What is oxalaturia, why do salt crystals form in the urine? Symptoms and treatment of the disease: nutritional correction and drug treatment, list of medications. Prevention of oxalaturia.
The content of the article:- What is oxalaturia
- Why does it occur
- Main symptoms
- Diet
- How to treat oxalaturia
- Prevention
Oxalaturia is a pathology caused by metabolic disorders in the human body. Dysfunction of the excretory system leads to the formation of stones in the patient’s urine. Ignoring the problem can lead to the development of urolithiasis and the need for surgical intervention. And with early diagnosis and treatment, the prognosis is quite favorable. A diet for oxalaturia helps fight unpleasant and even painful symptoms of the disease and normalize metabolic processes. But disease prevention also plays an important role, since the appearance of salts in the urine is influenced by many factors.
What is oxalaturia?
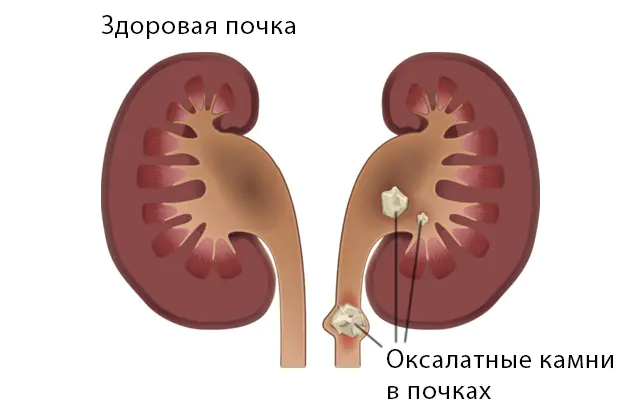
Oxalaturia is characterized by the presence of oxalates (oxalic acid salts) in urine. In a healthy person, from 15 to 29 mg of acid are excreted from the body per day, but with impaired metabolism, the figures increase to 1000 mg per day. Oxalic acid enters the body from the outside with food or is formed in the body as a result of metabolism during the breakdown of carbohydrates under the influence of intestinal bacteria. Excessive amounts of acid lead to its reaction with calcium or ammonium, the resulting salts are called oxalates.
A diet for oxalaturia allows you to control the consumption of oxalic acid, and as a result, reduce the amount of oxalates in the urine. However, if the cause of salt formation is not eliminated, the disease will continue to progress. The accumulation of salt crystals in the kidneys and renal canals creates a complex urological problem - oxalate stones.
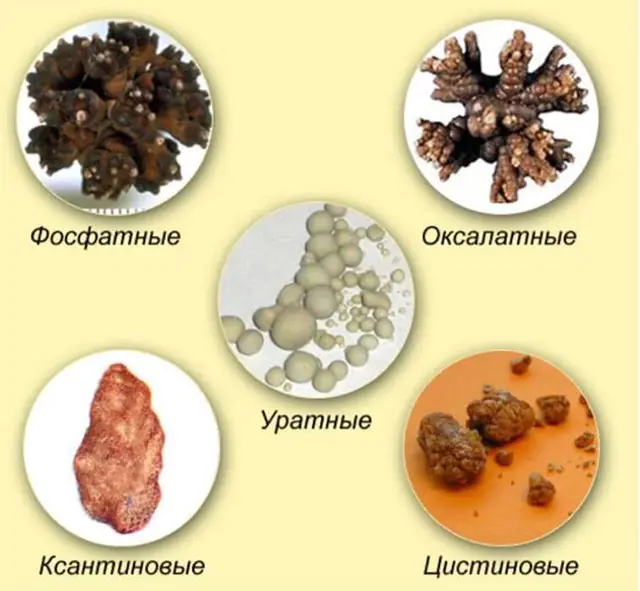

The photo shows types of kidney stones
Formations of this type have been identified in 70% of patients with urolithiasis; they are difficult to dissolve with medication. Salt crystals are very hard, have an uneven surface with spikes, and their size ranges from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
With their uneven surface, stones damage the mucous membrane of the excretory system. The protruding blood gives the calculus a characteristic brownish-brown hue. Treatment of oxalaturia should be undertaken when the first signs of the disease are detected, avoiding the formation of large crystals or stones, especially when it comes to oxalaturia in children.
Note! The pathology is also known as “oxalate nephropathy” and “oxalic acid diathesis”. Kidney damage can occur at any age, regardless of gender.Why does oxalaturia occur?
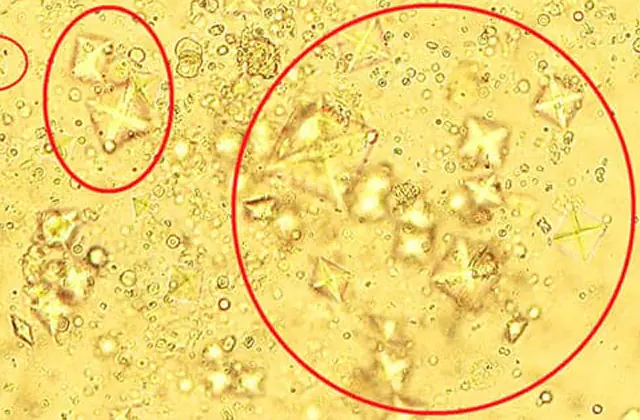
In the photo there are oxalates in the urine
Before starting treatment for oxalaturia, it is extremely important to establish the causes of the pathology and stop their effects. Otherwise, the therapy will only have a temporary effect, and the likelihood of re-formation of stones will not decrease.
The causes of oxalaturia are divided into primary and secondary. Primary is a rare congenital metabolic abnormality. Hereditary fermentopathy is associated with deficiency of D-glycerate dehydrogenase. Due to the lack of a catalyst, more oxalates are formed during the metabolic process: oxalic acid reacts with calcium, forming insoluble salt crystals. Accumulating on the tissues of the kidneys and renal canals, crystals lead to a serious complication - renal failure.
Oxalosis (primary pathology) manifests itself in children already at the age of 1-4 years. The pathology is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, that is, from both parents. But even if the patient is of the heterozygous type (that is, the defective gene was passed on from only one parent), the levels of oxalic acid in the urine may be slightly higher than normal. If oxalaturia in children is diagnosed in the early stages, treatment is prescribed to prevent the development of complications.
The appearance of secondary oxalaturia in adults and children is usually associated with exposure to external factors:
- unbalanced menu - the diet is dominated by dishes with a high content of oxalic acid or a small amount of magnesium and vitamin B6 and at the same time an excessive amount of vitamin C in food;
- stressful situations - a relationship has been established between an increase in the amount of oxalic acid in urine samples and nervous overexcitation;
- diseases associated with metabolic disorders - diabetes, pyelonephritis, obesity and others;
- pathologies whose treatment requires prolonged bed rest - ulcerative colitis, cystitis, abdominal surgery;
- disruption of the urinary system of various etiologies.
If we are talking about a secondary pathology, oxalaturia in adults is endemic. There is a relationship between the incidence of dysfunction and the patient’s living conditions. This can be explained both by a certain chemical composition of the external environment and by the cultural characteristics of the region (the eating habits of the population). Moreover, if the primary disease is not gender specific, then in adulthood the clinical picture more often manifests itself in men.
Note! A one-time spike in urinary oxalate levels is usually caused by stressful situations and eating foods high in oxalic acid. After normalizing the diet, this condition will pass. The danger is a systematic imbalance.Main symptoms of oxalaturia

People predisposed to metabolic disorders and leading an unhealthy lifestyle need to know the symptoms of oxalaturia in order to consult a doctor in time and begin treatment. Unfortunately, most patients simply ignore the disease, since its signs are not clearly expressed.
In the early stages, the patient experiences:
- frequent urge to urinate, excessive urination;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- increased fatigue.
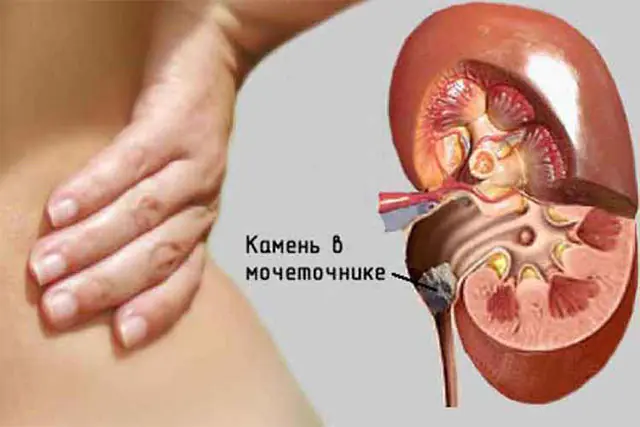
An important criterion is the regularity of such uncomfortable sensations. If at this stage the pathology is not diagnosed and treatment is not started, then over time the formation of stones will begin. The patient's condition worsens, and the pathology develops into urolithiasis.
The symptoms of oxalaturia in its advanced state are quite unpleasant:
- nagging pain in the lumbar region;
- blood in the urine;
- the volume of urine decreases and the frequency of urges increases.
When the size of the stone increases enough to block the urinary tract, the patient feels severe pain in the kidney area. The discomfort is so strong that the person begins to feel sick and even vomit. From the lower back, pain can radiate to the groin area. Such conditions require immediate treatment.
Important! In children, the disease manifests itself only as renal colic. Other symptoms may be hidden at a young age.Diet for oxalaturia
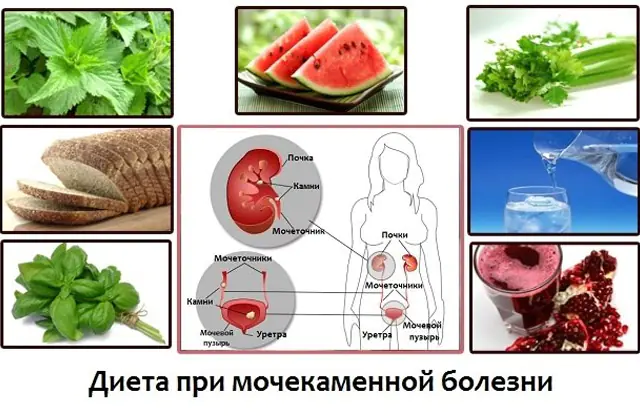
For treatment, first of all, a special menu is prescribed for oxalaturia. If diet therapy does not produce the expected effect, therapy is supplemented by taking special medications.
It is necessary to understand that formations in the renal system may have different chemical compositions. Correction of the acidity of fluids in the body through the foods consumed must correspond to the composition of the crystals formed. If the patient has oxalaturia, the menu should include foods rich in magnesium and vitamin B6, but with a minimal amount of ascorbic or oxalic acid.
Nutrition rules for oxalaturia:
- The basis of the diet is soups made from permitted vegetables, as well as fruits in any form (except prohibited ones).
- It is imperative to control the drinking regime; the amount of pure water must correspond to individual standards.
- It is recommended to control portions - overeating leads to an imbalance of metabolic processes and can provoke the formation of oxalates.
- Among fruits, preference should be given to apples and pears, grapes, but plums, gooseberries, and currants, on the contrary, contribute to the formation of salts in the urine.
- In case of oxalaturia, consumption of eggs, mushrooms, dairy products, meat and fish is allowed in limited quantities.
- The consumption of table salt and foods rich in fast carbohydrates, as well as hard cheeses, is limited.
- The patient must exclude spinach, cocoa, chocolate, beets, and legumes from the diet. Fatty broths and jellies, kidneys and brains are also prohibited.
- The consumption of alcohol, coffee and tea is kept to a minimum.
How to treat oxalaturia?
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor conducts a detailed diagnosis of the patient’s condition. It is important to know not only the amount of oxalates in the urine, but also the causes of oxalaturia. Therapy is aimed both at eliminating salt crystals and eliminating the causes that caused them.
To accurately diagnose the disease, you will need to take a urine test. In the patient, the analyzed composition will contain increased doses of leukocytes, erythrocytes and other components. You will also need to undergo an x-ray or ultrasound of the urinary canals to determine the presence of stones in the system and their size.
Diagnosis of the disease in children is carried out only as part of a comprehensive examination. In some cases, salt crystals in the urine are an indicator of age-related instability of the kidney membranes; with age, the child’s condition may normalize.
Correction of nutrition for oxalaturia, on the recommendation of a doctor, can be supplemented by taking medications. The selection of agents is carried out based on the principle of complex therapy: for antimicrobial effects, relieving inflammation, helping to dissolve oxalates.
The photo shows drugs for the treatment of oxalates in the urine
A patient with the formation of oxalates in the urine may be prescribed courses of the following medications:
- Blémarin. Used to dissolve salts and prevent their formation. A package of the product costs 478 hryvnia, 1111 rubles. Complete analogues of the drug have not been developed, but depending on the degree of the disease, herbal remedies with similar effects may be recommended - Fitolit, Fitolysin and others.
- Canephron. Widely used in urology, promotes the removal of uric acid. A bottle of solution for oral use costs 211 hryvnia, 450 rubles. Analogues of the drug can also be used - Amazestin, Aflazin and others.
- Asparkam. A means of replenishing the amount of magnesium in the body. Asparkam costs 14 hryvnia, 49 rubles. Additionally, vitamin complexes may also be prescribed. The composition of vitamins is consistent with the individual needs of the patient’s body and the medications already prescribed.
For severe pain, we can take antispasmodics - Baralgin, No-shpa. The use of drugs should only be carried out with the permission of a doctor and in compliance with dosage standards. A package of Baralgin will cost 210 hryvnia, 241 rubles.
Prevention from the formation of oxalates in urine
In the case of primary pathology caused by genetic metabolic disorders, the disease cannot be prevented. However, the patient is able to reduce unpleasant symptoms and monitor the progress of the pathology. Special dietary therapy should become the daily norm, and the amount of water consumed should comply with medical recommendations.
Prevention of secondary oxalaturia consists of timely treatment of provoking diseases, a healthy diet, moderate physical activity and taking care of the health of the excretory system. Hypothermia, which provokes kidney diseases of various etiologies, should be avoided.
Oxalaturia as a separate indicator of impaired metabolism is not a critically life-threatening condition. However, ignoring the problem can lead to the development of serious complications - urolithiasis or kidney failure. To maintain health, it is recommended to regularly take urine tests for early diagnosis of pathology. And if salt crystals are detected in the urine, begin the treatment recommended by your doctor. After normalizing metabolism, a person needs to follow preventive measures - eat rationally, avoid stress, and exercise. Such measures generally improve health and standard of living and have a beneficial effect on other functional systems of the body.
Video on the topic of what oxalaturia is, how dangerous it is and how to prevent the formation of oxalates in the urine:



