Causes of trachoma. Symptoms of the disease at different stages of its development. Diagnostic methods, testing visual function after recovery. Treatment methods for trachoma and prevention.
The content of the article:- Reasons for appearance
- Symptoms of trachoma
- Diagnostic methods
- Treatment options
- Antibacterial drugs
- External means
- Squeezing out follicles
- Prevention measures
Trachoma is an infectious disease that affects the cornea and mucous tissues of the eye. It occurs in people of all genders and ages, but women and children are considered most vulnerable to infection. Residents of developed countries in Europe and America rarely suffer from this disease. But among the population of Africa and Southeast Asia, the disease is widespread and poses a serious threat to visual health.
Causes of trachoma
The causative agent of trachoma is the intracellular parasite chlamydia, which combines the characteristics of viruses and bacteria. It grows and multiplies inside cells, and after breaking their membrane, it penetrates into new cells of the skin and mucous tissue.
The carrier of chlamydia is a sick person. In this case, patients with a latent form of trachoma pose the greatest danger. The infection is transmitted through secretions (tears, mucus, pus) that remain on household items. Thus, the cause of the development of the disease may be the use of a dirty towel, handkerchief, clothing, or bed linen. In addition, the infection is transmitted mechanically, on the legs of insects.
Please note that the human body does not produce antibodies to chlamydia after recovery. This means that re-infection with the disease is possible.Trachoma is considered a disease of a social and everyday nature. Its distribution is influenced by:
- unsatisfactory living conditions;
- poor sanitary condition of housing;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
In addition, the causative agent of the disease “trachoma” attacks people with weak immunity, chronic diseases of the eyes and other organs.
Symptoms of the development of trachoma of the eye
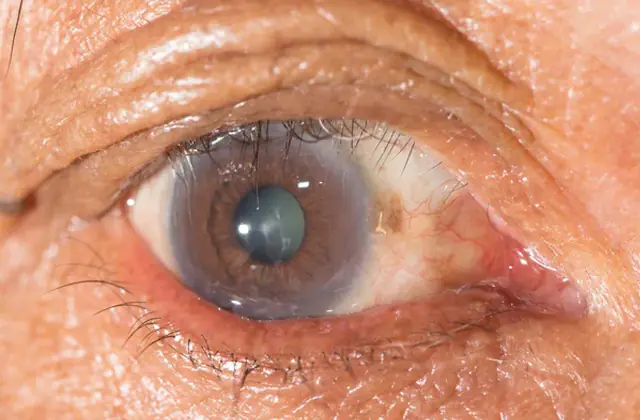
In the photo there is trachoma of the eye
The trachoma virus affects both eyes of a person. The incubation period lasts 7-16 days. During this time, the patient does not feel any unpleasant symptoms of infection. The only manifestations of this stage of the disease are rapid fatigue when reading, writing, and working with small details.
Doctors distinguish the following stages of development of trachoma:
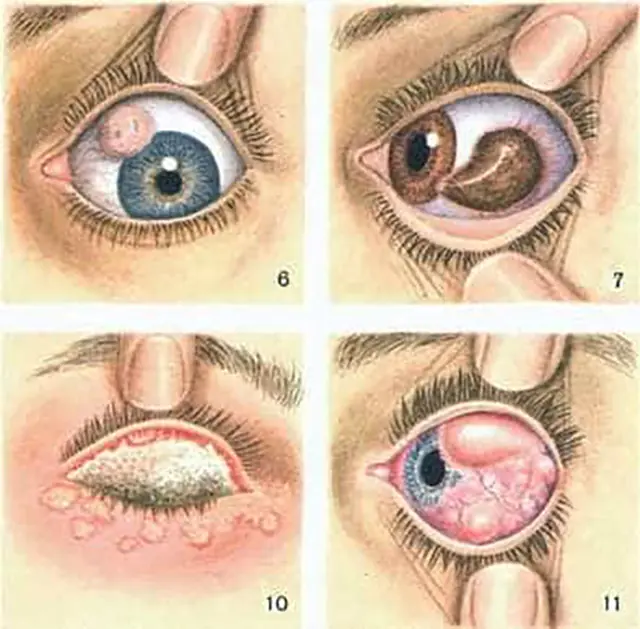
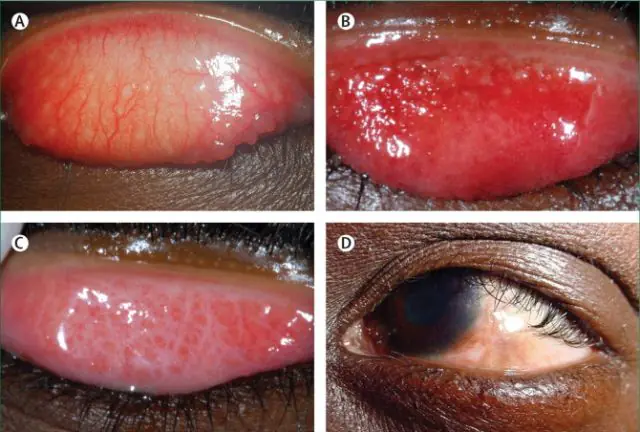
- Initial. The infection affects the conjunctival sac. At the same time, a person feels increased lacrimation, pain in the eyes, and roughness of the upper eyelid. The mucous membrane swells, the vascular network clearly protrudes on it.
