Causes of development of eye cataracts, symptoms of lens clouding. Diagnostic methods for identifying the disease. Conservative and surgical treatment methods, preventive measures.
The content of the article:- Reasons for appearance
- Symptoms of eye cataracts
- Diagnostic methods
- Treatment options
- Cataract surgery
- Medicines
- Prevention
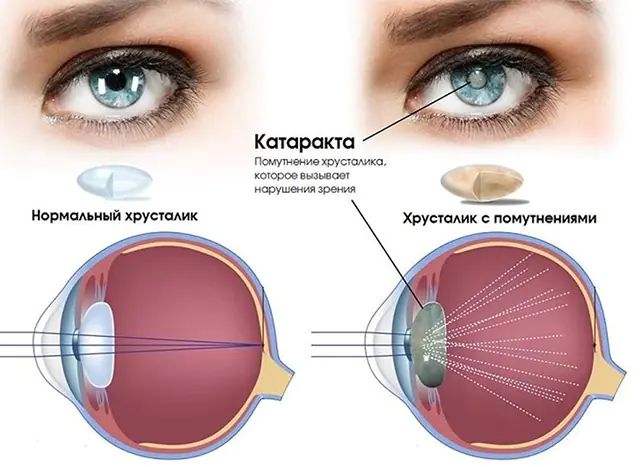
A cataract is a partial or complete clouding of the eye's lens, which is located inside the eyeball between the iris and the vitreous humor. The disease is considered age-related, as it is most often diagnosed in elderly and senile people. Without treatment, the disease leads to complete blindness in the affected eye.
- Related article: Cataracts in a child
Causes of eye cataracts
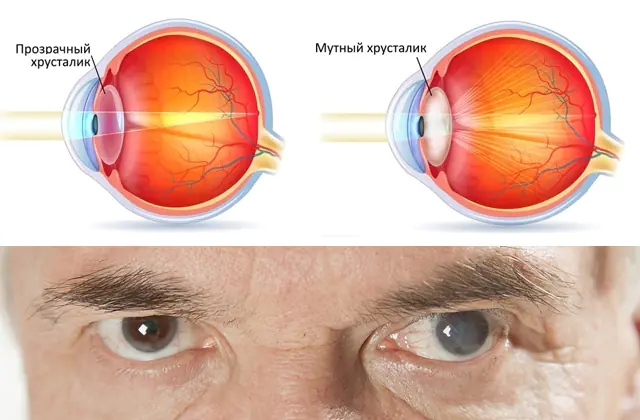
The lens is an element of the eye located behind the iris opposite the pupil. This biological lens is a capsule filled with a jelly-like protein component. Due to wear, injury, and metabolic disorders, structural changes in the protein occur. It becomes cloudy, thickens, and curdles.
Causes of cataracts:
- Age-related changes in the body. Clouding of the lens is a natural process. Therefore, the disease is detected in 50% of people over 60 years of age, and in 90% of people over 80 years of age. Please note that old age is not a contraindication to cataract surgery.
- Endocrine and autoimmune pathologies. Cloudiness of the lens is a complication of diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus, and thyroid dysfunction. The disease is caused by long-term use of hormonal and corticosteroid drugs.
- Concussions and injuries. Mechanical damage to the lens leads to clouding of its structure. In addition to accidents, cataracts are caused by unsuccessful surgical and diagnostic procedures, and improper laser treatment.
- Eye diseases. Cataract is a complication of glaucoma (increased intraocular pressure), iridocyclitis (inflammation of the iris), uveitis (inflammation of the blood vessels of the eye), retinal detachment and other ophthalmological diseases.
Congenital cataracts can affect a child during the prenatal period. The cause of its development is infectious diseases (rubella, herpes, toxoplasmosis) of the mother during pregnancy, as well as smoking, alcohol and drug use.
Please note that working in low light, frequent eye strain, and ignoring the symptoms of ophthalmic diseases cause changes in the structure of the lens and the early appearance of age-related cataracts.Main symptoms of eye cataracts
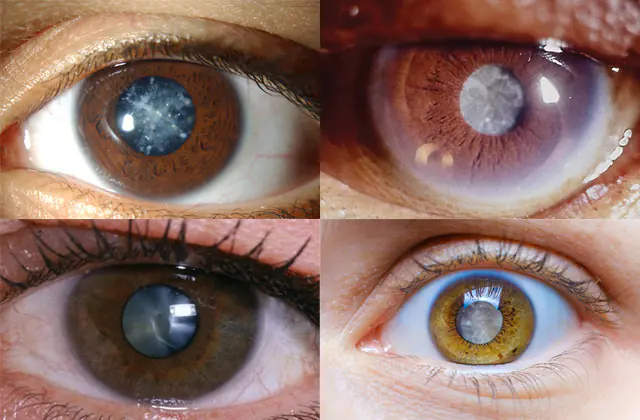
In the photo there is a cataract of the eye - a clouded crystal
From Greek “katarrhaktes” is translated as waterfall. That is, a person sees an image through a veil, similar to a stream of water. This symptom of the disease indicates clouding of the central zone of the lens.
Other signs of cataracts:
- double image, inability to focus on an object;
- the appearance of bright flashes, glare, dark spots before the eyes;
- increased eye sensitivity to bright light;
- weakening of color perception, decrease in image brightness;
- difficulties reading, writing, working with small objects;
- significant deterioration of vision at night;
- dizziness, discomfort while driving.
The insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that the early symptoms of cataracts do not appear clearly. Due to the fact that clouding often originates on the periphery of the lens, the disease is confused with fatigue or age-related weakening of visual acuity.
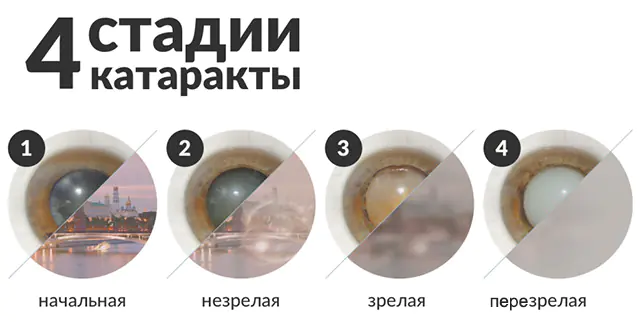
There are 4 stages of cataract development:
- initial;
- immature;
- mature;
- overripe;
Depending on the location of the opacities, three types of pathology are distinguished:
- Nuclear cataract
- Subcapsular cataract
- Cortical (cortical) cataract
Without treatment, a thin film forms in the upper layers of the lens. It prevents the penetration of light rays reflected from objects. The human eye ceases to perform its function, and complete blindness occurs.
Other complications of cataracts include:
- Lens luxation. The displacement of the biological lens is manifested by trembling of the iris, a change in the external structure of the eye. The patient feels a dull pain and decreased visual acuity. Reduction of the lens is carried out only surgically.
- Obstructive amblyopia. This complication is typical for congenital cataracts. Without lens treatment, the healthy retina atrophies because it does not receive visual signals. The disease is easily identified by the appearance of the eye and requires complex surgical treatment.
- Iridocyclitis. Cloudiness of the lens sometimes causes an inflammatory process to appear on the iris and ciliary body. The disease is manifested by darkening of the vascular network, headaches, and immobility of the pupil.
Methods for diagnosing cataracts
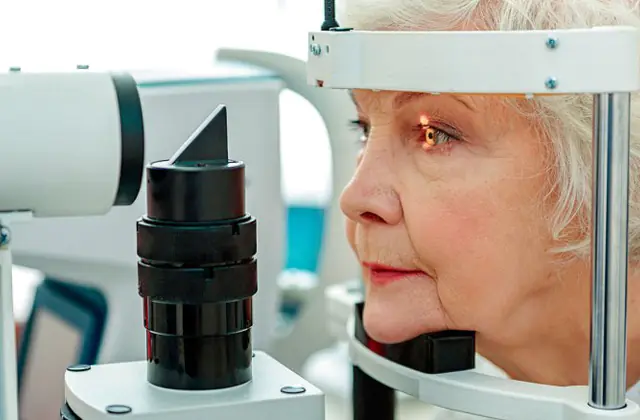
Lens opacities are often detected during an annual preventive examination. To confirm a preliminary diagnosis, the doctor examines the patient’s medical history, asks about the nature of the symptoms, and examines the organs of vision. Next, he directs the patient to undergo the following diagnostic procedures:
- Ophthalmoscopy. For a high-quality examination of the fundus, the doctor drops a drug into the patient’s eyes to dilate the pupils. Next, the patient sits in front of the slit lamp and fixes his head on its stand. An ophthalmologist examines the organs of vision using a lens and a lighting element. The study is also carried out with a small, portable device that resembles a flashlight.
- Biomicroscopy. A drug is instilled into the patient's eyes to dilate the pupil and relax the ciliary muscle. If necessary, a product is injected to tint corneal defects. Next, the patient is positioned in front of the diagnostic apparatus. The doctor directs a light beam into his eye and studies the degree of its transmission through transparent optical media.
- Refractometry. After instillation of the eyes with Atropine or its analogue, the patient is positioned in front of the device. The doctor fixes the head with a tripod and the eyelids with plastic corsets. Next, a beam of infrared light is directed into the person’s eyes. Part of the beam penetrates the internal sections, and the rest is reflected from the retina. The computer records these waves, analyzes them, and displays the results on the screen.
- Ultrasonography. The patient sits in a chair in front of the ultrasound machine and closes his eyes. The doctor moistens his eyelids with gel to improve signal transmission. Next, he moves a nozzle that emits ultrasonic waves. The result is transmitted to the computer screen in the form of a black and white image. To confirm the diagnosis, the patient, by order of the ophthalmologist, moves the pupils in different directions.
After studying the results of the analysis, the ophthalmologist explains to the patient what stage the disease is at and what to do to treat cataracts. He talks about treatment methods and the dangers of ignoring the disease.
Methods for treating eye cataracts
The only treatment for cataracts is surgery to remove them. Medicines and traditional medicine can slow down the clouding of the lens, but they cannot improve visual acuity.
Cataract surgery
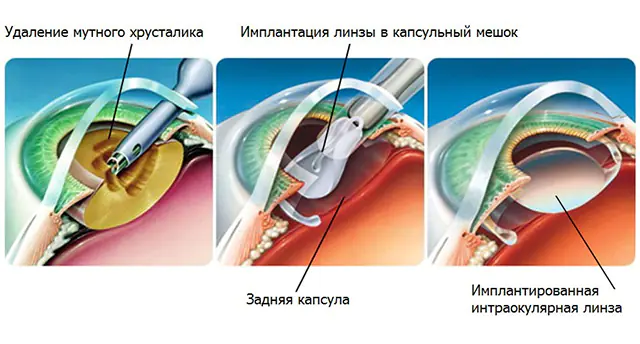
There are several ways to surgically remove cataracts. Remember, surgery is performed at any stage of the disease and in most cases requires replacing the lens with an artificial lens.
Methods for removing cataracts:
- Intracapsular extraction. At the first stage, the surgeon makes an incision in the cornea. Next, he removes the lens using a cryoextractor device. Its attachment freezes to such a temperature that the lens sticks to it and can be easily removed. The method is considered traumatic, so it is used in rare cases.
- Extracapsular extraction. The peculiarity of this operation is that not the entire lens is removed, but only its front and middle part. The rear compartment of the lens remains a protection for the vitreous body. At the last stage, the surgeon stitches the incision on the cornea. The duration of the procedure is 20-30 minutes.
- Ultrasound phacoemulsification. The surgeon makes a small incision on the cornea and inserts the device attachment into it. Using ultrasound, the device grinds the lens to the consistency of an emulsion. It is then removed using an aspirator. The advantage of the operation is low trauma, the disadvantage is the risk of damage to adjacent intraocular structures.
- Laser phacoemulsification. This method is considered the most effective and gentle. The laser beam is able to cut even a hardened lens, as well as remove its smallest fragments. At the same time, the high temperature of the beam seals the cornea, which eliminates the need for sutures. The disadvantage of this method is the high cost of the operation.
After removal of the affected lens, visual acuity decreases significantly. To replace it, the doctor may prescribe the wearing of contact or intraocular lenses. But most often, the patient undergoes an implant installation during the operation. The prosthesis is made from hypoallergenic materials. It does not require replacement or special care. It is enough to follow the general rules of hygiene, moisturize the cornea with Vizin, Oftolik and their analogues.
