According to medical statistics, from 20 to 30% of the population of our planet have suffered from urticaria at least once in their lives. And those who have never suffered this illness themselves, to one degree or another, have at least a general idea of it. The idea that this is a childhood disease is absolutely wrong. Urticaria (Urticaria), a skin disease (mainly of an allergic nature), can occur in people of all ages. In our review article we will try to tell you what causes urticaria in adults, how to treat it, and also talk about publicly available preventive measures that will help prevent this disease.
External signs of the disease
What does urticaria look like in adults? The main external signs of the disease are the appearance on the body of numerous severely itchy redness, induration, inflammation, spots and blisters (fairly flat) of red or pink color. In appearance, the swelling is largely reminiscent of nettle burns (hence the common name). The development of the disease can occur very quickly: neoplasms on the body can appear within just a few minutes. The size of the swelling varies from a few millimeters to tens of centimeters. Over time, several small blisters may merge into one. External symptoms of urticaria appear on the legs, arms, back, abdomen and other parts of the body. It is especially dangerous for human health when swelling affects the respiratory tract (the person begins to choke) and the genitals (which leads to the inability to urinate).
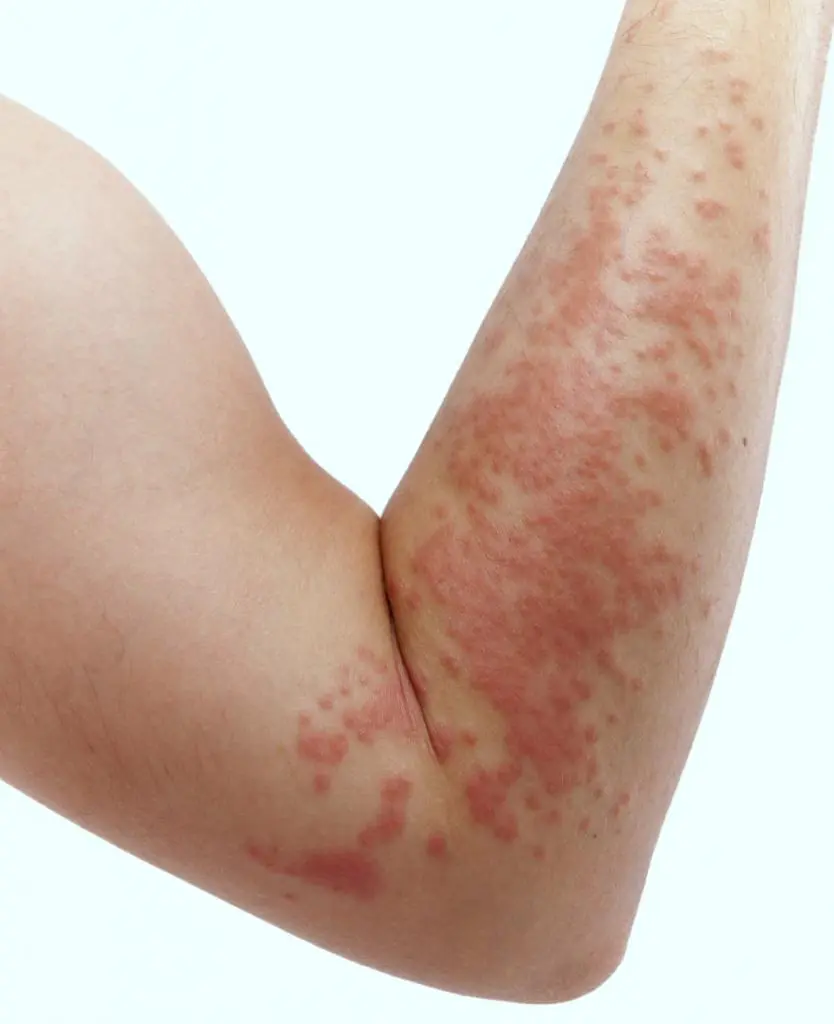
Minor signs
Associated symptoms of urticaria in adults include the sudden onset of muscle weakness, headache, nausea, chills, runny nose, diarrhea, fever, fever and cough. These secondary signs sometimes make it difficult to make a correct diagnosis, especially if the inflammation of the skin is not too obvious. It is easy to confuse the disease with, for example, ordinary food poisoning.
The mechanism of occurrence and development of urticaria
What causes urticaria in adults? The composition of human skin (and other connective tissues) includes mast cells that have capsules inside filled with histamine. When an allergic reaction occurs in the human body, this substance is released, enters the subcutaneous space through capillary vessels, accumulates and causes swelling and rash. That is, the mechanism of the disease is the rapid release of histamine from mast cells.
If the swelling can be stopped within 36 hours, then no damaged areas remain on the skin. Otherwise, damage to the walls of blood vessels begins.
Important! If, during the course of the disease, swelling spreads to the respiratory system, this can lead to the most severe consequences. In this case, emergency medical care is required!
Varieties
There are two main types of urticaria:
- Spicy. The duration of the disease usually does not exceed 5-6 weeks. As a rule, with proper and timely treatment, external manifestations can be eliminated within 24-36 hours.
- Chronic. Symptoms may last for several months (in particularly severe cases, even several years). According to experts, about 0.1% of humanity currently suffers from this disease.
Please note: one of the most dangerous types of acute urticaria is angioedema. It is accompanied by the rapid formation of compactions in the area of the eyes, lips and cheeks. The main danger is possible swelling of the larynx, which can lead to asphyxia (with all the ensuing consequences). To prevent death, urgent drug treatment is required.
Causes of allergic urticaria
The main cause of urticaria in adults is the body's reaction to a specific allergen. Moreover, a person may not even know what substance was the “provocateur” of the disease. The main triggers that cause a true allergic reaction in the body are food, medications, chemical compounds (including household detergents), pet hair, insect bites (bees, wasps, ticks, flies or cockroaches), pollen and, oddly enough, even ordinary household dust. In some cases (even with comprehensive examinations and numerous laboratory tests), the true cause of the disease cannot be determined.
One of the reasons for the appearance of urticaria in adults, no matter how paradoxical it may sound, is age. With its increase (especially after 40 years), the allergic reactions of the human body intensify. And, as a result, Urticaria can become a reaction to any everyday food product or habitual medicine.
On a note! If you find obvious signs of urticaria in an adult after sleep, then most likely the cause could be bites of the so-called bed tick. In addition to treating the disease itself, it is necessary to properly treat all bedding (mattress, pillows, blanket, etc.).
Non-allergic causes of the disease
In addition to allergies, the causes of urticaria in adults can be:
- various (especially chronic) diseases of the liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, endocrine system, thyroid gland;
- pathogenic bacteria and viruses;
- inflammatory processes;
- stressful situations;
- intestinal parasites;
- the body's reaction to a sharp drop in ambient temperature or solar activity.
Diagnostics
An experienced specialist, when examining a patient and visually examining the skin rash, can find out what causes urticaria in adults. To make a correct diagnosis, a doctor (dermatologist, allergist or immunologist), first of all, will need detailed answers from the patient to the questions posed to him:
- When did external signs begin to appear?
- Was there an insect bite before this and, if so, what kind?
- What medications (and in what dosages) was the person taking before the incident?
- What did the patient eat during the day?
- What chronic diseases does the patient suffer from?
- Was there any contact with animals or chemicals?
As a rule, detailed answers to the above questions will be enough for an experienced specialist to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. The main thing is to find out the reason that caused the hives, because the next encounter with this allergen can lead to more serious consequences.
For chronic urticaria, laboratory tests are prescribed:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- test to identify problems with the immune system;
- skin tests;
- determination of the content of immunoglobulin E (its increased concentration indicates a predisposition to allergic reactions of the body, including urticaria);
- stool analysis to identify the presence of parasites in the body;
- checking the functioning of the kidneys, liver, thyroid gland and gastrointestinal tract.
Since sometimes even numerous laboratory tests do not allow us to identify the true cause of urticaria, in case of a chronic recurrent disease, a journal with records of all the events preceding the incident will help to identify the trigger. Subsequent analysis of systematized data greatly simplifies the search for a “provocateur.”
Drug treatment of acute urticaria
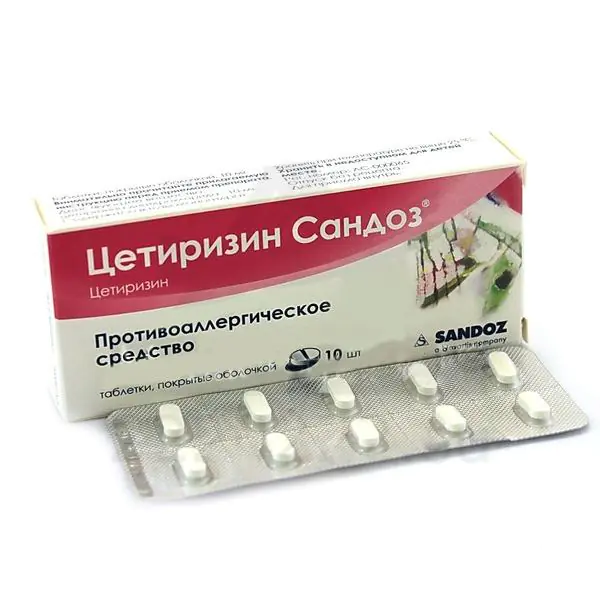
Various antihistamines have been successfully used to treat acute urticaria. Most of these medications are available without a prescription. And although experts do not recommend self-medication with medications, success in the fight against the disease largely depends on efficiency (often running to the pharmacy for medicine will take much less time than waiting for the local doctor to arrive).
The list of the most popular and very effective drugs taken for urticaria in adults: Diazolin, Cetrin (Cetirizine), Zyrtec, Fexofenadine, Erius. These medications help block the negative effects of histamine, reduce external rashes, and stop painful itching. In most cases, after the surgical use of these medications, a positive effect is observed. But further actions related to how and how to treat urticaria in adults should be done only after consultation with a specialist. It is he who will determine the duration of the course of treatment and give all the necessary recommendations.
