It is not for nothing that a chemical burn to the eye is considered a condition requiring emergency treatment. It can lead to deterioration or even complete loss of vision. Therefore, it is very important to provide the right assistance in a timely manner, since it is quickly taken measures that in most cases save from serious complications.
Description of injury
A chemical burn can be recognized immediately. A person’s eyes suddenly begin to hurt, and the following symptoms appear:
- severe local redness of the conjunctiva;
- profuse lacrimation:
- sensation of a foreign body in the eye;
- blepharospasm - inability to open the eyelids;
- edema.
Subsequently, more characteristic symptoms develop, which depend on the type of toxic compound that caused the burn.
Symptoms of damage by various substances
Doctors identify two main types of substances, contact with which most often causes burns:
- Acids - organic and inorganic, in any concentration. This group also includes complex toxic compounds with an acidic environment. Under their influence, the corneal protein coagulates and a scab is formed, which prevents further penetration of the substance. The exception is concentrated nitric and sulfuric acids: they have a strong corrosive effect.
- Alkalies - their contact with the mucous membrane of the eye is the most dangerous. These substances dissolve cell membranes and destroy the cells themselves. Therefore, they are able to penetrate deep into tissue and cause serious damage.
Only a doctor can determine characteristic changes in the eye using special equipment.
Recently, burns are often diagnosed after unprofessional eyelash extensions. Damage occurs due to glue getting into the eye mucosa during the procedure. The main signs of such a lesion are:
If you immediately rinse your eyes with water, the consequences of injury can be avoided.
Sterile saline sodium chloride solution is also used to remove adhesive residues..
Risk factors
A chemical burn occurs due to contact with the eyes of acidic or alkaline substances, which are contained in:
- household chemical solutions;
- paint and varnish products;
- aerosols;
- materials processed on industrial equipment.
The most severe burns to the cornea of the eye can be caused by pure acids and alkalis. They pose the greatest danger in concentrated form.
Risk factors that increase the likelihood of injury include:
- work related to the use of building materials containing lime and carbide;
- professional activities that involve constant contact with potent solutions - work in chemical laboratories, in hazardous industries;
- improper handling of household chemicals;
- interaction with batteries without appropriate training.
First aid
This type of damage requires immediate first aid: the likelihood of a favorable prognosis will depend on the speed of response.
After an accident, you need to call an ambulance as quickly as possible and not refuse hospitalization. It is impossible to completely eliminate the consequences of eye injury at home.
First aid before the medical team arrives is to wash the eyes with clean running water to remove the damaging substance as much as possible. If the exact nature of the compound that caused the burn is known, then additional treatment with the solution is carried out:
- boric acid - if alkalis come into contact with the mucous membrane;
- soda - when damaged by acids.
If there are solid foreign particles (powder, lime) at the site of injury, they are first removed with a napkin, and only then the eyes are washed. Otherwise, they dissolve in water, and the degree of damage becomes greater, as toxic compounds spread.
What not to do
Incorrect actions in the first hours after injury can lead to complete loss of vision. That is why it is important to remember what is strictly not recommended to do:
- Use available eye cleansers. This is especially true for rinsing with carbonated drinks and contaminated liquids.
- Rub the damaged area with your hands or napkins. This can lead to infection of the burned surface and deterioration of the general condition.
- Use any folk remedies. None of them is capable of restoring the membrane of the eyeball, so their use will not bring results. But there is a risk of aggravating the injury, especially in the case of a burn with an unknown substance. In this situation, only a qualified ophthalmologist can help..
Treatment
The treatment regimen is selected individually for each patient. In this case, the doctor will take into account the degree of damage and its cause. Sometimes the real extent of the damage can be assessed only on the second or third day - for example, with an eye burn from alkali. In severe cases, surgical treatment is resorted to.
Typically, the following groups of drugs are used in therapy:
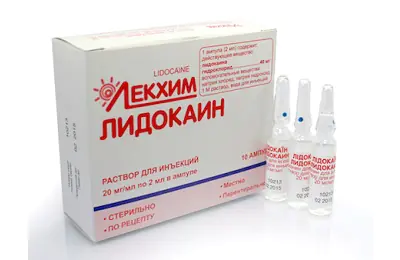
- Local anesthetics. They reduce pain and also allow further medical procedures to be carried out more effectively. Solutions of Lidocaine and Novocaine can be used.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. The glucocorticosteroid Dexamethasone is mainly used. It can be prescribed either in the form of drops or injections. The choice of administration method depends on the depth of tissue damage.
- Regenerants. The drugs stimulate cell restoration, which speeds up recovery (Solcoseryl gel, ascorbic acid).
- Natural tear products (Vizin). The consequences of injury lead to a decrease in the secretion of tear fluid, so the use of drops is mandatory.
- Antibacterial medications. They prevent the development of infection by pathogenic microorganisms. Most often, solutions based on chloramphenicol or Floxal are used.
A chemical burn to the eye requires emergency care, as the situation worsens over time.
The worst prognosis involves complete loss of vision. Therefore, it is forbidden to avoid hospitalization and self-medicate.
Eye burns are not uncommon. They may be different. But the most dangerous type is a chemical burn to the eye. What is it, what causes it, how can I help a person with burns of varying severity? Let's try to answer these questions.
Main characteristics of injury
A chemical burn is an injury to the eye caused by exposure to aggressive chemicals. First of all, there is damage to the conjunctiva - a thin connective membrane that covers the outer surface of the eye and the back surface of the eyelid. It performs an important function because it releases a special liquid that lubricates the eye and prevents it from drying out. Its damage often leads to impairment and even loss of vision.
Damaging substances
Chemical burns of the conjunctiva are not uncommon these days. According to statistics, 10% of all eye burns are of chemical origin. Most often, damage occurs when aggressive substances come into contact with the ocular surface. Among them are:

Acids. Most often, burns occur with the following acids:
- hydrochloric acid (HCl);
- sulfuric (H2SO4);
- acetic (HC, COOH);
- hydrofluoric(HF).
An acid burn is similar to a thermal burn. It affects the conjunctiva and cornea without spreading into the eyeball. The degree of damage is affected by the concentration of acids and the duration of their exposure. At the site of acid entry, a necrotic area appears, which is separated from healthy tissue (coagulation). In this case, a very strong pain syndrome appears, since the optic nerves are irritated.
Alkali. The most common alkalis that cause burns are:
- ammonia (ammonium hydroxide);
- caustic soda (sodium hydroxide);
- magnesium hydroxide;
- potassium hydroxide;
- slaked lime (calcium hydroxide).
Burns from alkaline substances are considered more dangerous because the damage extends deep into the eye, from where it is not easy to remove. At the same time, the time of negative impact increases.
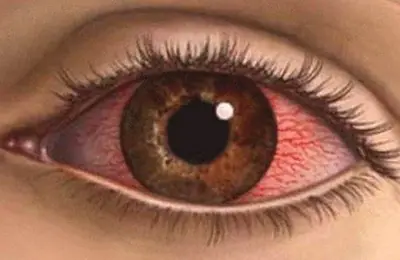
This occurs due to the fact that alkali provokes liquefaction necrosis in the proteins, which leads to their melting (myomalacia) and spreading throughout the eye. In this case, the optic nerves are damaged by alkali, which leads to their loss of sensitivity. That is why a person with alkaline burns practically does not feel pain. This often leads to underestimation of damage.
to contents ↑
Risk factors
How do chemical eye burns occur? This occurs through direct contact with acids or alkalis, when, due to carelessness or failure to comply with safety measures, these aggressive substances first enter the area of the conjunctiva of the eye, causing its necrosis (death). Among the risk factors contributing to the occurrence of such burns are:
- Construction or repair manipulations. These types of work often use chemicals that can cause burns.
- Using aggressive substances in everyday life without following safety rules. For example, improper or careless use of ammonia, household chemicals containing dangerous acids or alkalis. It is also risky to leave such substances within the reach of children.

Work involving frequent use of chemicals. This may be the production of concentrated acids and alkalis or other types of work where such substances are used.- Careless behavior with car batteries that contain sulfuric acid concentrate. This is especially true for car enthusiasts who do not have professional skills in working with cars.
- Alcohol abuse. In this state, very often people do not follow safety rules, which leads to unpleasant consequences.
Any type of burn is potentially dangerous. Therefore, first of all, a person needs emergency care for a chemical burn to the eyes.
The sooner it is provided, the more favorable the forecasts will be.
How does it manifest?
The severity of a chemical burn depends on many factors. Among them are:
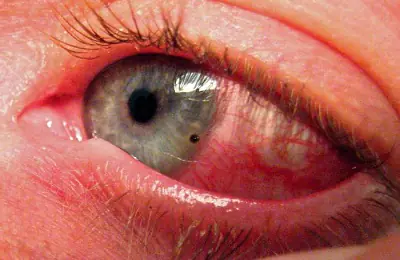
type of chemical (acid, alkali, etc.);- the amount of substance that has reached the surface of the eyes;
- concentration of the chemical (the more diluted it is, the less harm the burn will cause);
- temperature of the substance (the higher it is, the more complex the consequences);
- duration of exposure to the eyes.
The favorable outcome of treatment is also influenced by the patient’s age (the younger the person, the faster the recovery), as well as how timely and high-quality first aid was provided.
There are several degrees of eye damage from chemicals, which differ in the severity of the damage and are manifested by specific symptoms. There are 4 degrees of chemical burns:
The first is considered the mildest degree of burn. Its main features:
- sudden onset of pain;
- cloudiness in the eyes (vision problems);
- the appearance of red blood vessels in the whites of the eyes (hyperemia);
- conjunctival edema (chemosis);
- cloudiness of the fluid in the anterior chamber of the eye.
Healing procedures
For a chemical burn to the eye, first aid involves a set of certain actions. It must be provided on an emergency basis. It’s good if there is a person nearby with a medical education or basic knowledge in this area. But even an ordinary person can help.
First aid
So, what to do for chemical eye burns? There are several stages of emergency assistance:
First, it is urgent to rinse the affected eye (no later than 30 minutes after contact with the chemical). To do this, use a physiological solution of sodium chloride 0.9% (table salt) or a weak solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate). They have antiseptic properties.
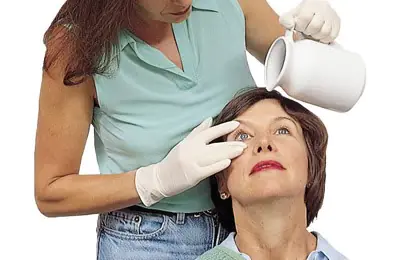
If nothing is available, rinse the eyes with plain water from the inner corner of the eye to the outer corner to avoid chemicals getting into the healthy eye. If there are solid particles of the chemical (lime) in the eye, they should be removed with a dry cotton swab before rinsing.
After all these manipulations, you should cover the affected area with a clean bandage, give the patient a sedative and send him to the hospital, where appropriate treatment will be carried out.
It depends on the severity of damage to the eyeball and the presence of concomitant conditions (inflammation, pain shock and others).
Further therapy
Medical centers offer these procedures to treat eyes damaged by chemicals. First of all, medications are used. Among them:
- local anesthesia for the purpose of carrying out manipulations to remove aggressive substances (Lidocaine);
- antitetanus serum;
antibiotics to prevent infection (drops containing ciprofloxacin, Levomycetin eye ointment);- cycloplegic drugs that reduce pain and prevent scarring (atropine sulfate solution);
- tear fluid substitutes (Lakrisin);
- drugs that reduce intraocular pressure (Timolol, acetazolamide solution);
- glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone) are prescribed when inflammation occurs.
Additionally, citrates (citric acid salts) or ascorbic acid are prescribed, which improve calcium metabolism in the affected area.
If extensive damage to the eyeball is observed (with burns of 3 or 4 degrees of severity, when defective conditions occur), then surgical intervention may be required:
- tarsography (suturing the skin of the eyelids during healing);
- tissue transplantation;
- autotransplantation;
- keratoplasty (to remove scars);
- prompt correction of the consequences of burns (glaucoma, cataracts).


In some conditions (subatrophy - slow death of the damaged eye), keratoprosthesis may be required - replacing the cloudy cornea with an artificial optical device.
Eye burns of chemical origin are common. Most often they are caused by acids and alkalis that enter the eye due to carelessness or failure to follow safety rules when in contact with aggressive chemicals. Such burns should be treated by a qualified physician.
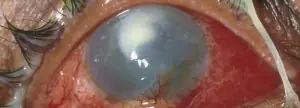
Eye burn from alkali – This is one of the most dangerous types of eye injuries that can occur. If alkali gets into the eyes, a chemical burn occurs.
When alkali gets on the mucous membrane of the eyes or on the skin, both around the eyes and on other parts of the body, severe tissue damage occurs, followed by penetration of the reagent into the deeper layers of the mucous membrane or skin. The degree of damage depends on the time of exposure to alkali. The alkaline reagent instantly, in a few minutes, penetrates into the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye through the cornea, the cornea and iris are injured, the outflow of intraocular fluid is disrupted, and the lens is damaged.
In other words, the damaging effect affects almost all structures of the eye. The proteins dissolve, the damage goes both inward and outward. With an alkali burn, the pain is less pronounced than with an acid burn, but do not underestimate the extent of the damage. It is difficult to remove alkali that has penetrated deeply; the effect takes longer and can last up to several days; the degree of damage is determined after the burn.
In case of burns with alkali, the injury can be domestic or industrial. The most dangerous injury from an alkaline reagent occurs in production conditions, since highly concentrated solutions and toxic substances are used in enterprises or factories; such an injury can have very negative consequences for a person. If an alkaline reagent gets on the mucous membrane of the eyes, on the skin around the eyes, timely assistance is an important step, otherwise the person may lose vision forever.
Therefore, it is important for enterprises to observe safety precautions when working with toxic and highly concentrated substances. With regard to a domestic injury, everything is a little simpler, but this does not make it any less dangerous. The consequences of an injury at home are milder than at work, since in everyday life a person deals with a certain and, in most cases, permissible concentration of substances. But despite this, chemical eye burn from alkali obtained at home is also extremely dangerous and can lead to loss of vision, therefore, if alkali gets into your eyes, you should immediately seek help from a specialized institution.
Eye burns from acids and alkalis are severe in nature, difficult to treat and, as a rule, treatment is very long and not without consequences. Emergency care for eye burns with alkali should follow for the first time minutes, even for the first time seconds after the injury, and after first aid has been provided, you need to call an ambulance. But after an ambulance has already been called, it is necessary to continue providing emergency care. It is precisely this point that we will pay attention to in this article, so that, God forbid, of course, you encounter such a case, you know what needs to be done.
Degree of damage
- In the first degree, the top layer of skin is damaged. Redness, swelling, mild pain.
- In the second degree, alkali affects the layers of the dermis. Blisters with liquid are added to the previous signs.
- The third degree is characterized by acute pain, the appearance of small and large blisters with cloudy liquid. Adipose tissue is affected. Burns can lead to decreased or loss of vision, it all depends on the area of the damage. Surgery is required.
- In the fourth degree, the bone structure is affected. Vision is lost, surgical treatment occurs, and partial recovery is possible.
Eye burn with alkali - first aid
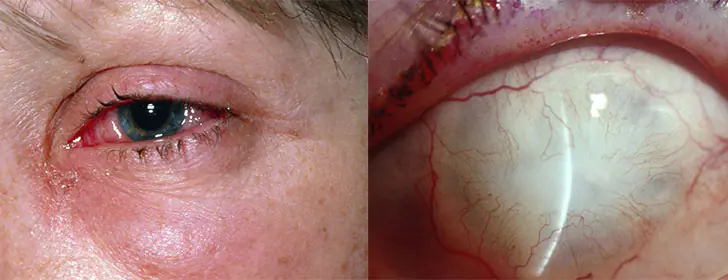
It is necessary to provide first aid in a timely manner; the severity of the injury depends on how quickly the first aid was provided, so you cannot waste a minute here and you cannot be scared and lost, no matter how it sounds. In this case, the expression is more than true: time is everything.
As a rule, before the ambulance arrives, the following actions are immediately carried out:
- the damaging substance is removed by washing the eyes for half an hour using a pear, a kettle, or with your hands under running water, not with water, as many believe, but with a sterile solution, for example, saline solution or Ringer's solution. If a suitable solution is not available, plain water will do, it’s better than nothing, but it’s still better not to use water. Ideally, before rinsing the eye, it is necessary to numb the eye with a 1% dicaine solution to reduce pain and blepharospasm. The earlier the rinsing is carried out, the more successful the treatment will be in the future; minutes and even seconds decide everything;
- eye drops of chloramphenicol or diclofenac are instilled repeatedly;
- the affected area is lubricated with sodium sulfacyl ointment, tetracycline or erythromycin ointment (1%), by placing it in the conjunctival sac. Alternatively, fish oil is used for the skin.
For burn injuries from II to IV degrees, the victim is hospitalized.
So, these actions will help the victim only until the doctor arrives; the main treatment is carried out by an ophthalmologist in a hospital setting and nothing more!
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Find out how your comment data is processed.
>



