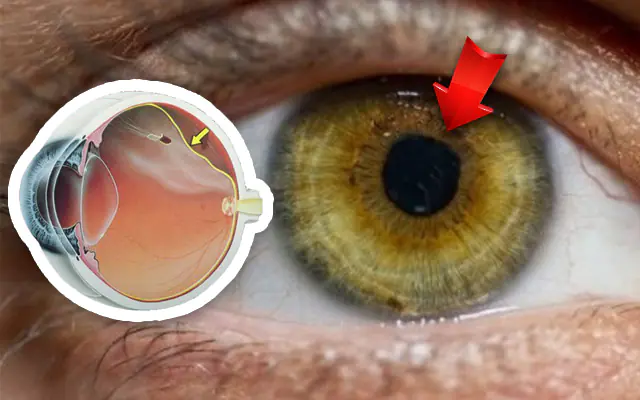
What causes retinal detachment, symptoms of ophthalmic disease. Methods for diagnosing and treating the disease. Prevention of detachment.
The content of the article:- What is retinal detachment
- Reasons for development
- Main symptoms
- Diagnostics
- What not to do
- Treatment methods
- Surgical intervention
- Laser therapy
- Food
- Prevention
Retinal detachment is a complex ophthalmic disease that requires surgical intervention. Occurs when the retina of the eye separates from the vascular network. There are several types of this disease and a number of reasons that could lead to it. The disease occurs in both children and adults. And in both categories of patients it can cause blindness. Therefore, it is extremely important to diagnose the disease in time and begin treatment as quickly as possible.
What is retinal detachment?
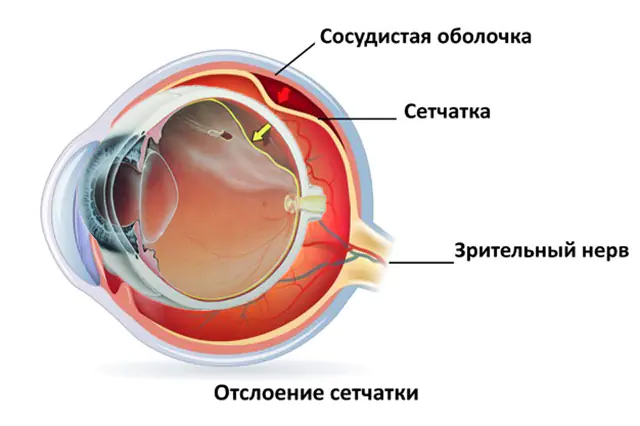
Photo of retinal detachment
The human eye consists of several sections. Its structure is often compared to a camera, in which the cornea and lens play the role of a lens, and the retina serves as a kind of photographic film. It has a very complex multilayer structure and transmits information through nerve fibers to the visual part of the brain. That is why you can often find information that it is not only part of the eye, but also a kind of part of the brain.
The separation of nerve fibers and blood vessels from the multilayer mesh structure is called detachment. This is a very dangerous disease, the essence of which is the loss of the ability to transmit information through nerve fibers to the brain and, thus, the loss of the ability to see. The process occurs progressively, since during detachment the retina does not receive nutrition from the vessels and becomes more and more separated, as a result, vision becomes worse and worse until it disappears completely.
Retinal detachment can be of several types:
- Primary (dystrophic or rhegmatogenous). It consists of the presence of foci of rupture through which fluid from the vitreous seeps under the retina. These tears occur due to thinning or excessive tension on the retina. Thinning most often forms in an area called the dystrophy zone. It is located on the periphery or at the equator of the eyeball. This happens mainly in older people. It can cause a through defect in the retinal tissue and is dangerous because through these holes, fluid from the vitreous can move into the adjacent space, creating a layer and thereby moving the retina away from the vessels and preventing its nutrition. In this case, the gaps are called perforated or, as they are also called, lattice. Dystrophy such as “snail trail” is also dangerous. It is called so because of its external resemblance to the tracks that snails leave - long, narrow, often dotted. As for excessive tension, this happens as follows. Most of the eyeball is represented by the vitreous body, which is filled with a clear gel-like liquid. When this fluid liquefies, excessive pressure occurs, which leads to retinal detachment and rupture. There are cases when the cause of detachment is both rupture and excessive tension.
- Secondary (exudative). It occurs as a result of concomitant ophthalmic diseases, accompanied by the flow of fluid under the retina. As in the mechanism described above, the fluid forms a layer that gradually disconnects the retina from the vascular network. This liquid is not able to provide a nutritional function, as a result of which the condition further spreads to areas that have not yet exfoliated. And if primary detachment is typical for older people, then secondary detachment occurs in young people, and, unfortunately, even in children.
- Traumatic. This is the case when the cause of the disease is injuries of a different nature. For example, a blow to the eye, contact with a sharp object or foreign body, burn, hypothermia. It is noted that most often traumatic detachment is caused by injuries associated with professional activities and childhood pranks. And sometimes for such a serious pathology, it is enough for cigarette scale to get into the eye, a collision with a branch, or contamination with a grain of sand after diving.
Causes of retinal detachment

This ophthalmological pathology belongs to a group of diseases, the development of which often does not depend on the patient. However, there are a number of provoking factors, the neutralization of which can significantly reduce the likelihood of the disease occurring. Therefore, let’s consider what leads to this diagnosis.
Causes of retinal detachment:
- Hereditary predisposition. As geneticists note, children inherit good health from their parents less often than diseases that have existed in the family for several generations. And ophthalmological ailments, unfortunately, are transmitted more often than others. Therefore, if your parents encountered a pathology such as retinal detachment, it is possible that you will also have to face this problem.
- Eye diseases. Most often, this disease is caused by high degrees of myopia (myopia), as well as prolonged or chronic inflammation of the iris and choroid, atrophy of the optic nerve, neoplasms, and hemorrhages. Separately, it is worth noting the presence of diabetes mellitus and the diabetic pathology of the retina that developed against its background.
- Injuries. In this case, there does not have to be any injury directly to the eyes; often a traumatic brain injury leads to detachment. Blows to the back of the head are especially dangerous, because it is in the occipital zone that the centers responsible for vision are located in the brain. And in this case, the consequence of retinal detachment can be rapid blindness. Even if the injury did not result in a serious concussion, but affected the visual center, this can give rise to sluggish changes in the ophthalmological series, which over time, after many years, can cause the development of the pathology we are considering. Therefore, at an appointment with an ophthalmologist, it is very important to talk about injuries, even if they happened quite a long time ago.
- Excessive exercise. Long-term professional activity in difficult working conditions significantly undermines health. Impacts, heavy lifting, temperature changes - all this has an extremely negative impact on eye health and can cause retinal detachment.
- Hypothermia and overheating. The development of many ophthalmological diseases, which can subsequently lead to retinal separation, includes prolonged exposure to unfavorable temperatures - both hot and cold. Vision problems are often observed in people of such professions as steelworkers, welders, as well as in those who in winter are forced to spend a long time at their workplace outside at very low temperatures.
- Hypertensive crisis. Regular increases in blood pressure contribute to increased intraocular pressure and excessive pressure of the vitreous body on the retina. Particularly dangerous in this regard are hypertensive crises, which can cause hemorrhage or retinal rupture.
Main symptoms of retinal detachment
It is worth noting that some of the symptoms described below may relate not only to detachment, but also to many other diseases with which patients consult an ophthalmologist. However, since they may also indicate detachment, we will consider them all.
Signs of retinal detachment:
- Deterioration of vision. A decrease in acuity may manifest itself in the need for more careful concentration of vision. For example, when it seems to you that objects are blurry, and in order to see them clearly, you need to “sharpen”.
- Tired eyes. Sometimes it happens that you haven’t actively used gadgets during the day, haven’t read or been at the computer more than usual, and your eyes are tired, you have a constant desire to close them, squint your eyes, and rub them.
- Photosensitivity. This refers to the inability to openly look ahead without squinting. Moreover, this condition may not necessarily manifest itself on a bright sunny day, on the beach or when there is a lot of white snow around, but also simply in clear weather, and sometimes in bright room lighting.
- Reduced field of view. It is quite difficult to independently determine that your field of vision has narrowed. This can be done by a doctor when carrying out certain diagnostic measures. Constantly brushing against side objects should be a cause for concern. For example, when a person often hits furniture, the legs of tables, chairs and armchairs, or door frames with the little fingers of the lower extremities. Also, a decrease in the field of vision may be indicated by touching door handles and any protruding objects with your hands. Hitting the head on wall cabinets, open doors, as well as brushing against tree branches and bushes, and traumatic entry into doorways are also common. This suggests that retinal detachment has rebuilt and disrupted proprioception - one’s own sense of space, due to a decrease in the visible part of it.
- Loss of lateral vision. This is the next stage in which vision narrows to a single point opposite. It looks like this. Looking at a person, the patient sees only his face, but does not see the space around him.
- Floating dots, flies, fireflies. So-called floating dots may appear in the visual image - dark marks that are not static. In addition, floaters may fly - these are also black dots that most often appear at the edge of vision. Fireflies, sparks, and lightning can also be seen there. These manifestations are often symptoms of retinal detachment.
- Veil before my eyes. In this case, you see the picture as if through a kind of veil. Can be compared to putting a bag on your head. Objects become fuzzy, blurry, and not as bright.