Treatment of chronic urticaria
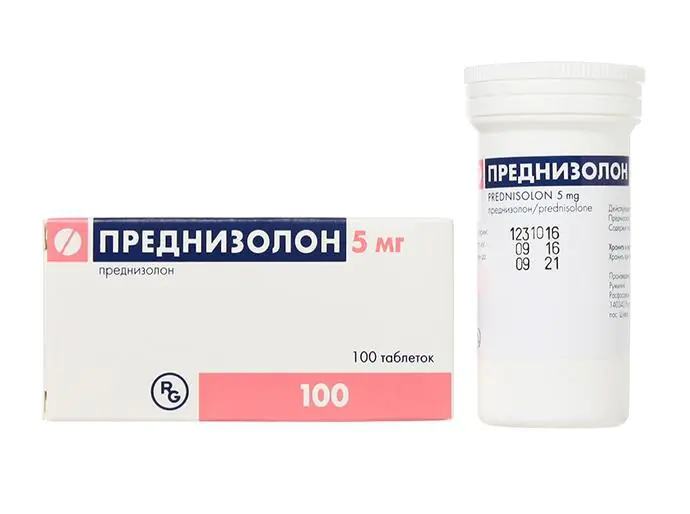
When treating chronic urticaria, antihistamines (even in fairly large doses) cannot quickly reduce swelling and itching. How to treat urticaria in adults in this case? Specialists use special hormonal drugs – glucocorticosteroids – to treat chronic urticaria. The most well-known and frequently used medications of this group, produced in the form of tablets or injections: Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Prednisone, Triamcinolone, Betamethasone.
Using hormones on a regular basis is difficult because of the risk of serious side effects such as osteoporosis, glaucoma, diabetes, and a weakened immune system in general. Therefore, so-called monoclonal antibodies have recently been successfully used to treat severe cases of frequently recurring urticaria. The injectable drug "Omalizumab" ("Omalizumab" or "Xolair") blocks molecules of the immunoglobulin E protein, which plays a major role in the body's allergic reactions. A positive effect is observed even in the treatment of urticaria of unknown origin. A course of use of this drug leads not only to the elimination of symptoms, but also removes the causes of the chronic disease until it is completely cured.
First aid for urticaria in adults
Before being examined by a doctor and prescribing treatment methods, the patient can provide first aid to himself at home:
- First of all, we ventilate the room;
- we take any antiallergic drug (if it is available in the home medicine cabinet);
- take off clothes or put on looser clothes (made of soft materials that do not injure the skin);
- take a cool shower or bath;
- apply cold compresses to the most itchy areas;
- We go to bed (under no circumstances should you tolerate hives on your legs).
When is emergency medical care required?
Severe cases of allergic urticaria require immediate medical attention. The main signs for calling emergency help are:
- swelling of the lining of the mouth, tongue, lips, and throat;
- labored breathing;
- high body temperature (39°C or more);
- loss of consciousness or inadequacy in expressing thoughts;
- cardiopalmus;
- severe nausea and vomiting;
- cold and clammy skin.
If a patient with the symptoms described above is not provided with emergency medical care, this can lead to very serious consequences, even fatal.
Diet
Strict adherence to a certain diet plays an important role in the treatment of urticaria. First of all, foods that have the greatest effect on the production of histamine in the body’s mast cells should be excluded from the diet. These include spinach, chocolate, strawberries, fatty meats, tomatoes, yoghurts, fish and other seafood (shrimp, crabs, etc.). Also, during the treatment period, you should not drink alcoholic beverages, honey (and other sweets), eggs, coffee and strong tea.

What you can eat if you have hives: porridge (oatmeal or rice), boiled potatoes, fresh vegetables (cabbage, zucchini or cucumbers), boiled lean meat (turkey, chicken breast or beef), pears and apples.
Folk remedies in the fight against urticaria
The treatment of urticaria with folk remedies in adults must be approached with extreme caution. Any ingredient (or maybe several at once) may be a trigger for an allergic reaction, which the patient may not even be aware of, since he has not encountered it in everyday life. Before putting into practice the recipes of traditional healers, it is better to first consult with a specialist.
How to relieve itching with urticaria in an adult:
- Pour boiling water over a mixture of equal parts of string, chamomile and oak bark. Let it brew for 1-1.5 hours. Strain the broth and gently moisten the blisters with it.
- A paste of grated raw potatoes applied to inflamed areas helps to significantly reduce itching and swelling.
- A bath with the addition of an infusion of valerian leaves, celandine, St. John's wort and string to the water helps reduce pain symptoms.
Two simple and affordable recipes for treating urticaria in adults with folk remedies:
- Pour boiling water over mint leaves and leave for 30-40 minutes. Take orally three times a day before meals.
- Tea from walnut leaves, prepared at the rate of 2 teaspoons per 0.5 liter of water. A special feature of the preparation is the brewing time - at least 10 minutes.

Preventive measures
We briefly addressed the question of what causes urticaria in adults and how to treat it. However, taking fairly simple preventive measures will help significantly reduce the risk of this disease:
First of all, it is necessary to completely eliminate contact with specific allergens known to a person from personal experience or identified during clinical studies.
Getting rid of bad habits (for example, drinking alcohol and smoking) will not only have a positive effect on overall physical health, but will also strengthen the body's anti-allergic capabilities. Timely treatment of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and kidneys will help reduce the likelihood of urticaria.
Both overheating and hypothermia of the body should be avoided. Therefore, sunbathing and walking in the cold need to be dosed wisely. Emotional stress not only weakens the nervous system, but can also be a trigger for the occurrence of hives. Therefore, naturally, if possible, they should be avoided or at least minimized.
Last (but not least) what you should pay attention to is your daily diet. Excluding highly allergenic foods from it significantly reduces the likelihood of developing the disease.
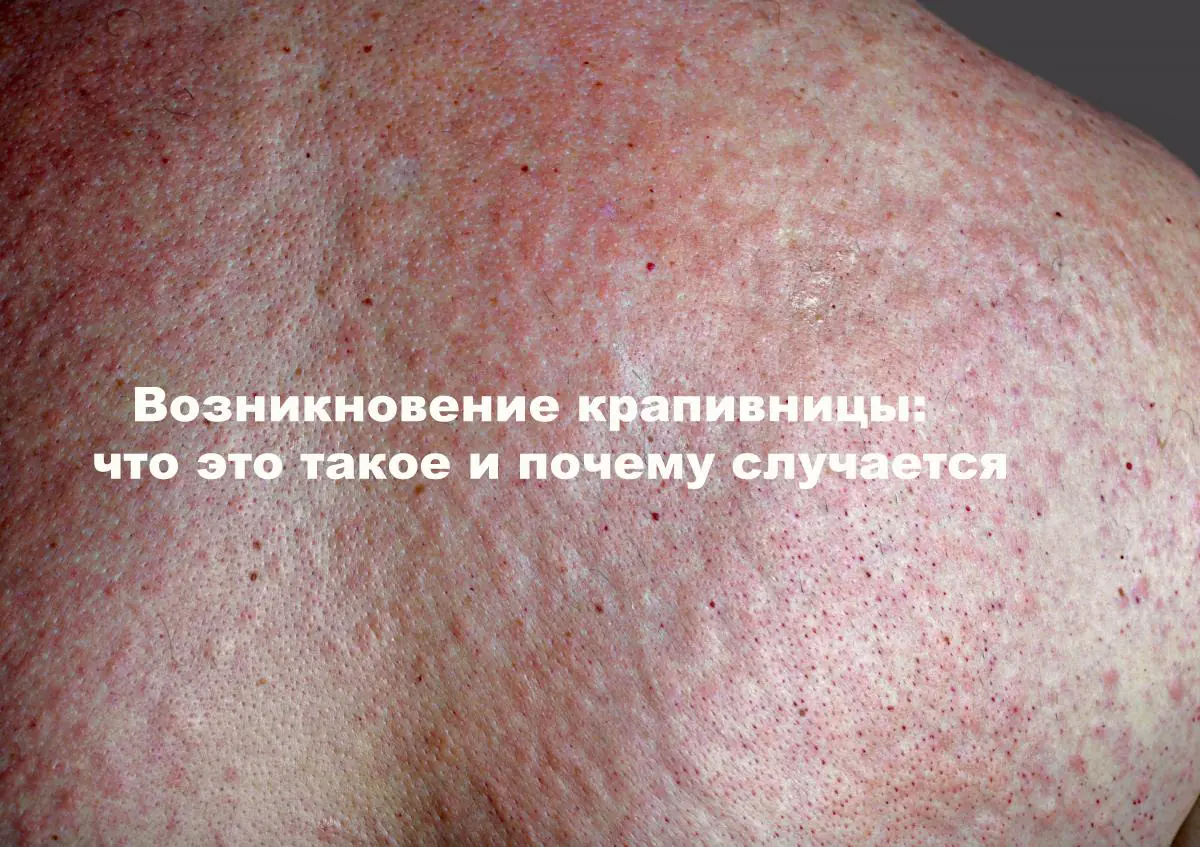
Urticaria is an allergic disease, the most obvious manifestation of which is blisters on the skin and mucous membranes. They are somewhat similar to a nettle burn, which is how the disease got its name.
More than 20% of the population have encountered its manifestations at least once. What is it - urticaria? This disease can be acute or chronic. Children are more susceptible to acute forms, while chronic forms are more common in adults.
Women make up about 30% of all patients. Possible reason: hormonal changes in the body during pregnancy, childbirth, menopause. Half of the cases proceed without complications. Almost 40% are accompanied by Quincke's edema. The disease is more difficult to treat in adults than in children.
Mechanism of disease development
The biologically active substance histamine is the main culprit in the development of allergic reactions, being responsible for what causes hives. Contact with an allergen causes a powerful dose of this substance to be released into the blood.
The further picture depends on the degree of sensitivity of the body to the allergen. He can react almost instantly. A reaction is possible due to repeated contact with the irritant.
With a high concentration of antibodies, symptoms of pathological processes may appear. The permeability of the capillary walls increases, fluid from the vessels enters the dermis, and blisters appear on the skin.
Symptoms
The main symptoms that may indicate urticaria are rash and itching.
- Blisters of pink and red shades protrude above the surface of the skin. Sizes from a few millimeters to ten centimeters. They disappear when pressure is applied to them. The rash can completely go away on its own within a day, leaving no traces of pigmentation.
- The itching that accompanies the rash intensifies in the evening. Both the blisters themselves and unaffected areas of the skin can itch.
- Fever, nausea, vomiting, rapid heartbeat, and increased blood pressure occur when the rash covers a large area of the skin. The number of blisters (20-50) along with the characteristics of itching (mild, moderate, severe) determine the severity of the patient’s condition.
Causes
There are many reasons causing this disease. Doctors often cannot find out for years what caused the development of pathological symptoms. What causes hives? Over the years of research, the most likely factors causing this condition have been identified.
- Medications. Antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are more likely to provoke allergies than other drugs. It often appears while taking nicotinic acid. The taken medication triggers pathological mechanisms within 10-15 minutes. Often, symptoms of the disease begin to appear a couple of weeks after the end of treatment.
- Insect bites. Poisonous bites of bees, wasps, and bumblebees give a clinical picture of an acute form. Blisters after bites do not disappear for about a day.
- Products, capable of causing allergies. Why does hives appear after eating citrus fruits, berries, dairy products, wine, chocolate, nuts, and seafood? Sometimes this food can cause the release of a large dose of histamine into the body, which is fraught with a response - the appearance of typical symptoms of the disorder.
- Existing diseases. There are many observations of what can cause hives. The disease may occur due to some irritant. A large percentage is a manifestation of hidden diseases. In a huge number of cases, the development of this pathology is due to infectious diseases (hepatitis, herpes). Chronic parasitic diseases play a major role. In children, worms can cause symptoms. The allergy disappears immediately as soon as measures are taken to expel parasites (worms). Foci of chronic infections in the nasopharynx (tonsillitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis) play a huge role. Urticaria accompanies gastritis, an ulcer whose development is caused by Helicobacter pylori.
- Disruptions in the immune and endocrine systems. Sometimes the body begins to perceive its own cells as foreign, rejecting them (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis). This condition is called an autoimmune infection. Pathology of an autoimmune nature takes a long time and is difficult. The fight with antihistamines gives insignificant results. The disorder alternates between stages of exacerbations and remissions.
- Direct contact with the allergen. Contact of an allergen with the skin often causes a rash. The allergen that provokes the symptoms of the disease is hidden in household chemicals (cleaning and detergents). This also includes pathologies of the thyroid gland (decreased, excessive production of the hormone thyroxine).
- Physical factors. The painful condition occurs as a result of sudden cooling, extreme heat, contact with water, vibration, fluctuations in body temperature, mechanical irritants, and increased physical activity.
- Vaccination, anesthesia. For the safety of allergy sufferers, they are recommended to use antihistamines before vaccination or anesthesia.
Doctors identify many causes of urticaria. Only an experienced specialist can tell which of them is it for you.
Features of the disease
With many skin diseases, the rash appears gradually. Urticaria is distinguished by the following circumstance: the majority of blisters appear in the first hour. This is explained simply: the concentration of histamine is very high.
Subsequently, some more rashes join the existing blisters. The blisters disappear without a trace within the first hours after their appearance. But sometimes it happens the other way around - a second wave of blisters appears. The blisters are painful and cause severe itching.
Could it be that urticaria is mistaken for a manifestation of another disease? The swollen, reddened skin around the blisters should convince the doctor that the diagnosis is correct. The situation when the affected area is small, the patient’s condition does not change. If the blisters continue to appear, spreading throughout the body, there may be an increase in temperature, increased weakness, and headaches.
Types of urticaria
Depending on the duration of allergic reactions, urticaria occurs:
Having found out what causes hives, we can distinguish the following forms:
- physical;
- medicinal;
- contact;
- idiopathic.
Physical urticaria has several types depending on the cause that caused it:
- cold weather
- solar;
- aquagenic;
- provoked by physical activity;
- allergies due to nerves;
- vibration
Allergies can affect a person of any age. Let's look at the cases that cause urticaria in adults.
Cold urticaria
From the name, the reason for its occurrence becomes clear - cold, low temperatures. Frost, swimming in ponds, ice holes, and pools with low water temperatures can cause allergic shock, accompanied by loss of consciousness.
The skin takes on a bright red tint, and the number of blisters covers a significant area. If a limited area of the body is exposed to cold, then all manifestations tend to go away on their own after the person warms up well.
In cases where the process affects internal systems (central nervous, cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal tract), serious complications are associated with the rash. They are manifested by headache, shortness of breath, drop in blood pressure, nausea, and vomiting. Patients with such symptoms are more likely than others to experience anaphylactic shock, which develops immediately. This situation requires urgent medical attention.
Solar urticaria
Solar allergy is a reaction of the body after contact of exposed areas of the body with the sun's rays. The rash covers only those fragments of skin that have been exposed to open sunlight. Blondes with fair skin are most often affected.
Aquagenic urticaria
There is often an unexpected skin reaction to contact with water, sweat, or tears. Water is not the direct cause of pathological processes. It’s all because of the substances dissolved in it. The allergy begins instantly. All its manifestations usually disappear after half an hour. Sometimes this takes several days. Question: “Is it possible to swim if you have hives?” requires caution. The best advice is to take a bath in boiled water for a while.

Each type of urticaria requires a specific treatment. In order to correctly choose the optimal course, it is important to consult a specialist for advice.
Exercise stress
Often the cause of the disease is physical activity aggravated by food intake.
Urticaria due to stress
The symptom complex caused by this form most often affects women and adolescents. They react more emotionally to stressful situations. The risk group includes people who are mentally unstable, have signs of emotional exhaustion, and are prone to displays of irritability, anger, and fear.
Drug-induced urticaria
Every year, medicinal substances increase the percentage of allergic reactions. What does it come from? Its manifestations can be observed after a few minutes of the drug entering the blood. A certain percentage of allergy cases occur a couple of weeks after the end of treatment. Most often, the body responds with a pathological reaction to antibiotics, NPS, antidepressants, and local anesthesia.
Contact
Develops in cases of direct interaction with an allergen. The irritants are the most common things: wool, dust, household chemicals, latex. To eliminate the symptoms, it is enough to simply eliminate the provoking factor.
Idiopathic
This form of pathology with an unidentified cause, occurring in 40% of all cases. The disease is chronic and does not go away for several years. Skin rashes last for more than a month. The disease is permanent or recurrent in nature (phases of exacerbation alternate with persistent remissions).
Complications
Often, rash-affected areas of the skin become a favorable environment for bacterial infections. Furunculosis and various purulent inflammations are added to the existing rashes.
Dangerous conditions that can cause death:
- Anaphylactic shock. It develops rapidly; in a matter of seconds, severe swelling of all tissues of the body develops, with a strong drop in pressure. Of particular danger is swelling of the larynx, which entails obstruction of the airways. Choking can cause rapid death. This condition requires emergency hospitalization.
- Quincke's edema - suddenly developing swelling of subcutaneous fatty tissue and mucous membranes. The lips, tongue, palate, and tonsils are especially often affected. Damage to the larynx gives symptoms of a “barking cough”, the voice becomes hoarse. Failure to provide timely assistance can lead to serious consequences for the patient, including death. The most dangerous is swelling of the face due to the possible involvement of the meninges in the process.
Such complications, even before the arrival of doctors, require first aid to be provided to the victim:
- Stop taking the medicine immediately (drug allergy).
- Give a laxative, rinse the stomach (food allergy).
- Pull out the insect sting to stop the flow of poison (bites of bees, wasps, hornets).
- Free the skin from the irritant (contact urticaria).
After the measures taken to alleviate the patient’s condition, all that remains is to wait for an ambulance. Doctors will assess the severity of the condition and determine the subsequent treatment regimen. Calling an ambulance is recommended if the rash appears for the first time in a child. This will help avoid possible complications, understand the reasons that caused the allergy (is it hives, or symptoms of another disease).
Urticaria is an allergic disease that manifests itself on the skin and mucous membranes in the form of blisters. Statistics show that women are more susceptible to this disease than men. The disease is common, a person faces this problem at least once in his life.
Causes of urticaria
According to doctors, the fact that urticaria is diagnosed in women twice as often as in men is explained by hormonal disorders that occur in the female body with age. The following factors can affect hormone levels:
- Pregnancy;
- Taking oral contraceptives;
- Menopause;
- Menstruation.
In most cases, doctors are unable to accurately determine the cause of a chronic allergic reaction. Therefore, you have to undergo a full examination and take a lot of tests. Chronic urticaria may appear for the following reasons:
- Infection entering the body;
- Decreased immunity;
- Allergy to specific foods;
- Physical effects on the skin;
- Presence of dermatitis;
- Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus of any group;
- Gastritis;
- Hepatitis;
- Leukemia;
- Herpes.
According to medical statistics, 15% of cases of urticaria occur precisely due to infection. Both viral and bacterial infections can cause rashes and skin irritation. It is important to immediately eliminate foci of inflammation, be it gastritis or caries. When immunity decreases, the body stops recognizing its cells and attacks them, which leads to autoimmune urticaria.
Physical factors provoking the disease
Doctors distinguish several types of physical urticaria, depending on the factors that provoked it:
- Sunlight. After exposure to sunlight on the skin of the patient (mostly women), a rash, redness and itching begins to appear. It is noteworthy that the rash is recorded only on those areas of the skin that are not covered by clothing.
- Cold. Unheated air or too cold water can also cause hives. In rare cases, symptoms of the disease are recorded when a person eats food that is too cold. Blisters appear around an area of skin that has been exposed to hypothermia.
- Water. Doctors call this type of urticaria aquagenic because it appears after a person comes into contact with water. It is noteworthy that there is usually no redness or blistering; the patient suffers from extremely severe itching.
- Strong vibrations. This type of urticaria is an occupational disease, as it occurs in people who, due to their occupation, are exposed to strong vibrations, for example, working with a jackhammer.
- Allergens. Hives can be caused by standard allergens: pollen during flowering, dust, animal hair. Symptoms completely disappear after a person protects himself from the allergen.
- A sharp increase in body temperature. Doctors call this type of urticaria cholinergic. It appears during a sharp increase in a person’s body temperature. This can happen not only due to illness, physical training, eating spicy or hot food, a surge of emotions - all this can cause a sharp rise in temperature. The blisters are small and pale, concentrated in the upper part of the patient's torso.
- Friction and compression. Hives may appear due to a too-tight belt, tight dress or shoes. It is noteworthy that physical pressure must continue for a long time for hives to appear. At the same time, the blisters here are oblong and do not appear on the skin at the same time as itching.
What does urticaria look like on the body?
The rash caused by urticaria is very similar to the rash caused by a nettle “burn.” Hence the name. Please note that inflammation and blisters may disappear and reappear. This course is called recurrent.
The rash is one of the main diagnostic symptoms of the described disease. Elements of the rash (blisters) can be round or oblong, small in size, slightly raised above the skin. Mostly pale pink in color. The skin around them is dark purple. The patient suffers from severe itching in the inflamed area.
The main feature of urticaria in adults is that it manifests itself quickly and then can also suddenly disappear. Itchy skin occurs due to irritated nerve endings. Much more of the neurotransmitter histamine enters the bloodstream than before. The level of itching (from tolerable to painful) varies precisely because of the amount of incoming substance.
Signs and symptoms
Essentially, urticaria is an allergic reaction exhibited by the body after contact with an allergen. Classic symptoms include:
- Redness of one or more areas of the skin;
- Blistering;
- Severe burning and itching in the area of inflammation;
- Temperature increase;
- Headache.
Depending on the course of the disease, urticaria can be acute or chronic. The acute form is recorded much more often than the chronic form.
Figure No. 1. Acute urticaria in a child.
