results in cracked heels, which, when severely affected, are associated with pain and inflammation.
However, the dryness associated with washing with strong detergents can affect the entire body equally. Washing your hands too often also tends to cause dry skin.
If you wash your hands too often, they can develop dry skin.
Sensitive skin
Dry skin on the body is often quite sensitive, but sensitivity is not always caused by dryness. Some people's skin is naturally very sensitive, even if it is well moisturized. In any case, it is important to avoid skin care products that contain irritating ingredients such as fragrances and dyes. Always make sure the product has been dermatologically tested on sensitive skin.
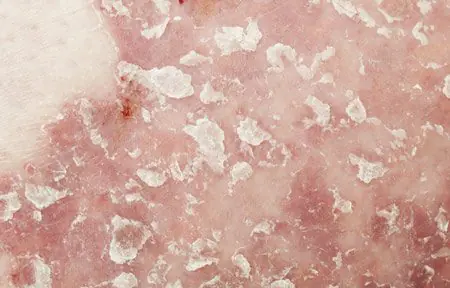
Dry skin due to illness
With conditions such as psoriasis or atopic dermatitis, the skin may appear red, flaky, and itchy.
Dry skin can also be associated with certain medical conditions:
- Xerosis is the medical term for dry skin. It comes from the Greek: “xero” means “dry” and “osis” means “disease”.
- Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis are also associated with dryness, although inflammatory processes underlie these diseases. As a rule, the skin affected by them appears reddened, peeling and very itchy.
- Metabolic diseases such as diabetes and kidney disease can also increase your risk of dry skin.
Main causes of dry skin
There are many reasons and factors that cause dry skin on the body: from environmental exposure and improper skin care to diseases such as psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. The skin acts as a barrier to the body, but this means that it is exposed to both external and internal influences.
- External factors cause disruption of the skin's function as a natural barrier, which leads to increased moisture loss through the skin.
- Violation of the skin's surface barrier by washing away the natural layer of lipids makes it impossible to retain moisture, and the rate of moisture loss increases.
- Finally, when dryness spreads to the lower layers of the skin, the transport of water through the buried tissues is disrupted, as the functioning of important hydration channels is disrupted.

A deficiency of natural humectant factors (HMFs), which bind moisture, leads to dehydration of the upper layers of the skin.
External factors that contribute to dryness
The main external causes of the process described above are environmental factors and skin care:
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays can lead to skin aging and, as a result, dryness.
- It is recommended to limit the bath time and reduce the water temperature, as prolonged baths can lead to evaporation of moisture.
- Since some medications can cause dry skin, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
External environment
- Harsh weather conditions - heat, cold and dry air - destroy the protective function of the skin.
- Seasonal Changes – Dry skin symptoms often worsen in winter or summer.
- Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun can speed up the aging of your skin, and as you age, your skin becomes more prone to dryness.
Skin care
- Frequent washing or long, hot baths or showers remove the layer of lipids that form the skin's protective barrier.
- Inappropriate skin care – It is important to follow the instructions and use products that are suitable for dry skin. It is especially important not to use strong soaps, which strip away the skin's natural lipids.
Taking medications
Dry skin occurs as a side effect of many medications. Common medications that have this side effect include diuretics to control blood pressure, which work by increasing the amount of water that is lost from the body through urine, as well as some antibiotics and oral acne medications. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist if you
Genetic influences
Heredity also affects the moisture balance in the skin. Some people have oily skin, others have dry skin, and these skin types are inherited, although a person will not necessarily have the same skin type that their parents had. Skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, diabetes mellitus and ichthyosis often have a genetic basis.
Hormonal influences
Changes in the concentrations of certain hormones, especially estrogen and testosterone, can affect skin moisture and lipid levels. This is especially noticeable after menopause, when the skin becomes dry due to decreased estrogen levels.
Dry skin can also develop during pregnancy due to hormonal changes as well as additional body fluid requirements.
Nutrition
Like any other organ, the skin requires a number of important nutrients to function properly. Among them are unsaturated fatty acids and vitamins. A lack of any of these can contribute to the development of dry skin.
Age
With age, the number of sebaceous and sweat glands in the skin decreases, which leads to a decrease in the ability to synthesize sweat and lipids. The skin's water content and ability to retain moisture also decreases. These factors lead to dryness, which in turn causes aging of the skin and the formation of fine lines and wrinkles. Learn more about age-related dryness.
Factors that cause dry skin
In addition to the main causes of dry skin on the body, there are several other factors that also affect the degree of dry skin. Understanding this will help you avoid them and thereby reduce their impact.
- The best time to moisturize is when the skin is clean and slightly damp, such as after a bath or shower.
- Dry skin needs special sunscreens without any irritating perfumes or dyes.
- Consistent use of protective gloves and hand cream can help some professions, such as doctors or hairdressers.

Lack of effective treatment
If dry skin is not treated quickly, the degree of dryness may increase and the hydration system in the deeper layers of the skin may be compromised. In such situations, it is necessary to use a moisturizer designed to solve this problem.
The influence of sun rays
While protecting dry skin from sun damage, it is important that the sunscreen also replenishes the lack of moisturizing factors, in addition to an appropriate sun protection factor (SPF). It is also important that sunscreen, like any other skin care product used on dry skin, does not contain irritating perfumes or dyes, as dry skin, especially on the face, is more prone to irritation than normal skin.
Occupational hazards
Some professions require working in environments that may increase the risk of dry skin. These are typically occupations that involve exposure to dry skin factors, such as working in hot or cold conditions (farmer/fisherman), or jobs that involve the use of detergents (doctor/nurse/hairdresser), or working with chemicals (mechanic/ cleaner).
Dehydration
The skin receives moisture from the body and therefore depends on the water balance in the body. When dehydrated, it reduces the supply of moisture to the skin, which slows down the natural movement of water through the skin, which can contribute to dryness. Older people are prone to dehydration because the feeling of thirst decreases with age.
Smoking
Cigarettes contain many toxins, including nicotine, which can reduce blood flow. This leads to a decrease in the metabolic rate in the skin. This means that the processes of premature aging and drying can begin in it.
Caring for dry body skin
Dry skin is caused by a violation of the skin's barrier function, which leads to loss of moisture and a decrease in the ability to retain water due to a deficiency of moisturizing factors. Thus, dry skin requires daily care that does not cause further deterioration of the skin barrier and restores the lack of natural moisturizing factors.
Dry and excessively dry skin, as well as dry skin associated with diabetes or psoriasis, require appropriate products depending on the degree of dryness, but atopic dermatitis requires special products for the daily skin care of infants and young children. When choosing a skin care product for children, always check the age requirements.
Recommendations for caring for dry skin
Cleansing dry body skin. Most often, skin becomes dry due to damage to the skin's surface barrier, so it is important that the cleanser is gentle enough not to strip away the skin's natural protective barrier. Additional natural moisturizing factors such as urea will also help restore the skin's moisture balance.
Moisturizing dry body skin. The first requirement for moisturizers for dry skin is to restore the moisture balance in the upper layers of the skin. Substances called “natural moisturizing factors” (NMFs), such as urea and lactic acid, retain moisture in the stratum corneum or upper layer of the skin. The minimum recommended concentration of urea, even for moderately dry skin, is 5%. Excessively dry skin typically requires a higher concentration of urea and other moisturizing factors.

Instead of wiping wet skin with a towel, pat it dry and apply cream or lotion immediately after.
It is important to follow the instructions and use products that are suitable for dry skin.
Dry, rough, and thickened skin can be caused by disturbances in the three main mechanisms of moisture control: damage to the surface barrier due to insufficient skin lipids, dehydration of the stratum corneum due to the lack of natural moisturizing factors, and poor distribution of moisture in the lower layers of the skin.
Protecting dry body skin from sun radiation
When going outside, you should reduce your exposure by wearing clothing that covers all parts of your body and using sunscreen. In addition, it is important that sunscreens also contain moisturizing factors. Sunscreens for dry skin should not contain irritating perfumes or dyes because dry skin is sensitive to irritation.

A moisturizer suitable for dry skin should be frequently applied to the affected area.
Avoiding factors that contribute to dryness
In addition to good daily cleansing and moisturizing, it is important to avoid factors that contribute to the development of dry skin. This will help alleviate the problem of dry skin and reduce the need for treatment:
- Avoid dry air by spending less time outside in hot, dry or cold weather and using humidifiers when the heating is on indoors.
- Reduce your time in hot water by taking quick, warm showers instead of long, hot baths.
- Wear gloves when washing dishes to avoid exposure to hot water and harsh detergents.
- Wear clothes made from natural materials such as cotton and silk, which are gentle on your skin. Wool is also a natural material, but can irritate dry skin and should be avoided.
- Try to use laundry detergents without dyes or fragrances to avoid irritation.
- Make sure you drink enough water - especially for older people.
Read this article if you want to know the reasons why your skin becomes dry and how to care for it. We will recommend effective products and give some useful tips for turning very dry skin into well-hydrated skin.
- Signs of dry skin
- Causes of dry skin
- How dry skin differs from normal and oily skin
- What to do for very dry skin
- Dry skin care
- Caring for dry body skin
- Precautions when caring for dry skin
- Tools Overview
Signs of dry skin
The tendency to dryness mainly has genetic causes. Therefore, fundamental changes cannot be achieved here. But making friends with your skin and improving its condition is quite possible. The main thing is proper care and preventive measures.
Typically, dryness is characteristic of both facial skin and body skin. Such skin is usually thinner and more sensitive.
When the sebaceous glands do not produce enough secretion, that is, sebum, which protects the epidermis from drying out and minor damage, the skin retains moisture less well, so it often dries out, reacts with irritation, and ages faster.
Dry skin is often sensitive. © iStock
Don't confuse dry skin with dehydration - a temporary and easily correctable condition. Oily skin can also be dehydrated. Moreover, due to lack of moisture, it begins to produce more fat.
Lack of moisture is often explained by improper care and other external factors, such as windy weather or dry indoor air.
To avoid confusion, remember the signs of dry skin.
Dry skin is rarely problematic, while oily skin (especially dehydrated skin) usually shows comedones, acne, and enlarged pores.
Dehydrated skin lacks water, dry skin lacks fat, which means the former needs hydrofixing agents (glycerin, hyaluronic acid), the latter needs moisture-locking or lipid-replenishing components (oil, ceramides).
Dry skin is often prone to sensitivity and does not tolerate polluted air and hard water well. It is more likely to react to common allergens (for example, honey).
To care for dry skin, choose light textures. © iStock
Causes of dry skin
Cleansers containing aggressive surfactants (surfactants) destroy the hydrolipid mantle of the skin.
The moisturizer was not rich enough for you, or the skin does not have enough nutrition to retain moisture inside.
Severe weather conditions, for example, heat with increased dry air or frost in combination with icy winds undermine the protective potential of the skin.
Insufficient indoor air humidity is a common problem in our latitudes when central heating is turned on.
Clothing made from synthetic fabrics and wool can cause discomfort, itching and flaking of the skin of the body if it is prone to dryness, especially in winter.
A hot shower is one of the main provocateurs of dry skin on the body, since high-temperature water, especially with prolonged contact, destroys the hydrolipidic barrier - the protective mantle that retains moisture in the skin cells.
An unbalanced diet, lack of fatty acids in the diet and lack of proteins can lead to dry skin - both face and body.
Some types of hormonal treatments or the use of retinoids provoke severe dry skin. You will have to wait until this side effect disappears, smoothing out its manifestation with the help of cosmetics.
How dry skin differs from normal and oily skin
Compared to oily and normal skin, dry skin has an insufficient hydrolipid layer. It is thinner, and the vessels are located so close to the surface that spasms are possible even after short-term exposure to frost.
For those with oily skin, the stratum corneum and sebum form a powerful defense, so it ages more slowly and withstands negative external influences more resistantly - from peelings to cold weather. But dry skin is protected from acne, blackheads, enlarged pores and other troubles that complicate life in youth.
The best moisturizing ingredients are glycerin, aloe vera and hyaluronic acid. © iStock
What to do for very dry skin
If the reasons are not related to health, we recommend listening to these tips:
moisturize your skin from the inside - maintain a drinking regime, drinking about 1.5 liters of water per day, at the rate of 30 ml per kilogram of weight;
remove alcohol-containing products from your cosmetic bag;
try to choose clothes from natural, smooth fabrics that do not irritate the skin (cotton and silk);
get tested for microelements and vitamin deficiencies in your body; you may be lacking vitamins A and E;
exclude an allergic reaction, it can be caused by household chemicals: washing powders, bleaches and disinfectants;
instead of alkaline cleansers, use delicate creamy textures;
If possible, install water filters.
If you decide to get rid of dryness, choose the right cosmetics for face and body care. Products with oils and lipid-replenishing components will suit you.
Dry skin care
Read and remember what you need to pay attention to when caring for dry skin.
The epidermis needs nutrition in the form of lipid-rich cream or oil.
Replace alkaline cleansing products with gentler ones.
Instead of cleansing gel, start using, for example, cleansing milk.
Make it a rule not to go to bed with makeup on your face - foundation left on overnight not only clogs your pores, but also dries out your skin.
In addition to hydration, dry skin needs nutrition. © iStock
Caring for dry body skin
Dry skin can occur in many different parts of the body.
If your scalp is itchy, itchy and flaky, it makes sense to consult a trichologist for advice.
Make it a rule to use hand cream at least twice a day: before going to bed and before going outside.
Regularly treat dry skin of the feet with fine-mesh pumice or a file, then lubricate with a cream containing urea and solid oils (shea, cocoa).
For cleansing, choose soft shower and bath gels, as well as syndets, oils, and products that do not contain aggressive surfactants.
Do not stand in the shower for a long time and try to wean yourself from too hot water, gradually reducing the degree day by day.
Moisturize your skin every time after water treatments. For dry skin, rich nourishing textures are most suitable: balm or cream.
Apply body cream/milk/balm while the skin is still slightly damp.
Precautions when caring for dry skin
If your skin type is dry, we recommend avoiding harsh scrubs, high concentrations of acids in care products, aggressive alkaline cleansing and alcohol-containing cosmetic products.
On the beach, use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. Thin and dry skin burns faster. And do not forget that ultraviolet radiation provokes the formation of free radicals - the main enemies of youthful skin. Otherwise, you will subsequently have to fight not only dryness, but also wrinkles and age spots.
In the cold season, before going outside, apply nourishing cream to your face, protective cream to your hands, and don’t forget about a scarf and gloves.
Tools Overview
For face
| Product name | Mode of application | Active components |
| moisturizing cream for dry and very dry skin of the face and body, Cerave | Apply twice daily to cleansed face and/or any area of the body. | ceramides, hyaluronic acid |
| Extraordinary facial oil “Luxury Nourishment”, L’Oréal Paris | Use as the last step of evening care - instead of or on top of cream. | oils of clove, rosemary, chamomile, lavender |
| Rich toleriane sensitive cream with prebiotic formula, La Roche-Posay | Use morning and evening, after cleansing. | La Roche-Posay thermal water in high concentration, niacinamide, shea butter |
| Day cream for sensitive skin “Moisturizing Expert”, L’Oréal Paris | After cleansing the skin, use the cream, avoiding the area around the eyes. | glycerin, rice bran oil |
For body
| Product name | Mode of application | Active components |
| Soothing shower gel with protective properties Lipikar Gel Lavant, La Roche-Posay | Pour a small amount onto a washcloth or palm and massage into damp skin. | niacinamide, shea butter |
| Nourishing body cream, Kiehl’s | Apply the cream to wet or dry body skin with light massaging movements. | squalane, avocado and sesame seed oils, aloe vera, beta-carotene |
| Melting body milk, Garnier | Apply daily to body skin with massaging movements. | bifidocomplex, shea butter |
For arms and legs
| Product name | Mode of application | Active components |
| Intensive restorative hand cream for very dry skin, Garnier | Use as needed. To achieve the best results, we recommend applying the cream after each hand wash. | glycerin, allantoin |
Apply after washing your hands, and before going outside or doing household chores;
shea butter, niacinamide
Apply to clean feet twice daily or at night.
ceramides, salicylic and lactic acidApply as needed.
corn oil, rice oil, soybean oil, shea butter, passion flower oil, vitamin E, hazelnut proteins.
Now consolidate your knowledge by watching a short video.