Surgery for eye cataracts is not performed on pregnant women, nursing mothers, or infants under 1 month. The procedure is postponed until intraocular pressure normalizes and chronic diseases are in remission. In addition, it is necessary to make sure that there are no infectious eye diseases (conjunctivitis, blepharitis, scleritis).
Please note that cataract surgery is not performed in the later stages of multiple sclerosis, diabetes, or cancer.Medicines for eye cataracts
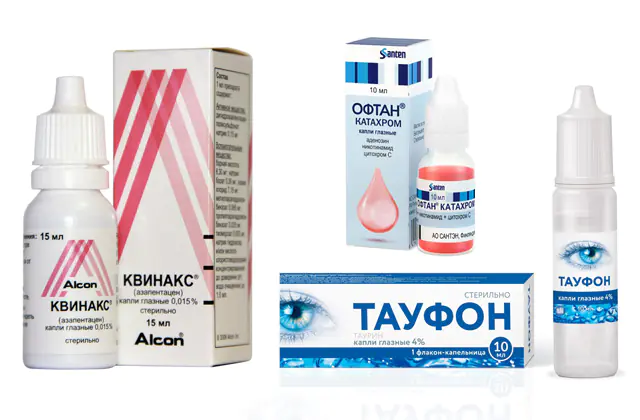
Since the operation has contraindications, the doctor explains to such patients how to treat cataracts with medication, how to slow down its progression, and how to avoid the development of complications.
Drugs for the conservative treatment of cataract disease:
- Quinax. The medicine prevents protein oxidation, resolves cloudy areas, and activates the protective function. The drug is dripped 3-4 times a day, 2 drops into the conjunctival sac of the affected eye. Please note that Quinax is designed for long-term treatment, which cannot be interrupted even if visual acuity significantly improves. Price - from 650 rubles in Russia (320 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 15 ml.
- Oftan Katahrom. The drug performs several important tasks. The cytochrome C component slows down oxidative processes, adenosine normalizes metabolism in the lens, and nicotinamide saturates it with vitamins. The product easily penetrates the cornea and is not absorbed into the general bloodstream. Treatment is carried out for several months, 2 drops 3 times a day. Price - from 220 rubles in Russia (82 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 10 ml.
- Taufon. The main active ingredient in the drug is a sulfur-containing amino acid. It is produced by the body to regenerate damaged cells of the cornea, retina, and nerve fibers. Taufon participates in metabolic processes and normalizes intraocular pressure. Treatment with drops is often prescribed before and after cataract surgery. Price - from 92 rubles in Russia (50 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 10 ml.
Drug treatment for cataracts is painless and safe. The only contraindication to eye drops is individual intolerance to the components of the medicine.
- Read also about traditional treatment of cataracts
Prevention of eye cataracts
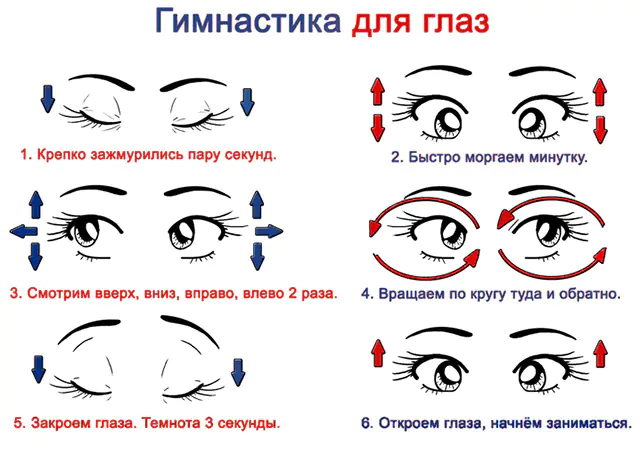
The photo shows visual gymnastics
Maintain a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy. Give up bad habits and heavy physical activity. Avoid crowds of people, protect yourself as much as possible from communicating with patients in infectious diseases clinics.
Avoid eye strain while studying and working. Take breaks, massage your head, and perform ophthalmic gymnastics exercises. After 40 years, moisturize the cornea with preparations containing human tear components.
Cataract prevention includes annual medical examinations. Examine not only the eyes, but also other organs and systems. Treat diseases at an early stage, prevent clouding of the lens and the development of other complications.
Video about cataracts - why they occur and how to get rid of them:



