- 1. Stomach hurts after laparoscopy
- 2. Basic characteristics of laparoscopy
- 2.1. Benefits of laparoscopy
Pain after laparoscopy is not an uncommon problem. In this article we will look at all the causes of discomfort in the abdomen after surgery, as well as methods for getting rid of pain.
Stomach hurts after laparoscopy
All patients complain of pain after laparoscopy, which is caused by injury to soft tissue structures in the area of the anterior abdominal wall, as well as internal organs and peritoneum. The sensation of pain is provoked by argon or carbon dioxide molecules that enter the abdominal cavity during the operating period.
The pain after laparoscopy is not very strong. The sensations are much weaker than after a conventional operation, moreover, traces of the intervention heal much faster, and the rehabilitation process is much easier. To make the pain less pronounced, doctors prescribe narcotic analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics. Within a day, or even 12 hours, the pain subsides, however, the patient may still experience slight discomfort.
The most common complaints from patients:
- the entire abdominal area hurts without any specific localization;
- after laparoscopy the ovary hurts;
- after laparoscopy my side hurts;
- navel hurts;
- After laparoscopy surgery, the stitch hurts.
Basic characteristics of laparoscopy
The laparoscopy method is used quite often in modern medical practice, as it has more advantages than classical surgery (laparotomy). Firstly, the marks after laparoscopy are not so noticeable, and the healing process is much more intense. Secondly, the intervention is not so painful for the patient, therefore large doses of analgesics are not prescribed during the rehabilitation period, which significantly reduces the risk of side effects. After surgery, in the long term, adhesions form much less frequently, so there is practically no chronic pain as such.
So, the operation, as a rule, takes place under general endotracheal anesthesia. Local anesthesia is sometimes used. Local anesthesia is most often prescribed to elderly patients if there are any contraindications to other types of anesthesia. During the operation, pain is not felt, even if the person is awake. These are the properties of local anesthesia: the lower part of the body completely loses sensitivity.
Immediately after the administration of the anesthetic, several small incisions are made on the anterior abdominal wall, and then this area is expanded using a trocar. After this, surgical equipment is inserted into the open cavity, including a special video camera that displays the image on the screen. In addition, neutral or carbon dioxide is introduced into the cavity, due to which the space inside expands. Thus, the surgeon tracks his every action using images on the monitor. After all the manipulations have been performed, the doctor sews up the incisions. If pain occurs during the rehabilitation period, then special drugs are introduced into the cavity to reduce it.
Benefits of laparoscopy
- Injury is minimized;
- Short rehabilitation period;
- Rapid recovery;
- No scars;
- There are practically no painful sensations.
Causes of pain after laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopy is performed for both therapeutic and diagnostic purposes, and the causes of pain are different. Firstly, the procedure, one way or another, injures soft tissue structures and internal organs, and can also cause irritation of the abdominal cavity. The location of pain is the scar, parts of the abdomen that are associated with recent surgery. Secondly, the cause may be a strong impact of carbon dioxide introduced into the cavity (up to 4 liters), and pain is felt in the shoulders and back, in the upper abdomen.
After laparoscopy, the woman soon returns to normal life
The process of development of pain syndrome after laparoscopy has not been studied comprehensively. Some experts believe that irritation occurs after oversaturation with carbon dioxide, which is proven in a simple way: if carbon dioxide is replaced by argon or nitrogen, the effects are less noticeable. Other professionals argue that the pain is caused by mechanical manipulation of the peritoneum, where the gas bubble is located (under the diaphragm). Both versions are correct, although all these aspects together matter.
Another factor causing pain is a consequence of nerve irritation in the abdominal and diaphragmatic region, as well as a malfunction of blood vessels and blood flow. The pain pattern is characterized by the release of prostaglandin and cyclooxygenase, which are considered mediators of inflammation. The intensity of pain and the occurrence of the inflammatory process itself depend on the type of injury and the presence of complications, which can manifest themselves in the form of temperature and pus discharge from the wound area.
What complications may arise?
In general, the operation does not cause a deterioration in the general condition of patients who have undergone it, and complications occur extremely rarely. Of course, one should take into account some individual characteristics that come from the anatomical structure and physiological mechanisms occurring in the body. Acute complications occur only in a small percentage of patients, however, they can be avoided by consulting with a surgeon in advance. Only a doctor can determine the potential risk to the body.
The most common complications after laparoscopy
As a rule, the most common complications after laparoscopy include injury to the walls of blood vessels and internal organs by the trocar. It is not uncommon for patients to suffer electrical burns that may not be noticed by the surgeon. One should take into account the fact that cold gases are used during the operation, so injuries in the abdominal cavity are a phenomenon that occurs in medical practice.
Additional risk factors may include scars from previous surgery, as well as abnormalities related to platelet function. To avoid many problems, it is better to immediately warn the doctor about existing pathologies, especially if they are associated with disruption of the respiratory tract - this can lead to danger after pneumoperitoneum, and to resolve these issues it will be necessary to resort to open surgery.
Stories from our readers:
Natalya - was able to
shrink vagina
after childbirth
Natalya, 32 years old:
After giving birth, intimate life with my husband ceased to bring former pleasure. Natural childbirth greatly stretched the vagina, my husband did not feel anything, and neither did I. Kegel exercises and vaginal balls did not help - the latter literally fell out of me. In addition, I suffered from pain and dryness in the vagina.
I was very afraid that my husband would get tired of this and he would “go to the left”
My last hope was Virgin Star cream, I learned about it at one of the large women’s communities, where mothers like me shared their stories and miraculous recovery. This cream restored my vagina in literally a matter of days. The pain and dryness went away, intimacy became even better than on our honeymoon! My husband never tires of complimenting me on how narrow everything is “there” for me! I ordered this cream on the official website.
How does your stomach hurt after laparoscopy?
The period after laparoscopy may be characterized by pain of a different nature. Upon completion of the operation, the patient feels quite severe pain, which gradually decreases during the first 12 hours. After a day it finally subsides, but does not disappear completely. There are cases when the pain lasts longer. For example, in women who have undergone gynecological surgery. If the pain is severe and excruciating, this may be a sign that a nerve was damaged during surgery and blood flow was disrupted. If several days have passed since laparoscopy, and the pain only intensifies, this may signal the onset of infection of the internal structures. The first side sign is an increase in temperature.
It is quite natural when, on the first day after surgery, the stomach ache in the places where the punctures were made. The pain may gradually move into the diaphragmatic area. The second day can be characterized as a period of pain easing, however, unpleasant sensations may occur in the shoulder girdle, back, and upper abdomen. All these sensations are associated with the fact that a large amount of gas is introduced into the abdominal cavity. As a rule, after laparoscopy, the greatest discomfort occurs on the right side. Some patients may experience a sore throat after endotracheal anesthesia, but it goes away quickly enough and does not require medication.
In less than a week, the pain should disappear. Of course, this period is too short for complete recovery, so sudden movements may still cause discomfort. For the first month, you should protect yourself from overexertion, do not lift heavy objects, and do not play sports. If quite a lot of time has passed after the operation, and the pain has not disappeared, you should consult a doctor - perhaps an infection or ischemia of an organ is developing in the body. If pain periodically makes itself felt several months after laparoscopy, this may signal the beginning of the adhesive process.
Sometimes after laparoscopy the area around the navel may hurt. There are almost no nerve endings near the navel, however, trauma to surrounding tissues can cause increased innervation at the surgical site.
If additional symptoms appear against the background of pain, then you clearly cannot do without medical help. These symptoms include:
- Fever and associated chills;
- Cutting pain in the lower abdomen;
- Periodic fainting;
- Redness of the areas around post-operative scars;
- Purulent or bloody discharge from the wound;
- Difficulty urinating;
- General weakness, headache, frequent fainting conditions.
Sudden movements can cause discomfort in the lower abdomen in patients who have undergone a laparoscopy procedure, although this phenomenon is not a deviation from the norm and does not require treatment. If the pain is unbearable, then you cannot do without the help of a doctor who will help you choose painkillers. The main thing is not to self-medicate.
Patients also often complain of lumbar pain and discomfort in the middle abdomen. To reduce pain, it is necessary to increase the rest time and leave strong physical activity for a while. If after three days the situation does not change for the better, contact your doctor immediately to avoid potential complications.
During the first three days, you may experience side effects from laparoscopy such as lethargy, bloating, and vomiting. You should not panic, this is quite normal after an intervention. During this period, you should take a closer look at your diet, cutting out heavy foods, sweets, and starchy foods, choosing low-fat dairy products, light broths, and biscuits. Since the digestive system has not yet recovered from the intervention, it is better not to overload its organs. You can return to your usual type of diet after a few days if the pain and other symptoms have disappeared.
Remember that any intervention is a shock to the body, so your lifestyle during the rehabilitation period should be reconsidered. It is necessary to include outdoor walking in your schedule, however, the main thing is not to bring yourself to a state of fatigue. Considering these simple rules, the postoperative period will pass quickly and painlessly.
It should also be understood that not all symptoms are abnormal. Doctors say that pain in the lower abdomen is a completely natural phenomenon that occurs in more than 80% of cases. Of course, intense, ongoing pain is clear evidence of a problem, in solving which you should not rely on yourself by self-medicating.
Treatment of pain after laparoscopy
In order to reduce the intensity of pain, the method of injecting the surgical area with lidocaine, novocaine or other anesthetics is used. Sometimes the drug is injected directly under the diaphragmatic area or into the abdominal cavity. After laparoscopy, the suture area is infiltrated with analgesics. The patient may be prescribed small doses of opiates. Narcotic analgesics have both a number of advantages and a whole set of disadvantages. They are good for fighting pain, but can also cause side effects such as vomiting, inhibition of consciousness, and the overall picture of the patient’s condition may become unclear.
Non-steroidal medications that fight inflammation are also effective against pain and discomfort. They are used both after and before the intervention. The active substances block the production of prostaglandin, which is an inflammatory factor. However, these drugs also belong to the group of narcotics, so their doses are strictly regulated. Drugs such as ketanov and ketotifen tend to block renal blood flow and inhibit the formation of prostacyclin. As a result, the filtration capacity of the kidneys slows down.
tubules, as well as renal failure. Less dangerous drugs, such as analgin or paracetamol, are often used. However, analgin negatively affects hematopoietic function. The active substances of these medications prevent the spread of factors that cause inflammation in the central nervous system, and also do not have such a strong effect on the circulatory system.
To treat pain after laparoscopy, especially if it radiates to the shoulders, back or abdomen, a comprehensive approach is needed, which consists of taking non-narcotic local anesthetics and NSAIDs, which are required both before and during the intervention, as well as the administration of opiates after the procedure . Thus, anesthetics and other elements combine to relieve pain. All drugs are prescribed taking into account contraindications and patient tolerance of a particular substance.
So, if after laparoscopy various kinds of problems appear, they need to be solved only with the help of a specialist. When relief occurs, analgesics are stopped to reduce the likelihood of a side effect. Pain after laparoscopy requires certain diagnostic measures, as it may indicate complications. During the rehabilitation period, you should avoid excessive physical activity. As for gynecology, the main recommendation is temporary sexual rest.
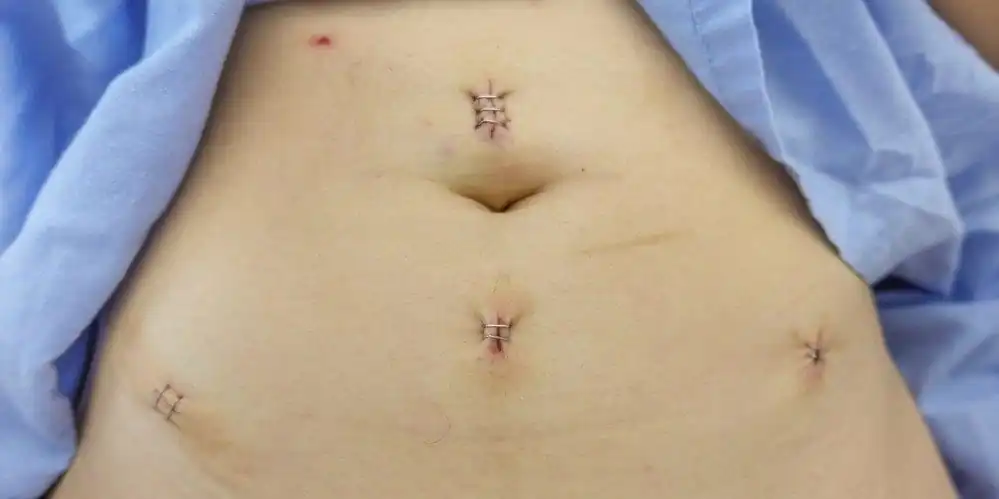
When the topic comes to operations, of course, all patients are interested in how long it will take for the stitch to heal and the process of restoring the body as a whole. Often women go to the hospital with a complaint that the suture hurts after laparoscopy. Unpleasant sensations such as itching, redness, and the appearance of compactions in the suture area may indicate the occurrence of an inflammatory process, which is not the norm. So what are the causes of pain in the suture area after laparoscopy?
1. Thread rejection (ligature fistula)
Sometimes it happens that after surgery, inflammation appears at the site of sutures, accompanied by serous and purulent discharge. All this indicates that a fistula has formed, as a result of which the body has started the process of rejecting the surgical threads. Naturally, if after laparoscopy the suture hurts, this is not the norm, and then there is a need to seek help from specialists.
Causes of ligature fistula after laparoscopy:
- infection entering the seam through injured tissue due to non-compliance with hygiene rules;
- allergy to the material from which the threads are made.
In addition, the following factors can cause a fistula::
- the patient's unsatisfactory health condition;
- high level of immune reactivity of the body (observed at a young age);
- the presence of other specific infectious diseases (syphilis, tuberculosis and others);
- place and type of surgical procedures (surgery on the ovary, cyst removal);
- the presence of cancer that weakens the body’s protective functions;
- vitamin deficiency;
- diseases leading to metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, excess body weight).
Symptoms of the formation of a ligature fistula
- formation of compactions in the first days after laparoscopy;
- heat;
- swelling in the suture area;
- the seam hurts;
- release of fluid when pressing on the seam.
Treatment of fistula
First of all, local antiseptics can be prescribed to relieve inflammation (ointments, medicinal powders), antibiotics (if the wound does not heal for a long time), as well as enzymes that help dissolve dead tissue. In addition, physiotherapeutic procedures (UHF therapy, quartz treatment) show positive results. If local therapy does not completely relieve inflammation, another operation (laparoscopy) will be required, after which local therapy will be performed again.
2. Seams coming apart
Postoperative sutures often cause a lot of inconvenience (for example, if the umbilical suture hurts after laparoscopy) and can cause the development of inflammatory processes. There are rare cases when the internal seams come apart, and in such a situation you should not think long about what to do, but rather seek help from a specialist as quickly as possible.
Causes of seam divergence:
- non-compliance with rest after surgery;
- sudden movements;
- carrying heavy loads;
- infections entering the wound;
- neglect of hygiene rules.
Symptoms of suture dehiscence after laparoscopy:
- pain when pressing on the seam;
- the appearance of liquid or purulent discharge when pressed;
- swelling and redness of the area around the suture;
- heat.
Treatment of suture dehiscence
Undoubtedly, there is no other option than re-suturing. If the suture is already damaged, then for the normal course of the regeneration process of tissues injured after laparoscopy, the suture must be restored in order to avoid the risk of infections entering the open wound. In addition, when the suture is healed, it forms unaesthetic scars, which is an unfavorable indicator for most women.
After re-suturing, the pain from laparoscopy should go away, but it is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations for caring for the suture. Therapy in this case does not present any difficulties: it consists of systematically treating the seam with antiseptic agents to eliminate the risk of infection. In addition, later you can resort to the help of wound healing agents (ointments), which can reduce tissue scarring.
3. Adhesions after laparoscopy
Adhesions are compactions that are formed from connective cells. They help unite internal tissues. This process is contradictory for the human body. Adhesions that appear after laparoscopy look like white stripes, which lead to deviations in the functioning of body systems, depending on where they are formed. The appearance of adhesions in a woman’s body, especially in the pelvic organs, creates a lot of health difficulties.
Reasons for the formation of adhesions:
- diabetes mellitus (due to reduced regenerative capacity of the body);
- connection with gas compositions used during surgical operations and the air environment (due to drying of tissues);
- excess body weight (excess fat tissue causes fusion in the abdomen and navel);
- infections (due to the appearance of the inflammatory process, tissue regeneration processes are hampered and compactions form).
The symptoms of adhesions are very limited. Their presence can only be detected by inspection and pulping, when small compactions are felt. The only symptom that may appear is if the stitches hurt for a long time (more than a month).
Treatment of adhesions
As a rule, physiotherapeutic procedures and medications are prescribed to treat adhesions. If a positive result cannot be achieved with local treatment, relaparoscopy can be performed (repeated surgery to remove adhesive formations, which is carried out by cauterizing them).
4. Inflammation of sutures after laparoscopy
Inflammation of sutures is not the worst ailment if you promptly seek the help of a specialist. After determining the cause that led to the inflammatory process, the most appropriate method of removing it and restoring the source of inflammation can be selected.
Causes of suture inflammation:
- weak immunity;
- entry of bacteria and viruses;
- non-compliance with hygiene and suture care;
- divergence of seams.
Symptoms of suture inflammation after laparoscopy are reduced to pain in the wound area, increased body temperature, and possible discharge from the suture. General malaise and chills may also occur.
Treatment of suture inflammation involves eliminating the root cause of the development of the inflammatory process and prescribing local therapy to relieve pain after laparoscopy: solutions for treating the suture and ointments with antibiotics.
5. Traumatization of the subcutaneous fat layer
Under certain circumstances, during the operation, the doctor may injure the subcutaneous fat layer, which does not always occur due to his incompetence. Sometimes it is simply not possible to sew up a wound any other way. This occurs when there is a process of tissue necrosis after laparoscopy.
The most striking sign that tissue trauma has occurred during laparoscopy is the formation of a hematoma in the suture area. It also provokes pain.
Therapy for this disease consists of local treatment, and physiotherapeutic procedures can also have a positive effect on relieving inflammation.
Which doctor should I contact?
In the postoperative period (after laparoscopy), the suture needs careful care and treatment. But there are situations that even with full compliance with the doctor’s recommendations for treating the seam, for one reason or another, an inflammatory process may begin, which is always accompanied by painful sensations. A qualified surgeon will be able to help you understand this problem, who will determine the possible reason why the postoperative suture hurts and suggest the most effective ways to eliminate it.
Other causes of pain in the suture area after laparoscopy
- If the sutures after laparoscopy take a long time to heal and severe itching does not go away during the entire healing period, then this may indicate a poor-quality thread used during the operation. All this provokes unpleasant sensations in the area of the seam, and can even cause the development of inflammatory processes.
- There are situations when, for one reason or another, the threads of the internal suture do not dissolve. This may be caused by an allergic reaction to the material of the threads and the functional characteristics of the body. In this case, the tissues begin to reject the foreign body (threads), as a result of which the process of rotting and divergence of the suture placed after laparoscopy may begin. Of course, all these factors cause such an unpleasant symptom as stitches hurting after laparoscopy. In this case, the patient’s temperature may rise and general health may deteriorate.
- If the suture looks like an inflamed, swollen wound, then this is a sign of a medical error. That is, most likely, due to the incompetence of the surgeon, the suture was performed incorrectly, which stopped the processes of tissue regeneration and provoked inflammatory processes.
In this case, only a qualified specialist can eliminate the pain in the sutures, who will prescribe the most appropriate treatment to relieve inflammation and increase regenerative functions. In addition, improper treatment of the seam with antiseptic agents can lead to this condition.
Summarizing
Despite the fact that laparoscopy is a gentle surgical method of treatment, it should be treated with the utmost responsibility.. It is necessary to give preference only to proven, qualified specialists who will not only perform a high-quality operation (laparoscopy), but also provide proper postoperative care (observation, care recommendations).
Although inflammation of the suture does not pose a threat to life, if this symptom appears in the postoperative period, it is necessary to immediately begin taking measures to relieve the inflammatory process, as this can lead to serious complications.
Found an error? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter.
Laparoscopy is the most gentle type of surgery. The postoperative recovery period is easier, and the likelihood of complications is minimal.
Pain after laparoscopy is mild. They decrease after 12-24 hours. Most often, patients complain that they have pain in the chest or stomach after laparoscopy. To distinguish normal from pathology, it is necessary to pay attention to the intensity and nature of pain.
Pain during the procedure
Laparoscopic surgeries are becoming popular. They are increasingly used in gynecology, when removing stones in the gall or bladder, as well as when removing abdominal organs. The operation is performed through several small punctures of soft tissue.
Progress of the surgical intervention:
- The patient is given anesthesia.
- 3-4 punctures are made on the anterior abdominal wall, through which a surgical instrument and camera are inserted.
- The abdominal cavity is filled with argon or carbon dioxide to expand the intra-abdominal space.
- An image is displayed on the monitor, the surgeon observes all his manipulations.
- After the operation is completed, the instruments are removed and sutures are applied to the punctures. If the surgical intervention is complex, for example, removal of the uterus, then drainage is left in the wounds for 1-2 days. In this case, sutures are applied for 5-6 days.
Before going on the operating table, patients are concerned about the progress of laparoscopy and whether it hurts. No. The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia, so the person does not feel any manipulation.
More often, general endotracheal anesthesia is used, in which the patient is put to sleep. He regains consciousness after the end of the operation. Local (epidural) anesthesia is done less frequently, only if there are contraindications to general anesthesia. An anesthetic substance is injected into the spine, the patient does not feel anything below the area where the anesthesia was injected. Very rarely discomfort is possible, but these are isolated cases.
Unlike laparotomy (cavity surgery), laparoscopy is much easier to tolerate. In some cases, the patient is discharged from the hospital the very next day. Analgesics, NSAIDs and lidocaine are used to relieve pain.
Causes of pain after surgery
Painful sensations appear after surgery in all patients. Compared to laparotomy, the pain is minor and goes away much faster. The severity of pain largely depends on the patient's pain threshold.
More often, pain occurs in those places where punctures were made, as well as:
- in the abdominal area;
- near the navel (when filled with gas, the umbilical ring stretches);
- in the chest, in the side, under the ribs, in the shoulder area;
- in the throat;
- in the genital area.
During the first 12 hours, the most pronounced pain is observed. If epidural anesthesia was used during the operation, the person experiences pain in the lumbar region.
Pain after laparoscopy occurs for the following reasons:
- Injury to soft tissues and internal organs with a surgical instrument. In this case, pain is felt in the area of the incisions.
- Stretching, as well as irritation of the abdominal cavity with carbon dioxide, which was introduced during the operation. Up to 3-4 liters of gas are pumped into the patient's stomach. After the anesthesia wears off, the intensity of pain increases. The patient feels severe pain in the upper abdomen, in the back, under the ribs, and the shoulder may even hurt. Some people who have laparoscopy have difficulty breathing. This is caused by the compression of the diaphragm. It may be painful for a person to straighten up.
- The use of a tube through which the patient breathes during surgery. This tube is inserted into the throat and anesthesia is delivered through it. After using it, the patient feels a sore and sore throat, but does not experience any particular discomfort.
The intensity of pain depends not only on the pain threshold, but also on the indications for surgery.
If the pain does not subside, the temperature rises after laparoscopy, the suture festers, and tension in the abdominal wall is felt, then you need to contact a surgeon. These are symptoms of an infectious process.
You should also seek medical help in the following cases:
- cutting pain in the lower abdomen;
- redness of the seam;
- blood in the incision area;
- difficulty urinating;
- dizziness, headache, weakness;
- fainting.
Acute pain in the first 12 hours is not normal. This is a sign of a failed operation.
Abdominal pain
Patients often complain of pain in the upper abdomen, even if this area was not affected during the operation. The reason was described above. But you need to know how your stomach hurts after laparoscopy.
Painful sensations appear 2 hours after the operation, when the anesthesia stops working. The pain is severe, sometimes you cannot do without analgesics. More than 70% of patients rated the severity of pain at 30 points out of 100. Pain disappears after 12-24 hours.
It is impossible to determine where the pain is localized, whether the intestines, stomach or liver hurt. Sudden movements can cause abdominal pain. Unpleasant sensations should subside after three days, and disappear by 5-6 days. If this does not happen, you need to consult a doctor.
After laparoscopy, the area around the navel sometimes hurts, although there are no nerve endings there. The cause is injury to surrounding tissues.
Pain in the upper abdomen, side and under the ribs always occurs when internal abdominal organs are removed. The peritoneum is stretched, the walls are irritated by carbon dioxide, and therefore painful sensations appear.
Accordingly, pain after removal of the gallbladder is localized in the abdomen, hypochondrium, side, as well as in places of punctures and incisions. After surgery to remove an organ of the digestive tract, pain persists for more than a month until the functioning of the digestive system normalizes. The pain syndrome can be relieved with analgesics - “Spazmalgon” or “Ketanov”. If it does not go away 2-3 months after laparoscopy, then this indicates adhesions.
Pain in the suture area after surgery
After the anesthesia wears off, patients most clearly feel pain in the area of the incisions. It decreases after 12-24 hours. The occurrence of severe pain several days after surgery may be associated with the development of complications. In this case, you need to consult a doctor.
The puncture sites heal quickly, since their size is only up to 1.5 cm. They heal for 7-14 days, it all depends on the puncture site. The sutures in the navel area take a long time to heal, and the likelihood of suppuration is high.
During the first week after laparoscopy, the suture hurts. Normally, the following signs appear:
- It's a dull pain;
- abdominal pain;
- slight suppuration and redness of the incision site;
- bloating.
Such unpleasant sensations should subside within 7-14 days; it is during this period that the sutures are removed. If self-absorbable threads are used during the operation, they disappear within 5-7 days. The punctures heal completely after 30 days.
Is it painful to remove stitches after surgery?
If this is done on time, the wound does not fester, there are no complications, and the threads do not grow into the skin, then there will be no pain. The patient may experience discomfort from the instrument, but not pain.
Only a doctor should remove threads; you cannot do it yourself. It is important to go to the hospital within the specified time. If the suture material grows into the skin, then removing it will be painful.
Shoulder and chest pain
This type of pain occurs very often because carbon dioxide is introduced into the abdominal cavity. It expands the peritoneum, but compresses the internal organs. Within 1-2 days after laparoscopy, there is pain in the collarbone, chest, left or right side, under the ribs. But the pain is moderate, it is easily tolerated without taking painkillers. It's more of an uncomfortable feeling.
After removal of the gallbladder or appendicitis, the shoulders hurt, the right side hurts, the back on the right side hurts, as well as the upper abdomen. The most pronounced pain is at the puncture sites.
Why does the shoulder and neck area hurt after laparoscopy? The neck, shoulders and chest hurt in almost all patients who have undergone this type of surgery. This is due to the introduction of carbon dioxide, which is released through the lungs for several days after surgery. This is why the neck, collarbone, throat and other parts of the body hurt.
The most intense pain is the first two days after surgery, as well as during movement.
Pain in the genital area
Women often have to undergo laparoscopy due to gynecological diseases. This type of surgical intervention is used for the following purposes:
- diagnosis of genital diseases;
- tube removal for ectopic pregnancy;
- treatment of endometriosis;
- removal of ovarian cysts, adhesions, fibroids or fibroids, as well as the uterus;
- treatment of inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs.
Laparoscopy is also common among men with diseases of the genital organs. After laparoscopy of an inguinal hernia, men experience minor pain that goes away after 2-3 days. The pain radiates to the lower abdomen, side, lower back or sacrum.
After surgery, there is a high risk of complications. There is a risk of damaging nearby organs with the laparoscope. These are the intestines, liver and stomach.
Complications after laparoscopy are indicated by sharp cramping pain.
Pain in the lower abdomen after genital surgery in women is the most common. Other types of pain after laparoscopy in gynecology:
- the navel or the entire stomach hurts;
- pulling in the lower abdomen;
- the postoperative suture hurts;
- pain is felt in the right side, closer to the ribs;
- chest, shoulders, lower back hurt.
The localization of pain depends on the disease.
After laparoscopy to remove an ovarian cyst, pain in the lower abdomen and bloating occur. Painful sensations may bother the patient for 7 to 30 days. The most severe pain after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is felt in the first day. There is also severe pain at the puncture sites.
Do not be alarmed if your ovary hurts after laparoscopy. This is normal, since when a cyst is removed, soft tissue is injured. You need to be wary if the pain becomes cutting. It is acute, the pain in the ovaries increases. In this case, hospitalization is required.
Women who have undergone laparoscopic genital surgery have an increased risk of inflammation of the appendix, so it is necessary to pay attention to the nature of the pain. Painful sensations in the lower abdomen may be associated with menstruation, which usually begins a short time after surgery.
After laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes for an ectopic pregnancy, the lower abdomen will drag for at least a month. But such pain is mild. It should not cause discomfort or lead to loss of ability to work. Painful sensations may intensify with sudden movements. After laparoscopy of the uterus, it is painful to write and also to defecate.
Other characteristic pain syndromes
Very often, patients experience back pain. Pain syndrome occurs due to epidural anesthesia. The pain is mild and may bother the patient for several months after surgery. Sometimes my back hurts because of carbon dioxide.
After anesthesia, the whole body may ache, muscle weakness, dizziness and headache may be felt. If an anesthetic substance was injected into a vein, your arms may hurt, and after a couple of days your legs may hurt. Pain in the limbs can occur when carbon dioxide enters the vascular bed.
If a nerve is damaged by a surgical instrument, the patient's skin hurts or there is no sensitivity of the skin at all. The pain should go away over time. If this does not happen, then adhesions may be the cause.
Pain relief in the postoperative period
Laparoscopy is an operation with the least severe pain syndrome in the postoperative period. Immediately after surgery, the puncture sites are injected with an analgesic so that after recovery from anesthesia the patient does not feel severe pain.
Narcotic analgesics (opiates) are rarely used because they cause a number of side effects. They also quickly relieve pain, which interferes with the timely diagnosis of postoperative complications. If acute pain occurs after 12 hours, then this is not the norm.
In the first days after surgery, doctors may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They not only relieve pain, but also eliminate foci of inflammation. The most popular are “Ketanov” and “Ketotifen”.
To relieve pain after laparoscopy to remove a cyst in the ovary, NSAIDs and non-narcotic analgesics are used simultaneously. But you shouldn’t get carried away with painkillers, they negatively affect your health.
After laparoscopy, pain can be localized in different parts of the body, but it is not as severe as after abdominal surgery. This benefit is especially important for patients with a low pain threshold.