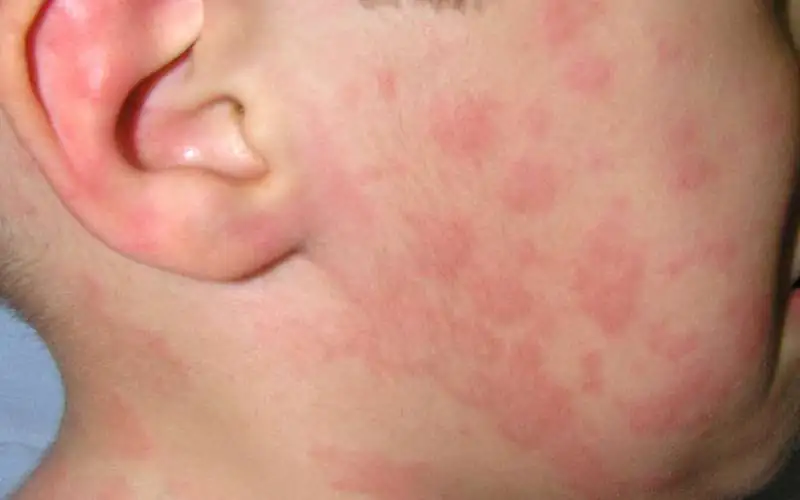
It can be diagnosed in young children and adolescents and can be a consequence of Quincke's edema. The diameter of the blisters in the acute form can reach one centimeter, and the rashes are concentrated not on individual areas of the skin, but throughout the body. The acute form of the disease can be cured in up to six weeks, but medical practice shows that this requires no more than a couple of days.
Chronic urticaria can be treated for longer than one and a half months; only adults from 20 to 40 years old are susceptible to this type. During treatment, periods of improvement and deterioration of the patient's condition may be observed. The rashes are light pink in color and change during exacerbations.
Course of the disease by period
The development of urticaria in the body occurs through immune and non-immune mechanisms. The first includes four more scenarios, based on four types of allergic reactions. According to the immune type, urticaria can appear on the skin and mucous membranes literally within a few minutes from the moment the allergen enters the patient’s body.
There are several mechanisms for the development of allergies, and they are all quite complex. It is important to know that swelling (rash) with urticaria occurs because the permeability of the capillaries increases and fluid accumulates around them. A substance such as histamine triggers the allergy mechanism. It is formed and accumulates in special cells - mast or mast cells. And the rupture of such a cell, and the release of histamine, leads to changes in the microcirculation and all the signs of allergies.
Figure No. 2. What does hives look like?
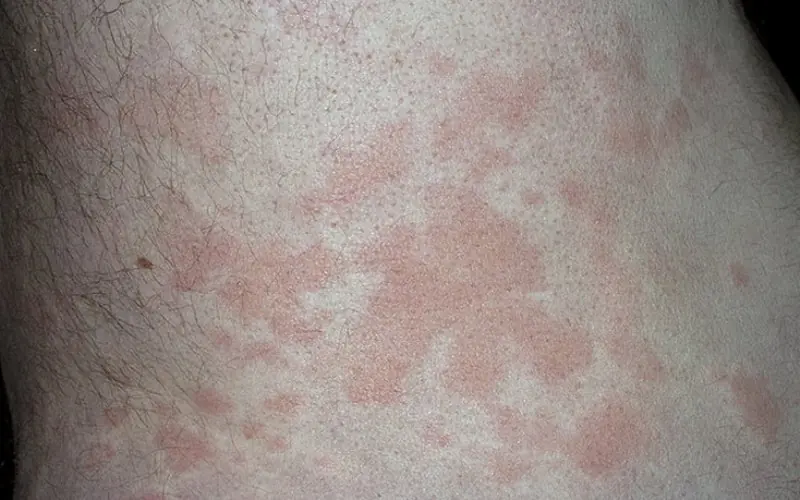
The patient feels itching, swelling on the skin, inflammation and blisters appear. All this is a consequence of the fact that the blood vessels have dilated, and the allergen has reached a critical point in the body. The non-immune course of the disease develops without major immune reactions. When an allergen enters the body, histamine and other biologically active substances are released. This form of urticaria is called chronic or idiopathic.
Establishing diagnosis
If you suspect urticaria, you need to make an appointment with a dermatologist or allergist. The specialist makes a diagnosis based on a patient interview and the manifestation of clinical signs of the disease. The doctor is able to determine what exactly the allergen is. For this, an in-depth examination is carried out. The patient will need to take allergy tests to identify the exact type of allergen. And a blood test for immunoglobulins (their level is increased with allergies).
Treatment
The most effective way to treat urticaria is to identify and eliminate the allergen that triggered the rash. If this was not possible, or when the disease is episodic, the doctor may prescribe antihistamines that will relieve the main symptoms. Moreover, during treatment you need to switch to a hypoallergenic diet and give up perfumes and cosmetics (in addition to hypoallergenic ones). Everything together will help prevent the appearance of new rashes and worsening the patient’s condition.
If classical treatment does not help, then the doctor may prescribe hormone-based medications. An equally effective addition to drug treatment would be immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive therapy.
Is hives contagious?
Many people worry about whether it is possible to catch hives from another person. The disease does not belong to the category of infectious, so the patient is not able to infect a healthy person, even if he is in very close contact with him. But you should be vigilant, because urticaria can become a symptom of infectious processes occurring in the body. Then infection from the infectious agent is possible.
Bathing for hives
Another popular question is whether it is possible to swim if you have hives. Taking a shower when you have hives is simply necessary, because it is important to maintain body hygiene. Without this, the disease may begin to progress and affect a larger area of skin. In order not to harm yourself, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- The water should be warm, but not hot or cold. The ideal option would be 35 degrees. Hot or cold water can irritate the skin and trigger hives.
- Avoid using hard sponges, as well as shower gels and scrubs with abrasive particles. Personal hygiene products should not irritate the skin or damage it mechanically.
- Give preference to hypoallergenic personal care products, without fragrances or dyes; they are safer for the skin and will not cause allergies.
- You should not take a shower for longer than 15 minutes, and in case of an acute form of the disease, you should be in contact with water for no more than 5 minutes.
- After taking a shower, pat your skin dry with a natural fabric towel and apply medications or creams to the dermis.
If there are pustules on the skin, you need to shower very carefully. Contact with the affected area should be kept to a minimum, as should the time of the water procedure.
Who is most susceptible to the disease?
Today it is believed that women are more susceptible to urticaria than men. However, the manifestation of the disease in the latter is recorded quite often. So, men suffer from it between the ages of 30 and 50 years. The occurrence of rashes in old age is considered a very rare occurrence.
Artificial urticaria is recorded in people aged 20 to 30 years. It is called artificial because the rash and inflammation occurs as a result of physical friction against the skin, squeezing or scratching. Cholinergic urticaria, caused by heavy exercise, taking too hot a bath, or eating spicy foods, occurs in both men and women.
Figure No. 3. Cholinergic urticaria
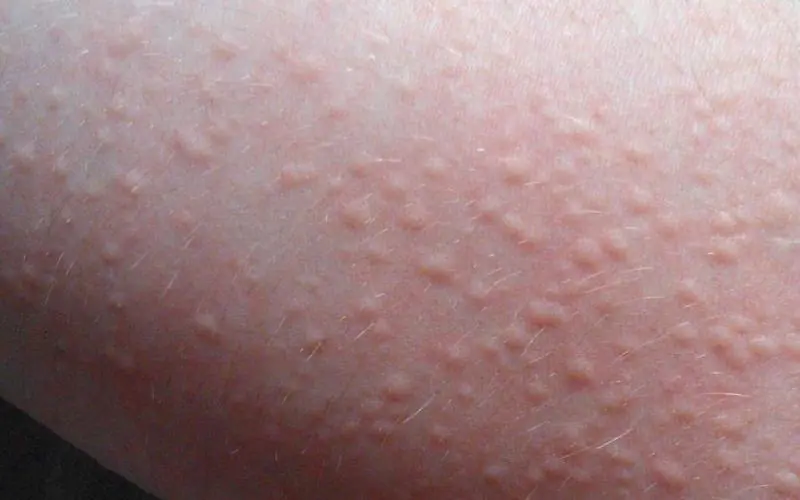
Moreover, the average age of patients is from 15 to 25 years.
Disease prevention
If the allergen that caused the rash has not been identified, then it is recommended to use the following preventive measures:
- Stop taking medications that could cause allergies;
- Minimize stress;
- Stop using tobacco and alcohol;
- Do not go to baths or saunas, which can cause overheating;
- Stop intense physical training;
- Adhere to a hypoallergenic diet, without seasonings and dyes;
- It is necessary to remove all animals from the apartment or house where the patient lives;
- Completely stop using feather pillows/blankets, completely switch to hypoallergenic cosmetics and hygiene products;
- Cure chronic diseases.
If the allergen has been identified, the patient must be completely isolated from it. The substance should not be contained in powders, household and hygiene products.
Consequences of the disease and complications
Many people who are faced with the problem of urticaria, even after undergoing tests, cannot determine the allergen that caused the rash. In such cases, idiopathic urticaria is diagnosed.
Figure No. 3. Idiopathic urticaria
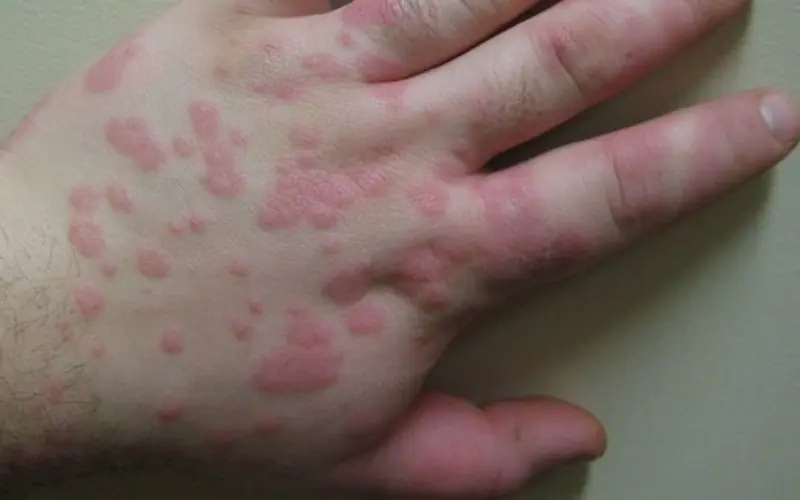
In such cases, the disease can become chronic and unpleasant to remind of itself. A significant proportion of cases end in angioedema (Quincke's edema), that is, swelling of the subcutaneous tissue, asphyxia (if the edema affects the larynx) and suffocation. When an allergen is detected in specific products or medications, the patient has to completely stop using them, which causes inconvenience.
This approach may complicate the treatment of other diseases. For example, people often have allergies to drugs used for anesthesia in dentistry, then the doctor has to select other drugs that do not harm the patient’s health.



