Moles have the peculiarity of appearing not only on human skin, but also on mucous membranes, for example in the eyes. In this article we will talk in detail about such a neoplasm as pigmented nevus of the retina. We learn methods of diagnosis and treatment.
What is a retinal pigmented nevus?
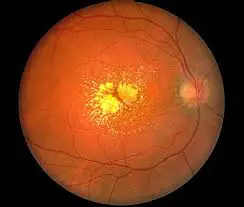
Pigmented nevus is a benign tumor of the retina.
Pigmented nevus is a benign tumor formed from pigment cells that are part of the choroid of the eye. The danger lies in the ability of a nevus to degenerate into melanoma.
In medicine, a retinal nevus is called a tumor of the choroid (the choroid that nourishes the retina and maintains normal intraocular pressure). The choroid consists of several layers and has no nerve endings. Therefore, the resulting formation does not cause discomfort.
Choroidal nevus usually occurs at birth. But at first it is not pigmented. Pigment accumulation occurs twice:
at 10-12 years old; after 30 years.The causes of the tumor are unknown. It can occur in both men and women, usually in one eye.
Types and forms of pathology
Choroidal nevus occurs:
Stationary (typical). Does not change size and shape throughout life; dynamic monitoring is required. Progressive (suspicious). Grows and changes over time, can become cancerous and requires constant monitoring. Atypical. Urgent treatment is required. flat; gray or gray-green; with clear or feathery outlines. grow and change color; have a yellow halo; change boundaries; compress blood vessels.do not contain pigment; have areas of degeneration; surrounded by a paler zone of the choroid.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The neoplasm has no external symptoms; a person does not feel it in the eye. Only when the nevus enlarges is observed:
Decreased vision. Foreign body sensation. Limitation of field of view.The main diagnostic method is ophthalmoscopy. The doctor may also use:
Fundus examination using red and green lenses. Fluorescein angiography to detect melanoma. Sonography to detect areas of pigmentation on the choroid.How to treat
Typical nevi do not require intervention, only observation.

Typical nevi do not require treatment, only dynamic observation.
If growth and change in the nevus is observed over 6-12 months, surgical treatment is necessary. The same as when diagnosing an atypical nevus.
The operation performed is laser coagulation of the retina or photocoagulation.
Stationary and progressive nevi have a favorable prognosis. Atypical ones are considered as a malignant formation and the prognosis is made according to the behavior of the tumor.
Most Caucasians have moles (nevi). Pigment spots form on the body, face and even the eyeball. Nevi differ in shape, color, size, and location. A mole in the eye occurs in people belonging to different age groups. Nevus tumor is found in adults, elderly patients, adolescents and young children. Eye moles are benign.
Causes
Moles in the eye are formed under the influence of melanocytes - cells containing pigment. Melanin, accumulating in tissues, gives them a certain color. The color of skin, hair, iris, and birthmarks depends on this substance.
The following factors lead to the formation of nevi in the eye:
Light-skinned people are at risk. Their epithelial tissues contain a small amount of melanin. The likelihood of mole formation decreases with a sufficient concentration of pigment in the skin cells.
Types of moles in the eye
There are 2 types of birthmarks in the eye:
- Vascular moles. Red nevus spots and hemangiomas appear when blood or lymphatic vessels are damaged.
- Non-vascular (pigmented) moles. Neoplasms develop from melanocytes. The spots are colored brown and black. There are no blood vessels passing through them.
Among pigmented nevi there are:
By nature, ocular nevi are:
- benign;
- malignant.
Based on location, there are 2 types of moles in the eye:
- Nevus of the conjunctiva. The spot forms on the mucous layer of the eyeball. Such moles are easy to notice. The unusual pigmentation on the protein itself catches the eye of people around it.
- Choroidal nevus. The doctor identifies the spots by examining the patient using specialized equipment. Moles appear in the deep layers of the eyeball.
The ICD 10 code for an ocular mole is assigned depending on the type of neoplasm: D31-36.
Conjunctival nevus
Vascular moles that appear on the conjunctiva cover the entire thickness of the mucous layer in the eye. New growths of pink and red shades are formed from capillaries.
Pigmented nevus of the conjunctiva occurs when there is an excessive concentration of melanin on the mucous membrane of the eye. The spots are colored brown and black.
Cyst-shaped nevi that appear on the conjunctiva are formed from lymphatic vessels. They are cystic formations, the internal cavity of which is filled with colorless exudate. The outgrowths from the inside look like a honeycomb.
In stationary conjunctival nevi, the shape and size are unchanged. They are benign and do not threaten health or life. Such growths are not treated or removed. The doctor simply observes the dynamics of the tumors. For preventive purposes, the doctor examines such patients once a year.
Progressive birthmarks constantly change:
- increase in size;
- transform, take on different shapes;
- compress the vessels.
If the need arises, the doctor insists on removing the transforming birthmark. The mole is removed using microsurgery methods or laser.
Treatment of progressive nevus is carried out in the following cases:
- if dystrophic changes appear in the retina or epithelial tissues with pigmentation;
- tissue detachment occurs.
Choroidal nevi
Birthmarks can form on the vascular membranes of the eyes. Such outgrowths are formed from vascular cells.
Birthmarks on the choroid appear during periods of hormonal changes. Outgrowths appear singly and do not form groups. Usually a mole forms in one eye. Bilateral lesions are quite rare.
Choroidal birthmarks, like iris nevi, are divided into stationary and progressive. Stationary growths are benign.
Progressive spots transform: they take on different shapes and grow. Large tumors limit vision, impair vision, and compress blood vessels. In this case, patients focus on the presence of a foreign body in the eye.
Locations
Birthmarks form in different areas of the eye:
- external and internal areas of the protein;
- tearful month;
- semilunar fold;
- iris or retina;
- limbo.
Location of conjunctival nevi
An ocular nevus forms on the inner and outer parts of the conjunctiva. Birthmarks are detected on the inner corner of the eye, the periphery of the cornea, the lacrimal month, and the semilunar fold. Sometimes neoplasms appear on the inside of the eyelid. Although moles are located near the pupil, they do not block the view or impair vision.
Localization of choroidal nevi
- on the back of the eyeball;
- on the fundus;
- at the ocular equator.
The spots are invisible to others; they are discovered by a doctor who performs diagnostics using specialized equipment. But an ophthalmologist is not always able to identify a nevus of the choroid of the eye. Diagnosis is difficult if the tumor lacks pigment.
Color and size
Eye birthmarks vary in size and color.
Conjunctival moles
The color of conjunctival nevi is influenced by the cells from which the tumor is formed. The color of the spots varies from pink to black. Some moles do not develop pigmentation. With a sharp hormonal surge, the color of the nevi changes. In some people, tumors become discolored as they age.
The shape of such pigment spots is flat, with clear outlines and a velvety surface. The size of the iris in diameter reaches 4 mm.
Choroidal moles
The outgrowths that arise on the choroid have a flat shape with pronounced outlines. They are clearly visible when examining the patient. The spots are painted in dark colors. If moles do not contain pigment, they cannot be seen. The size of the growths in diameter reaches 6 mm.
What is the danger
Eye moles do not manifest themselves for many years and do not cause a person any discomfort. However, when certain factors come together, they begin to undergo transformation. Progressive nevus is the most dangerous type of eye mole. Changing pigment spots cause:
- deterioration and loss of vision;
- degenerate into a cancerous tumor - melanoma.
After discovering a birthmark, you should regularly visit an ophthalmologist. This will prevent the development of melanoma. In case of negative dynamics, the doctor will draw up a treatment regimen or decide to remove the nevus.
You should consult a doctor immediately if the following complications occur:
- a mole makes it difficult to see;
- the quality of vision decreases;
- a foreign body is felt in the eye;
- the size and color of the spot changes.
With timely consultation with a doctor and proper treatment, the prognosis of the disease is favorable. A nevus in the eye transforms into cancer in 1 patient out of 500. Close attention must be paid to the spots:
- the thickening of which has reached 2 mm;
- with subretinal exudate;
- with orange pigmentation;
- located on the posterior disc of the eyeball.
Removal
Before removing a nevus in the eye, the doctor determines the nature of the neoplasm. Interfering birthmarks can be removed in several ways. The ophthalmologist chooses the method of excision of a dangerous tumor. Patients are given:
- electroexcision followed by plastic surgery of affected tissues;
- microsurgical operation;
- laser excision.
With progressive choroidal nevus, the individual characteristics of the patient are taken into account. Treatment tactics are influenced by:
- localization of the birthmark;
- tumor growth rate;
- age and condition of the patient;
- accompanying pathologies.
Progressive growths are removed using traditional microsurgery techniques or laser coagulation. Hard-to-reach moles are removed with laser. Removing problematic moles allows you to avoid the development of a cancerous tumor, the transformation of a nevus into melanoma.
In a child, a nevus is treated as a last resort when the eye mole grows rapidly.
Progressive medical technologies prevent the degeneration of eye nevi into cancerous tumors. Thanks to them, it is possible to preserve vision and health. The main thing is to seek medical help in a timely manner and undergo regular preventive examinations with an ophthalmologist.
Nevi or in common parlance, every person has moles. The number and location of their localization are different. It is believed that on average there are nine to fifteen moles on the body of an adult.
Sometimes a nevus can be located in the most seemingly inappropriate place, for example on the eyeball! In this case, nevus in the eyes occurs at any age. It can occur in both infants and the elderly.
Causes of nevus formation on the eye
A nevus on the eye is an accumulation on a very small area of the tissue of the eyeball of a special pigment - melanin, which is responsible for the color of hair, skin and eyes. The reasons for this can be a variety of factors, but most often it is caused by changes in hormonal levels.
Often, a nevus on the eye occurs during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding), against the background of severe stress, infectious diseases, taking oral contraceptives, inflammatory skin diseases, natural aging of the body and as a result of ultraviolet and/or ionizing radiation.
It has been proven that there is also a genetic predisposition to the formation of a nevus on the eyeball. It is the hereditary factor that usually explains the occurrence of this pathology in children.
Clinical manifestations
A nevus on the eye can be located on the outer or inner part of the tunica albuginea, the lacrimal caruncle, the limbus, and sometimes on the retina. True, in the latter case it is not visible to the naked eye and is detected only during ophthalmoscopy (examination of the fundus). An ocular nevus can have different colors (pinkish, black, brown, yellow), shape and size.
As statistics show, the more melanin a person has in his skin, the lower the likelihood of developing a nevus on his eye. That is why pathology is more often observed in fair-skinned and blue-eyed people, in particular residents of Scandinavian countries.
Why is a nevus on the eye dangerous?
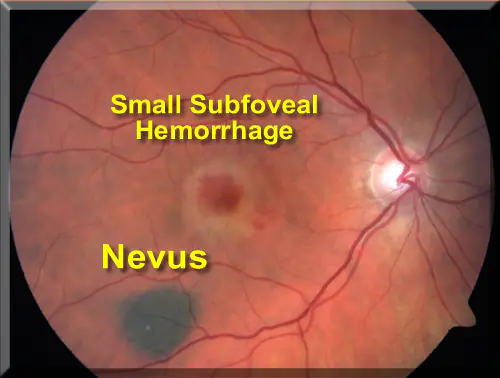
Regardless of its location, a nevus is dangerous due to its ability to degenerate into a malignant tumor - melanoma. A mole that is benign in nature usually practically does not change its color and size, while melanoma is characterized by fairly rapid growth. But it is practically impossible to determine the malignancy or benignity of a birthmark on the eyeball by this sign, because Nevus of the eye is characterized by changes in both size and color, regardless of the characteristics of the histological structure.
What to do with an ocular nevus?
If you suddenly notice a nevus appearing on your eye or your loved ones, then under no circumstances try to get rid of it using home methods. This can cause irreparable damage to your visual function!
You should contact an ophthalmologist and be registered with him at the dispensary. If the doctor has doubts about the benign quality of the formation or if it suddenly begins to change its color and size, the doctor will most likely recommend removing it, as this will prevent the development of melanoma.
How to remove a nevus on the eye?
Until recently, the only safe treatment for nevus on the eye was its surgical removal. The operation was performed under a special microscope using a radioscalpel or microscalpel. The use of a laser beam was considered dangerous by many experts, since it could damage neighboring eye tissues.
But currently, the development of modern laser technologies has made it possible to develop new methods of surgical treatment of nevus. And now it is increasingly being removed from the eye using laser radiation. The main advantages of these techniques are their painlessness, bloodlessness, and most importantly, the absence of a rough postoperative scar.
Prevention

If you have a nevus on your eye, you should be especially careful to protect your eyes from ultraviolet radiation. To do this, you should use contact lenses and glasses with a UV filter. Visit your ophthalmologist regularly and monitor the condition of the tumor.