- Active. The main symptom of this stage of trachoma is the appearance of follicles on the inner lining of the eyelid. The bags grow and merge with each other. Some of them disintegrate and become scarred. This stage is considered the most contagious.
- Scarring. The growth of follicles decreases, and the sacs actively disintegrate. Scars at this stage look like voluminous white stripes. They injure the cornea, causing discomfort and pain when blinking. Due to the inability to completely close the eyelids, a feeling of dryness of the cornea appears.
- Scar. The inflammatory process subsides. Follicles no longer appear on the eyelids, but many scars give the person continuous pain. In addition, the cornea of the eye becomes covered with a veil, and visual acuity decreases.
In childhood, the disease often occurs in a latent form. It is characterized by a feeling of heaviness in the eyelids, a feeling of sand in the eyes, and sticking together of eyelashes during sleep.
Despite the small number of follicles and the soft structure of the scars, trachoma is considered a dangerous disease that requires immediate qualified treatment.
Ophthalmologists explain that trachoma is treatable. With timely initiation of therapy, more than 90% of patients completely recover from the disease within 2-3 months. However, if you ignore the symptoms and do not follow the doctor’s instructions, a relapse or the following complications may occur:
- Entropion of the eyelids. Scar tissue on the eyelids causes the eyelash edge to curl deeper into the eye. As a result, the hairs damage the cornea and cause pain when blinking. Other symptoms include excessive tearing, reddening of the whites, and a foreign object sensation. The only way to treat the disease is surgery.
- Dry eye syndrome. In the second and third stages of trachoma, the eyelid becomes covered with follicles and scars. Because of this, it shortens and becomes rougher. Such changes cause incomplete closure of the eyelid during sleep. As a result, the cornea dries out, turns red, and hurts. A person feels photophobia, pain, a desire to close his eyes tightly, and rub his eyes with his hands.
- Corneal ulcer. Without treatment, the infection multiplies, spreading to new areas of the eye. The most dangerous complication of trachoma is the appearance of ulcers on the tissues of the eyeball. It is a crater-shaped defect, manifested by sharp unbearable pain, blepharospasm, photophobia, and profuse lacrimation.
- Attachment of a secondary infection. All stages of trachoma development are accompanied by pain in the eyes and a desire to rub the eyelids with fingers. Because of this, another bacterial, viral or fungal infection may join the disease. It blurs the clinical picture of the disease and causes difficulties with diagnosis and treatment.
Methods for diagnosing trachoma
When the first signs of trachoma appear, you should consult an ophthalmologist. The doctor determines the disease and its stage, and chooses the most effective treatment method. To confirm the diagnosis, he prescribes the following procedures:
- Conjunctival scraping. The patient's eye is instilled with Novocaine solution. When the anesthesia takes effect, the doctor presses the closed eyelids with his fingers so that their inner layer turns outward. He then removes the top layers of the epithelium with a scalpel with rounded corners. The ophthalmologist applies the biomaterial to degreased glass, fixes it and submits it to the laboratory.
- Bacteriological research. The contents of the scraping are placed in a nutrient medium. After a few days, a colony of bacteria grows. The doctor identifies the pathogen and examines its sensitivity to various antibiotics. The advantages of the method include high information content, and the disadvantages are the impossibility of obtaining an instant result.
After the course of treatment, the patient is prescribed new diagnostic tests. With their help, the doctor assesses the consequences of trachoma and determines how to restore visual function. To do this, a person goes through the following procedures:
- Visual acuity test. The patient is located at a distance of 5 meters from the test table. The doctor points with a pointer at letters of different sizes, and the person names them. The smaller the signs he is able to see, the higher (sharper) his vision.
- Biomicroscopy. After instillation of the drug to dilate the pupil, the patient is positioned in front of the slit lamp. He fixes his head on the supports, looks at the screen and tries to blink less. The doctor examines the structures of the eye through the lens.
- Fluorescein test. A fluorescein solution is dropped into the patient's eyes. Next, the cornea is examined with a slit lamp using a blue filter. All defects in the anterior part of the eyeball remain unpainted.
Treatment methods for trachoma
Trachoma is considered a contagious disease. Therefore, the patient is isolated from family members and treated in a clinic. At the same time, medical personnel observe all the rules of precaution and hygiene in order to extinguish the source of infection and not become infected themselves.
Antibacterial drugs for trachoma
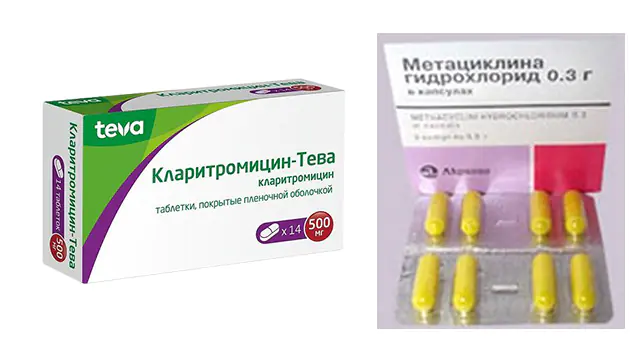
The causative agent of trachoma is a bacteria, so to treat the disease, the doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics. The most effective drugs include:
- Clarithromycin. The main component of the drug is a derivative of erythromycin. Thanks to the change in the molecule, the bioavailability and absorption (absorption) of the substance improved. The medicine is taken 2 times a day for 7-10 days. Price - from 120 rubles in Russia (53 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 10 tablets.
- Metacycline. The antibiotic is active against bacteria, large viruses and some protozoa. The medicine can destroy the causative agent of trachoma in 7-10 days if you take capsules 2 times a day after meals. The dosage of the drug is prescribed by the doctor during an individual consultation. Price - from 480 rubles in Russia (260 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 8 capsules.
External remedies against trachoma
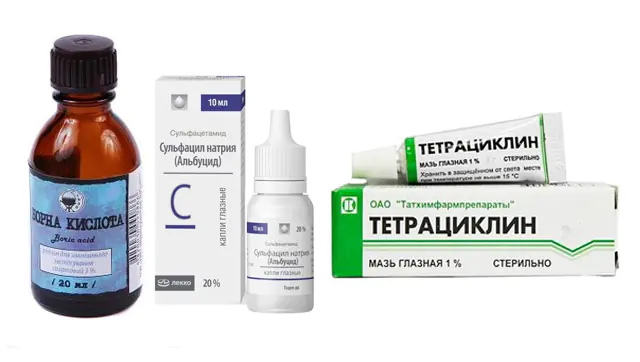
In the first two stages of trachoma, the patient's eyelids become covered with follicles, which disintegrate and secrete mucus and pus. In addition, during illness, a person’s tear production increases. Because of this, his eyes require local treatment with the following drugs:
- Boric acid. A two percent aqueous solution of the drug is used to wash the eyes. To do this, use cotton pads generously moistened with liquid or a syringe without a needle. At the same time, the patient tilts his head down so that the discharge with infection falls into the tray. Price - from 12 rubles in Russia (4 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 20 mg of the product.
- Tetracycline ointment. In addition to tetracycline, the drug contains petrolatum, lanolin, and sodium disulfite. The medicine is packaged in a soft tube with a long nozzle. For treatment, the patient needs to pull back the lower eyelid and squeeze the ointment into it. After this, you need to lie down and wait until the medicine is absorbed into the tissue. Price - from 115 rubles in Russia (53 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 15 g.
- Albucid. The main substance of the drug (sodium sulfacetamide) has a pronounced antimicrobial effect. The medicine penetrates the tissues and fluids of the eye and is not absorbed into the general bloodstream. To treat trachoma, it is recommended to drip it 5-6 times a day for 7-10 days. Price - from 58 rubles in Russia (26 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 10 ml.
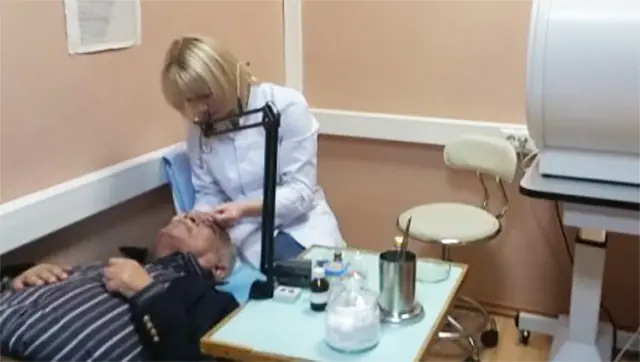
Medical squeezing of follicles for trachoma
If the blisters increase in size, fester, and cause vivid painful symptoms, the doctor prescribes a procedure for expressing (squeezing out) the follicles. To do this, under local anesthesia, the patient's eyelid is turned out and pressure is applied to the purulent lumps with special tweezers.
After the procedure, the patient feels better. The intensity of symptoms decreases and the duration of the disease decreases. If necessary, the expression session is repeated after 10-14 days.
Trachoma prevention measures

The main measure to prevent trachoma is personal hygiene. And first wash your hands with soap, and then wash your face and remove makeup from your eyes. Always carry a clean tissue or disposable paper napkins with you.
Never use someone else's towel, powder brush, or eyelash tinting brush. Make sure your makeup and skin care products are of high quality. Otherwise, they cause pain in the eyes and a desire to scratch the eyelids.
Dispose of waste promptly. Food waste provides food for flies and other vectors of infection. Do not buy products at the spontaneous market, where they may be attacked by insects. At home, use mosquito nets, Velcro, and repellents.
Don't skip preventive examinations. Consult a doctor if any manifestations of eye disease appear. An ophthalmologist will determine the disease, its cause and stage, tell you how to properly treat trachoma and prevent the development of complications.
What is trachoma - watch the video:



