Acne scars can occur on any skin type and at any age. They are unlikely to be hidden under foundation, but cosmetologists can offer several ways to solve this problem.
You can use home remedies, the effectiveness of which is in question, you can turn to professionals in beauty salons, but in any case you will need a preliminary consultation with a doctor.
Read in this article
Why do acne scars appear?
In simple terms, a certain space forms at the site of the pimple, which is gradually filled with connective tissue. In this way, the body takes care of its own integrity, completely disregarding the aesthetic side of the issue. Dermatologists and cosmetologists identify several possible causes of acne scars:
- Mechanical squeezing of pimples and/or blackheads. With such exposure, the skin will certainly be damaged, its healing may take an indefinite period of time, which provokes the formation of scars.
- Prolonged acne without proper treatment. It is accompanied by disruption of the sebaceous glands, clogging of pores with their secretions, and the spread of the inflammatory process. As a result, numerous pustules form on the skin, which are a traumatic factor.
It is not at all necessary that scars will be formed only with prolonged acne or squeezing out pimples. Scars often appear even with single rashes - it all depends on the type of skin, the general state of human health, and the level of functionality of internal organs and systems.
In medicine, there are three types of acne scars, which will “dictate” the solution to the problem.
Atrophic
This is the most common type of scar that forms after acne. They look like pits and tubercles, formed by connective tissue, which grows to a small extent at the site of deformation of the skin.
A distinctive feature of atrophic acne scars is that they do not grow and do not change over the years (they do not become deeper).
Keloid
The connective tissue at the site of pimples and blackheads grows excessively, which leads to the formation of rather voluminous, convex scars. They are often irregular in shape and red or purple in color.
Keloid scars can grow not only in specific locations of pimples/acne, but also involve healthy skin tissue close to the site of pathology.
Normotrophic
This is the “safest” type of scar, as it consists of fairly elastic, thin connective tissue. The appearance of such scars does not deteriorate much, since the lesions are pale in color and practically merge with the main background.
Normotrophic scars are a normal reaction of the skin to injury.
Hypertrophic
Scars of this type are located above the level of the skin and are a consequence of excess collagen production. These excesses do not have time to dissolve, which leads to the formation of a scar.
The doctor will be able to accurately determine the type of scar after acne; based on the results of the examination, he will prescribe treatment.
Effective ointments for the face against the effects of acne
For many, the solution to scars after acne and acne involves turning to plastic surgeons or hardware cosmetology. But doctors say that with regular use, pharmaceutical ointments will get rid of scars or make them less noticeable. There are several effective drugs:
- Contratubeks. The ointment contains several components, which together provide accelerated exfoliation of epidermal particles and stop the growth of connective tissue cells. The drug is especially effective for normotrophic scars; it can be used as a prophylactic agent at the risk of keloid and hypertrophic scars.
Contratubeks is applied locally, rubbed directly into the scar twice a day. The duration of therapy is 30 days, further treatment is prescribed by the doctor based on the results of previous procedures.
- Fermenkol. The product contains animal enzymes that are responsible for the normal functioning of their digestive system. These substances have the ability to break down collagen fibers, which makes the formation of connective tissue impossible. Most often, this ointment is used for physiotherapy. In particular, it demonstrates particular effectiveness when performing electrophoresis.
Fermenkol set for scars and Elfor electrophoresis device
It is strictly not recommended to use Fermenkol on your own! The appointment must be made by a dermatologist/cosmetologist, who will also determine the number of procedures and the total duration of the course of treatment.
- Zinc, synthomycin and salicylic ointments. These three drugs are especially popular because they combine two positive aspects - high efficiency and low cost. Regular use of the drugs ensures exfoliation of epidermal particles, normalization of metabolic processes in the skin and lightening them. Ointments have a comprehensive effect on the lesion and can eliminate all traces of post-acne.
Zinc, salicylic and synthomycin ointments are used in the same way: they are applied in a fairly thick layer to the scars, and after 50 - 60 minutes they are washed off with warm water. The course of therapy is unlimited, usually procedures are performed twice a day until the desired result is obtained.
- Dermatix. This ointment does not belong to the medicinal category; doctors recommend it to those patients who already have scars with a high risk of turning into hypertrophic and keloid scars. When applied to the problem area, the drug forms a film on the surface, which is designed to protect the scar from external factors.
Dermatix should be applied every day in a thin layer, preferably in the morning. Whether acne scars will disappear is a controversial issue, but the formation of other, more durable and “gnarly” scars will be stopped.
To learn how the drug Collost is administered for the treatment of post-acne scars, watch this video:
How to remove scars and scars using mesotherapy
This type of cosmetic procedure involves injections of vitamins, amino acids and other substances. The essence of the method: the mesotherapy drug fills any “gaps/pits/cracks” in the epidermis, which causes visual smoothing of the surface of the skin. At the same time as this “hiding”, the active substances of the drug have a beneficial effect on the condition of the skin - they saturate it with vitamins, make it firmer and more elastic, and correct the color.
The advantage of mesotherapy in the fight against scars is obtaining a quick, almost instant result. But the effect will not last long - after a maximum of six months you will have to repeat the injections, which can be attributed to the disadvantages of the method.
Mesotherapy has a large number of contraindications, so before starting treatment for post-acne conditions, you need to consult a doctor. For example, if there are keloid scars, then the administration of corticosteroid drugs will be required, and they are prohibited for some diseases.
Which peeling is better
In general, the peeling procedure is considered one of the most effective in the process of eliminating scars and acne scars. Cosmetologists know several types of such procedures, but if we consider them specifically in relation to the post-acne condition, it is worth highlighting the following:
- Deep phenolic peeling. This is a rather painful and aggressive procedure; phenol acts not only on the surface of the skin, but also penetrates into the deeper layers of the dermis. To visually hide the presence of scars, only 1 procedure is required. Rehabilitation will last 2 weeks, but this method can even get rid of deep keloid scars.
Disadvantages include soreness and increased pigmentation of the skin during the recovery period.
- Medium chemical peel. The procedure is carried out using salicylic, trichloroacetic or glycolic acids. These substances actively exfoliate the already pathologically altered epidermis, while simultaneously having a stimulating effect on the regenerative abilities of the body. As a result, the connective tissue is replaced by a healthy, normal epidermis.
To get rid of scars, you will need to undergo at least 5 procedures with an interval of 10 - 14 days.
Laser removal of acne effects
This method of dealing with scars and scars after acne and acne is considered the most effective; it can solve the problem of even hypertrophic “marks”. The laser burns scar tissue and activates the regeneration of epidermal cells.
To obtain the desired result, you will need to do 3 - 5 procedures with an interval of 60 - 90 days. A more precise amount of laser exposure will be determined by a specialist, since much depends on the “age” of the scar, the level of elasticity of the skin and the general health of the patient.
Laser removal of acne is a painful procedure and is therefore performed under local anesthesia. If the pain threshold is too low, the patient will be offered general anesthesia. The rehabilitation time after each treatment is at least 2 weeks, but it is possible to get rid of even “ancient” scars.
Other cosmetic procedures
Some clinics may offer other procedures that can get rid of the problem in question. These include:
- Fractional photothermolysis. This is a laser procedure that differs from the usual one in that it affects the skin not with a single beam/spot, but with scattering rays. Fractional photothermolysis allows you to solve the problem of not only scars, but also other consequences of acne and blackheads - increased pigmentation, too open pores.
Typically, a course of therapy using this method is 5 procedures, between which there should be a gap of 10 days. Rehabilitation is 3 days.
- Dermabrasion. This is a mechanical procedure that involves applying special brushes to the surface of the skin. By friction, the scar tissue is abraded, the scars are leveled into the same plane as the cover and become less noticeable. Dermabrasion is not one of the most effective procedures, but it helps solve the problem of “fresh” acne and blackheads.
- Ozone therapy. Medical ozone is injected under the skin of the face, which accelerates the healing of wounds and relieves inflammation. It will take 5 - 6 procedures, in some cases this number can increase to 10 - 15. In any case, ozone therapy requires long-term use and additional correction.
Treatment of scars with surgery
Full-fledged surgical intervention for post-acne conditions is performed extremely rarely, for example, in the absence of results after cosmetic procedures or too extensive lesions of the facial skin. Doctors can offer three options for surgical treatment of acne scars:
- Undercutting (subsidy). An already formed scar is separated from the skin with a scalpel. In the resulting wound, blood and lymph accumulate, they form connective tissue, which is almost invisible. Often, undercutting is combined with laser resurfacing, then the result will be excellent - the skin will become smooth and even.
- Excision. The doctor simply excises the scar/scar and then applies cosmetic stitches. In most cases, new, small scars form at the site of such intervention, which are removed with a laser.
- Skin grafting. This is a radical way to combat scars and scars after acne, which involves transplanting individual areas of the skin. Typically, this treatment is used for burns; in the case of the problem under consideration, it is inappropriate, as it can lead to serious complications.
For post-acne treatment, watch this video:
Preventing the consequences of acne
The consequences are very difficult to eliminate, most often you cannot do it with ointments alone; you will need both cosmetic procedures and hardware therapy. It is much easier to take some actions that will prevent the formation of scars, acne scars:
- do not squeeze out the rashes, but wait for them to mature and break out on their own;
- regularly use special cosmetics to treat acne;
- carry out therapy for extensive rashes only under the supervision of a cosmetologist or dermatologist;
- You will need to adjust your diet to exclude fatty foods and baked goods with sweets;
- Decorative and medicinal cosmetics should be selected by a specialist.
Scars after acne are an unpleasant thing, causing a lot of inconvenience in life. It is quite possible to solve the problem, but you need to contact specialists and not wait for the final formation of scars.
Post-acne scars (acne scars) - skin changes at the site of healing of acne inflammatory elements associated with the formation of connective tissue.
In our company you can purchase the following equipment for removing acne scars:
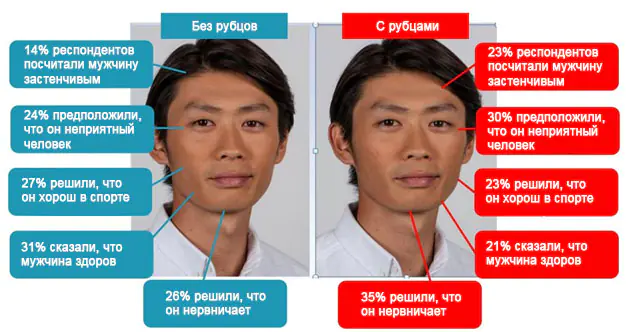
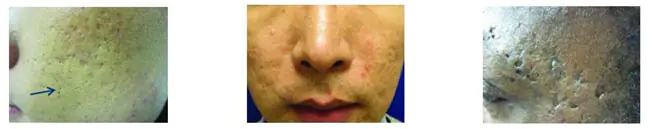
Acne poses a serious threat to appearance not only during the development of this disease. Thus, in one study involving 2133 people, it was found that acne scars occur in 1% of cases, but every seventh scar is disfiguring. In another study involving 4,618 people, two photographs of the same man were studied: the first with a clean face, and the second with acne scars. The man in the second photo received lower marks (rice. 1).
Rice. 1. The perception of a person by others depending on the presence of post-acne scars on the face (Dréno B., et al. Poster presented at: AAD 73rd Annual Meeting, San Francisco, California, USA, 20–24 March 2015)
Etiology and pathogenesis
It has been established that in 99% of cases, post-acne scars develop in the place of papules or pustules, and only in 1% of cases - in the place of comedones. The healing of such defects is due to a complex interaction of tissue, humoral and cellular mechanisms. If the skin is damaged at the level of the papillary (upper) layer of the dermis, when fragments of the basement membrane between the epidermis and dermis are preserved, restoration can take place without gross defects. In such places, depigmented areas with focal atrophy remain on the skin.
However, when the basement membrane is completely destroyed, a scar is formed, which differs in structure and function from the surrounding skin. In its area, coarse fibrous collagen grows, blood and lymphatic vessels are deformed, and their number sharply decreases. First the scar is immature, but gradually it becomes more natural in color and softer, forming mature scar.
If catabolic processes (synthesis) exceed anabolic processes (destruction), excess collagen is formed - the scar begins to grow and becomes hypertrophic. It is distinguished by a pink tint and bulge above the skin level. At keloid the scar area increases significantly due to tumor-like proliferation of immature connective tissue due to the uncontrolled activity of fibroblasts. Features of keloid scars are their rapid growth with paresthesia (tingling), itching and pain.
The likelihood of the appearance and severity of scars after acne is influenced by the individual tendency to scar tissue, the time of onset and effectiveness of acne treatment, the activity of acne (mild, moderate, severe), the number of papules, pustules and comedones and other factors.
Clinical manifestations
The main types of post-acne scars (Fig. 2 and 3):
- Hypertrophic.
- Keloids.
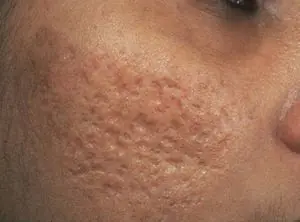
- Atrophic:
- chipped (icepick scars) - 60–70% of cases;
- rounded (rolling scars) - 20–30% of cases;
- rectangular (boxcar scars) - 15–25% of cases.
Atrophic scars after acne occur on average 3 times more often than hypertrophic and keloid scars.
Severity of post-acne scars:
- Macular - flat hyper- or hypopigmented (dark or light) lesions that do not change the skin texture.
- Mild - small atrophic or hypertrophic scars, invisible from a distance of more than 0.5 meters from a person. It is enough to simply hide them with decorative cosmetics or a beard (for men).
- Moderate - atrophic or hypertrophic scars of moderate severity, visible from a distance of more than 0.5 meters. They are not so easy to hide with makeup or natural facial hair, but you can straighten them with your fingers, stretching the skin in different directions.
- Severe - pronounced atrophic or hypertrophic scars, clearly visible from a distance of more than 0.5 meters. They cannot be straightened with your fingers when the skin is stretched.
In Russia, specialists from the Research Institute of Surgery named after. A.V. Vishnevsky was developed modified Vancouver scale. It can also be used in the analysis of post-acne scars (table 1).
Table 1. Modified Vancouver Scar Scale
Points
Description
By color
Normally pigmented (color of surrounding healthy skin)
Hyper- or hypopigmented (brighter or paler)
Various shades of red (immature scars)
In relation to the level of surrounding healthy skin
By relief and surface quality
With hyperkeratosis and ulcerations
By shape
Scar cord or fold (the length of the scar is greater than its width)
Scar mass (the length and width of the scar correspond to each other)
About half of all acne scars are of clinical significance, i.e. disrupt the structure and/or function of a specific area of the skin. By disfiguring the face, they negatively affect the emotional state of patients, reducing their self-esteem, causing psychological disorders and social maladjustment. Severe acne scars are considered a risk factor for suicide.
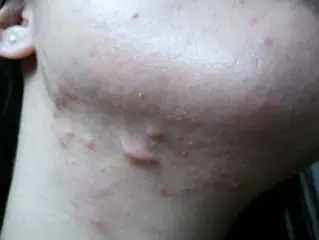
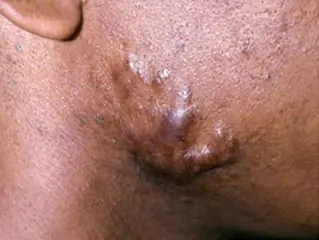
Rice. 1. Hypertrophic and keloid post-acne scars (www.acne.org, www.healthjade.com)
- Hypertrophic scars - appear within a month after healing, are located strictly at the site of the acne rash, are usually painless, lighten over time and can regress.
- Keloid scars - appear 3 or more months after healing, go beyond the boundaries of the acne rash, cause pain and itching, darken over time and can continue to grow.
 |
 |
Hypertrophic
Keloid
Rice. 2. Atrophic post-acne scars and their relative depth (Jacob C. I., et al. J Am Acad Dermatol 2001; 45: 109–117. Hession MT, et al. JCAD 2015; 8:50–58)
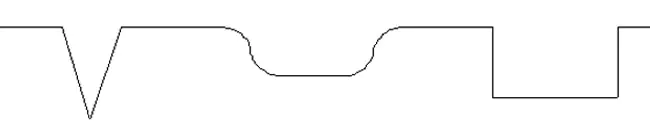
- Icepick scars - small in size (less than 2 mm), with clearly defined edges, cone-shaped (expand upward), deep (extend to the dermis and subcutaneous fat).
- Rolling scars - long (more than 4–5 mm), superficial, extending to the dermis, giving the skin surface a wavy appearance.
- Rectangular (boxcar scars) - medium size (1.5–4.0 mm), the edges are smooth and steep (never tapering downwards), the shape is round or oval, they can be superficial or deep.
Principles of treatment
When treating post-acne scars, the following points should be taken into account:
- Adjacent areas of scar tissue may have different histological structures and be at different stages of development (sometimes even opposite).
- The variety of options for scar development brings to the fore an individual approach to treatment not only for each patient, but also for individual areas of the scar itself.
- Widely known and proven drugs may be ineffective in a particular patient.
- Incorrect technology for using a medicine reduces or completely eliminates its effectiveness.
Atrophic scars:
- Dermabrasion is a mechanical peeling.
- Microneedling is piercing the skin with a special roller with many thin needles (additional use of medications is possible).
- Chemical peeling - trichloroacetic acid, glycolic acid, Jessner's solution (14% lactic acid + 14% salicylic acid + 14% resorcinol).
- Chemical reconstruction of scars using trichloroacetic acid - TCA CROSS (Chemical Reconstruction Of Skin Scarring) method. In this case, acid in high concentration (50–100%) is applied strictly to the scars.
- Volumizing techniques - injection of hyaluronic acid, collagen or fat fillers into scar defects. Allows you to lift the skin and smooth its surface.
- Subcision is the intersection of strands of connective tissue extending to the scars from the dermis. Allows you to eliminate skin tension and straighten the defect.
- Using your own skin to cover scar defects is the Punch Grafting method. First, the scar area is carefully excised, and then a small piece of the patient’s skin, usually taken from behind the ear, is attached to the defect site. The method is suitable for extensive scars.
- Laser and other hardware techniques.
Hypertrophic and keloid scars:
- Local application of corticosteroids under occlusion (tight bandage) for several weeks.
- Corticosteroid injections into the scar.
- Continuous application of silicone gels to the scar for several months (silicone dressings).
- Cryotherapy is the use of cold to break up excess scar tissue.
- Surgical excision of the scar.
- Laser and other hardware techniques.
Unfortunately, even with complete removal of a hypertrophic or keloid scar, they may reappear after some time.
When laser resurfacing appeared in the 90s of the last century, it was regarded as a very promising method for smoothing out post-acne skin. Full ablative resurfacing using CO2-laser can produce significant results, but this type of treatment is associated with very long rehabilitation and risks of complications. Therefore, today the number 1 laser method in the treatment of post-acne is non-ablative fractional photothermolysis and fractional ablation.
The methods for removing scars and scars are based on dosed destruction of scar tissue: the creation of microfractions of photothermolysis or ablation in it. Similar microfractions are also created in the tissue surrounding the scar. As a result of these two processes, gradual tissue remodeling occurs with smoothing of the scar boundaries and raising its bottom. The result of fractional laser treatment is smoother skin. With small post-acne scars and at a young age, significant improvement can be achieved up to the complete disappearance of scars.
Fractional techniques work directly with scar tissue - this means that the bottom of the atrophic acne scar must be accessible to the laser beam. In this regard, chipped acne scars are very difficult to treat.
Non-ablative fractional lasers, such as ResurFX M22 and Fraxel, are safer and more convenient to use, but require 4 or more procedures at intervals of 1–1.5 months. Fractional CO2-lasers, such as Acupulse and Ultrapulse, require patient rehabilitation, but provide significant results even with one procedure, including because fractional effects when used can be combined with continuous ones.
Prolonged course of acne and severe forms of inflammation, improper and untimely treatment of the disease lead to the development of post-acne - secondary persistent changes in the skin. Post-acne can manifest itself as enlarged pores, hyperpigmentation, and red stagnant spots.
But in 90% of cases, scars and cicatrices remain on the skin after acne, which are no less serious a problem than acne itself. There are various methods to combat unaesthetic skin defects. The choice of the optimal method of therapy is determined by the type and timing of appearance, and the area of scar localization.
Therapy methods: features of choice
Scars that develop from granulation tissue cells and transform into rough connective tissue formations deform the skin texture. The shape of the scars depends on the nature of the damage; it can be linear and stellate, V-shaped and U-shaped.
At the initial stages of formation, the color of the damaged areas is pinkish, then they become white or, conversely, darken. Scar tissue can fit tightly to the subcutaneous structures or move freely to the sides, which is easily determined by palpation.
Scar structures are classified into 4 types based on morphological characteristics.
- Normotrophic. Formations with a smooth surface are located on the same level as intact skin and are practically no different from it in elasticity and color.
- Atrophic. Smooth and thin, have a whitish tint. Formed due to insufficient collagen synthesis. Their surface is located below the level of normal skin, so externally atrophic scars look like depressions of different shapes and sizes.
- Hypertrophic. Caused by the formation of a small number of pathological collagen fibers. They rise sharply above the skin and come in various colors from pale pink to bluish or burgundy. They don't grow.
- Keloids. Rough, deforming skin defects occur when a large number of pathological collagen fibers are formed. Like hypertrophic structures, they rise above the skin, but unlike them they can grow, protruding beyond the boundaries of the initial damage, and are very difficult to treat.
In areas of strong skin tension, the likelihood of the formation of hypertrophic and keloid structures is greatest. Also, these types of scar structures often form on the skin in the upper back and sternum, and shoulder girdle.
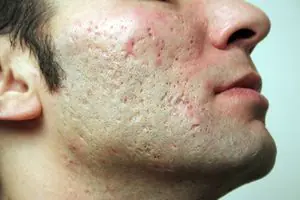
To remove acne scars, modern pharmacology and cosmetology offer many means and methods. The choice of the optimal method of therapy is determined by the type of scar, its shape, size, and timing of occurrence.
All methods of treating acne scars can be divided into 4 groups:
- medications (external pharmacological agents: ointments, creams, gels);
- folk (masks prepared according to alternative medicine recipes);
- cosmetology (mesotherapy, resurfacing, peeling, laser treatment);
- surgical.

The therapeutic effect of ointments and other dosage forms for topical use is due to the action of the components included in the composition: surfactants, enzymes, vitamins, plant extracts. They improve microcirculation and metabolism in tissues, stimulate regeneration processes, promote the exfoliation of upper keratinized cells, soften rough skin defects, making them softer and more elastic, less noticeable.
The main advantages of these products are ease of use and the possibility of treatment at home. However, pharmacological agents can affect scar defects that formed no more than 2 years ago - fresh scars, in which metabolic processes have not yet stopped, are much easier to treat. And pharmacological drugs may not be able to cope with old scars.

To combat unaesthetic skin defects, the following drugs are used:
- Contractubex. A gel containing heparin, allantoin and onion extract reduces inflammation, has an antimicrobial effect, inhibits the growth and division of connective scar tissue cells, helps saturate damaged skin with water, thereby softening rough skin defects. As a result, the height of the scar decreases, elasticity increases, and the shade approaches the color of normal, undamaged skin. It is used to treat atrophic, hypertrophic and keloid type scars.
- Strataderm. A gel with purified silicone polymers normalizes collagen production in the damaged area and has a protective effect. Due to silicone, after applying the product, a moisture-proof but oxygen-permeable film is formed on the skin. It protects damaged tissues from damage, infection and fluid loss, which is necessary for normal collagen production. Under the film, the scar softens and brightens. The gel is indicated for the treatment of all types of formations.
- Fermenkol. A gel based on 9 enzymes (collagenases) effectively eliminates acne scars due to the ability to break down pathological collagen into amino acids and oligosaccharides and at the same time stimulate the regeneration processes of healthy cells. When using the product, itching and pain are eliminated, rough scar tissue softens, is compared with the level of the skin, and acquires the shade of nearby healthy tissue.
- Zeraderm Ultra. The gel is similar in action to the drug Strataderm. In addition to silicone polymers, it contains vitamin K (strengthens vascular walls, eliminates redness), coenzyme Q10 (stimulates the restoration of normal skin cells), vitamin E (exhibits antioxidant properties, normalizes the water balance of the skin), sun filter (protects tissues from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation). It is used to prevent and treat already formed hypertrophic and keloid type scars.
- Kelofibrase. A cream based on urea, heparin and camphor softens and moisturizes rough scar tissue, increases their elasticity, improves microcirculation and metabolic processes, activates regeneration, reduces swelling and inflammation, promotes the resorption of scar structures, smoothes and compares the protruding parts of the skin defect with the level of the skin.
Masks

To make acne scars less noticeable, in addition to pharmacological drugs, you can use masks prepared according to alternative medicine recipes. For their preparation, food, essential and vegetable oils, vitamins, and sometimes pharmaceuticals can be used. An example of such products is badyagi powder.
Badyaga are sponges that live in fresh water bodies. Their skeleton consists of interconnected microscopic silica needles. Powdered badyaga has a local anti-inflammatory, analgesic and irritant effect. In folk medicine, this remedy has long been used to treat acne and post-acne, hyperpigmentation, and stagnant spots. It has absorbable properties, activates microcirculation, reduces inflammation and stimulates protein synthesis.
To treat scars, badyagi powder is mixed with a solution of hydrogen peroxide until a foamy mass is obtained. The product is applied with massaging movements, rubbed into the skin for 3 minutes, after 15 minutes, washed off with water.

In addition to badyagi, alternative medicine can offer many other recipes for masks for acne scars.
- Aloe and lemon. Mix a tablespoon of fresh aloe pulp (grind in a blender) with a teaspoon of lemon juice. Apply the product to the face, rinse with warm water after 10-15 minutes. Lubricate the skin with moisturizer. Carry out the procedure three times a week.
- Cinnamon and honey. Mix a teaspoon of cinnamon powder with 2 teaspoons of honey. Apply the product to damp skin, rinse with warm water after 10-15 minutes. Make a mask 2-3 times a week.
- Tomatoes. Apply tomato puree to the scars and rinse with water after drying. Carry out the procedures daily.
- Pineapples. Apply pineapple pulp crushed into puree onto scars daily, rinse off after 10 minutes.
- Blue cosmetic clay. Dilute a little product with water to a thick mushy mass, add a drop of rosemary essential oil. Apply to skin, rinse after 15 minutes. Carry out the procedure twice a week.
To remove old, deep scars, the use of folk remedies will be ineffective. But homemade masks can cope with small fresh skin defects left after squeezing out a pimple: they will make the scar less noticeable, even out the skin texture, and restore the color of the skin in the area of damage.
Cosmetology procedures
If skin defects do not respond to drug treatment, they resort to more aggressive effects on scar formation. Treatment of acne scars with physical, chemical or injection cosmetic methods helps to even out and smooth the skin texture. The procedures differ in the degree of aggressive impact on the skin. Some of them are quite painful and are characterized by a long recovery period.
Mesotherapy

Mesotherapy (injection intradermal administration of therapeutic agents directly into the problem area) is carried out in the early stages of scar tissue formation. Usually medications and meso-cocktails (a mixture of medicinal products) are administered based on:
- biologically active substances;
- amino acids;
- vitamins;
- minerals;
- placenta extract;
- plant extracts.
For keloid scars, glucocorticosteroids are used. To smooth out atrophic scars, hyaluronic acid or fat cell fillers are injected under the bottom of the skin defect.
Mechanical grinding
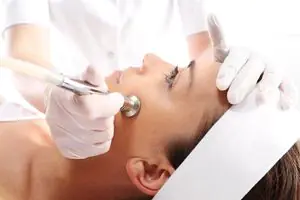
There are several methods of mechanical skin resurfacing:
- diamond dermabrasion – skin polishing using a special device, the nozzle of which is covered with diamond dust (microscopic particles);
- deep dermabrasion - a procedure in which the upper layer of the epidermis is removed from the problem area using a Schumann device (a high-speed cutter);
- microdermabrasion - grinding with microscopic crystals of aluminum dioxide.
The choice of method depends on the nature and severity of scar structures. For superficial changes, microdermabrasion gives good results. Diamond grinding smoothes shallow U-shaped and V-shaped defects. Severe atrophic and hypertrophic structures can be corrected using deep dermabrasion.
It is worth noting that microdermabrasion is easier to tolerate and causes fewer complications. Diamond and deep grinding are traumatic methods and require longer rehabilitation. Recovery in most cases is quite difficult. In addition, these procedures can provoke the growth of keloid structures and irreversible pigmentation disorders.
Peeling
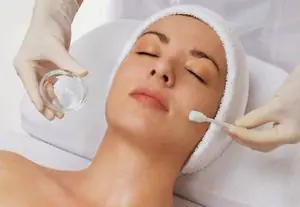
An alternative to mechanical grinding is chemical peeling with acids:
- salicylic;
- trichloroacetic;
- alpha hydroxy acids (glycolic, lactic).
For deep skin defects, acids are used in a concentration of 35-70%.
When carrying out peeling, it is quite difficult to control the depth of exposure, so the procedure can lead to the development of unwanted complications: allergies, hyperpigmentation, and the formation of new scars.
Laser
According to many experts, laser removal of acne scars is the best way to correct cosmetic defects, regardless of their type and severity. There are several methods of laser treatment, which are carried out using ablative (carbon dioxide) or non-ablative (erbium, neodymium) laser devices.
The effectiveness of the carbon dioxide laser is visible after the first procedure, especially when removing atrophic scars: the severity of the skin defect is reduced by 50-80%. However, the procedure requires high professionalism of the cosmetologist, since the risk of complications is quite high. Possible consequences include:
- formation of new scars;
- infection;
- long-lasting erythema (redness) and inflammation of the treatment area.
When using an erbium laser, the risks of developing unpleasant consequences are much lower, since the impact extends to a shallower depth, but it is also inferior in efficiency.
Surgical
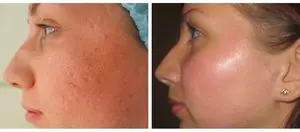
Surgical removal of acne scars is a radical method, carried out to correct coarse formations of the hypertrophic and keloid type, and less commonly used to eliminate atrophic scar changes.
To eliminate skin defects, excision of a rough scar is performed with the application of a cosmetic suture or undercutting (subsission) of the tissue under the scar (when correcting atrophic scars). The operation makes it possible to get rid of deep skin defects, but still a fresh linear scar remains on the skin, requiring further correction using cosmetic methods.
Acne scars become no less, and sometimes even more of a cosmetic problem than acne itself. There are many methods for correcting skin defects: from the relatively safe use of drugs and folk remedies to radical surgical operations. There is no one universal remedy that allows you to remove unaesthetic defects - in each case an individual method or a combination of them is selected.



