In some diseases, the metabolism changes in such a way that diffuse hyperpigmentation develops, that is, the skin darkens over large areas of the body and on the face. To exclude regular tanning, examine the inner surface of the forearms. The skin on these parts of the body is usually lighter in color. In addition, you need to ask the patient if he visits a solarium.
Why the skin on the face and body darkens and what disorders this may be associated with will be discussed in this article.
Causes
There are the following groups of reasons why the skin on the face and body darkens:
- Increased production of melanocyte-stimulating hormone.
- Other internal diseases accompanied by metabolic disorders.
- Taking certain medications.
- Malignant tumors of internal organs.
Hypersecretion of melanocyte-stimulating hormone
The skin darkens when the level of melanin, a coloring pigment contained in special cells called melanocytes, increases. The production and release of this substance into the skin is activated under the influence of one of the pituitary hormones - melanocyte-stimulating.
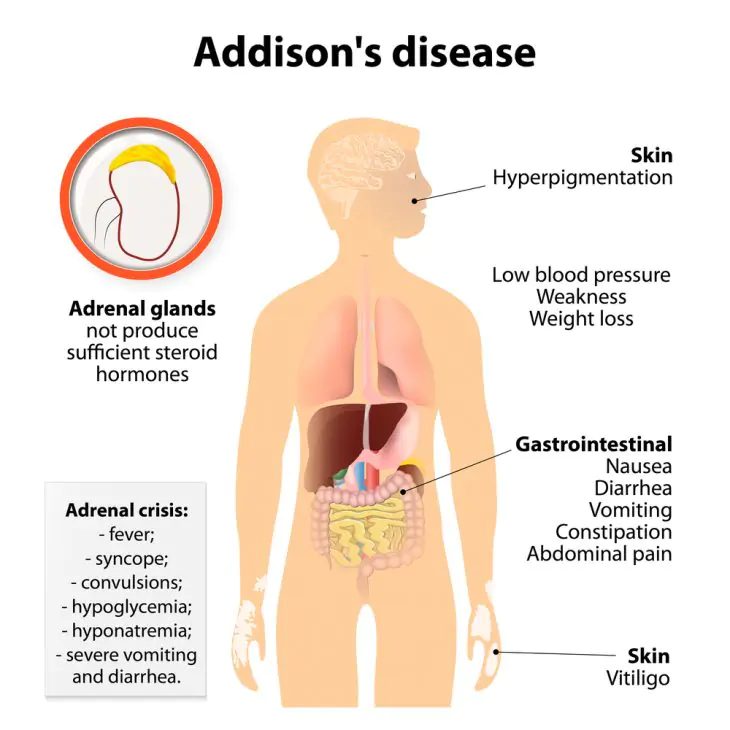
Active synthesis of this hormone occurs in Addison's disease, one of the main causes of skin hyperpigmentation.
Addison's disease is a chronic adrenal insufficiency that occurs due to tuberculosis, infection, amyloidosis and other damage to these important organs. The adrenal glands stop synthesizing hormones, to which the body responds with increased secretion of a substance that stimulates their hormonal activity - adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), thus trying to restore their activity. The physiology of this process is such that, simultaneously with the increased production of ACTH, the release of melanocyte-stimulating hormone, which causes darkening of the skin, also increases.
In Addison's disease, the skin is bronze, golden brown, or dark gray in color, often looking like a deep tan. Pigmentation is especially noticeable in open areas - the face, hands, as well as in places where clothing rubs, for example, on the neck. The skin also darkens in the genital area, nipple areolas, and postoperative scars. Dark spots also appear on the oral mucosa.
If you suspect Addison's disease, you should consult an endocrinologist.
Internal diseases with metabolic disorders
Some diseases and physiological conditions cause darkening of the skin, for example:
Hemochromatosis is a hereditary disease in which the absorption of iron from food in the intestines increases. Iron-containing pigments are deposited in all organs and tissues, disrupting their functions.
Skin pigmentation in this disease is smoky, gray, bronze in color, most pronounced on the face and hands, as well as in the genital area, in the armpits, and the area of postoperative scars. With this disease, the liver and heart are affected, endocrine disorders develop, including diabetes mellitus. If you suspect hemochromatosis, you should consult a gastroenterologist.
Liver cirrhosis is characterized by a violation of the neutralization of bile, the absorption of bile pigments into the blood and their deposition in tissues. In patients with liver cirrhosis, parenchymal jaundice develops, accompanied by dark brown pigmentation of the skin. Liver cirrhosis is also characterized by itchy skin and pain in the right hypochondrium. This disease is treated by a gastroenterologist.
Porphyrias are a group of hereditary diseases associated with impaired hemoglobin formation. Intermediate products of its metabolism - porphyrins - accumulate in the skin, where they oxidize under the influence of sunlight. As a result, the skin turns brown. It is easily damaged, becoming covered with ulcers and scars.
Sun exposure is contraindicated for patients with porphyria. A hematologist can help with this disease.
Hyperpigmentation due to medications
If the cause of darkening of the skin is unclear, the doctor should ask the patient if he is taking any of the following medications:
- oral contraceptives;
- chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine;
- preparations of silver, gold;
- amiodarone;
- busulfan and bleomycin;
- aminazine
Combined oral contraceptives can cause liver dysfunction with the development of parenchymal jaundice. Chloroquine and its derivatives are used to treat malaria, photodermatoses, as well as connective tissue diseases - systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis. These products may cause the skin to turn bluish-gray.
The use of silver in dietary supplements, the use of salts of this metal as antiseptics for washing urinary catheters, and long-term use of protargol can cause argyrosis: gray-blue discoloration of the skin. The use of krizanol (a gold preparation) can lead to a purple coloration of the skin.
Long-term use of amiodarone or cordarone for cardiac arrhythmias sometimes causes exposed skin to turn brown or gray.
Busulfan and bleomycin are used to treat malignant tumors. These drugs often cause darkening and other changes in the skin.
Aminazine is used in psychiatric practice. With prolonged use, it turns the skin gray.
Darkening of the skin due to malignant tumors
Skin color may change due to malignant tumors of internal organs, including lymphomas. This phenomenon is called acanthosis nigricans maligna (malignant acanthosis nigricans) and is accompanied by dark symmetrical spots and stripes in the neck, armpits, external genitalia, and inguinal folds.
Acanthosis nigricans also occurs in benign diseases of the nervous and endocrine systems in young people.
For any change in skin color of unknown origin, you should consult a dermatologist. After the initial diagnosis, this doctor can refer the patient to an appropriate specialist. Darkening of the skin cannot be ignored, because this sign is a symptom of many serious diseases.
Which doctor should I contact?
If there is widespread or limited discoloration of the skin, you should consult a dermatologist. After ruling out skin diseases, the patient is usually referred to a general practitioner, where he undergoes an examination of the internal organs. After clarifying the diagnosis, a consultation with a specialized specialist is scheduled: endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, hepatologist, hematologist, oncologist.
Any change in skin tone, if it did not occur under the influence of sunlight, is a serious signal of a disruption in the functioning of internal organs.
So, for example, if the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, the shade of the face may change from healthy to gray; it may turn blue if there is impaired blood circulation, diseases of the cardiovascular system or respiratory failure; in addition, a violet hue indicates congenital heart disease, and a yellow hue indicates liver diseases.
Gray facial skin - a disease or a consequence of bad habits
A sudden and noticeable change in complexion tone from natural and healthy to gray is most often a sign of dysfunction digestive system. At best, your face may turn gray due to banal constipation or poor nutrition, at worst, due to gastritis or the development of a stomach ulcer. It is hardly possible to independently diagnose the disease on the basis of dyschrony alone, so in this situation it is better to go to an appointment with a gastroenterologist.
In addition, gray facial skin does not always portend illness. Often, against the background of smoking, sedentary work and constant stress, people's blood circulation is impaired and blood vessels narrow, which is also manifested by a deterioration in complexion.
Earthy tint and sharp darkening of the skin - pancreatic disease or oncology
Changes of this kind indicate more serious illnesses. Often, of course, an earthy tint appears due to diseases of the pancreas, adrenal glands, or against the background of long-term use of antibiotics, but if such options are excluded, then the best recommendation in this case would be to turn to modern medicine. Diagnosis of the disease by the skin and on the basis of examinations will allow you to correctly and accurately determine the cause of the change in complexion, as well as timely diagnose the disease that provoked it.
Blue skin color – cyanosis disease
The skin acquires a bluish and sometimes dark purple tint when the blood is insufficiently oxygenated and blood circulation slows down. Such symptoms indicate cyanosis, a disease that combines many disorders of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
It happens that cyanosis occurs due to hypothermia. Then, mainly the limbs acquire a blue tint as a result of deterioration of blood circulation in the damaged areas.
Bruises on the skin – diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems
It is in the form of the formation of bluish areas and bluish areas of the mucous membranes that diseases such as heart disease and gas exchange disorders in the lungs make themselves felt. Such changes, however, can provoke the formation of methemoglobin against the background of intoxication and poisoning.
Cyanosis - purple skin disease
The appearance of dark shades or spots on the face and body (purple or cast iron color) indicates increased airiness of the lungs, pulmonary artery sclerosis or congenital heart disease. In any case, if you notice any of the above symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Vasculitis is a disease of blood vessels in the skin.
This disease involves damage to the blood vessels and tissues of the damaged organ. If the skin vessels are affected, the main symptoms of the disease will be redness, rash and itching. Vasculitis can also affect the circulatory system of the brain, which causes a stroke, the heart, which increases the risk of heart attack, etc., quite often small hemorrhages under the skin are a sign of vasculitis of other organs.
The main symptoms of this disease include: general weakness, fever, loss of appetite, weight loss, rash and itching, joint pain.
A similar syndrome can also occur with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases characterized by damage to connective tissue.
Cuperosis is a vascular skin disease
Couperosis appears in the form of small red vascular mesh or so-called “spiders” on the cheeks, chin and nose when the blood vessels dilate against the background of increased blood circulation. At the same time, the connective tissue squeezes the vessels from the outside, which makes them more visible on the face. This disease occurs among older people, as well as among those with thin and sensitive skin.
Couperosis can be treated either in a cosmetology salon or using traditional methods. Although the first method allows you to get rid of the signs of rosacea in the shortest possible time. But in case of lack of funds or opportunities - facial massage. This way you can normalize blood circulation and tone the blood vessels and muscles of the face. In addition, supplement your diet with foods or dietary supplements rich in vitamins C, P, K, antioxidants, Omega 3 and 6 fatty acids - they strengthen the walls of blood vessels and help normalize blood circulation.
Yellow skin – liver disease
Most often, yellowing of the face and body is accompanied by a change in the shade of the eye sclera, mucous membranes, especially under the tongue, feet and palms. At the same time, the color of the urine changes - it acquires a rich dark shade.
Such changes most often occur against the background of increased levels of carotene or bilirubin. In the first case, the skin can become yellow if you follow a diet consisting of oranges or carrots for a long time. If these did not occur, then most likely the matter is an increase in the content of bilirubin - a bile pigment that appears as a result of the breakdown of hemoglobin. The latter is responsible for saturating the blood with oxygen and transporting nutrients not only to skin cells, but throughout the body. When there is a decrease in hemoglobin and an increase in bilirubin, changes occur not only in the layers of the dermis, but also in the liver. Then there is a risk of jaundice. In addition, yellowness may indicate diseases such as hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, the formation of cysts, as well as disorders of the gallbladder and biliary tract.
The disease acanthosis nigricans was described in the 9th century and is considered quite rare. The development of acanthosis is accompanied by the appearance of areas of hyperkeratosis in the area of natural skin folds. In these areas, increased pigmentation and skin papillomatosis are found. Large folds of skin are usually affected - the armpits, groin and neck. Timely detection of acanthosis in the early stages can indicate serious processes. Why acanthosis is dangerous and how to recognize it, read on estet-portal. com.
The main causes of the development of acanthosis nigricans
Acanthosis nigricans can develop in a person of any gender and age, and the causes for each patient are individual and specific.
Predisposing factors for the development of acanthosis nigricans are:
- Pathologies in the functioning of endocrine organs.
- Malignant neoplasms provoke many complex biochemical and immune system reactions. Men are susceptible to acanthosis in the presence of pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, women - in the presence of ovarian and mammary gland cancer.
- Heredity influences the development of acanthosis. In case of metabolic disorders and mental inferiority, which are caused by hereditary pathology, for example, with Rood and Miescher syndromes, acanthosis develops.
- Taking estrogen hormones and certain other medications.
Thus, in young people, the causes of acanthosis are often obesity, endocrine disorders and genetic pathologies; in older people, the causes are often neoplasms.
What symptoms indicate acanthosis? Forms of acanthosis nigricans
Acanthosis has several forms of progression depending on the cause, which determines the intensity of the development of the process. Dermatologists have identified 3 main forms of acanthosis nigricans:
- Juvenile or benign, which is associated with endocrine and genetic pathologies.
- Malignant or paraneoplastic, which develops with malignant tumors of internal organs.
- Pseudoacanthosis, which develops with obesity and metabolic disorders. This form disappears without a trace when weight is normalized and has the best prognosis.
Clinical manifestations of acanthosis have 3 main symptoms:
- Increased pigmentation - the appearance of black or dark brown spots on the skin.
- Papillomatosis is the presence of fibromas or papillomas on the skin, which are popularly called warts.
- Hyperkeratosis, which provokes roughening and exfoliation of the skin.
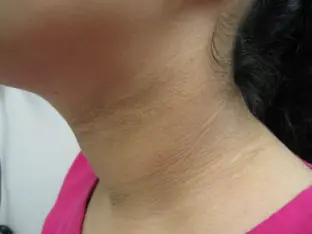
Localization of acanthosis on the skin. What symptoms accompany the progression of acanthosis?
The above-described skin changes are most often found on the skin of the inguinal-femoral fold, intergluteal region, elbow bends, on the fold between the back of the head and neck, on the skin of the armpits, in the popliteal region, on the skin under the mammary glands. It is possible that a triad of symptoms may appear on other parts of the body (face, side of the neck and navel area).
In the early stages of acanthosis development, the patient's skin gradually darkens. Many people try to wash their skin thoroughly, thinking that it is dirty. As the disease progresses, the skin begins to darken even more, becomes rough, dry, and thickens. The natural pattern of the skin becomes more pronounced and deep.
At later stages, growths in the form of fibromas and small papillomas appear on the affected areas of the skin. The growths are papillary in shape and arranged in dense rows, giving the skin a warty appearance. These lesions may also be hyperpigmented. All symptoms of acanthosis on the skin are accompanied by mild itching and tingling. There is no hair on the affected areas of the skin.
What are the aspects of diagnosis and treatment of acanthosis nigricans?
If darkening of the skin is detected in certain areas of the skin, which does not go away, but only progresses, you should consult a dermatologist. The specialist will conduct a differential diagnosis with Addison's disease, ichthyosis, and Darier's disease. The final diagnosis of acanthosis nigricans is established based on histological examination of the biopsy specimen. If a malignant form is suspected, consultation with an oncologist is required.
Treatment includes therapy for the underlying disease that led to acanthosis and symptomatic therapy. Prescribe general tonic drugs, vitamin complexes, anti-inflammatory ointments, baths with potassium permanganate, zinc preparations, aromatic retinoids. In severe cases - cytostatics and hormonal drugs, neurotropic drugs, antibacterial therapy. All this must be accompanied by a diet.
In case of massive growths of papillomas, they are surgically removed using cryodestruction or electrocoagulation.
Thus, simple darkening of the skin may hide the course of the oncological process, which is not yet manifested by general symptoms, but only by acanthosis. Therefore, contacting a doctor if you suspect acanthosis can improve the prognosis of the course of pathological processes.