- Deformation of objects. It consists in the curvature of familiar forms. For example, a doorway seems to you not rectangular, but with rounded corners, and a globe - not round, but oval. Also, the deformation of visible objects can manifest itself in a change in their shape depending on the viewing angle.
Diagnosis of retinal detachment
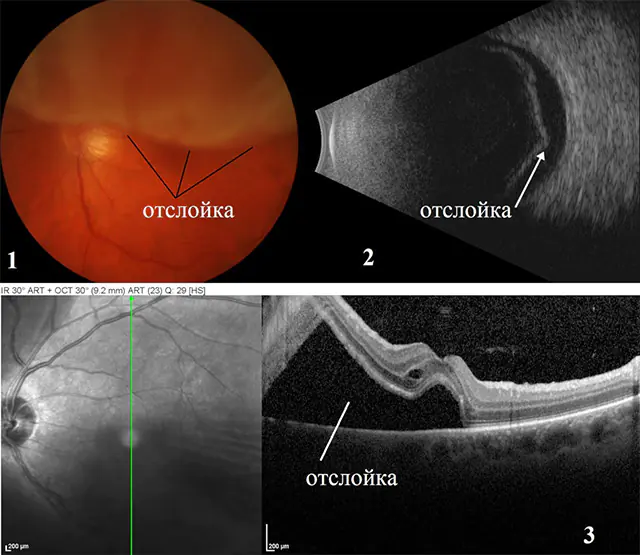
The main problem in diagnosing this disease is that patients often hesitate to see an ophthalmologist. Retinal detachment, as a rule, comes as a surprise to a person, since before the onset of the disease the patient could not complain at all about vision and not feel any discomfort in the ophthalmological area. The danger is that the disease spreads very quickly, and sometimes even a day of delay can significantly reduce the patient’s chances of a successful outcome of the situation.
What to do if you have a retinal detachment:
- Visit to an ophthalmologist. This is where you need to start making a diagnosis. In this case, it is recommended to visit a specialist who has modern research methods in his arsenal, since a basic ophthalmological examination will not be enough; a full examination is necessary.
- Perimetry. This is a visual field study that involves assessing the condition of the retina in the peripheral zone.
- Electrophysiological examination. During this manipulation, the ophthalmologist determines the viability of the retinal nerve cells and assesses the condition of the optic nerve, which helps to assess whether retinal detachment has reduced vision dramatically or has not yet deeply affected this process.
- B-scan. It consists of an ultrasound examination of the internal structure of the eye.
- Ophthalmoscopy. This is a procedure that involves examining the fundus of the eye.
- Angiography. Fluorescence study, the purpose of which is to assess the condition of the vascular network of the fundus.
- Tomography. Optical coherence examination is a kind of examination of the retina under a microscope with very high resolution, which allows you to thoroughly examine its structure.
What should you not do if you have a retinal detachment?
Folk remedies are prohibited for retinal detachment!
On the Internet you can find many advertising offers about non-surgical treatment of pathology with the help of medications. However, we would like to immediately note that doctors unanimously declare: injections for retinal detachment, as well as tablets, drops, ointments, all kinds of lotions, compresses and other medications are not effective in the fight against this disease.
If we consider the retina as a tissue, then its rupture or detachment from the overall structure cannot be corrected by washing, ironing or bleaching - all this will only worsen the situation. You need to take it and sew it. So here, the only question is which methods to choose - surgical or laser. Often both are needed.
What else should not be done in case of retinal detachment:
- Prescribe any treatment on your own without consulting a doctor;
- Instill any drops of herbal or chemical origin into the eyes;
- Massage the eyelids;
- Do visual gymnastics;
- Apply compresses and bandages.
The eye is such a fragile mechanism that it costs nothing to damage it, but then it is very difficult to restore the structure and regain lost vision. Therefore, doctors categorically prohibit engaging in any self-medication aimed at neutralizing the disease, or using folk remedies for retinal detachment, since no effective methods have been identified, but there are many that can cause irreparable harm.
Methods for treating retinal detachment
Retinal detachment must be treated immediately. Depending on the stage of the disease and the general health of the patient, a method is selected to restore structure and vision. There are surgical and laser treatments for the disease. Let's look at what each of these types of therapy is.
Surgery for retinal detachment
The photo shows scleral filling for retinal detachment (using a silicone filling)
The urgency of surgical intervention for this disease is evidenced by the fact that, for example, in Germany, detachment is a reason for surgery within 24 hours. There is no such protocol anywhere in the post-Soviet space, but it is noted that treatment of retinal detachment should be carried out immediately.
Unfortunately, it is unlikely that vision will be restored to its original state after this procedure. Its main task is to stop the process, block the disconnection and make sure that the situation does not get worse. In addition, the surgical method reduces the risk of increasing myopia and astigmatism, if the patient is also diagnosed with them. Therefore, once again we conclude in favor of carrying out the manipulation as quickly as possible.
Doctors give positive prognoses if the detachment and ruptures did not have time to reach the central areas of the eyeball. If they affected them, restoring central vision will be problematic, but everything must be done to improve the diagnostic picture.
To ensure that the retina is tightly attached to the adjacent tissue, extrascleral ballooning and filling procedures are performed. A vitrectomy may also be necessary, the purpose of which is to remove tissue scars that have pathologically changed or blood from the vitreous area.
Laser therapy for retinal detachment
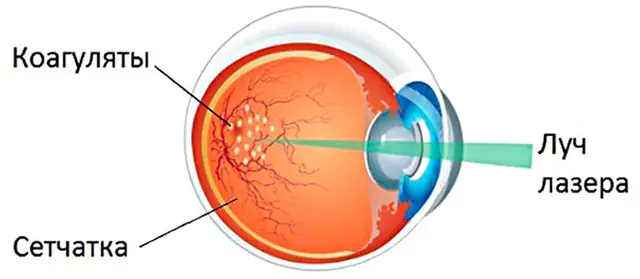
After surgery, additional laser therapy may be needed, since it is problematic to cure retinal detachment with traditional surgery alone. Using an ultra-fine and precise laser, tissue coagulation occurs. This is a kind of attachment of the choroid to the retina.
This procedure occurs by installing a lens through which a laser beam is fired. Thanks to this, it penetrates deep into the eye and bloodlessly helps to cope with the task. The operation of the laser beam is adjusted using a stereomicroscope. It also helps to point and focus the laser beam supplied using light guides. What is important, peripheral laser coagulation also helps prevent recurrent detachments.
Thus, laser treatment of retinal detachments is considered a very effective modern way of combating this disease.
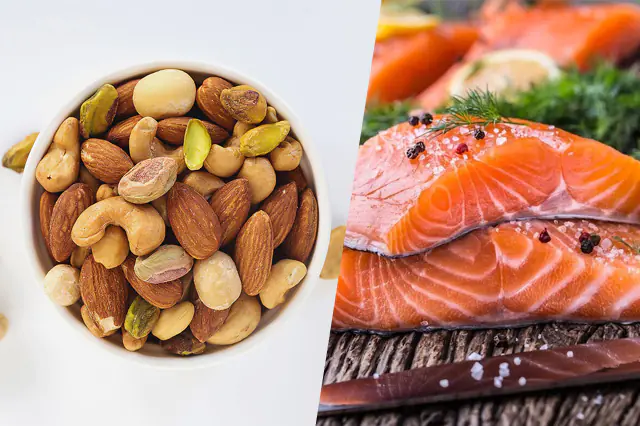
Foods for retinal detachment

To help the ophthalmological system, it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle and eat well. Therefore, if you have retinal detachment, you should pay attention to increased consumption of healthy foods.
What foods are good for vision:
- Nuts. They are rich in fats, riboflavin and vitamin E, which fight free radicals, which have an extremely negative effect on the retina.
- Fatty fish. It is recommended to give preference to red fish rich in omega acids.
- Yolks. Mostly chicken with a high content of lutein, which protects the eyes from the damaging effects of ultraviolet radiation.
- Carrot. An irreplaceable storehouse of vitamin A, considered one of the most important substances for the full functioning of the visual apparatus.
- Blueberry. It contains anthocyanins, flavonoids and tannins, which nourish blood vessels and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Prevention of retinal detachment

The most important way to prevent the disease is to regularly visit an ophthalmologist, even if nothing bothers you, and an unscheduled visit to the doctor after injuries or the appearance of any visual disturbances.
In addition, measures to prevent retinal detachment include the following recommendations:
- Maintaining sleep and rest patterns;
- Good nutrition;
- Quitting smoking and excessive drinking of alcohol;
- Strong physical activity;
- Attention to eye diseases;
- Timely treatment of chronic diseases;
- Maintaining a temperature that is comfortable for the eyes;
- Change in difficult working conditions;
- Wearing sunglasses.
On the Internet you can find information about drops for retinal detachment, however, as noted above, there are no medications for this disease. But some drugs are used as prophylaxis. They help improve the nutrition of the eye, strengthen the capillaries, prevent the cornea from drying out, etc. However, only a doctor should prescribe them, depending on the individual characteristics of your visual system.
Summarizing the above, we note that retinal detachment is a serious pathology that necessarily requires treatment. Therefore, do not hesitate to contact an ophthalmologist. Your vision and not only its sharpness, but also its presence may depend on this.
Video about retinal detachment - what it is and how to treat it:



