Causes of laryngitis. Main symptoms and types of pathology. Possible complications. Methods for treating laryngitis - pharmaceutical drugs and folk remedies.
The content of the article:- Reasons for development
- Types of laryngitis
- Spicy
- Chronic
- Basic forms
- Symptoms and diagnosis
- How to treat laryngitis
- Folk remedies
- Complications
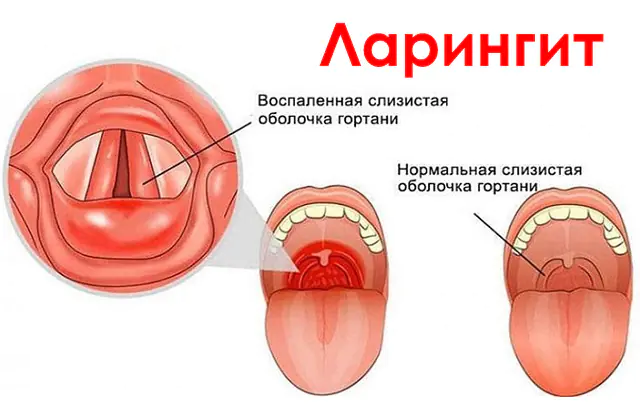
Laryngitis is an inflammation that most often develops in the mucous membrane of the vocal glands or in the larynx. Pathology can be caused by a bacterial, viral or fungal infection. Differs in acute or chronic course. For a quick cure and restoration of health, it is very important to identify the disease in time and carry out treatment.
Reasons for the development of laryngitis

The vocal cords are located in the larynx and consist of two folds of mucous membrane. They cover cartilage and muscle, and their opening and closing is designed to allow air to pass through. Normally, the process occurs smoothly, but when laryngitis develops, the ligaments become inflamed and swollen, which leads to distortion of the sound passing through them. A person's voice becomes hoarse, and in very severe cases, disappears completely. Inflammation can spread to the mucous membrane of the vocal cords, causing hoarseness.
The development of some forms of laryngitis in children can be dangerous. When the airways are completely or partially blocked by inflamed and enlarged tissues, breathing may become difficult. With laryngitis in adults, the described blockage does not occur.
Laryngitis can cause:
- ARVI. The disease can be caused by influenza, adenoviral infection, or parainfluenza.
- Infectious respiratory pathologies. Rhinitis, bronchitis or pharyngitis. Exacerbation of infectious diseases or secondary infection. This could be tonsillitis, diphtheria, whooping cough, measles, rubella or scarlet fever.
- Vocal cord overstrain. Laryngitis is often diagnosed in singers, prompters, after a conversation in a raised voice.
- Thermal impact. Drinking very cold or hot liquids can lead to inflammation of the larynx.
- Allergy. Upon contact with an allergen (food, wasp or bee stings, plant pollen, tree blossoms), swelling of the larynx occurs. This leads to a decrease in the flow of air into the lungs.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease. Accompanied by the reflux of stomach contents into the throat and esophagus.
- Irritation caused by chemicals. Inhalation of gas, dust.
The larynx is part of the respiratory system, so the disease can lead to inflammation in the bronchi, trachea, pharynx and even in the lungs. With timely prescribed and correctly administered therapy, the disease quickly resolves.
Main types of laryngitis
Depending on the condition of the mucosa, there are several types of disease. Let's look at their features in more detail.
Acute laryngitis
Inflammation occurs in the mucous membrane of the larynx. Pathology can be independent or provoked by infectious (flu, ARVI), general somatic (gout, rheumatism) diseases. The development of acute laryngitis is caused by infection, unfavorable working and living conditions, and prolonged strain on the vocal apparatus.
Acute laryngitis is characterized by a rapid onset. The disease develops against the background of the patient’s satisfactory condition and low-grade fever.
Main symptomatic manifestations:
- Painful sensations. Headache, muscle pain, sore throat and sore throat.
- Voice change. Hoarseness is noted. Manifestations are associated with swelling of the mucous membrane of the larynx and vocal folds, increased production of sputum.
- Dry cough. Begins on the 2-3rd day of illness. Over time, it turns into wet, accompanied by the release of mucous discharge.
- Temperature (up to 38 degrees). It is most often observed when laryngitis is viral in nature or during the transition of the catarrhal form of inflammation to phlegmonous.
Acute laryngitis in infiltrative or abscessive form is accompanied by painful sensations in the throat, the inability to perform swallowing movements (difficulties apply even to liquid forms of products), intoxication, and laryngeal stenosis. The severity of symptoms directly depends on the severity of inflammation.
The duration of catarrhal laryngitis, which is often diagnosed, takes 5-10 days. If the voice mode is disturbed or therapy is carried out incorrectly, the disease is accompanied by an infiltrative, phlegmonous or chronic course. The purulent form is dangerous because often provokes complications (abscess), swelling of the mucous membrane.
It is important that the condition is identified in a timely manner, because... it poses a danger not only to the health, but also to the life of the patient.Chronic laryngitis
In this case, inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa lasts more than 3 weeks.
Chronic laryngitis provokes:
- Infection. It can be fungal, bacterial, mycoplasma, viral, chlamydial infection. The presence of caries, sinusitis, and otitis in a person can lead to the development of an inflammatory process in the larynx.
- Injuries of the neck, larynx. Lesions can be both external and internal, for example, inhalation, foreign body.
- Allergens. Laryngitis often occurs when a person has prolonged contact with chemicals (dust, gas), high temperature or allergens.
- Acute laryngitis. The transition from one form to another is associated with its duration. If the course of the pathology is observed for 3 weeks or more, we can say that the inflammation has become chronic.
- Load on ligaments. Prolonged exposure to these muscles can cause damage.
This course of laryngitis is characterized by hoarseness, soreness and pain when swallowing, and a feeling of a foreign body in the throat.
Main forms of laryngitis
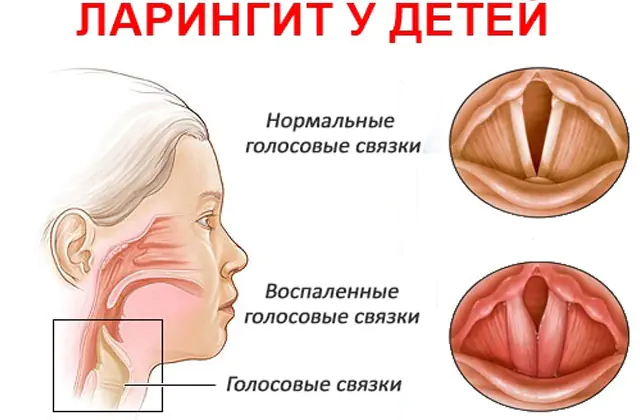
Only a specialist, through a visual examination, after collecting an anamnesis and studying test results, can determine the form of the disease and prescribe treatment. Independent diagnosis and selection of treatment is unacceptable!
The following forms of laryngitis are distinguished:
- Hyperplastic. It is characterized by a change in the color of the mucous membrane to gray or blue-red. Hyperplasia of the ligaments or areas under them is noted.
- Catarrhal. The most common, but not dangerous form of pathology. It is caused by infection, so it is important to start treatment on time so as not to provoke loss of voice and increased respiratory failure.
- Atrophic. A common form of laryngitis in adults. Associated with a decrease in cell regeneration, the appearance of fibrosis and a decrease in tissue size. These signs are most often characteristic of age-related laryngeal dysfunction.
- Viral croup. Inflammation is diagnosed in the larynx and upper respiratory tract. Occurs in children aged 3 months to 3 years. Provokes narrowing of the airways. Croup can be true (diphtheria, entry of a foreign object into the larynx) and false (formed during the acute course of stenosing laryngitis).
- Hypertrophic. A rare form of the disease, it can occur as a separate disease (pathologies in the oral cavity, nasopharynx) or as a complication (catarrhal laryngitis, throat surgery). Characteristic are small seals and nodules that need to be cauterized or undergo surgery to remove them.
- Diphtheria. Typical for preschool children. It spreads when corynebacteria penetrate and move from the tonsils to the larynx. Transmitted by airborne droplets. Causes inflammation and severe intoxication. A whitish coating is noted on the mucous membrane, the discharge of which provokes the closure of the respiratory tract.
- Subglottic. A dangerous pathology that leads to rapid narrowing of the lumen in the larynx.
- Hemorrhagic. The cause of development is toxic flu or problems of the hematopoietic organs. Accompanied by hemorrhage in the larynx, when coughing, expectoration of veins and blood clots.
- Purulent. Phlegmonous inflammation in the larynx can be caused by catarrhal laryngitis.
- Allergic. The impetus for development is chemical substances that get on the mucous membrane (dust, smoke, insect bites), and the consumption of certain foods (citrus fruits, eggs, milk, chocolate). Inflammation in the larynx is characterized by blueness of the nasolabial triangle, severe swelling, allergic rashes, suffocation, which can lead to asphyxia.
- Fungal. Caused by exposure to Candida fungi. Candidal laryngitis often develops after antibiotic therapy. A white cheesy coating can be seen on the laryngeal mucosa.
Symptoms and diagnosis of laryngitis
Symptoms of laryngitis are manifested by voice disturbance. Hoarseness is explained by the fact that the ligaments become inflamed and swollen. A person may feel pain while talking. Due to the narrowing of the lumen in the larynx, there is a deterioration in respiratory function; in children it can develop into false croup - a dangerous complication of laryngitis.

In addition to the main symptoms of laryngitis, the pathology is also characterized by accompanying manifestations:
- weakness;
- loss of appetite;
- chills, fever to subfebrile levels;
- headache;
- spasm of the muscles of the larynx;
- dry cough caused by a feeling of a foreign object in the throat;
- unpleasant sensations during swallowing;
- enlarged and painful lymph nodes.
In the case when not only the larynx is inflamed, but also the pharynx, tonsils and other parts (lungs, bronchi, trachea), signs characteristic of these pathologies are noted.
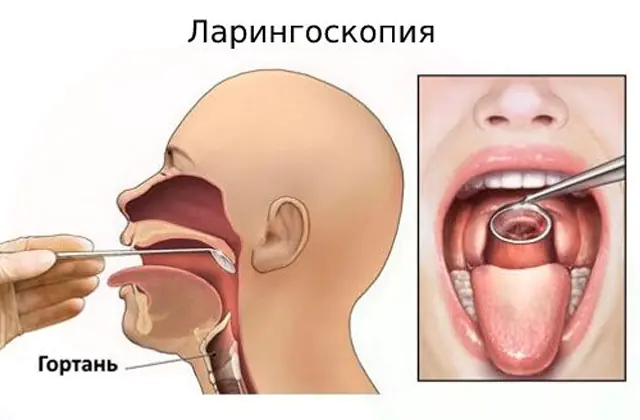
Symptomatic manifestations of laryngitis are similar to those of infectious diseases. To clarify the diagnosis, clinical diagnostics are carried out, which includes:
- History taking. The doctor checks with the patient for the presence of a sore throat, how the disease began, its main symptoms and manifestations.
- Physical examination. During a visual examination of the throat, the outer contour of the neck and larynx, the mobility of the vocal cords by palpation and during swallowing are studied. The presence of stenosis, enlarged cervical lymph nodes, redness and swelling of the larynx is determined. The throat is also examined for the presence of plaque of a mucous or purulent structure, and the capillary pattern is taken into account.
- Taking a smear. With its help, you can identify the causative agent of infection.
- Allergy tests. Exclude or confirm the patient's allergy.
- Blood and urine analysis. The study allows you to determine the nature of the developed pathology (viral or bacterial).
To detect a foreign object in the larynx, to exclude an abscess, tumors or other pathologies accompanied by similar symptoms, laryngoscopy, rhino- or pharyngoscopy, X-ray, ultrasound, and tomography may additionally be prescribed.
To identify the disease, an examination is carried out by a therapist (pediatrician). If necessary or to clarify the diagnosis, consultation with an otolaryngologist may be required. Using a laryngoscope, your doctor will be able to study how the vocal cords move.
Another widely used diagnostic method is endoscopy. To carry out the manipulation, an endoscope is used, a flexible tube equipped with a video camera at the end. If there are changes in the area of the larynx, the doctor may take a fragment for a biopsy.
A differential diagnosis of laryngitis with signs of laryngeal syphilis, tuberculosis, and the presence of cancer cells is mandatory. If tumor lesions are present, CT or MRI is performed.
The effectiveness of laryngitis treatment at the initial stage depends on the thoroughness of the diagnosis, which makes it possible to reduce the likelihood of relapses.
How and with what to treat laryngitis?
Hospitalization is carried out in case of a complex form of the disease, laryngeal stenosis, which can provoke the development of croup, allergies, the presence of pathologies of the central nervous system and other prerequisites that can aggravate the course of the disease.
After the diagnosis is made, a laryngitis treatment method is determined, consisting of three areas:
- Antibiotic therapy. Even taking into account the fact that the disease is viral in nature, a weakened body is susceptible to bacteria. To eliminate them and prevent relapse, antibiotics are prescribed for laryngitis (in tablets, in soluble form, in the form of injections). To confirm a bacterial infection, a swab is taken from the patient's throat, which is then examined for the presence of streptococci or staphylococci. Antibiotics are prescribed in the presence of purulent discharge during coughing, laryngeal stenosis, prolonged course of the disease, a tendency to relapse, and the presence of fibrinous crusts on the laryngeal mucosa. To treat prolonged laryngitis, broad-spectrum antibiotics - carbapenems - are prescribed.
- Detoxification. The goal of this area of therapy is to remove waste products of bacteria from the body, increase immunity and strengthen a weakened body. For these purposes, fermented preparations (Movinase, Trypsin), vitamins (group B, ascorbic acid) or vitamin complexes are used.
- Recovery. Includes physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis with novocaine, UHF therapy, electrophoresis on the throat area, microwave exposure, UV irradiation, Sollux lamp). A gentle regime for inflamed vocal cords is also required. During treatment, it is recommended to talk less, not drink alcoholic beverages, and not take very cold or hot food or drinks.
How to treat laryngitis is determined by the doctor after studying the test results and taking into account the patient’s condition. In adults, the acute form of the disease is more common. If present, inhalation or clinical therapy is prescribed. Antibiotics for this form of the disease are prescribed only if there is no effect from therapy carried out for 4-5 days, with inflammation of the lower respiratory tract or with the addition of purulent exudation. Therapy for chronic laryngitis is identical to the acute form of the pathology, but antibiotics are not prescribed.
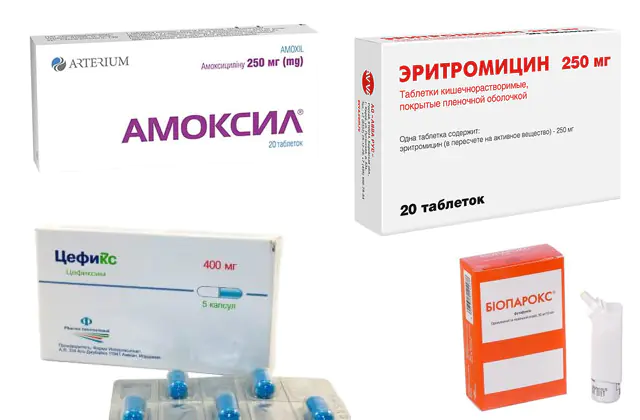
Drugs for the treatment of laryngitis:
- Amoxil. Antibiotic penicillin with a wide spectrum of action. When exposed to the cell wall, it destroys pathogenic bacteria. Taken orally. The tablet can be drunk whole or diluted with water (20-100 ml) to form a suspension. Prescribed with caution during pregnancy (especially in the 1st trimester). The standard dosage is 150-300 mg per day, taken in 3 divided doses. Price - 360 rub. (150 UAH). Analogs: Amoxicillin, Amofast.
- Cefix. Antibiotic from the group of cephalosporins. Shows broad bactericidal activity for gram-positive and gram-negative species of microorganisms. For children, the dosage is 8 mg per 1 kg of body weight per day, for adults - 400 mg per day. Duration of treatment is 7 days; if necessary, therapy can be extended to 14 days. Price - 530 rub. (220 UAH) Analogs: Cefepime, Ceftriaxone, Suprax.
- Erythromycin. Macrolide antibiotic with bacteriostatic effect. Recommended if there is a risk of developing stenosing laryngitis. Contraindications for use include allergies to macrolides or high sensitivity to Erythromycin. Before starting to take the drug, it is important to identify the causative agent of the disease. This will prevent the formation of resistant forms of bacteria. Dosage for adults: 200-500 mg up to 5 doses per day. Price - 50 rub. (21 UAH) Analogue - Clarithromycin.
- Bioparox. Local polypeptide antibiotic with anti-inflammatory properties. Relieves the symptoms of laryngitis, the action is aimed at treating a viral infection. Taking the drug leads to the death of the microorganism that caused the infection. There is no cross-resistance with other systemically administered antibiotics. Contraindicated for children under 2 years of age, pregnant and lactating women. Treatment is carried out using 4 sprays into the mouth (4 times) or into each nostril of the nose (twice). Manipulation is recommended to be carried out 4 times a day. Analogs: Fusafungin, Erespal. Price - 310 rub. (130 UAH).
- Suprastin. Antihistamine systemic agent. Prescribed for allergic and skin pathologies. Effective for allergy symptoms associated with taking medications. Helps relieve swelling. Suprastin is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the components that make up the drug. Not prescribed during pregnancy, breastfeeding and children under 14 years of age. The standard dosage is 25 mg (three times a day) with meals. Analogue - Loratadine. Price - 180 rub. (75 UAH).
To improve sputum discharge, alkaline drinks, infusions of medicinal herbs (marshmallow), and potassium iodide solution (3%) are prescribed. These remedies are useful for all forms of laryngitis, because alleviate the patient's condition, stimulate the functioning of the bronchi. Syrups (licorice root, Ambroxol, Lazolvan) may be prescribed.
An effective treatment option is inhalation for laryngitis. They can be alkaline (mineral water, soda), antibacterial or oil (lavender, pine, eucalyptus). With the development of stenosing laryngotracheitis, the doctor may prescribe glucocorticoid inhalations with Salbutamol, Berodual.
To cure a severe cough and reduce the manifestations of laryngitis, a special device is used - a nebulizer. Enzymes (Chymotrypsin) and hormones (Dexamethasone) are used for spraying. Their action is aimed at relieving swelling, dilating the bronchi, and removing phlegm. To create an antiseptic effect, decoctions (infusions) of herbs are added to the nebulizer: chamomile, coltsfoot, sage, calendula.
During the procedure, medications are inhaled through the mouth and exhaled through the nose. The duration of the manipulation is about 10 minutes, the optimal frequency is three times a day. After the procedure, it is not advisable to go outside, talk, or eat for half an hour.
If treatment of laryngitis in adults does not produce results and the patient’s condition does not improve, surgery is performed after the appointment of an otolaryngologist. Thanks to this, it is possible to prevent the degeneration into malignant tissues affected by inflammation. With the help of surgical intervention, it is possible to eliminate the main symptomatic manifestations and reduce exacerbation in the chronic course of the disease.
Important! Stenosing laryngotracheitis and acute laryngitis in infants are treated only in a hospital setting!The development of pathology during pregnancy is dangerous, because Bacteria and viruses can cross the placenta and harm the embryo. Congenital pathologies in a newborn are possible, for example, heart defects and nervous system defects. To quickly relieve the symptoms of laryngitis and prevent complications, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor. Taking into account the trimester, the specialist will select the most effective and harmless treatment.
Note! It is not allowed to independently stop taking medications for laryngitis prescribed by a specialist, or to replace them; this can lead to the expansion of lesions and the disease becoming chronic.Folk remedies against laryngitis

Treatment of laryngitis at home is effective only at the very beginning of the development of the disease. The main goal is to reduce the severity of symptoms and exposure to irritating factors.
The most effective folk methods for treating laryngitis include:
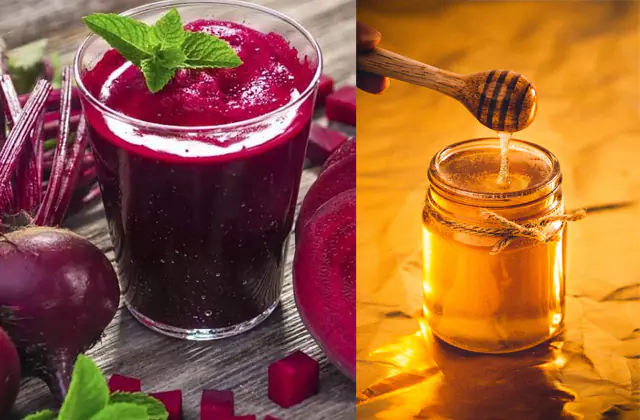
- Rinse. Use beet juice diluted with water (1:1), with the addition of 1 tsp. lemon juice. The procedure should be performed 5-6 times a day.
- Warming up. Mustard foot baths are effective. For laryngitis in children, it is recommended to place jars or mustard plasters or a warm compress on the throat for 30 minutes on the interscapular area.
- Inhalations with honey. To carry out the procedure, you need to dissolve 1 tbsp. honey in 125 ml of water. Inhalation duration is 10 minutes.
Infusions and teas should be taken warm; they should not contain components that irritate the mucous membrane.
Note! You can use folk recipes for additional treatment of laryngitis only after consultation with your doctor.Complications of laryngitis
The photo shows the prevention of relapses of chronic laryngitis
If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner or choose the wrong treatment tactics for laryngitis, severe complications develop.
Characteristic consequences of the acute form of the disease:
- Narrowing of the throat walls. Provokes disruptions in breathing function.
- Benign formations. Polyps and granulomas form in the larynx.
- Loss of voice. Often has a direct correlation with problems in the vocal folds.
The chronic course of the disease causes a narrowing of the walls of the larynx. Infectious - pneumonia, bronchitis.
The purulent form of laryngitis can lead to:
- Lung abscess. A cavity filled with pus is formed in them.
- Sepsis. It is noted in case of infection of the bloodstream.
- Phlegmon. This is the name for purulent inflammation of the tissues of the neck.
- Mediastinitis. Development of the inflammatory process in the chest cavity.
- False croup. Laryngeal stenosis caused by swelling of the vocal cords.
- Epiglottitis. In this case, the cartilage of the larynx closes the entrance to the epiglottis during the passage of food.
- True croup. There is obstruction of the respiratory tract by a foreign body or diphtheria films.
A dangerous complication of laryngitis is false croup, i.e. Laryngeal stenosis caused by swelling of the vocal cords. It develops due to infection with viruses, allergies, or reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus. Not only the vocal cords become inflamed, but also other parts of the larynx. To relieve an attack, a healthcare worker performs inhalation with Pulmicort. If there is no result, Dexamethasone or Prednisolone is administered intramuscularly.
Video about laryngitis - development mechanism, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment:



